pre-class quizzes + dc worksheets (lifesci) (wrong answers)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
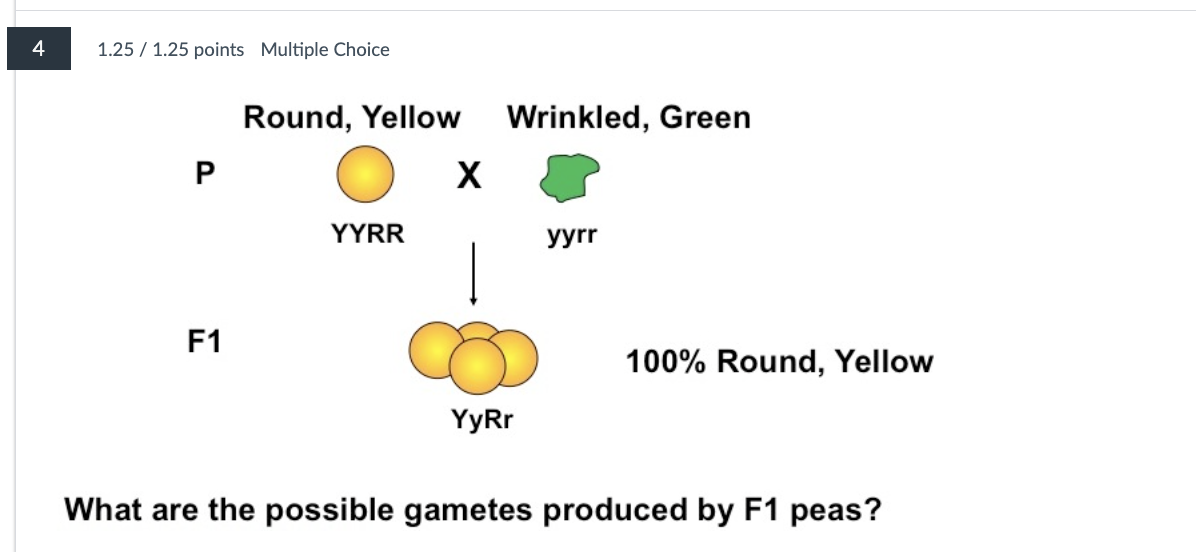


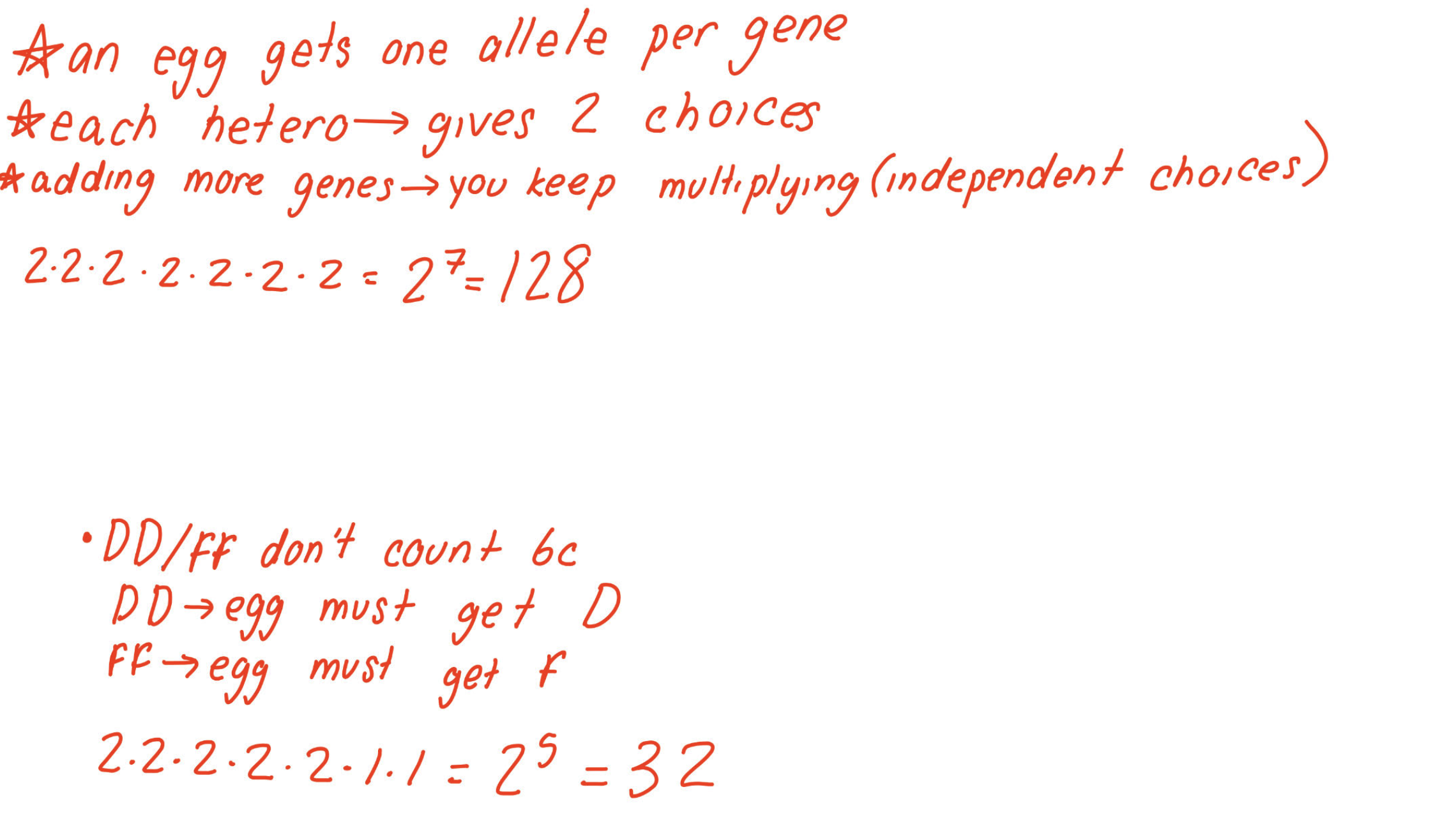


Galactosemia is a recessive human disease. Susan and her husband are both
heterozygous for the galactosemia gene.
a. If they have four children, what is the probability that none of their children
will have galactosemia?
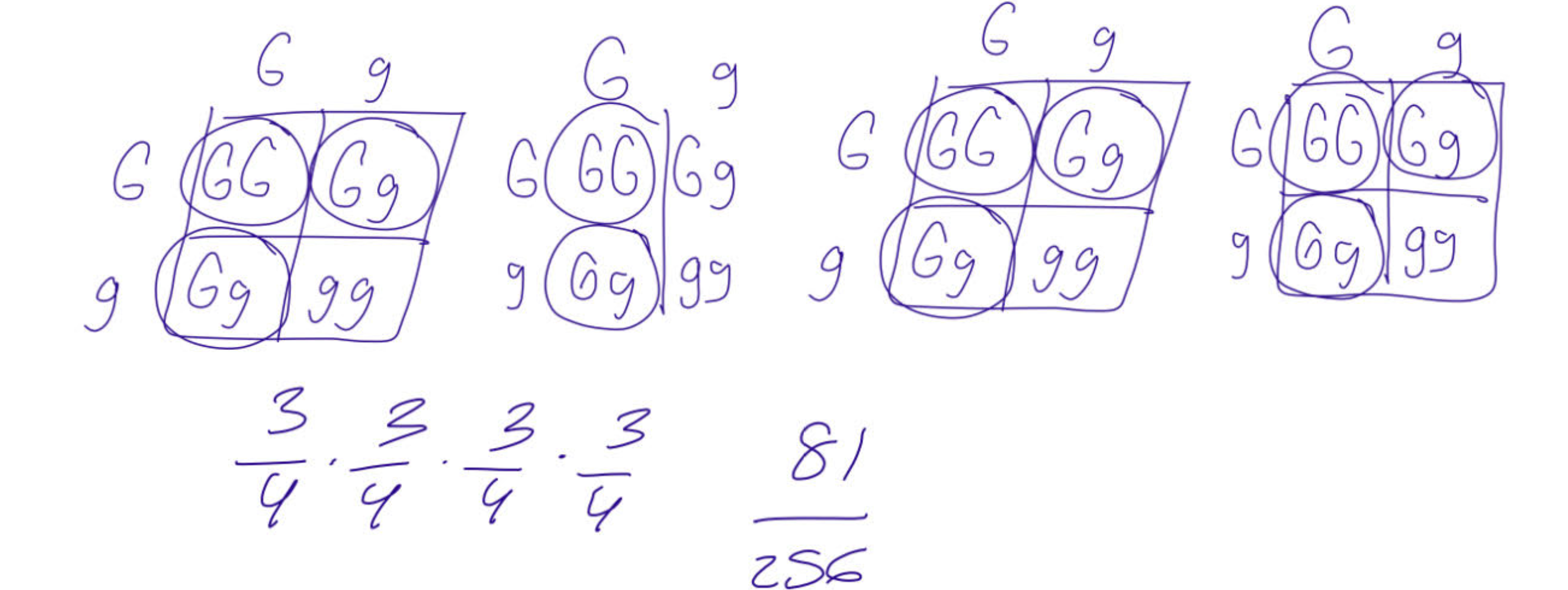
Galactosemia is a recessive human disease. Susan and her husband are both heterozygous for the galactosemia gene. If they have four children, what is the probability that at least one child will have galactosemia?
Galactosemia is a recessive human disease. Susan and her husband are both heterozygous for the galactosemia gene. If they have three children, what is the probability that one of their children will have galactosemia and two will not?
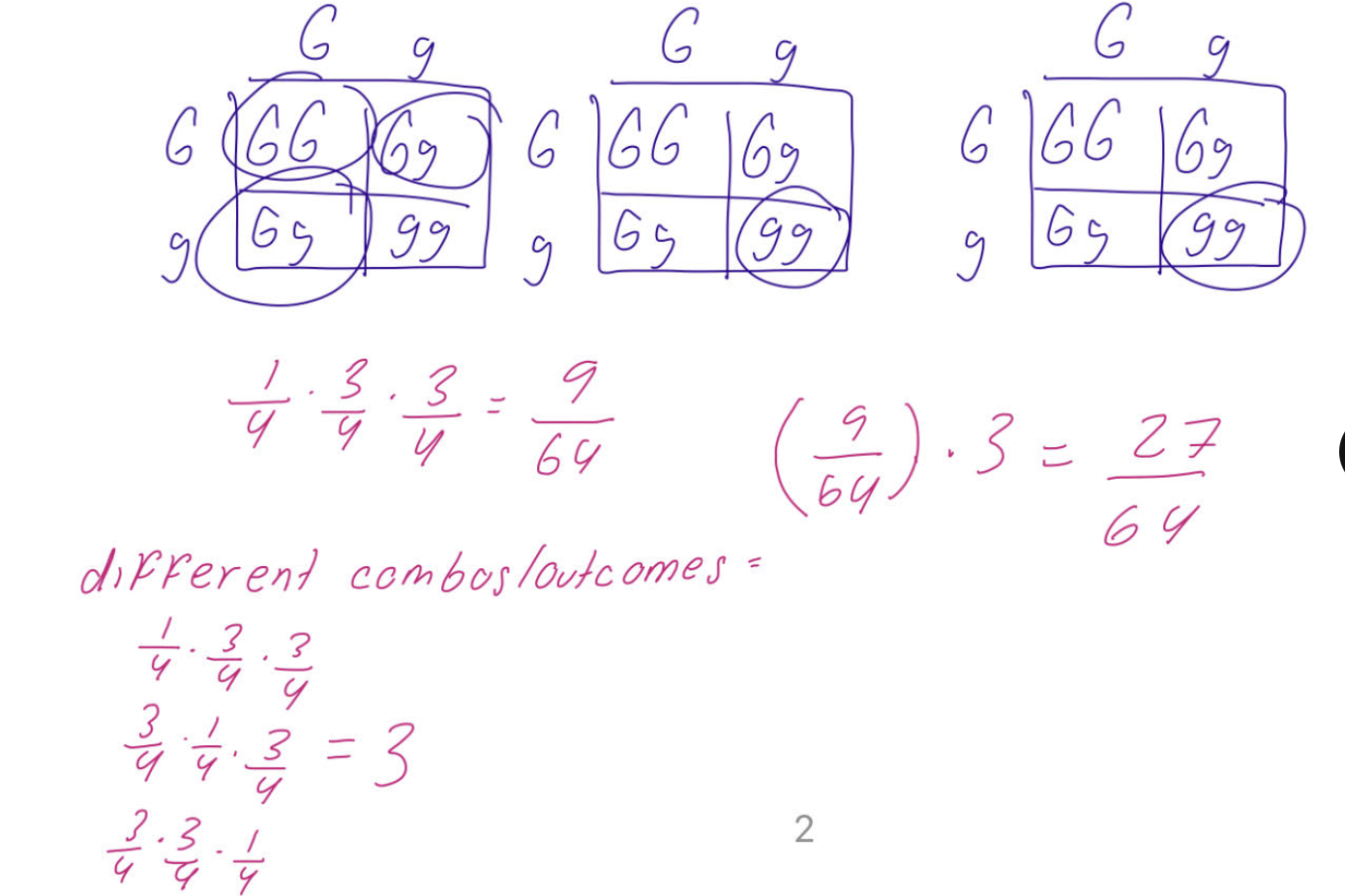
what does at least mean?
1-minus none
Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive genetic disorder.
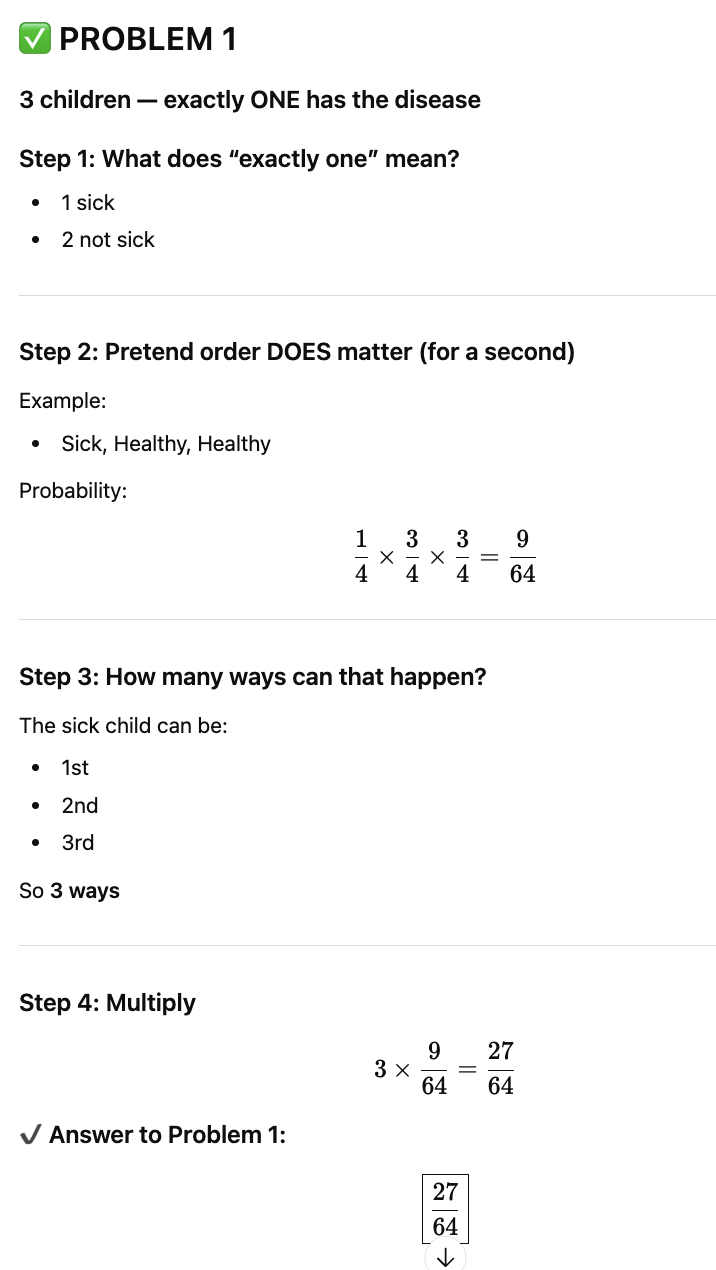
Alex and Jordan are both heterozygous carriers. Problem 1 (Exactly)
Alex and Jordan have 3 children.
What is the probability that exactly one child has Tay-Sachs disease?
Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive genetic disorder.
Alex and Jordan are both heterozygous carriers. Alex and Jordan have 4 children.
What is the probability that at least one child has Tay-Sachs disease?

Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive genetic disorder.
Alex and Jordan are both heterozygous carriers. Alex and Jordan have 5 children.
What is the probability that exactly two children have Tay-Sachs disease?

Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive genetic disorder.
Alex and Jordan are both heterozygous carriers. What is the probability that none of the 3 children have Tay-Sachs disease?



A man with blood type A and a woman with blood type B have a child with blood type O. This couple can also have children with which blood types?
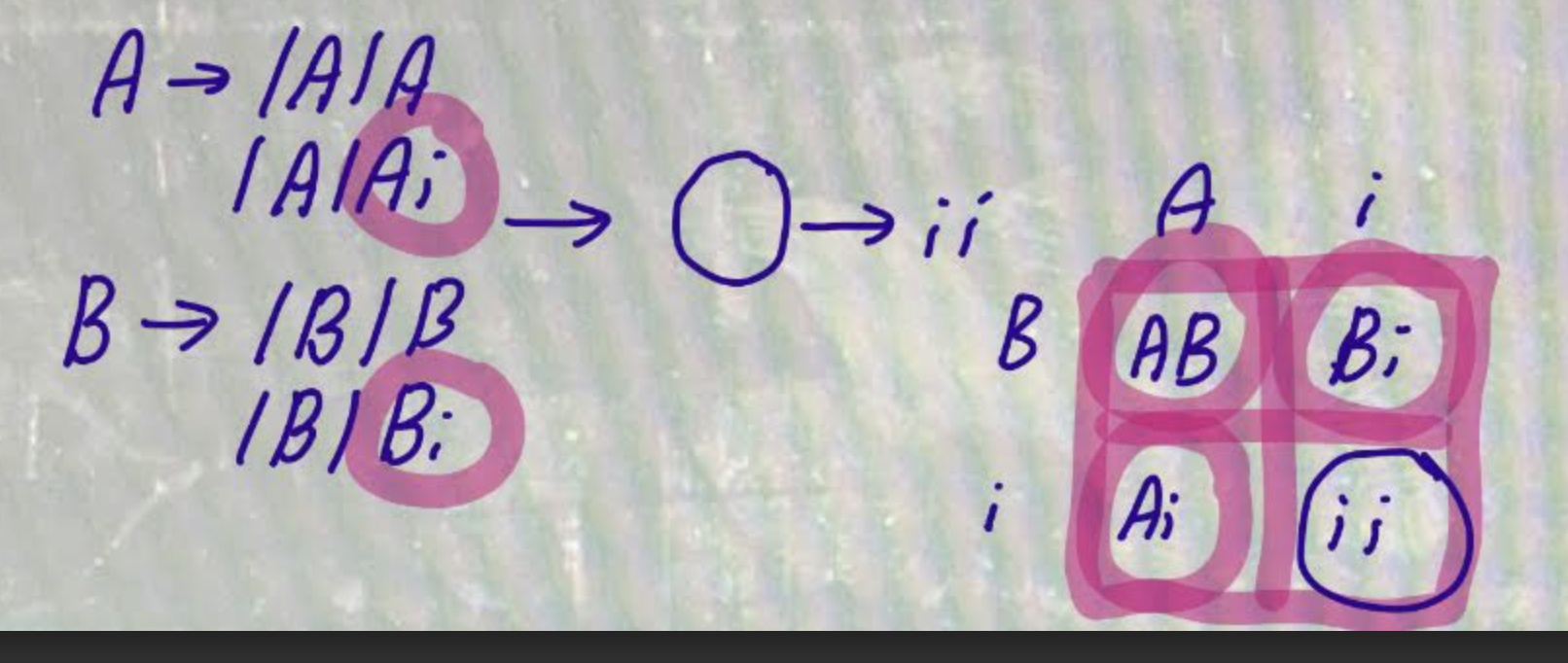

how many of the offspring will be blind?


how many of the offspring will be blind?

Epistasis is about gene masking in ratios (in what generation)?
F2