CHEM 1410
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
CH 1 What is Chemistry
Which of the following would a chemist that works at the US Chemical Safety Board investigate?
Answer: A refinery explosion
Which of the following (choose all that apply) would a conservation chemists likely do?
Answer: Identify the specific resin used in a painting and
Determine the composition of paints used by a particular artist
Which of the following is likely to occur frequently when conducting innovative research?
Answer: Success a small fraction of the time (failure much of the time)
Which of the following provides a one sentence summary of Video 1.5?
Answer: Scientific discoveries require keen observation, broad knowledge of what is unknown and needed in society, persistence, and, sometimes, luck.
Which atoms are found in Figure 1.2? This is not a trick question and is meant to have you think about different representations of molecules before we get started. Figure 1.2 is a skeletal structure for which the symbols for carbon and hydrogens bonded to carbon are not drawn. Watch this 2 minute video if you don't know how to draw and interpret these structures.
Answer: Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen
Which of the following have been associated with rising levels of CO in the atmosphere? Select all that apply.
Answer: Ocean acidification, Climate change, and Health concerns
Which category of the chemistry research being done here at UVA did you find most interesting? You may select more than one response.
Answer: Astrochemistry, Super-resolution imaging, Renewable energy sources, Cancer therapies, Drug addiction studies
CH 2 Atomic orbitals: energy, shape, and electron density
Which of the following images best depicts the 2pz orbital?
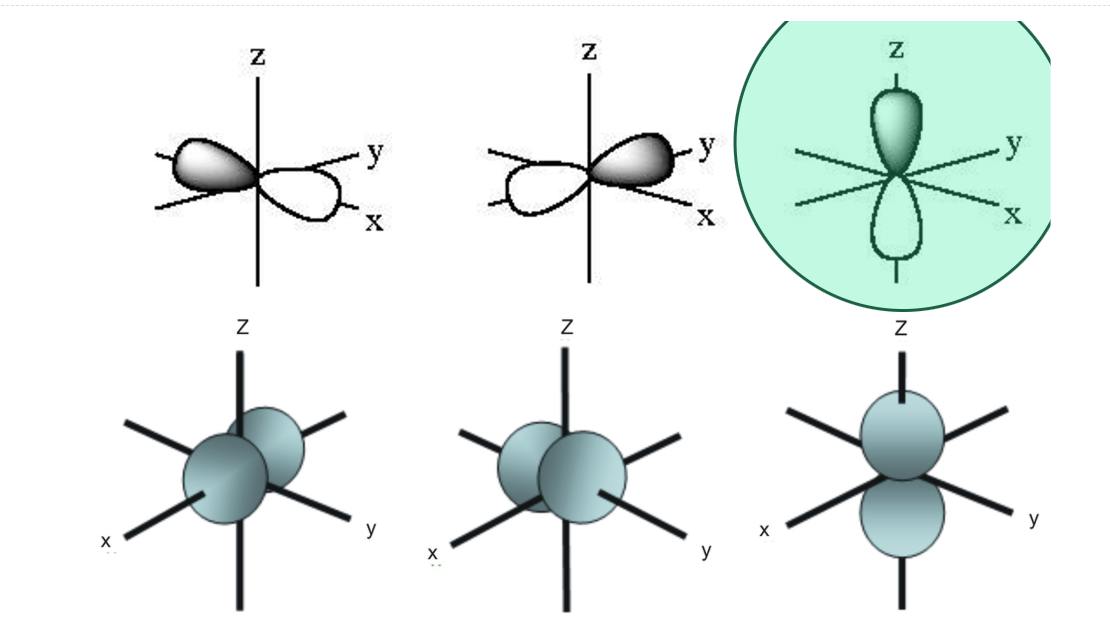
Which orbital type is depicted in the image?
Answer: dxy
Which of the following represents a valid set of quantum numbers (n, ℓ, mℓ, ms) describing an electron in a 4s orbital?
Answer: 4, 0, 0, ½
Which of the following represents a valid set of quantum numbers (n, ℓ, mℓ, ms) describing an electron in a 2p orbital?
Answer: 2, 1, 0, ½
Which of the following represents a valid set of quantum numbers (n, ℓ, mℓ, ms) describing an electron in a 3d orbital?
3, 2, 0, ½
CH 6 Valence Bond Theory and a Comparison to Molecular Orbital Theory
Choose the best Lewis structure for HNO2 from those presented below.
Answer: D
Choose the best Lewis structure for C2H3O?
Answer: A
What is the electron domain geometry about aluminum in AlCl3?
Answer: Trigonal planar
What is the electron domain geometry about NA in the molecule below?
Answer: Trigonal planar
What is the electron domain geometry of the nitrogen atom of ammonia (NH3)
Answer: Tetrahedral
What is the hybridization about the nitrogen atom in the drawing below?
Answer: Sp³
Click on all sp² hybridized atoms in the molecule below.
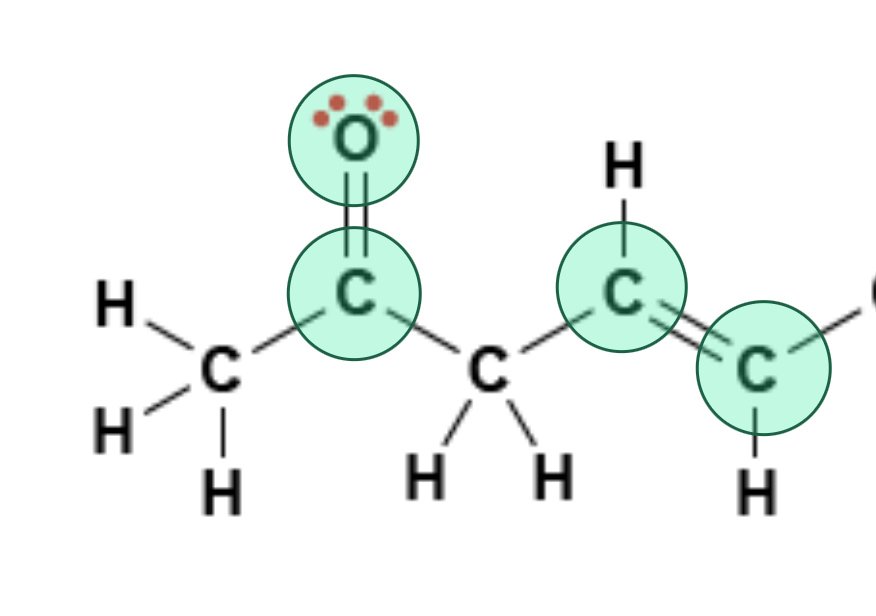
Fill in the Blanks: Match the indicated atom (red) to the correct hybridization. Use only the letter (A, B, or C) in your answer.
C
B
A
B
Determine the hybrid orbitals that each indicated atom (red) uses to make σ bonds and/or contain lone pairs. Use only the letter (A, B, etc.) in your answer.
B
D
A
C
E
For each of the bonds listed below, select the two types of atomic or hybrid orbitals that are involved in the bonding between the two atoms in valence bond theory. Use just one letter (A, B, etc.) in each blank.

How many of the nine non-hydrogen atoms in the molecule shown have each of the following hybridizations?

The sigma bond between the carbon and oxygen in CO2 is formed from which two orbitals (select two).
Answer: A carbon sp orbital and An oxygen sp2 orbital
The pi bond between the carbon and oxygen in CO2 is formed from which two orbitals (select two).
Answer: A carbon p orbital and An oxygen p orbital
In which of the following compounds does the chlorine atom have sp3 hybridization in the valence bond model?
Answer: ClO2–
and ClO3–
CH 7 Bond and molecular polarity
Fill in the Blanks
Which is a more polar bond, the C–O bond or the S–O bond?
Answer: They have approximately the same polarity.
Using VSEPR theory, what are the electron domain geometries of the CO
Answer: CO2 is linear. SO2 is trigonal planar.
Which of the following molecules with a trigonal planar electron geometry will be polar? Select all that apply. The first atom listed is the central atom for all the molecules.
Answer: CH2O and PHO2
CH 8 Non-covalent Interactions
Classify each of the molecules (not the bonds) below as either polar or non-polar.
Which direction would you expect the dipole moment for PBr3F2 to be oriented? You may click on multiple boxes if necessary?
Answer: Right
Shown below is a molecular representation of the reaction given in Equation 10.1. Both the intramolecular and intermolecular forces involved in this reaction are illustrated with either lines or dashes. Which of the two forces, intramolecular or intermolecular, are represented by the dashes?
Answer: Intermolecular
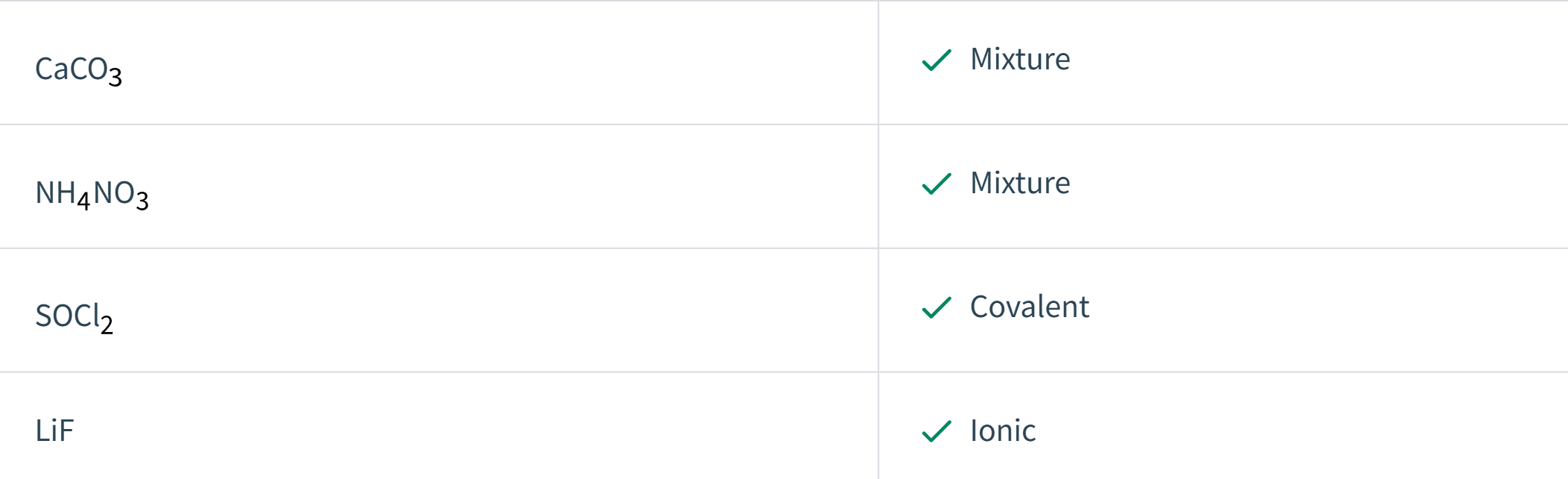
Consider the molecular formulas below and classify the following compounds as ionic, covalent, or a mixture of ionic and covalent.
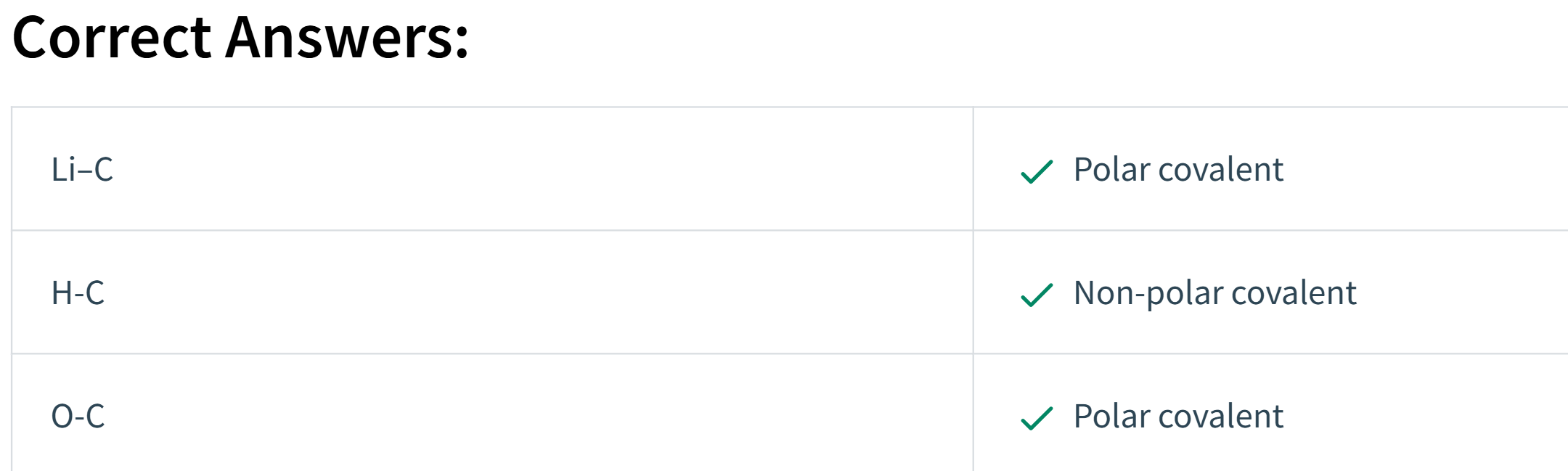
Use the electronegativity values from Table 10.2 to determine if the following bonds are likely to be non-polar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Match each bond to its appropriate classification.
Which of the following pairs of molecules have dipole–dipole forces between them?
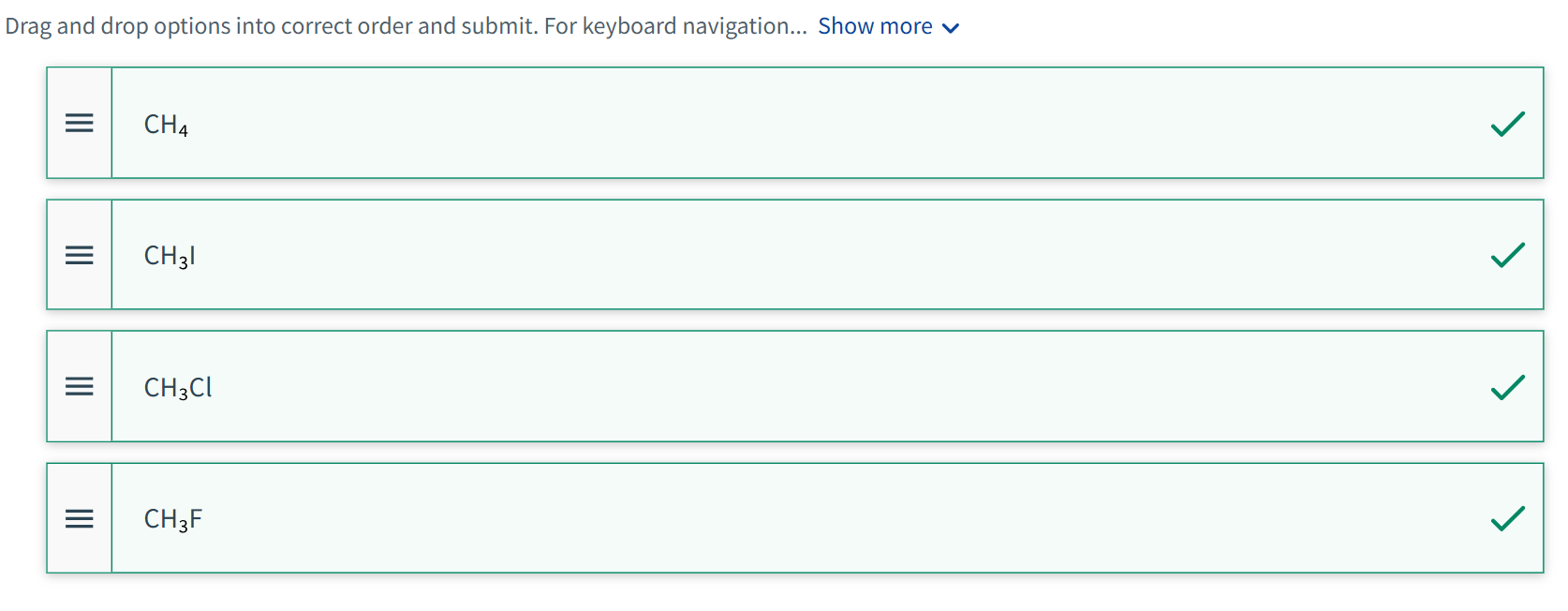
Arrange the following in order of increasing dipole–dipole interaction. List the molecule with the least dipole-dipole interaction at the top.
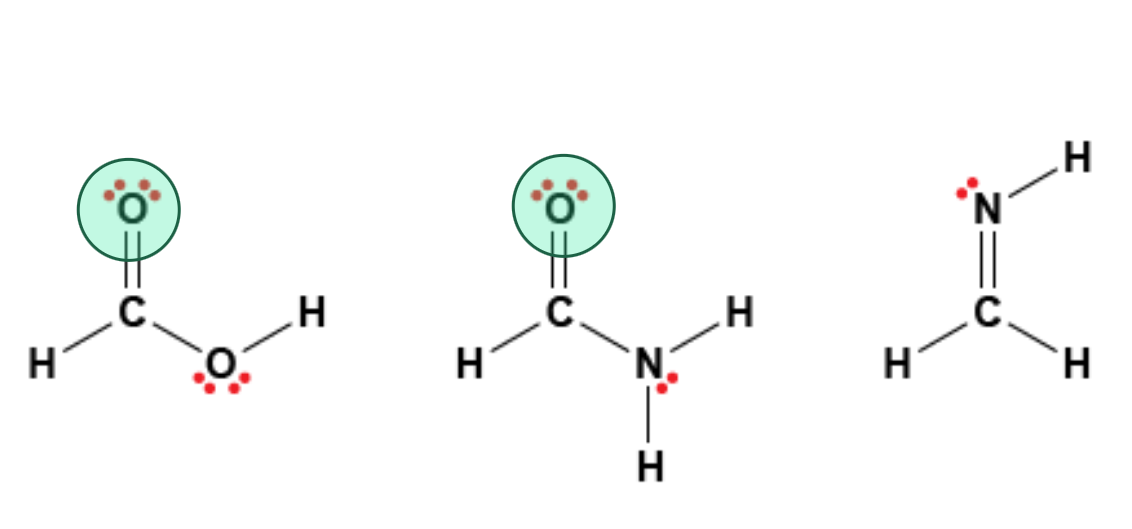
Shown below are the molecular structures of three molecules. Which atoms on these molecules are hydrogen bond acceptors only?
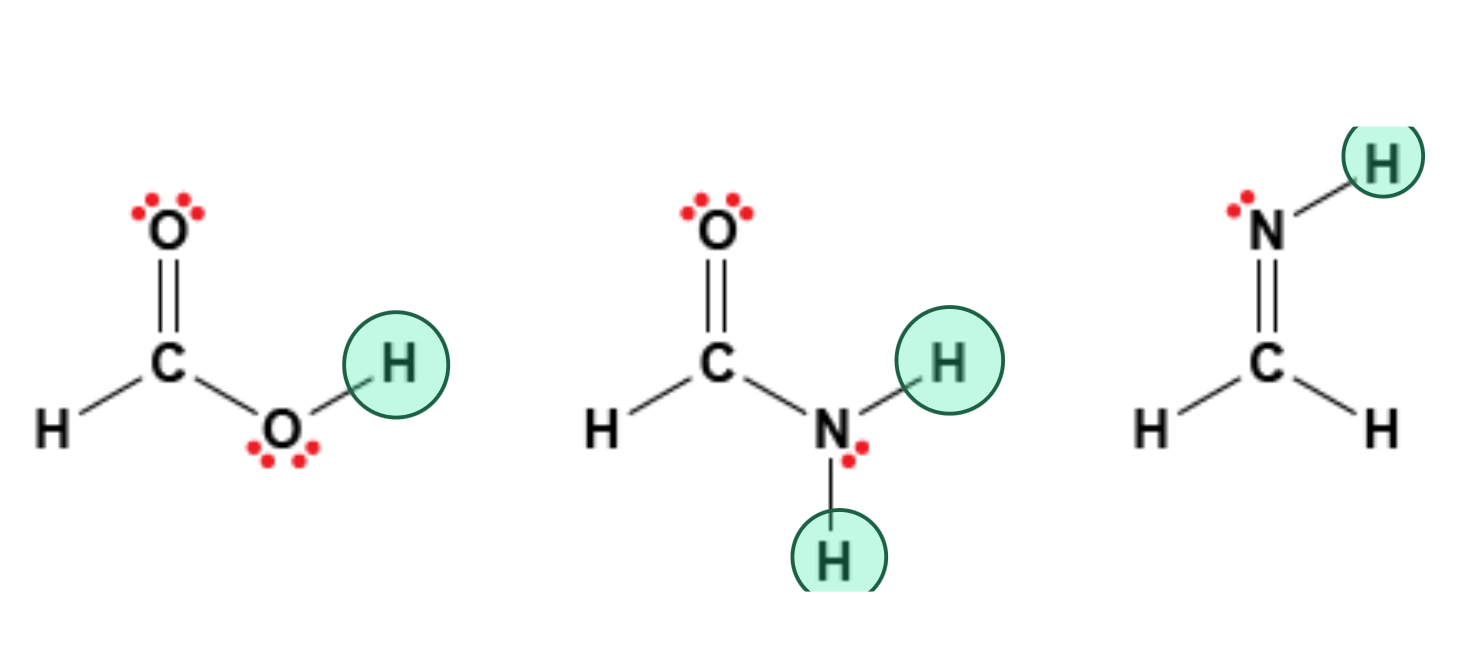
Shown below are the molecular structures of three molecules. Which hydrogen atoms on these molecules could participate in hydrogen bonds?
Which of the following substances does not have ion–dipole forces? Note: (aq) means an aqueous solution (i.e. in water) and (s) means solid (i.e. no water around).
Answer: Cacl2(s)
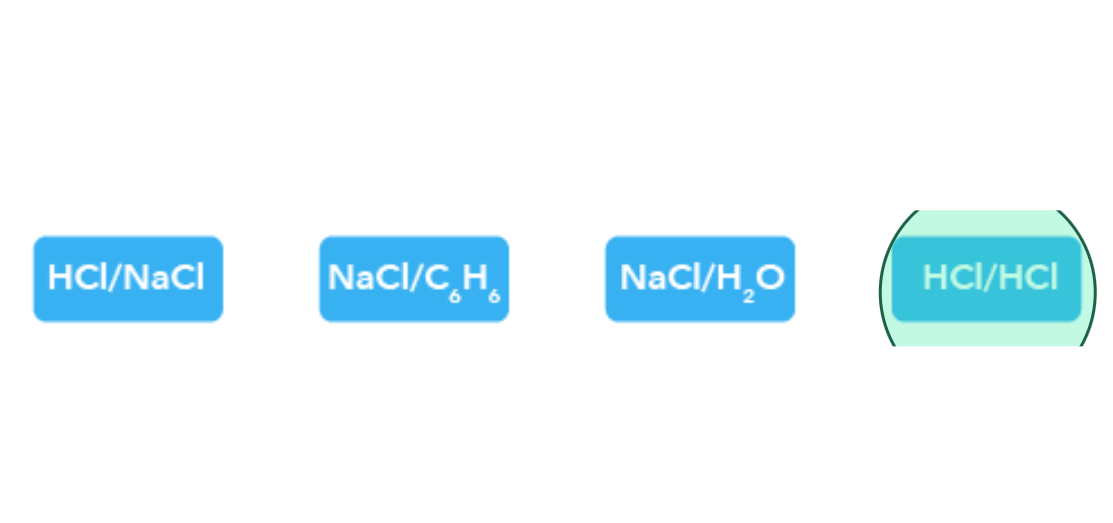
Which of the following mixtures/compounds have ion-dipole forces between them?
Answer: NaCl/H2O
Choose the correct intermolecular force from Column B that matches the compound given in Column A.
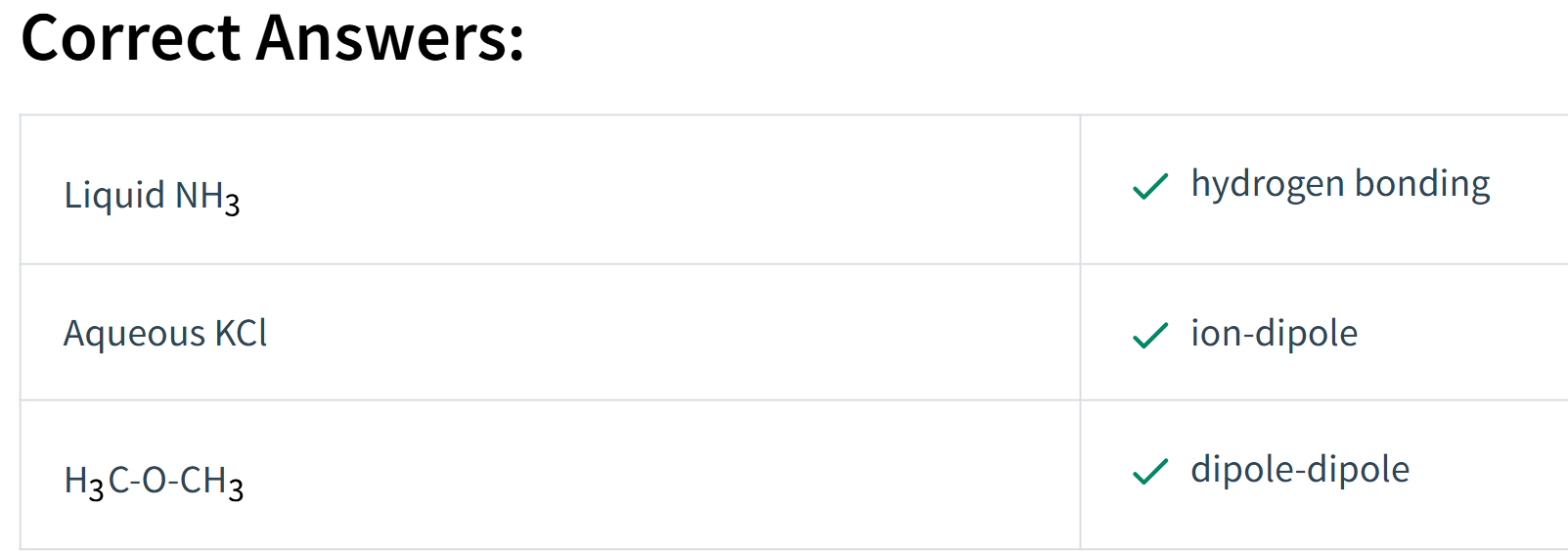
Match the substances given in Column A with the correct intermolecular forces shown in Column B. (Hint: You will need to draw Lewis dot structures.)

Select all intermolecular forces experienced between molecules in a pure sample of the following compound.
Answers: London dispersion, Dipole-dipole, and Hydrogen bonding
Select the dominant intermolecular force experienced between molecules in a pure sample of the following compounds. Remember that lone electron pairs are not drawn.
Answer: Dipole-dipole
Select the dominant intermolecular force experienced between molecules in a pure sample of the following compounds. Remember that the lone electron pairs are not drawn.
Hydrogen bonding
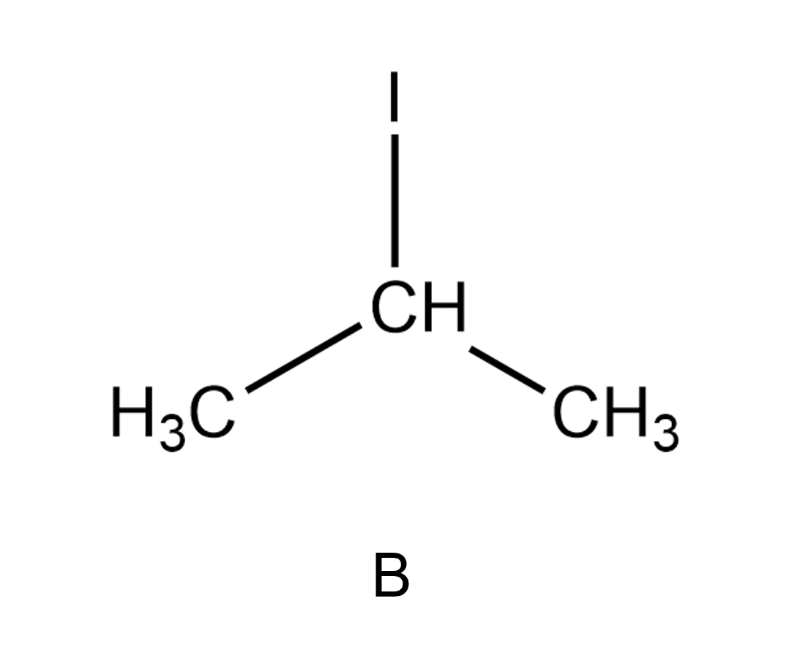
Choose the molecule that would have the strongest London dispersion forces. Remember that lone electron pairs are not drawn.
Which of the following substances has the highest boiling point?
Answer: Xe
Shown in the figure below are the molecular structures of three compounds that all have the molecular formula C8H18 Arrange these substances according to increasing boiling point (lowest boiling point on the top and highest boiling point on the bottom).
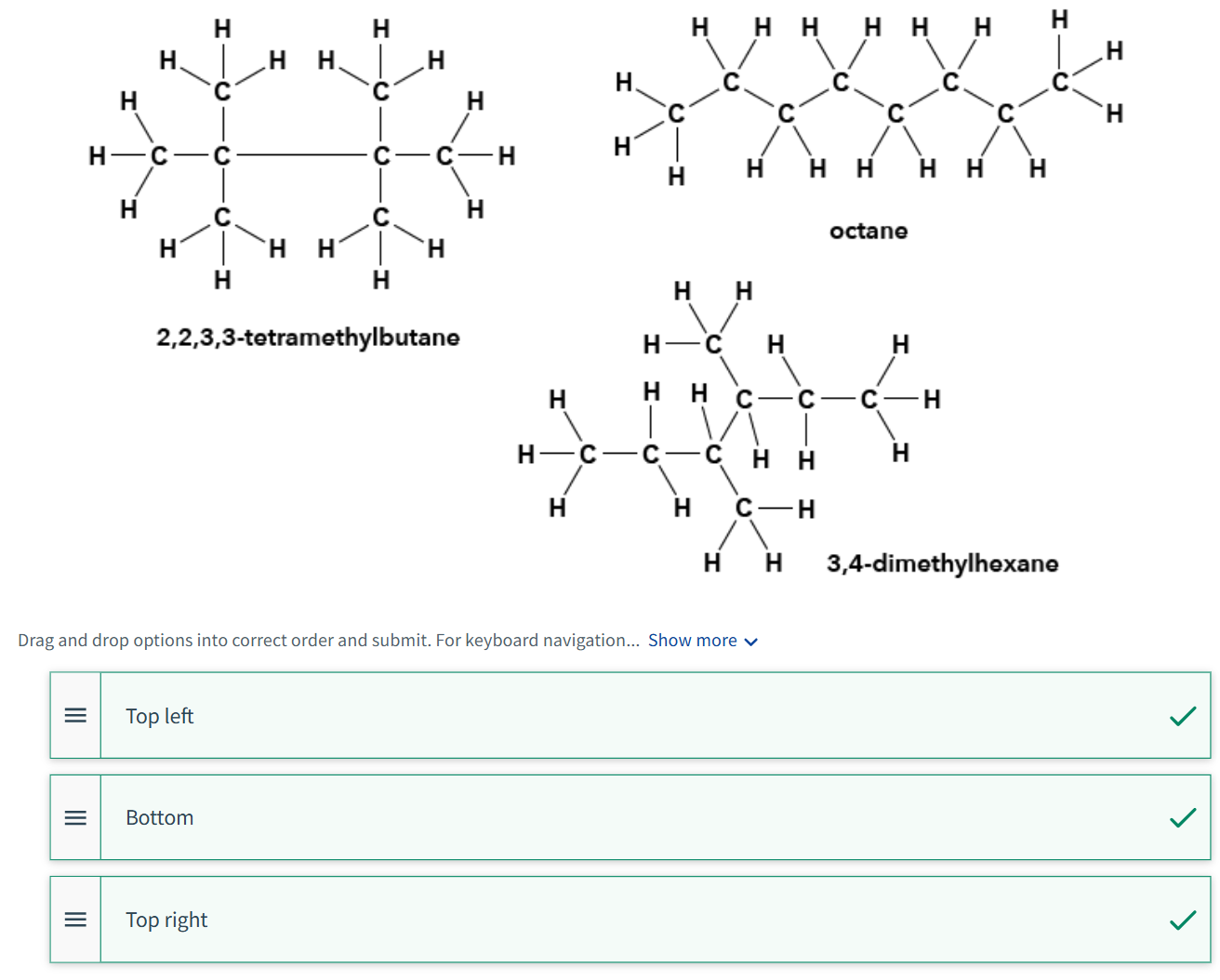
Do you expect these substances to mix?
Answer: High misciblity
Which non-covalent interactions (dashed lines) are occuring between the molecules shown in panel A of the figure above?
Answer: hydrogen bonding
Which non-covalent interactions (dashed lines) are occuring between the molecules shown in panel B of the figure above?
Answer: dipole - dipole interactions
Which non-covalent interactions are occuring between the hydrocarbon chains (just carbon and hydrogen) of the lipid molecules shown in panel C (a section of a cell membrane) of the figure above?
Answer: dispersion interactions
In this figure, 2-phosphoglycerate, an intermediate in the glycolysis pathway, interacting with two Mg+2 ions in the active site of a glycolytic enzyme called enolase is shown. These interactions are essential for glycolysis. What is the strongest non-covalent interaction occurring to stabilize the complex.
Answer: ion - dipole interactions
Which molecule will be more soluble in water and why?
Answer: Ethanol because it is a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor and, therefore can form three hydrogen bonds with water.
The graph below is similar to the one discussed in CH09 Video 1 with additional molecules plotted. Why does NH3 have a higher boiling point than PH3 but CH4 has a lower boiling point than SiH4?

Click on the molecule that has the lowest boiling point.
CH 11 Color of Inorganic Molecules