Understanding Gait: Phases, Terminology, and Abnormalities
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Gait
A person's manner of walking, measured through kinematic (movement), kinetic (forces), and observational analysis.
Heel Strike
Initial contact.
Foot Flat
Loading response.
Midstance
Body progresses over foot.
Heel Off
Terminal stance.
Toe Off
Pre swing.
Acceleration
Initial swing.
Mid Swing
Tibia vertical; limb swings forward.
Deceleration
Terminal swing.
Stride
One full gait cycle (heel to heel of same foot).
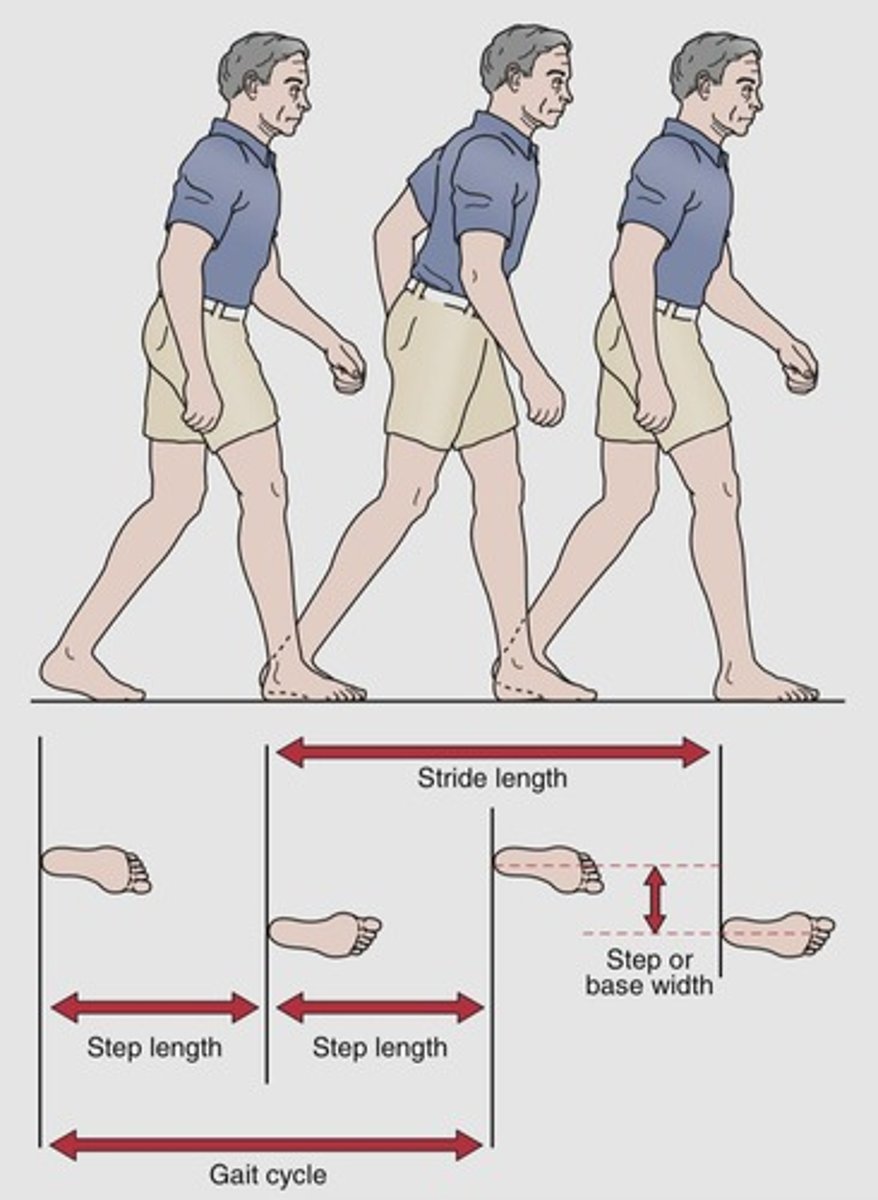
Step
Heel to heel of opposite foot.
Cadence
Steps per minute.
Step Length
Distance between heel strikes of opposite feet.
Stride Length
Distance between heel strikes of the same foot.
Walking Velocity
Speed of walking.
Initial Contact Phase
Heel touches the ground.
Loading Response Phase
Weight transferred onto limb.
Midstance Phase
Body progresses over foot.
Terminal Stance Phase
Heel rises; weight moves forward.
Preswing Phase
Toe-off; weight transferred to other foot.
Initial Swing Phase
Thigh advances; foot lifts off.
Midswing Phase
Tibia vertical; limb swings forward.
Terminal Swing Phase
Knee extends in preparation for contact.
Pelvic Tilt
Weak gluteus medius leads to pelvic drop on the opposite (swing) side — called uncompensated Trendelenburg, normally ~5°.
Lateral Pelvic Displacement
In compensated Trendelenburg, the person leans toward the weak side; normal shift is about 2.5 cm.
Pelvic Rotation
Occurs in the transverse plane, with ~4° forward rotation during swing and 4° backward during stance.
Foot Angle
Measured using the second toe and ankle center; normal is 5°-18° toe-out.
Base of Support
Normal step width is 5-10 cm.
Antalgic Gait
Shortened stance phase on painful side; limp to avoid weight bearing.
Trendelenburg Gait
Pelvic drop on swing side; may lean trunk toward stance side (compensated).
Hemiplegic Gait
Leg is stiff; circumduction or hip hiking during swing; arm often held flexed.
Ataxic Gait
Wide base, unsteady, irregular steps, poor coordination.
Shuffling Gait
Small steps, reduced arm swing, stooped posture, difficulty initiating steps.
Flaccidity
A state of reduced muscle tone.
Spastic synergy patterns
Patterns of movement that occur due to spasticity, where muscles work together in a fixed pattern.
Isolated movements
Movements that occur independently of other muscle groups.
Hamstrings
The muscle group that decelerates the leg during terminal swing.
Tibialis anterior
The muscle that causes foot drop during gait due to weakness.
Mid-stance
The phase that involves the body weight shifting over a single limb.
Gluteus medius
The muscle that prevents hip drop on the opposite side during gait.
Soleus
The muscle that eccentrically controls forward tibial movement during midstance.
Initial swing
The phase that begins the swing phase of gait.
Stance phase
The phase during which the joint moves from flexion to extension.
Brunnstrom Stage 1 gait pattern
Characterized by no voluntary movement.
Gastrocnemius
The muscle group that controls knee extension during terminal stance.
Heel strike
The moment when the foot contacts the ground to prevent foot slap.
Toe-off
An event that occurs in the pre-swing phase.
Pelvis tilt
The movement of the pelvis laterally towards the swing leg during normal gait.
Trendelenburg sign
A sign due to weakness in the gluteus medius muscle.
Brunnstrom recovery stages
Focus on motor function and synergy patterns.
Dorsiflexion
The movement that occurs most at the ankle during gait.
Steppage gait
Typically due to dorsiflexor paralysis.
Terminal stance
Involves heel rise and forward propulsion.
Initial contact
The position of the foot, which is neutral.
Quadriceps
The muscle group responsible for knee extension control during loading response.
Brunnstrom Stage 6
Characterized by isolated, coordinated movements.
Gait movement plane
Primarily described by the sagittal plane.
Pelvic stability
Maintained during single-leg stance by the gluteus minimus.
Deep peroneal nerve injury
Causes foot drop.
Ankle position during mid-swing
Should be neutral.
Extensor synergy gait deviation
Characterized by knee hyperextension.
Brunnstrom Stage 5
Indicates complex movements possible.