Executive Branch
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The Executive Branch in order:
President, Vice president, cabinet, executive office of the president, executive departments
What does “Glorious Burden” mean?
Presidency is a great job, but it is stressful and has a lot of critiques.
Qualifications for presidency
-Native born citizen
-At least 35 years old
-U.S. resident for 14 years
President’s term of office
-elected to a 4-year term
-no term limits in the constitution
-22nd amendment sets a 2 term limit
Salary and benefits for the president
-$400,000 a year plus $50,000 allowance
-Use of Air Force One and a fleet of cars and helicopters
-White House and Camp David
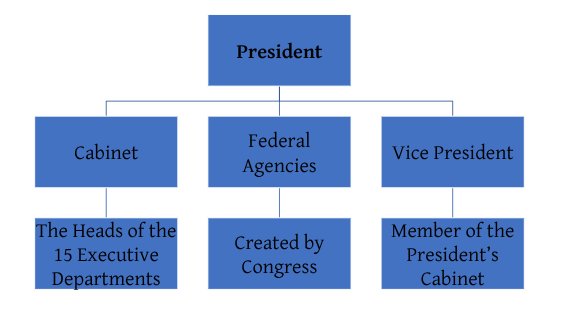
The President receives help from the:
Cabinet Members
Vice President
Heads of Independent and Executive Agencies.
Unlike the powers of the President, their responsibilities are not defined in the Constitution.
Vice President qualification
Must meet same Constitutional requirements as President
Vice President duties and responsibilities
-Takes over if the President dies or is removed from Office
-presides over the senate
Salary and benefits
$235,000 annual salary plus $10,000 allowance
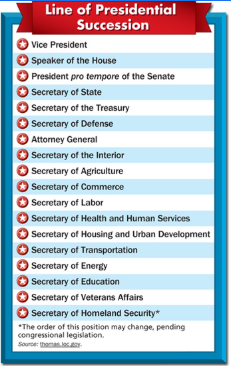
Presidential succession…
Vice President
Speaker of the House
President Pro Tempore of the Senate
Secretary of State
Secretary of the Treasury
Powerful Jobs not listed in Constitution
-Chief of staff
-Whitehouse Press Secretary
Chief of staff
“President’s Gatekeeper” - manages schedule and who can see the President
Whitehouse Press Secretary
-senior White House official
-primary responsibility is to act as spokesperson for the executive branch of the federal government
-Does NOT need Congressional approval.
7 Major Roles of the President
1.) Chief Executive
2.) Chief Diplomat
3.) Commander in Chief
4.) Legislative Leader
5.) Judicial Leader
6.) Chief of State
7.) Political Party Leader
1.) Chief executive
Carries out the nation’s laws
Issues Executive Orders (a command that the President issues that has the force of law; usually during time of crisis)
Appoints cabinet members, ambassadors, judges, heads of govt. agencies (*approval by the Senate)
2.) Chief Diplomat
Responsible for making treaties with other countries with Senate ratification - Agreed Law!
Meets with foreign leaders
Can make Executive Agreements with leaders of other countries, not law without Senate approval
Has some force, but is not law and does not require Senate approval
Responsible for appointing ambassadors with Senate approval
An official representative of a country’s government
3.) Commander in Chief
The President is the final authority over all military matters
- Founding Fathers believed in civilian control over the military; the person elected by the people has final say over all military matters
President can use military in times of war.
1973: War Powers Act passed by Congress
President must notify Congress when troops sent anywhere
Troops must be brought home after 60 days unless
Congress declares war, or gives approval for troops to stay.
This is a controversial Law which has never been challenged in the Supreme Court; Checks and Balances issue?
Who has the Power to Declare War?
Congress
-Article I, Section 8 of the constitution
4.) Legislative leader
Proposes legislation and uses many tactics to get a bill passed
Prepares a federal budget
Approves or vetoes legislation
5.) Judicial Leader
Appoints judges to Federal Courts and the U.S. Supreme Court, with Senate Approval
Appoints Justices whose point of view is similar to their own (Senate approval)
Can Pardon anyone for a Federal Offense (there is not a check on this power)
6.) Chief of state
This role is symbolic – President represents all Americans
- Gives a human face to the US government
- Can be demonstrated in many ways
-Greets heroes
-Speeches, Ceremonies
7.) Political Party Leader
Supports party members in election campaigns and helps unify the party
Appoints members of party to key government jobs
Executive Branch checks on the Legislative Branch
Vetoes bills
Calls Congress into special session
Executive Branch checks on the Judicial Branch
Appoints (recommends) federal judges
Judicial Branch Checks Powers over the President
The US Supreme Court can rule Executive Acts Unconstitutional
Legislative Branch Checks
Powers OVER the President
Senate may or may not approve treaties, presidential appointments, federal judges and US Supreme Court Justices
The House of Representatives appropriates money; “power of the purse”
Congress can override veto with ⅔ majority vote in each house
Congress can impeach and convict the President and Vice President
The Executive Branch influences policy making (laws) by:
-Proposing legislation (giving Congress ideas for laws)
-Giving the State of the Union Address
-Annual speech to Congress that is an important way for a President’s agenda to be communicated to the public and to Congress
-Approving or Vetoing bills
-Appointing officials that carry out the laws
-The President appoints the heads of cabinet departments, independent agencies and regulatory commissions.
-Appealing directly to the people
Budget Proposal
Congress must pass the final budget bill
must be approved by the President in order for the Federal Government to operate.
If not Approved --> Government Shutdown
Budget deadlock
Congress did not pass appropriations bills to fund the government by the deadline.
Political stalemate
A major point of contention was the Democratic party's demand to include the extension of healthcare subsidies in the funding bill, which Republicans and the President opposed.
Revenue
the total amount of money collected by the government through various sources such as taxes on income, consumption goods, investment goods, property, and wealth.
Mandatory Spending
money that is appropriated by law and must be spent as part of the budget, such as Social Security.
Discretionary Spending
money that is not mandated by law to spend and can change is quantity as needed, such as the Military.
Congressional Budget Office
CBO is strictly nonpartisan; conducts objective, impartial analysis; and hires its employees solely on the basis of professional competence without regard to political affiliation.
Tariff
a tax imposed by a government on goods and services imported from other countries
Trade War
an economic conflict often resulting from extreme protectionism, in which countries raise or implement tariffs or other trade barriers against each other as part of their commercial policies to damage the other country’s economy, in response to similar measures imposed by the opposing party.
According to the Constitution, which branch of government has the legal power to impose tariffs?
Legislative branch
Executive Departments
-Congress has the power to establish, reorganize and to eliminate executive departments
-Each department as a specific area of responsibility
-Heads of the 15 Executive Departments make up the President’s Cabinet
Cabinet
Not mentioned in the Constitution, but every President has had a Cabinet
Advise the President and help implement federal laws
Title of most cabinet members is Secretary
EXCEPT the Head of the Department of Justice is the Attorney General
Is there Cabinet Constitutional Authority?
Not a formal organization mandated by the Constitution, but has been created and funded by Congress through legislation (laws).
Article II, Section 2, Clause 1… “he may require the Opinion, in writing of the principal Officer in each of the executive Departments, upon any Subject relating to the Duties of their respective Offices…”
The First Executive Departments:
George Washington’s Presidency
Department of State - Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson
Department of the Treasury - Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton
Department of War - Secretary of Defense Henry Knox (became the Department of Defense)
Office of the Attorney General - Edmund Randolph (became the Department of Justice)
Today there are 15 departments.
Steps in the Process of Appointing Members of the Cabinet
Presidential nomination
White House review
Paperwork financial disclosure
FBI investigation
Senate confirmation hearings
Senate vote (majority needed)
Department of State (1789)
Handles the foreign policy of the nation
Staffs US Embassies
US Ambassador - the President’s highest ranking official to a specific nation
Analyzes data about American interests in other nations
Speaks for the U.S. at the United Nations
Department of the Treasury (1789)
Serves as the financial division of the government
Manages public debt
Prints money and postage stamps; makes coins
Collects taxes (Internal Revenue Service, IRS)
Manufactures coins and currency
Administers explosive and firearm laws
Regulates the production and distribution of alcohol and tobacco
Department of Defense (1789)
Protects the security of the United States
Maintains the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Air Force.
Oversees the armed forces through the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Until 1949 was called the Department of War
Department of Justice (1789)
Oversees the nation’s legal affairs
Supervises the agencies that serve as the nation’s police and prison system
Investigates and prosecutes violation of federal laws.
Operate federal prisons.
Runs the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
Enforces antitrust laws
Department of Homeland Security (2002)
Charged with protecting the security of America’s borders, shores, land and the safety of its people
Oversees the activities of 22 agencies including the Coast Guard, Border Patrol, customs services, Transportation Security Administration (TSA), Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and cyber security
Protects the President and Vice President through the Secret Service
Newest department created in 2002 after September 11, 2001
Department of Interior
Protects the public lands, fish, wildlife, and other natural resources throughout the U.S.
Oversees relationships with Native Americans
Department of Agriculture
Helps farmers improve incomes and production for home and abroad
Develops conservation programs
Safeguards the nation’s food supply (USDA Certified Stamp)
Inspects food processing plants
Runs the food stamp and school lunch programs
Works to control animal and plant diseases.
Department of Commerce
Promotes and protects the industrial and commercial parts of the economy
Provides assistance to American businesses.
Carries out the census
Department of Labor
Ensures safe working conditions
Oversees minimum wages and protects pensions
Collects and analyzes data on employment
Department of Health and
Human Services
Oversees programs concerned with health and social services of the American people
Manages federal Medicare and Medicaid
Runs the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Department of Housing and
Urban Development
Works to assist communities in the nation
Ensures equal housing opportunities
Helps provide housing for low-income citizens.
Assists state and local governments in financing community development and housing projects.
Department of Transportation
Regulates America’s transportation needs, policies and planning
Works to ensure safe, efficient, and convenient land and air transportation
Helps state and local governments maintain highways.
Department of Energy
Plans energy policy
Promotes the conservation of fuel and electricity
Researches and develops energy technology
Department of Education
Coordinates federal assistance programs for public and private schools (elementary, high school, and college education)
Develops programs to help students with limited English proficiency and physically challenged students
Conducts research and provides statistics on education.
Department of Veterans Affairs
Oversees medical care for veterans and families
Manages educational programs for veterans
US Intelligence Community
coalition of 18 agencies and organizations, including the ODNI.
The IC’s mission is to provide timely, insightful, objective, and relevant intelligence to inform decisions on national security issues and events.
Independent Intelligence Agencies
only the ODNI and CIA
ODNI - Office of the Director of National Intelligence (2005)
Their goal is to effectively integrate foreign, military and domestic intelligence in defense of the homeland and of United States interests abroad.
CIA - Central Intelligence Agency (1947)
collecting, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence information to top U.S. government officials.
NSA - National Security Agency
collects, processes, and disseminates intelligence information from foreign electronic signals for national foreign intelligence and counterintelligence purposes and to support military operations.
NSA is also tasked with preventing foreign adversaries from gaining access to classified national security information.
Nation-state threat actors (hackers)
people or groups who use their technology skills to facilitate hacking, sabotage, theft, misinformation and other operations on behalf of a country.
Fancy Bear
is a cyberespionage group that is linked to the Russian government. The group has been in operation since 2008, targeting the energy, government, media, aerospace, and defense sectors via phishing campaigns and credential harvesting.
Cozy Bear
works with another Russian cyber espionage group, Fancy Bear (suspected as part of Russian military intelligence agency GRU or Soviet Military Intelligence). The latter is more infamous, but Cozy Bear is far more covert—possibly more dangerous than Fancy Bear.
Commander in Chief: Branches of Military
Army
Navy
Marines
AirForce
Coast Guard
Space Force
US Army - 1775
Land force
As the First Congress entered its final day on September 29, 1789, now-President Washington insisted that the lawmakers pass an Act clarifying the Army’s role under the new Constitution.
US Navy - 1775
Water Force
-Continental Congress passed a resolution calling for two battalions of Marines to be raised for service with the fleet.
US Marine Corps - 1775
FIRST RELIEF- very diverse
-Second Continental Congress meeting in Philadelphia passed a resolution stating that "two Battalions of Marines be raised" for service as landing forces with the fleet.
US Coast Guard 1790
Coast Force
Established in 1790
-the Coast Guard served as the nation's only armed force on the sea until Congress launched the Navy Department eight years later.
Since then,
What is the only branch of military that serves homeland security?
US Coast Guard
US Air Force 1907
-On Aug. 1, 1907, the U.S. Army Signal Corps established a small Aeronautical Division to take "charge of all matters pertaining to military ballooning, air machines and all kindred subjects."
- National Security Act of 1947 became law on July 26, 1947. It created the Department of the Air Force, headed by a Secretary of the Air Force.
Space Force - 2019
Working within the space domain, our people launch rockets, keep satellites safe and operational, and develop technology to defend our way of life on Earth through our interests in space.
NATO - 1949
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
-founded in response to the threat posed by the Soviet Union. (4/4/1949). Currently 32 nations.
3 Purposes of NATO:
1 - deter Soviet expansionism
2 - forbid the revival of nationalist militarism in Europe through a strong North American presence on the continent
3 - encourage European political integration
STOP THE SPREAD OF COMMUNISM
War Powers Act of 1973
-designed to limit the U.S. president’s ability to initiate or escalate military actions abroad
-the law stipulates that Presidents are required to end foreign military actions after 60 days unless Congress provides a declaration of war or an authorization for the operation to continue.
Independent Agencies and Regulatory Commissions
Created by Congress
Source of Administrative Laws: Laws not created by Congress, but by an agency Congress has given specific permission to create laws to carry out their assigned objectives.
Separate from the executive departments because they perform specialized duties.
Help to carry out federal laws
FCC
Federal Communications Commission
regulates interstate and international communications by radio, television, wire, satellite and cable
EPA
Environmental Protection Agency
protect human health and the environment; reduce environmental risks based on the best available scientific information
“The Fed”
The Federal Reserve System
The central banking system of the United States was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises
The Federal Bureaucracy
Formed by the departments and agencies in the executive branch to improve the effectiveness of the department.
Approximately 3 million people work in the bureaucracy
Operates under many rules and regulations that create “red tape”
Congress has written laws that allow these agencies to create rules/laws that improve their effectiveness
Who are the Inspectors General?
independent government watchdogs who conduct audits and investigations to fight waste, fraud, and abuse, and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of federal programs
What is the Electoral College?
Established by Founding Fathers: compromise between Congress and Popular Vote choosing the President.
Number of Electoral Votes
538 Total Electoral Votes
50 States + District of Columbia
Determined by population! Census every 10 years
Formula for each state:
Number of Senators (2) + Number of House Representatives = Electoral Votes
For Example:
In Minnesota: 2 Senators + 8 House Representatives = 10 Electoral Votes
How many electoral votes to Win?
270 Electoral Votes to Win the Presidency.
Except: Nebraska and Maine…
Proportional allocation.
Does popular vote always win?
No, electoral college needs to be factored in and overrides popular vote.
What is Impeachment?
1: a charge of misconduct made against the holder of a public office.
2: the action of calling into question the integrity or validity of something.
The President, Vice President and all civil officers of the United States, shall be removed from office on impeachment for, and conviction of:
Impeachment Trial Process
House of Representatives "shall have the sole Power of Impeachment"
“The Senate shall have the sole power to try all impeachments.
If House votes to impeach, then Chief Justice presides over trial in the Senate and the Senate may vote to remove the President by 2/3 majority
Impeachment Conviction
the party convicted shall nevertheless be liable and subject to indictment, trial, judgment, and punishment, according to law
Can members of congress be impeached?
No, because they are not civil officers.
Who is responsible for Ensuring Domestic Tranquility?
The Federal Government has the power to keep the peace; maintain law and order.
How to deal with Civil Unrest?
Bring in the National Guard (controlled by the state)
Presidents can “federalize” branches of the National Guard to respond to Civil Unrest --- but only by using the Insurrection Act
Insurrection Act
Gives U.S. presidents the authority to deploy active duty military to maintain or restore peace in times of crisis
What is Domestic Terrorism?
an act "dangerous to human life" that violates state or US law:
(i) intimidate or coerce a civilian population;
(ii) influence the policy of a government by intimidation or coercion; or
(iii) to affect the conduct of a government by mass destruction, assassination or kidnapping.
What is Sedition?
The act of inciting resistance, rebellion, or violence against a lawful government
-often through speech, writing, or organization
-intending to cause its overthrow or disruption, and is distinct from treason (actual betrayal/war) but is a serious federal crime in the U.S.
What is an Insurrection
An insurrection is a violent uprising or rebellion against a government or authority.
-typically characterized by organized and armed resistance, distinguishing it from a simple riot or disturbance.
-Insurrections aim to overthrow the existing government or change the political order.
What is a pardon
an executive action that relieves a person of some or all of the legal consequences of a criminal conviction
Who has the power to pardon?
The president
-it’s an unchecked power
What is an executive order
a directive by the president of the United States that manages operations of the federal government
can be struck down by the Courts
Examples:
The Emancipation Proclamation
The Manhattan Project
Japanese Internment Camps
Desegregating the US Military
National Guard Deployed to Desegregate Schools
Creation of the Peace Corps