Anatomy and Phisiology: Unit 2
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 5,6,7,8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Epiphysis
Articular Cartilage
Diaphysis
Periosteum
Medullary Cavity
Endosteum
Marrow
Yellow marrow stores fat; it is not active in blood cell production.
Magnesium
Sodium
Potassium
Carbonate Ions
Radium
Strontium.
What does the axial skeleton consist of?
Hyoid Bone
Vertebral Column
Thoracic Cage
Upper Limbs
Pelvic Girdle
Lower Limbs
Thoracic Vertebra
Sternum
Costal Cartilages
2 Scapulae
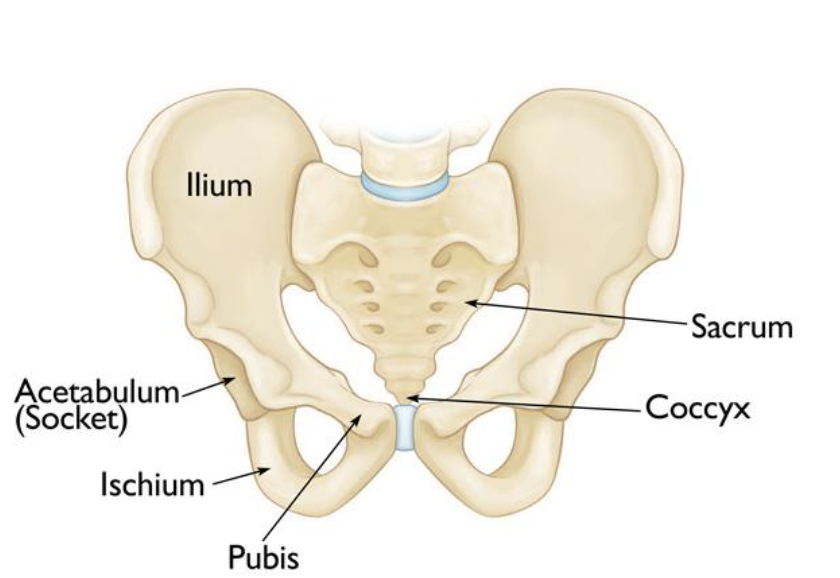
Ischium
Pubis
Body
Xiphoid Process
Acetabulum
Ischium
Pubis
Coccyx
Sacrum
Hinge
Pivot
Condyloid
Saddle
Ball and socket
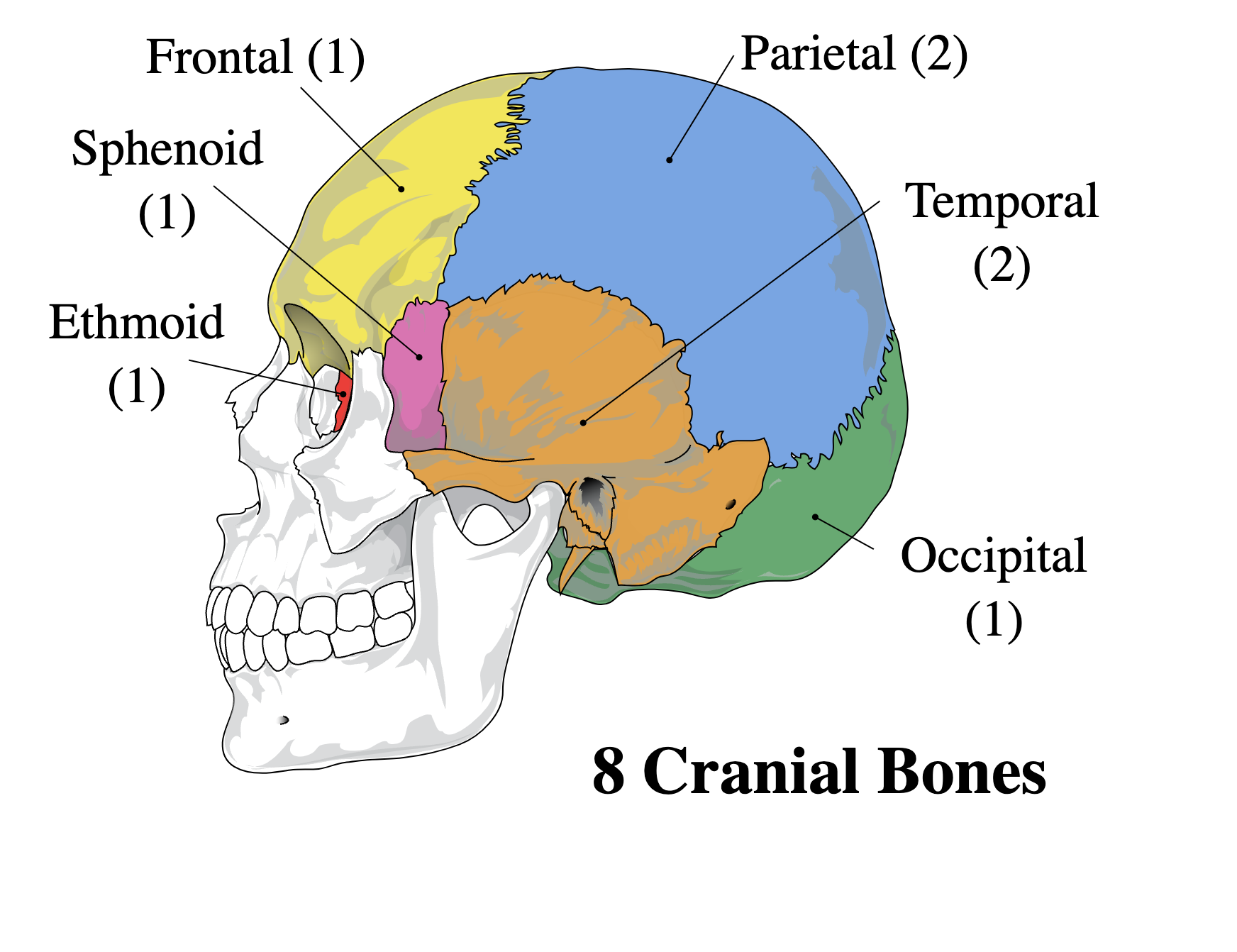
Parietal R&L
Occipital
Temporal R&L
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
True Ribs (Vertebrosternal)
Ribs 1-7. Directly attached to the sternum by costal cartilage.
False RIbs
Ribs 8-10. Do not attach to the sternum, some of the costal cartilage connects to the costal cartilage of the 7th true rib.
Floating Ribs
Ribs 11-12. Half the size of the other bones and don’t attach to the sternum at all.
Cervical Vertebrae
Consists of the first seven vertebrae in your spine. It provides support for the weight of your head, surrounds and protects your spinal cord, and allows for a wide range of head motions
Thoracic Vertebrae
Consist of 12 vertebrae and is the longest section in the spine. These bones help protect your spinal cord from injury while allowing you to twist and turn.
Lumbar Vertebrae
Consist of 5 vertebrae and is located under the thoracic vertebrae. It provides stability for your back and spinal column and allow for a point of attachment for many muscles and ligaments. It supports most of your body’s weight and also is the center of your body’s balance.
Describe how movements occur at a joint when a muscle contracts.
It pulls the bone from the insertion end towards the origin end, which creates a certain movement of a joint. Which type of movement depends on the type of synovial joint.
Which structures help keep the articulating surfaces of the hip together?
The ball-like head of the femur and the acetabulum(socket)of the hip bone. This type of joint is a synovial joint.
What terms describe movements at synovial joints?
Flexion where the angle between the bones of the joint decrease.
Extension where the angle between the bones increases.
Synarthrosis (Fibrous) Joint
Immovable and have no joint cavity.
Syndesmosis (Fibrous) Joint
Two adjacent bones are linked by a strong membrane or ligaments.
Gomphosis (Fibrous) Joint
Synarthrotic joint which a conical process is inserted into a socket-like portion.
Synchondrosis (Cartilaginous) Joint
Bones are joined by the hyaline cartilage.
Symphysis (Cartilaginous) Joint
Bones are joined by fibrocartilage.
How are joints classified?
Joints are classified into two groups based on their anatomical characteristics and functionally, based on the type of movement they permit.
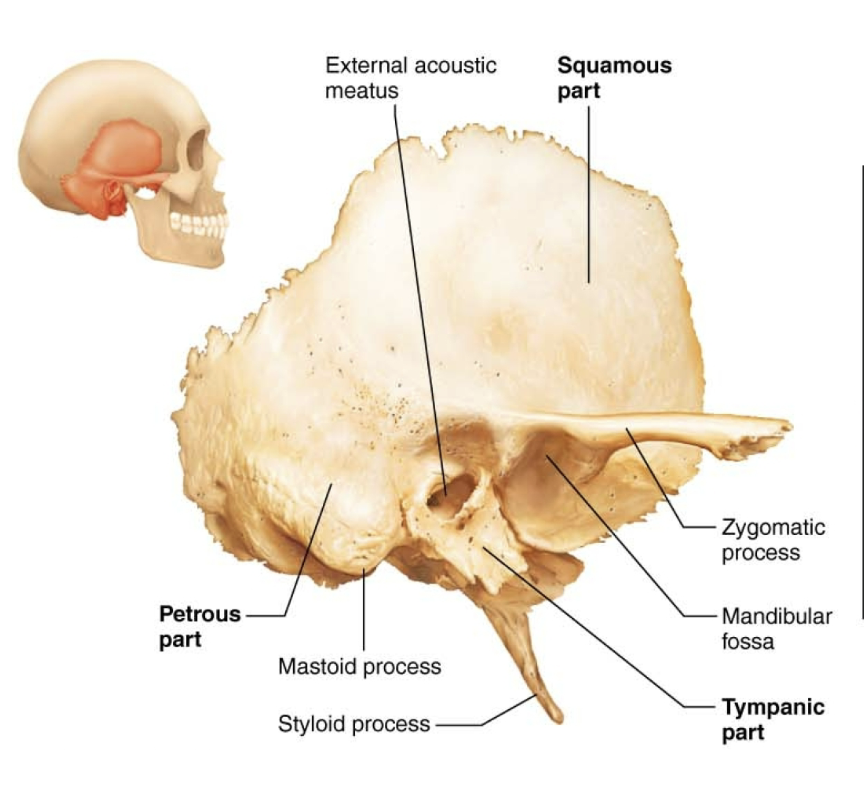
Temporal Bone
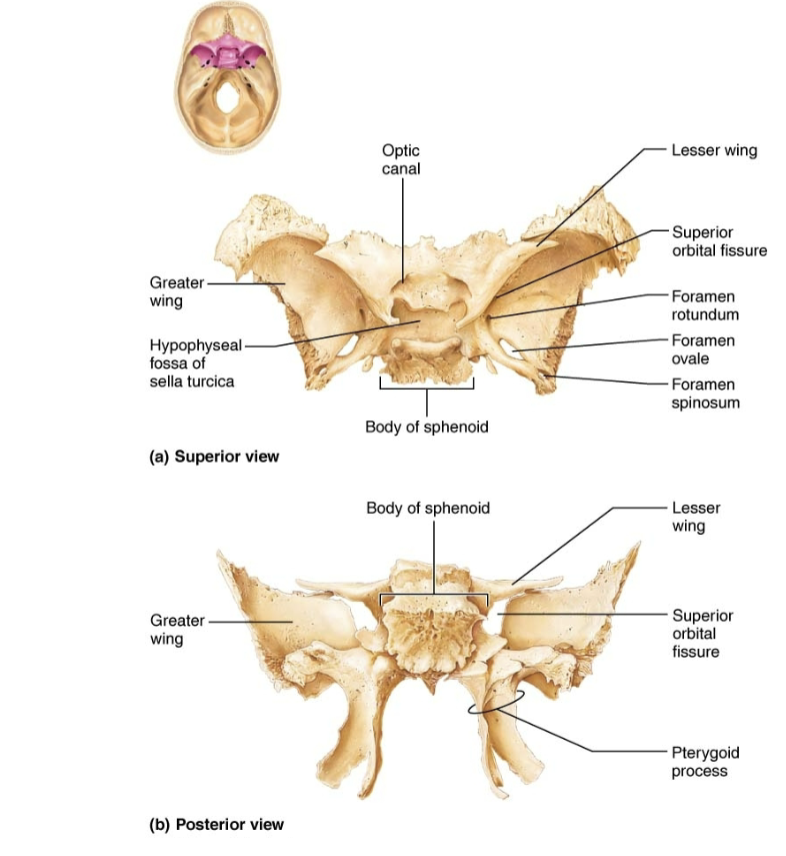
Sphenoid Bone
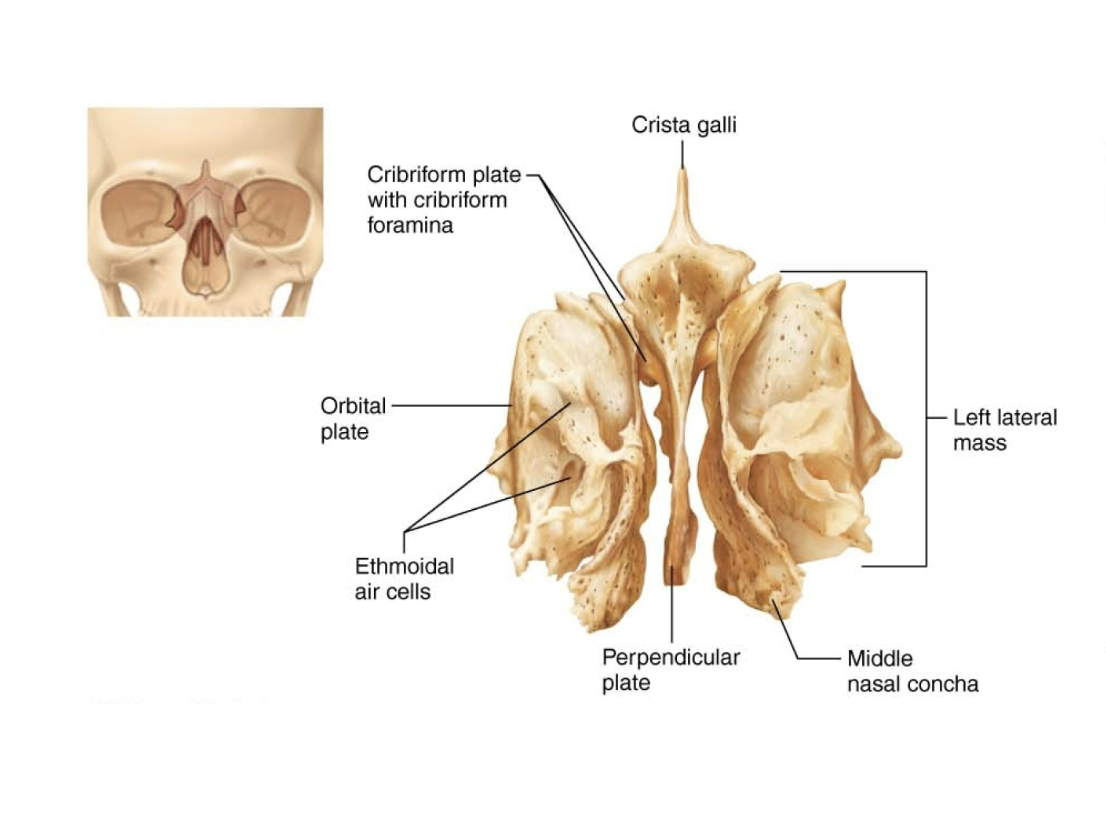
Ethmoid Bone
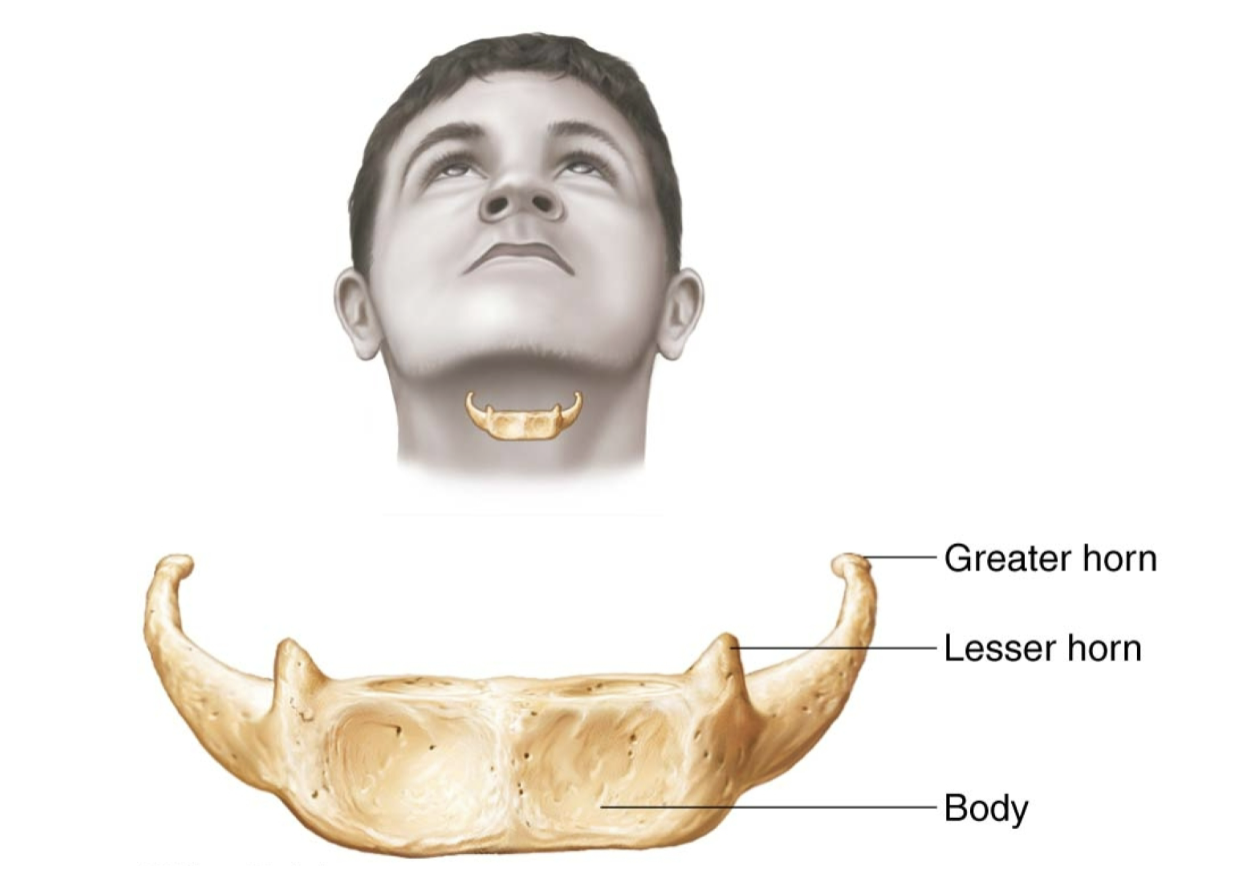
Hyoid Bone
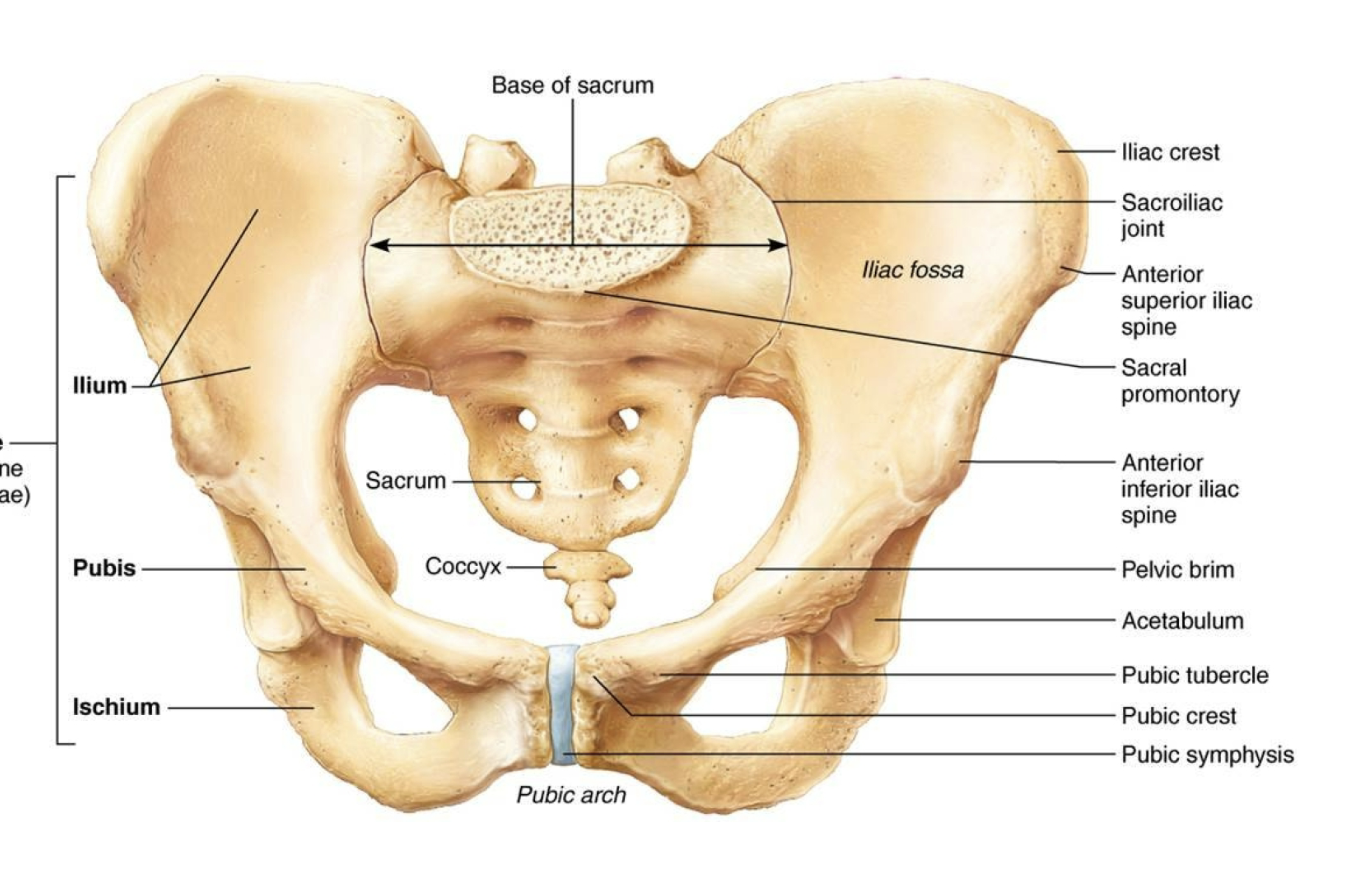
Pelvis
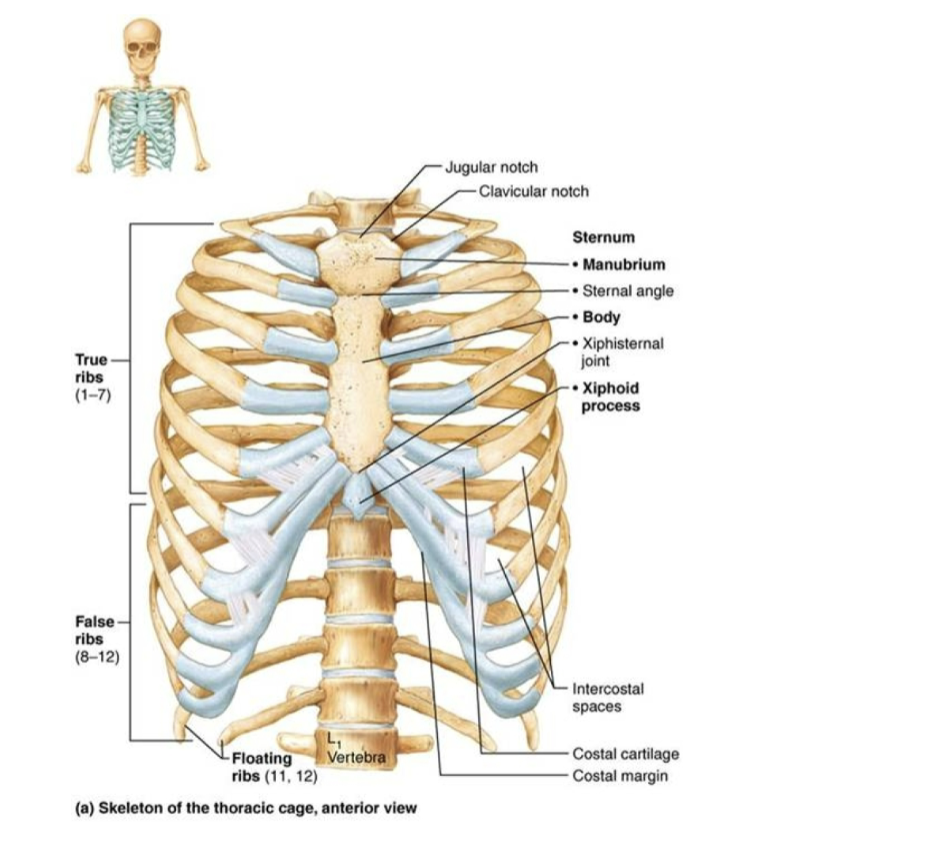
Thoracic Cage
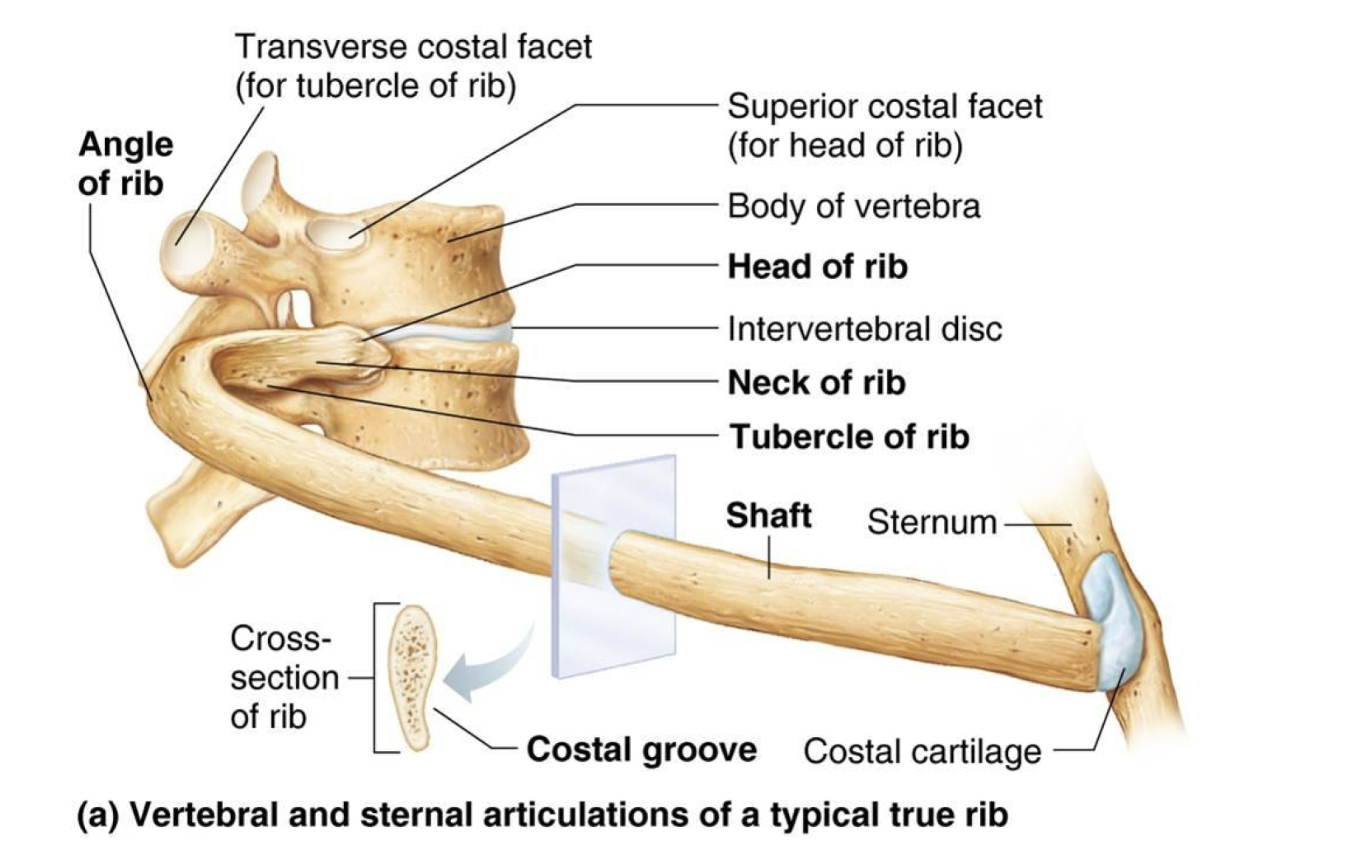
Rib
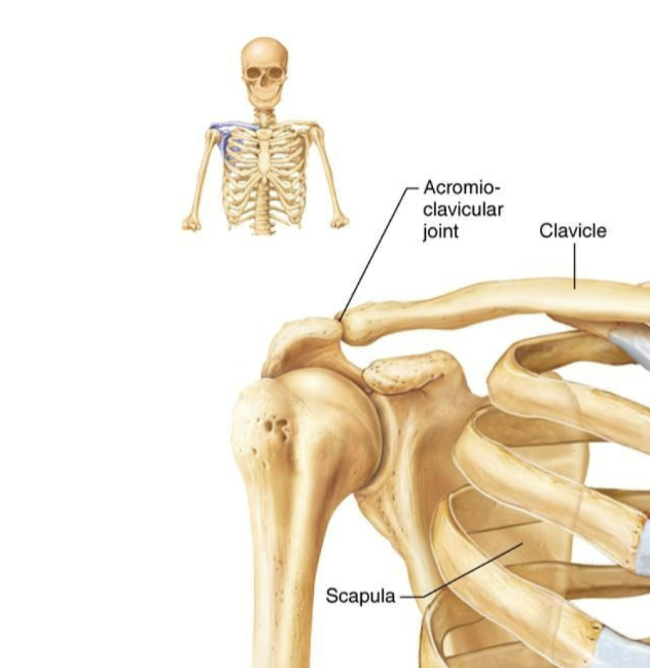
Pectoral Girdle
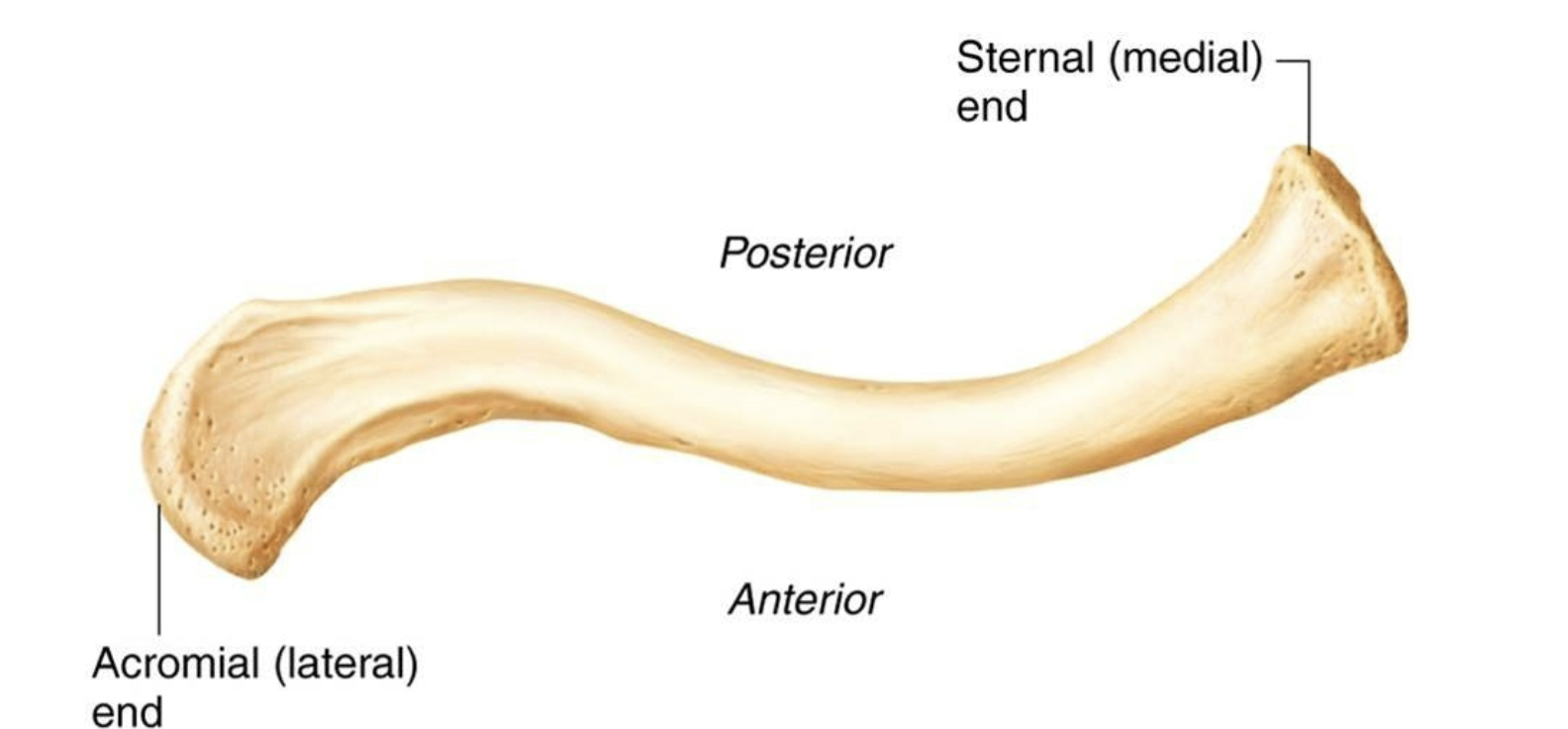
Clavicle Superior
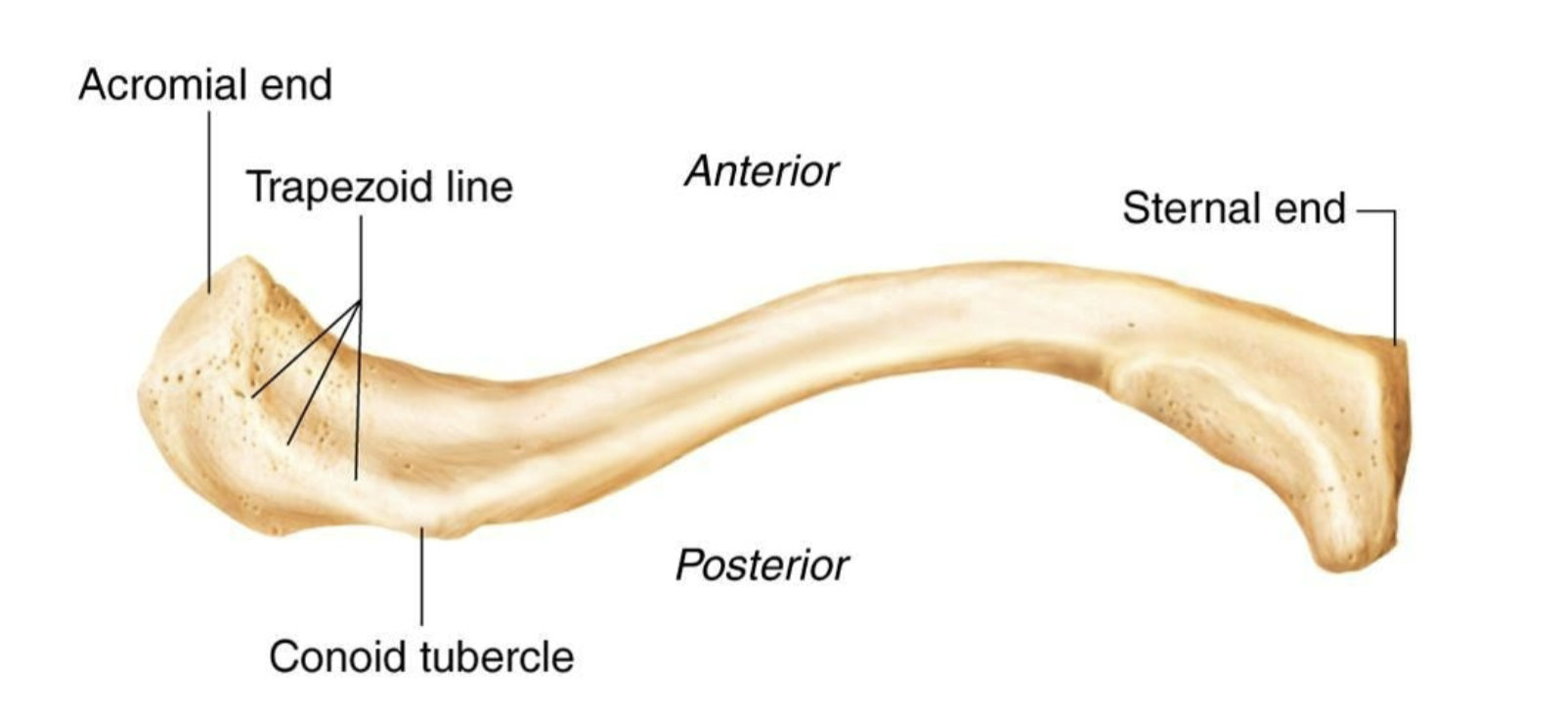
Clavicle Inferior
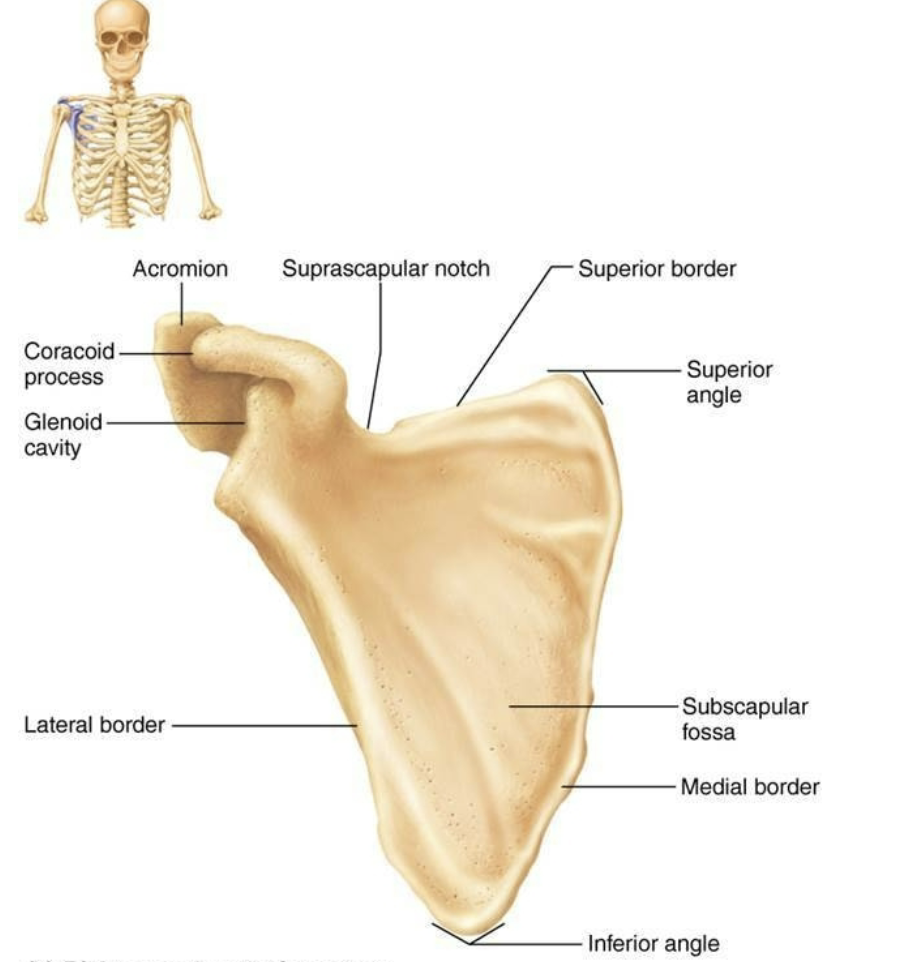
Scapula Anterior
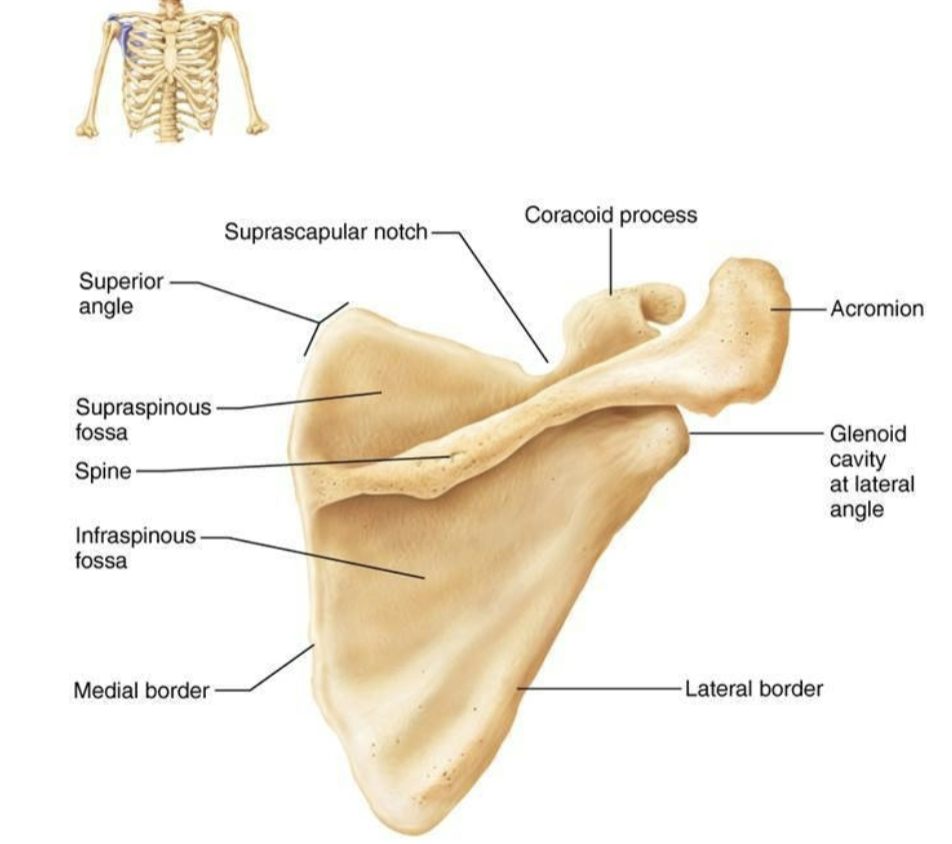
Scapula Posterior
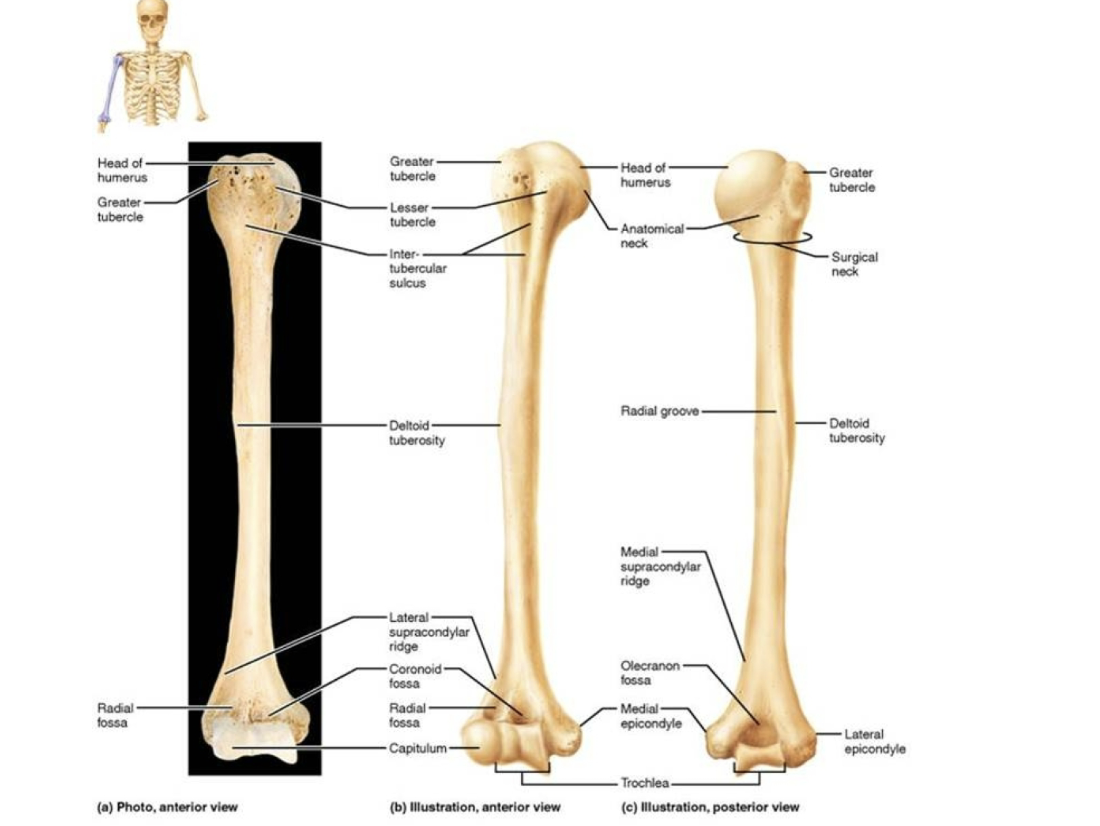
Humerus
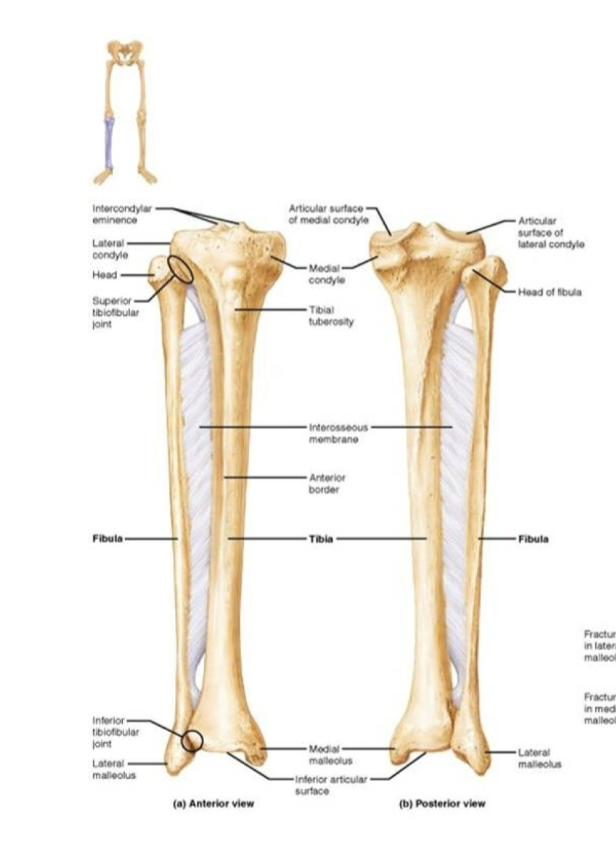
Fibula, Tibia
Name the layers of the epiphyseal plate.
Resting cartilage
Proliferating cartilage
Hypertrophy
Calcification
Resting cartilage layer
Full of deposited precursor chondrocytes. These cells will, later on, migrate to the proliferation zone. This layer serves reservoir purposes only.
Proliferating cartilage layer
organized in columns, isogenous chondrocytes are stacked on top of each other and undergo hypertrophy. While growing, the chondrocytes migrate from layer 2 into layer 3.
Hypertrophy layer
Chondrocytes from the zone of hypertrophy produce large amounts of extracellular matrix. The main component of this matrix is collagen. Because chondrocytes are trapped in the columns, they will enlarge and bones grow longitudinally.
Calcification layer
Apoptosis of chondrocytes occurs. After the removal of chondrocytes, this area will be colonized by osteoprogenitor cells and ossification will start.
What effects do hormones have on bone growth?
Growth hormone stimulated mitosis in the cartilage cells of the epiphyseal plates. Thyroid, Parathyroid, Male and Female Sex Hormones.