Physics T1: Motion, Forces and Energy
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
D. Speed
distance travelled per unit time
F. Speed
Speed = total distance/ time taken
U. Speed
m/s
Average speed
Total distance/ Total time taken
Difference between velocity and speed
Velocity has direction as well as magnitude
D. Acceleration
Change in velocity per unit time
F. Acceleration
Change in velocity/ change in time
U. Acceleration
m/s²
D. Mass
Amount of matter in an object which is at rest relative to the observer.
U. Mass
kg
D. Weight
Gravitational force that acts on an object with mass
U. Weight
Newtons
F. Gravitational Field Strength
Weight/ mass
U. Gravitational field strength
N/kg
D. Density
Substance’s mass per unit volume
F. Density
mass/ volume
How to find density of solid objects
1) Measure mass—balance
2) For irregular shaped object find volume through displacement—submerge in a beaker of water
3) Measure initial volume of water
4) Record the difference in volume
5) Use formula to find density
How to find density of liquids
1) Place a measuring cylinder on balance + zero the balance
2) Pour some liquid into measuring cylinder.
3) Record mass and volume of liquid
4) Use formula to find density
What has a higher density, water or oil?
Water—oil with float on its surface
D. Resultant force
Single Force that has the same effect as all forces acting at a single point
D. Vector quantities
Have magnitude and direction
D. Scalar quantities
Have only magnitude and no direction
Tip-To-Tail Method
1) Draw all forces acting on object to scale
2) Draw straight line from start to finish
3) Length—Magnitude
4) Angle—Direction
E.g: “5N at angle 37° East from North
5 ways forces change motion:
Start moving
Stop moving
Speed up
Slow down
Change direction
F. Force
Mass * Acceleration
Velocity in circular motion
Constantly changing—accelerating
Resultant force of circular motion
Perpendicular to direction of velocity
Towards centre of circle
D. Centripetal force
Force that keeps something moving in a circle
3 rules of centripetal force:
1) CP increased—speed increases
2) CP increased—radius of motion decreases
3) Mass increased—CP increases for speed and radius to stay constant
D. Solid friction
Force between 2 solid objects that are in contact, and are moving or trying to move relative to each other.
Impedes motion and results in heating.
D. Drag
Friction in a gas or a liquid
Uniform gravitational field near surface—
Without air resistance, objects would accelerate at a constant rate
Without air resistance:
Same acceleration of all objects
Same time to fall
The faster an object is moving…
The greater its air resistance
Describe objects falling through air:
1) Force of gravity much greater than resistance—accelerate
2) As speed increases—resistance increases
3) Acceleration is reduced
4) Resistance = Acceleration—resultant force is 0
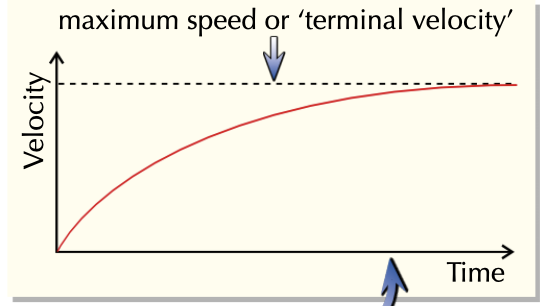
5) Terminal velocity—steady, maximum speed
Terminal velocity on graph:
Apart from motion, forces can:
Stretch, compress, bend or twist
(More than one force needed)
Permanently deformed object:
Doesnt return to its original shape and length after force is removed
Load extension graph
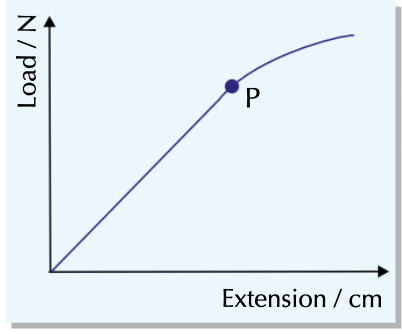
D. Limit of proportionality
Point at which the load and extension stop being proportional
D. Spring constant
Force per unit extension
F. Spring constant
Force/ Extension
U. Spring Constant
N/cm
Apparatus when investigating link between force and extension
Weighted stand
Clamp
Fixed ruler
Spring
Mass
Method when investigating link between force and extension
1) Measure natural length of the spring
2) Add a marker to bottom of spring
3) Add mass to spring + allow spring to come to rest
4) Record mass + New length of spring
5) Repeat this process
D. Moment
Measure of its turning effect
F. Moment
Force * perpendicular distance from pivot
U. moment
Nm
Principle of moments:
Balanced object means: total anticlockwise moments = total clockwise moments
An object is in equilibrium when
There is no resultant force on it and no resultant moment
Method: Investigating equilibrium
1) Rest a beam on a pivot until it balances
2) Hang a known mass on left side, at a fixed distance
3) Hang a second mass on right side—move mass until balanced
4) Measure distance between pivot and right mass
5) Calculate clockwise and anticlockwise moments
6) Repeat with a different mass on right
D. Center of gravity
The point through which the weight of the object acts.
Method to find center of gravity:
1) Suspend shape and plumb line from same point
2) Draw line along plumb line
3) Suspend shape from different pivot point
4) Draw another line
5) Center of gravity is where the 2 lines cross
Stable object:
1) Low center of gravity
2) wide base area
D. Momentum
Mass * velocity
What type of quantity is momentum?
Vector quantity
U. Momentum
kg m/s
Principle of conservation of momentum:
Total momentum before = total momentum after event, as long as no external forces act
D. Impulse
Size of force * length of time it acts for
F. Impulse
Force * time
Change in momentum
U. Impulse
Ns
F. Resultant force
Momentum/ change in time
7 energy stores:
1) Kinetic
2) Gravitational Potential
3) Chemical
4) Elastic
5) Nuclear
6) Electrostatic (charges)
7) Internal/ Thermal
4 ways of energy transfer:
1) Mechanically: work is done
2) Electrically: Electric current flows
3) Heating
4) Waves: e.g. light transfers energy. from sun to earth
Principle of Conservation of Energy:
Energy can be stored, transferred or dissipated—never created or destroyed.
F. Kinetic energy store
½ mass* velocity²
F. GPE energy store
Mass * gravitational field strength * change in height
Falling objects’ transfer of energy
Energy lost from gpe store = Energy gained in ke store
D. Work Done
= to energy transferred
F. Mechanical work done
Force * Distance moved
U. Work done
Joules
F. Power
Energy transferred/ time taken
U. Power
Watts or J/s
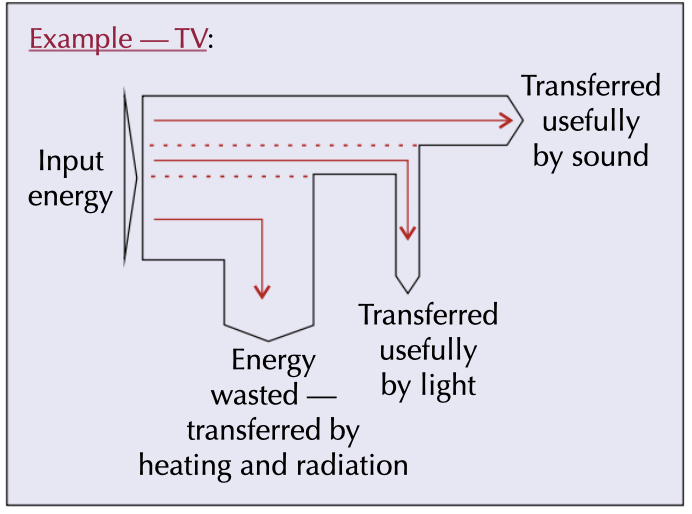
F. Efficiency
Useful energy output/total energy input * 100
TV efficiency on Sankey Diagram
F. Pressure
Force / Area
F. Pressure in liquids
Density * gravitational field strength * change in depth
U. Pressure
Pascals (Pa)
D. Non-renewable energy resource
Cannot be made at the same rate as it’s being used—will run out
2 fuels that are non-renewable
1) Fossil fuels—coal, oil, natural gas
2) Nuclear fuel—uranium, plutonium
D. Renewable energy resource
Can be made at same rate than it’s being used.
7 renewable resources
1) Solar
2) Wind
3) Water waves
4) Hydroelectricity
5) Biofuels
6) Tides
7) Geothermal
Most important use of energy resources
Generating electricity
Other uses of energy resources
heating
transport
Process in a fossil fuel power station
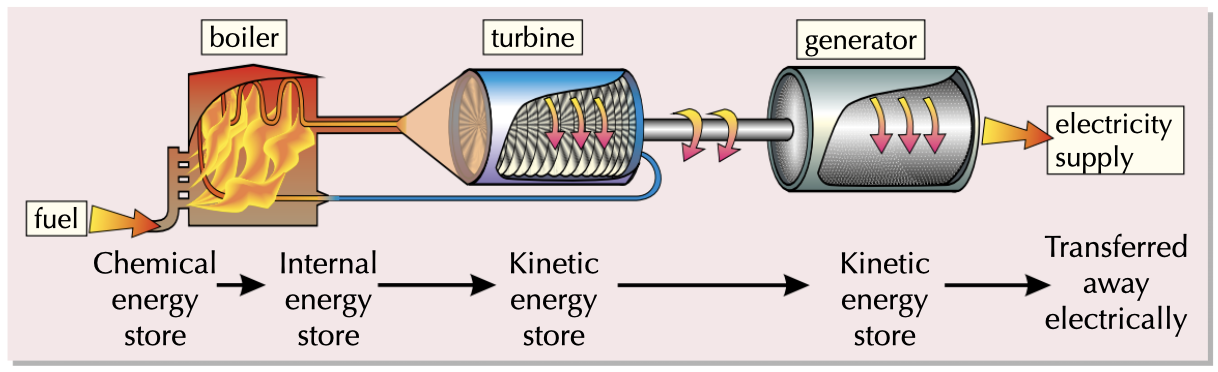
Process in Nuclear Power Stations
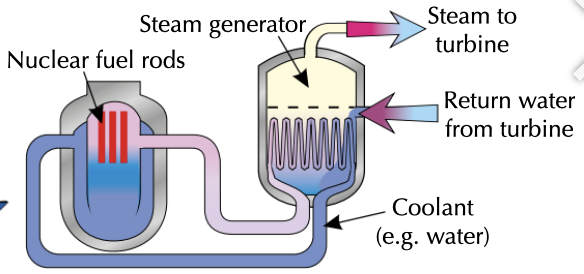
Environmental problems caused by burning non-renewable resources:
1) Sulfur dioxide—acid rain
2) Power stations—views spoiled
3) CO2—greenhouse effect
4) Oil Spillages—animals in sea affected
5) Nuclear waste—difficult to dispose of
6) Nuclear power stations—catastrophes
Nuclear fusion:
Nuclear reaction that releases more energy and less nuclear waste—unlimited.
Needs high temperatures
Describe how solar cells work
Generate electric currents directly from sunlight.
Pros of solar cells
1) No pollution
2) Can be used in remote areas
3) Don’t use much electricity
Cons of solar cells
1) Produce little power per unit space taken up
2) Solar power only available in daytime
3) Can’t increase power output when demand increases
D. Biofuels
Renewable energy resource created from plant products or animal dung.
Pros of biofuels:
1) Carbon neutral
2) Reliable
Cons of biofuels:
1) Lots of space needed
2) Lands of forests have been cleared out to grow biofuels.
Describe how wind turbines work
1) Sun is source of wind energy
2) Temperature of earth changes—wind made
3) Blades of turbine are rotated
4) Turn a generator
Pros of wind power
1) No pollution produced
2) No permanent damage to landscape
3) Work in large scale and small scale
Cons of Wind Power
1) Visual pollution
2) Noisy
3) Not always reliable
Describe how Geothermal Power works
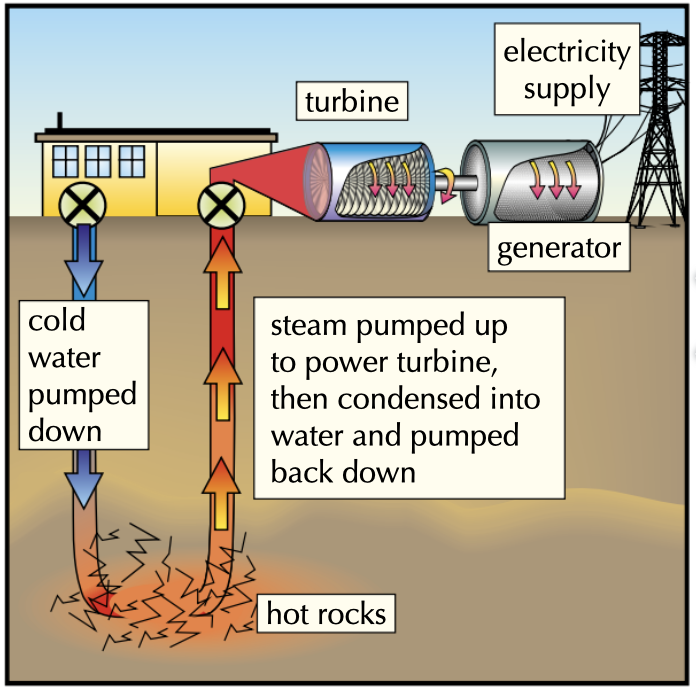
Pros of Geothermal Power
1) Very reliable
2) Few environmental problems
3) Used in large scale and small scale
Cons of Geothermal Power
1) Only available in volcanic areas—rocks near surface
2) Cost of building power stations high