EXAM 3 Chapter 10 The Muscular System II: Major Muscles of the Axial Skeleton単語カード | Quizlet
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
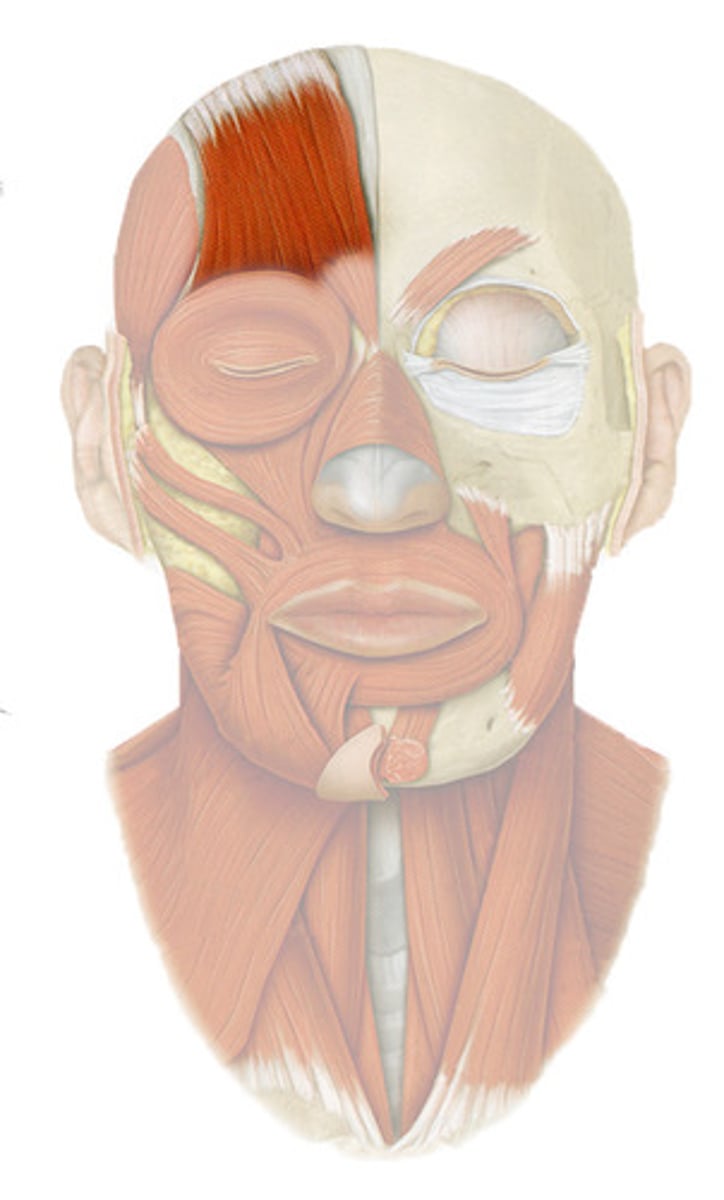
FRONTALIS
o: galea aponeurotica
i: skin of eyebrows
a: RAISES EYEBROWS
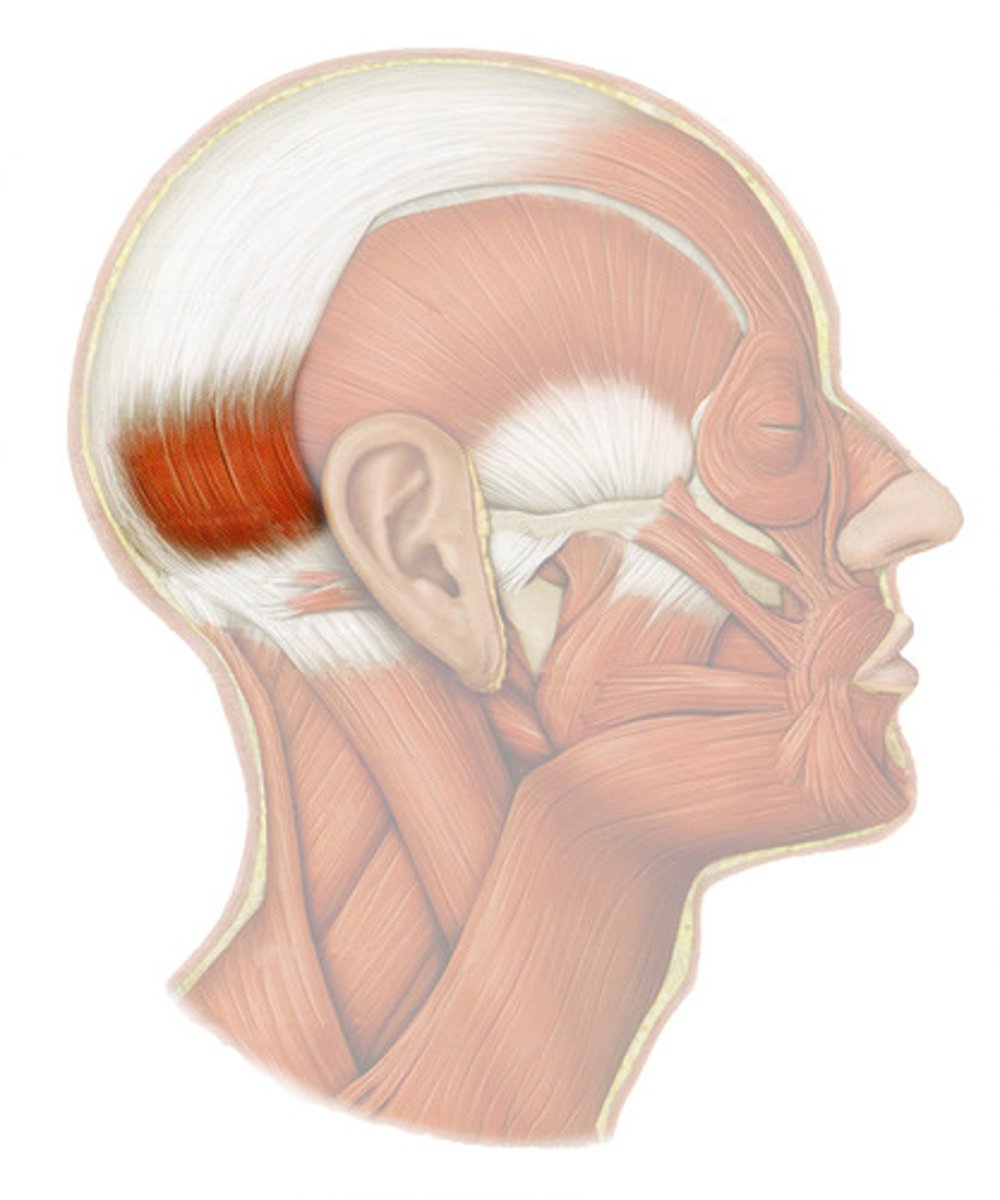
OCCIPITALIS
o: occipital and temporal bones
i: galea aponeurotica
a: PULLS ON SCALP POSTERIORLY
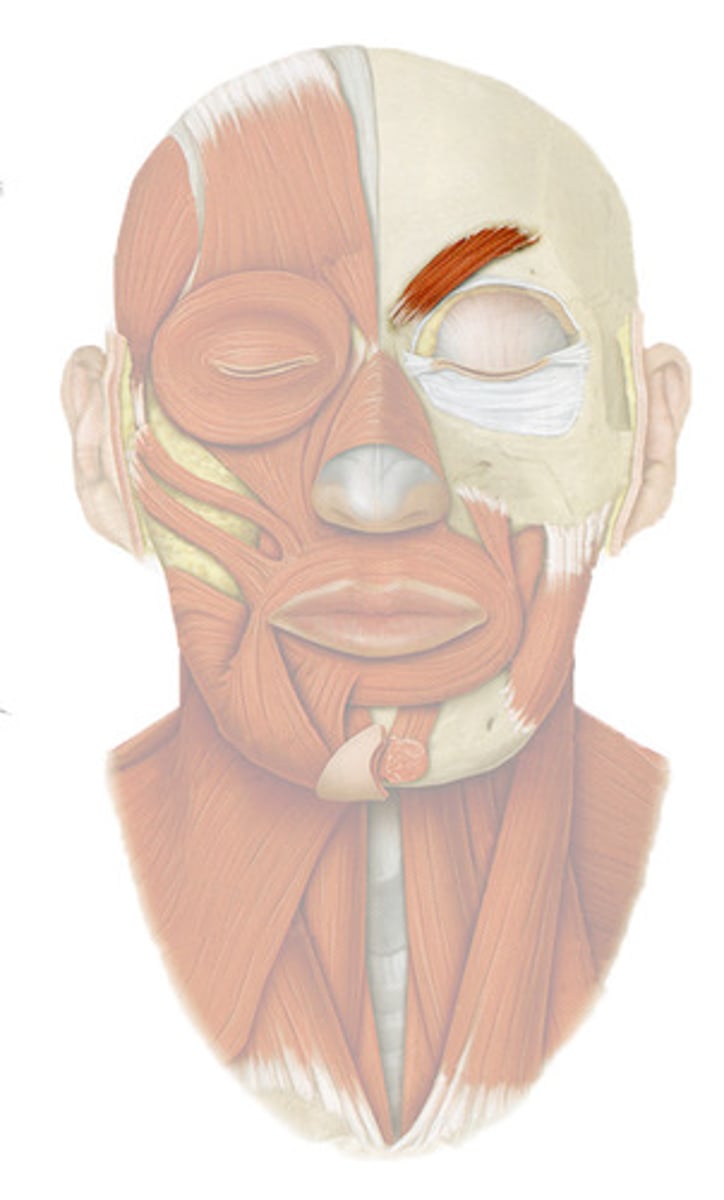
CORRUGATOR SUPERCILII
o: Frontal bone above nasal bone
i: skin of eyebrow
a: DRAWS EYEBROWS TOGETHER (FROWNING)
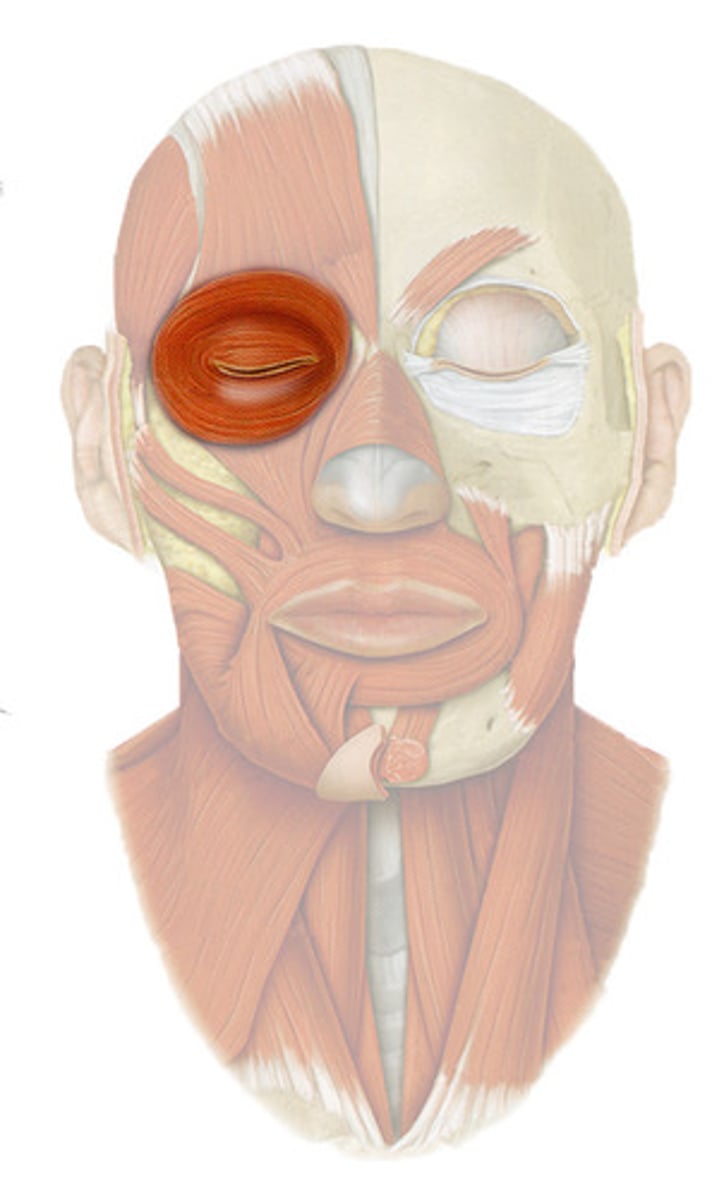
ORBICULARIS OCULI
o: frontal and maxillary bones around orbit
i: tissue of eyelid
a: CLOSES EYE
ZYGOMATICUS
o: zygomatic bone
i: corner of mouth
a: RAISES CORNERS OF MOUTH UPWARD
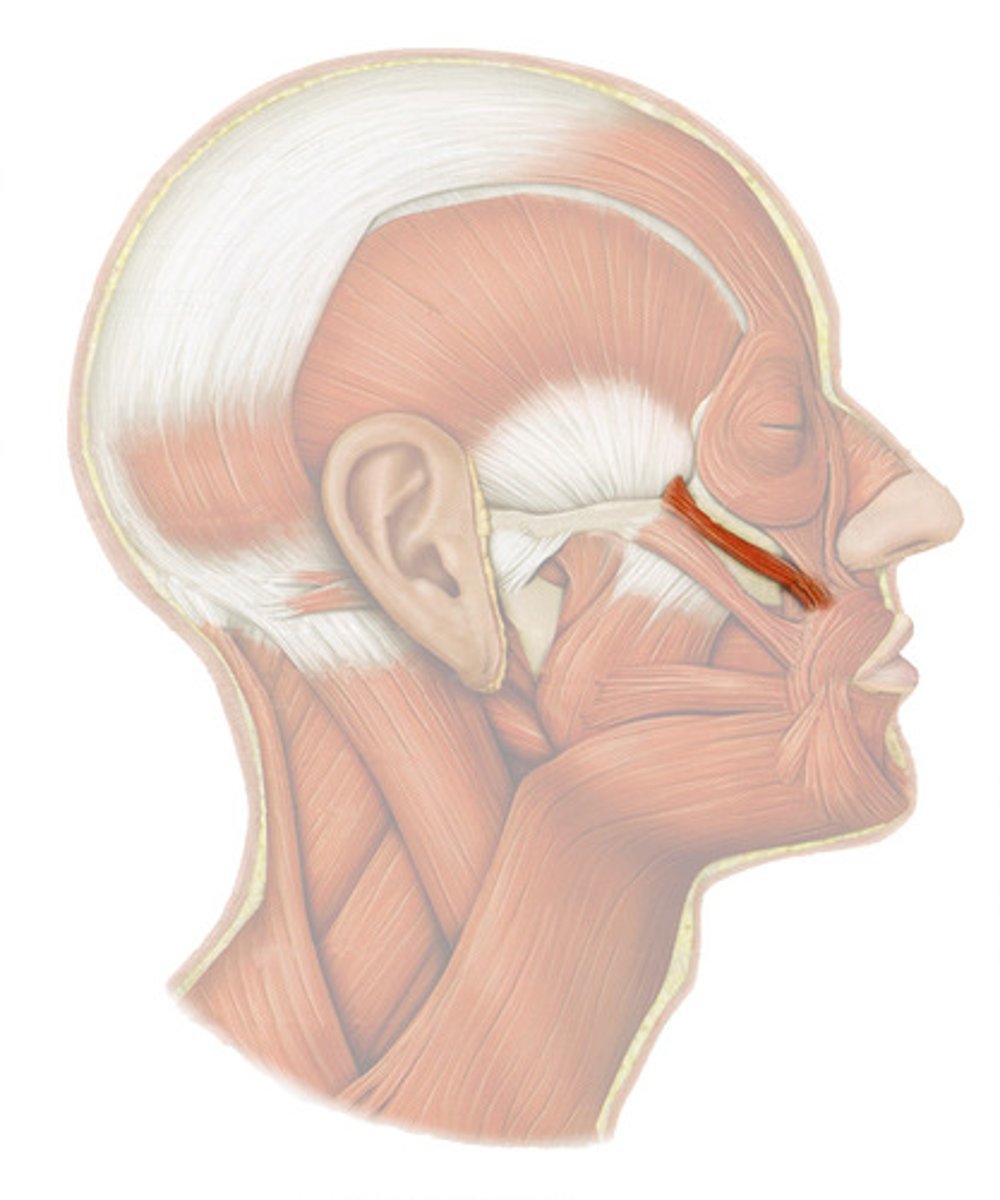
RISORIUS
inferior and lateral to zygomaticus
o: lateral fascia associated with masseter muscle
i: skin at angle of mouth
a: DRAWS CORNERS OF LIPS LATERALLY; SYNERGIST OF ZYGOMATICUS
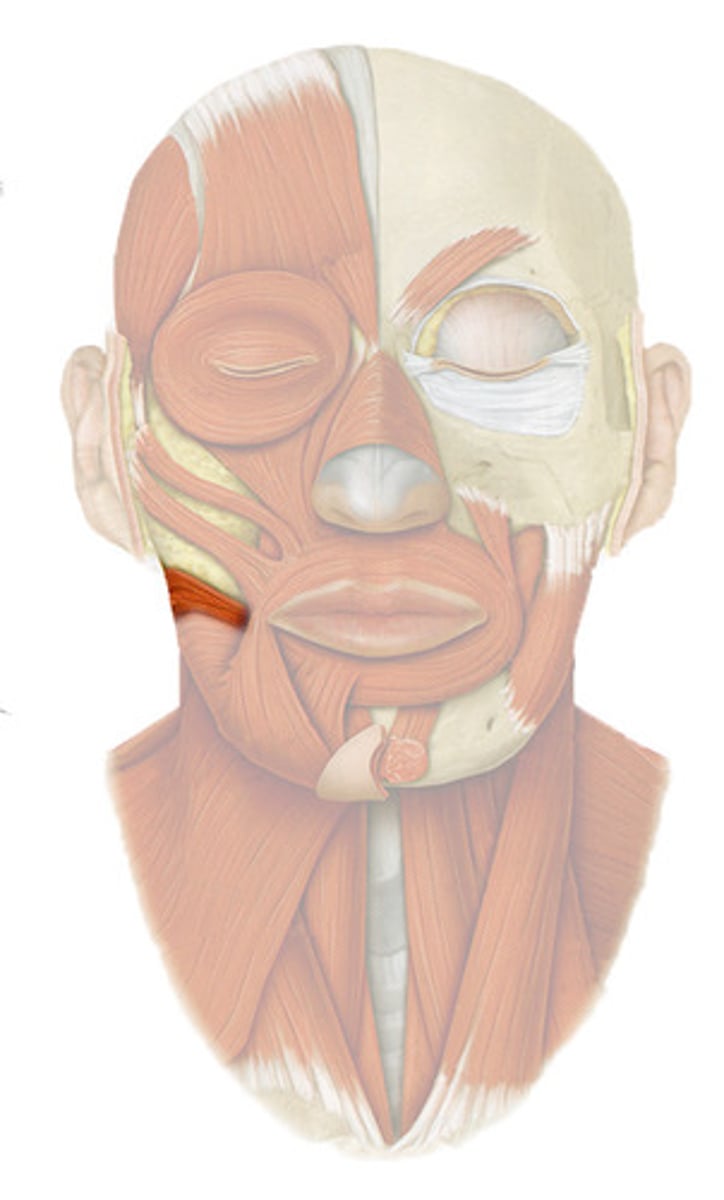
LEVATOR LABII SUPERIORIS
o: zygomatic bone and infraorbital margin of maxilla
i: skin and muscle of upper lip
a: OPENS LIPS
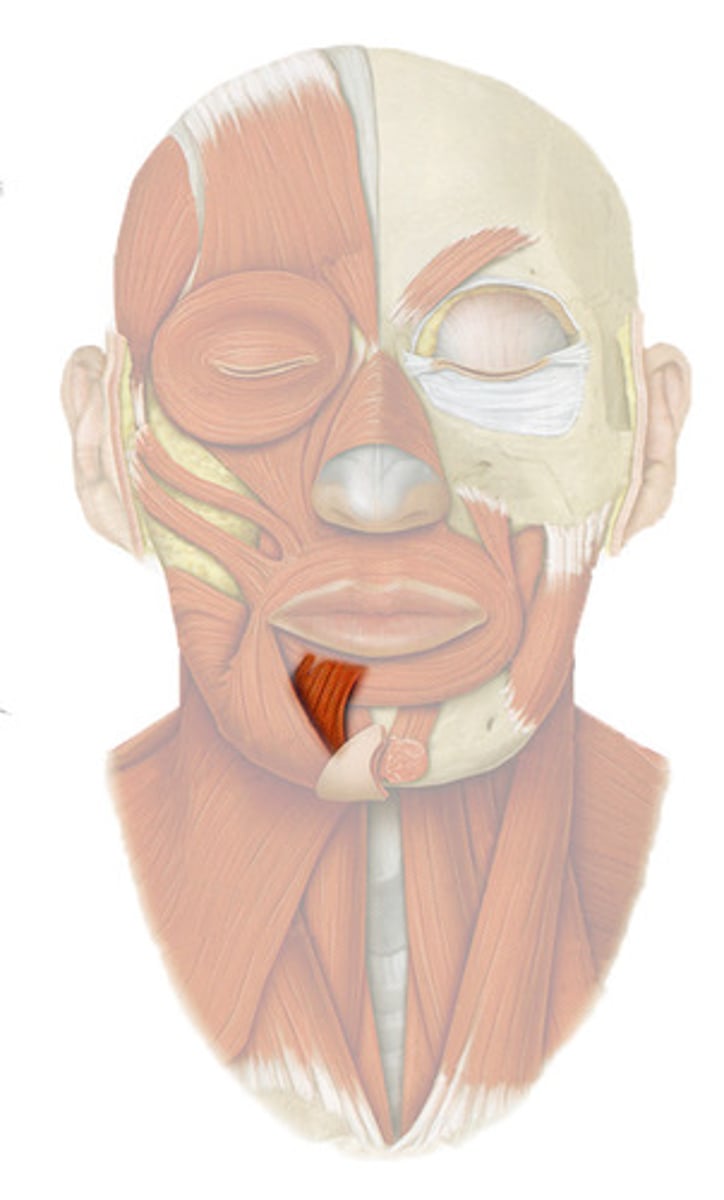
DEPRESSOR LABII INFERIORIS
o: body of mandible lateral to its midline
i: skin and muscle of lower lip
a: POUTS LOWER LIP
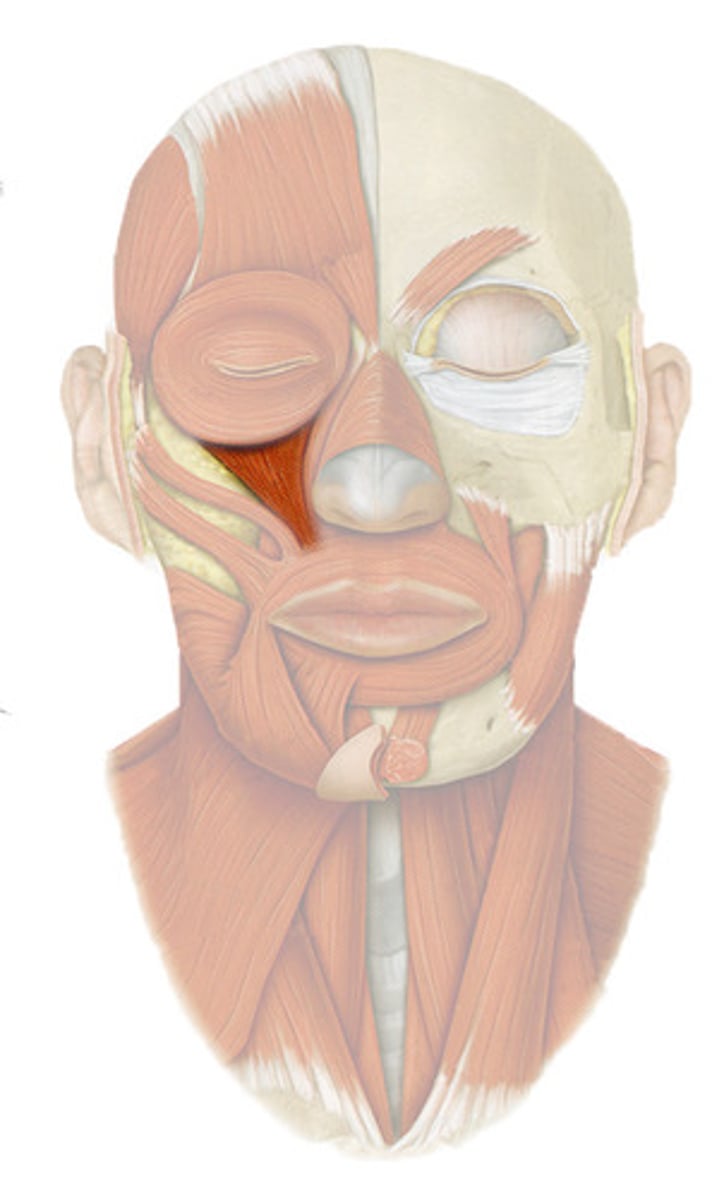
ORBICULARIS ORIS
o: maxilla and mandible
i: skin and muscle around mouth
a: CLOSES LIPS (KISS)
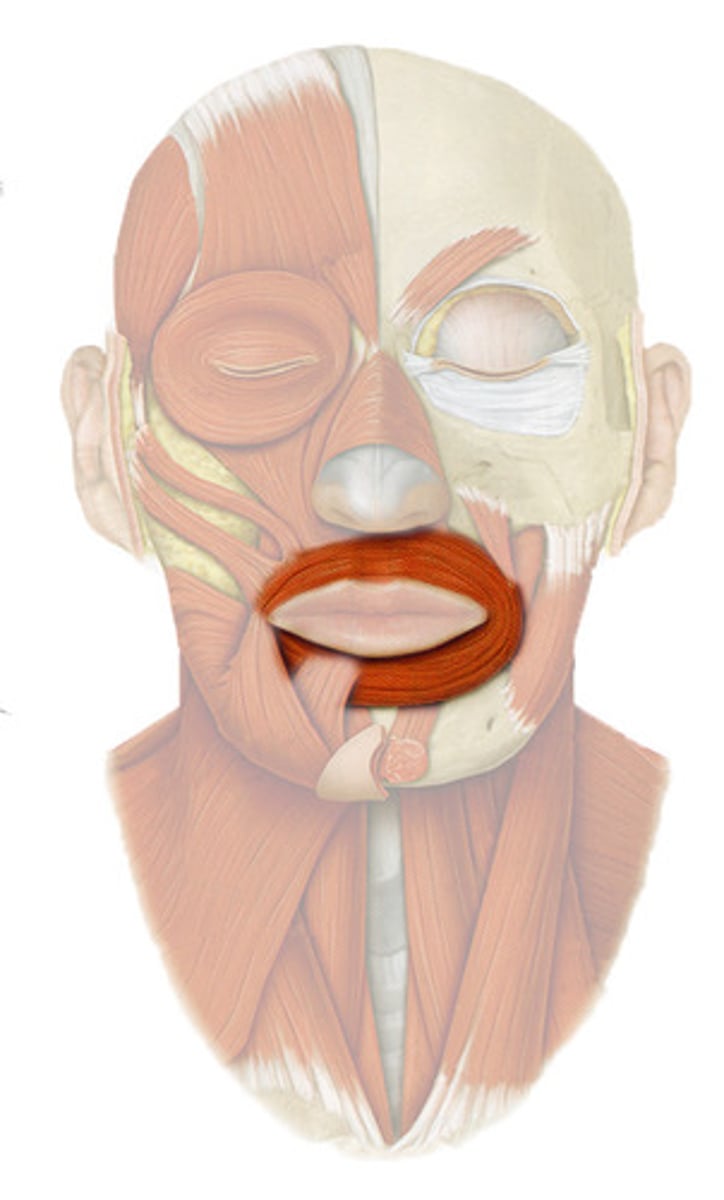
MENTALIS
o: mandible below incisors
i: skin of chin
a: WRINKLES CHIN
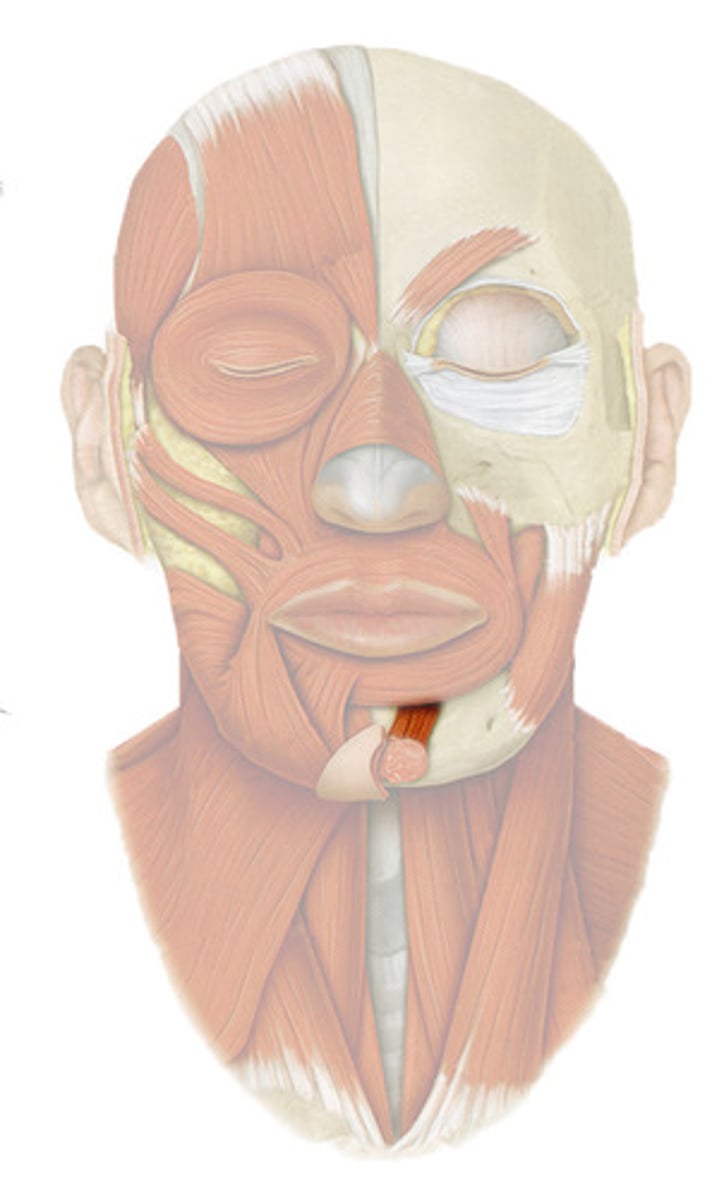
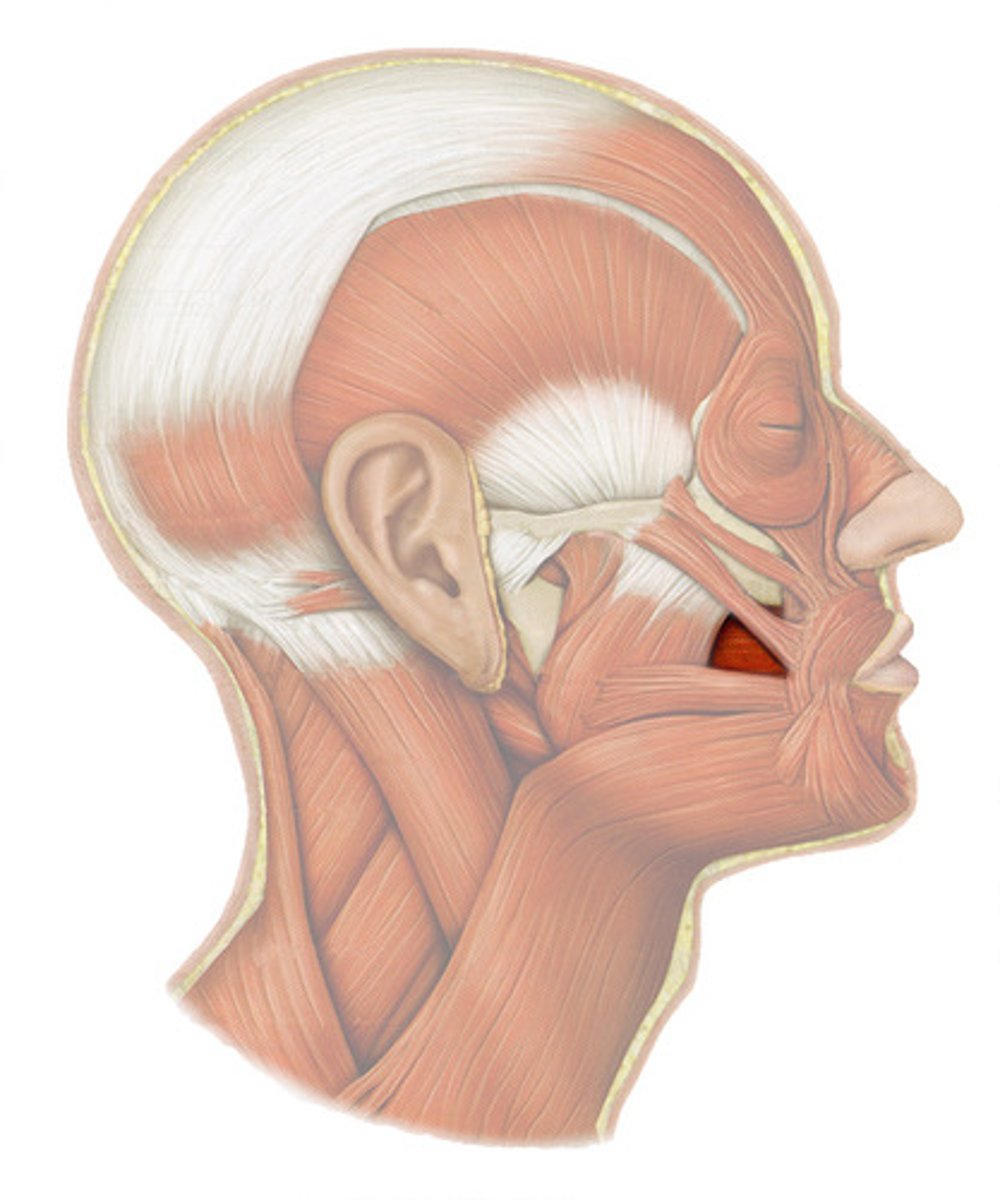
BUCCINATOR
horizontal cheek muscle, deep to masseter
o: molar region of maxilla and mandible
i: orbicularis oris
a: COMPRESSES CHEEK (SUCKING/WHISTLING)
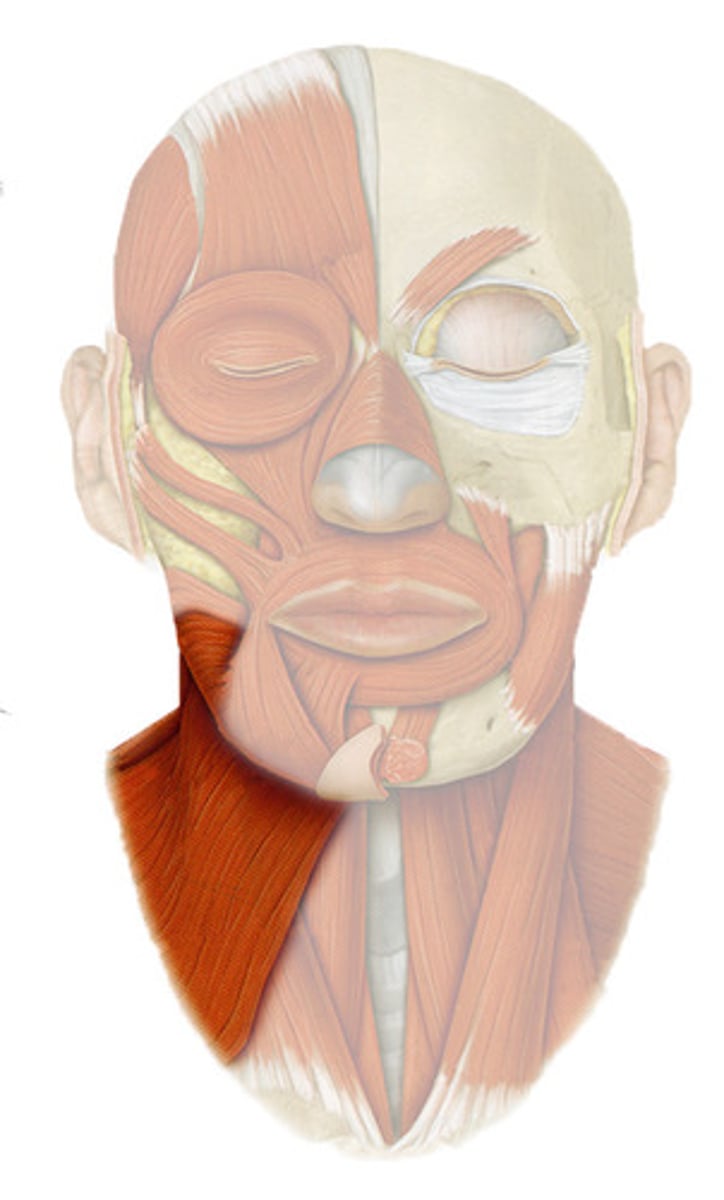
PLATYSMA
superficial neck muscle
o: over pectoral muscles and deltoid
i: lower margin of mandible; and skin and muscle at corner of mouth
a: TENSES SKIN OF NECK (SHAVING)
MASSETER
powerful muscle covers lateral aspect of the mandibular ramus
o: zygomatic arch/bone
i: angle and ramus of mandible
a: PRIME MOVER IN JAW CLOSURE
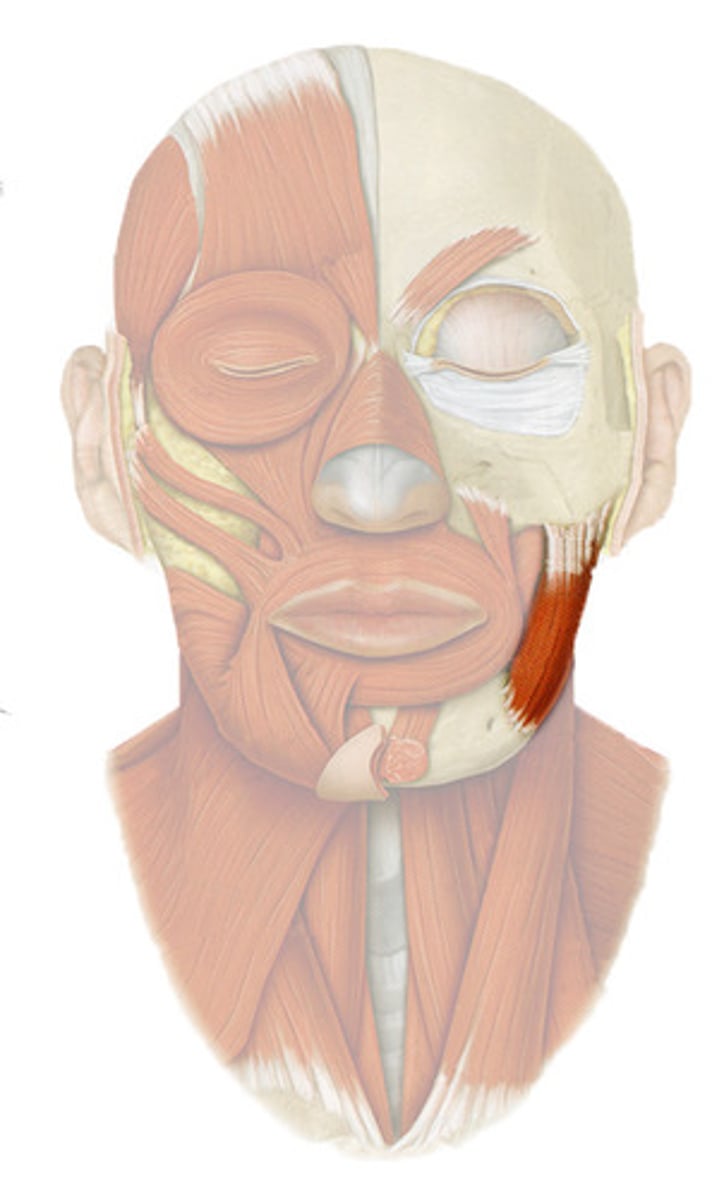
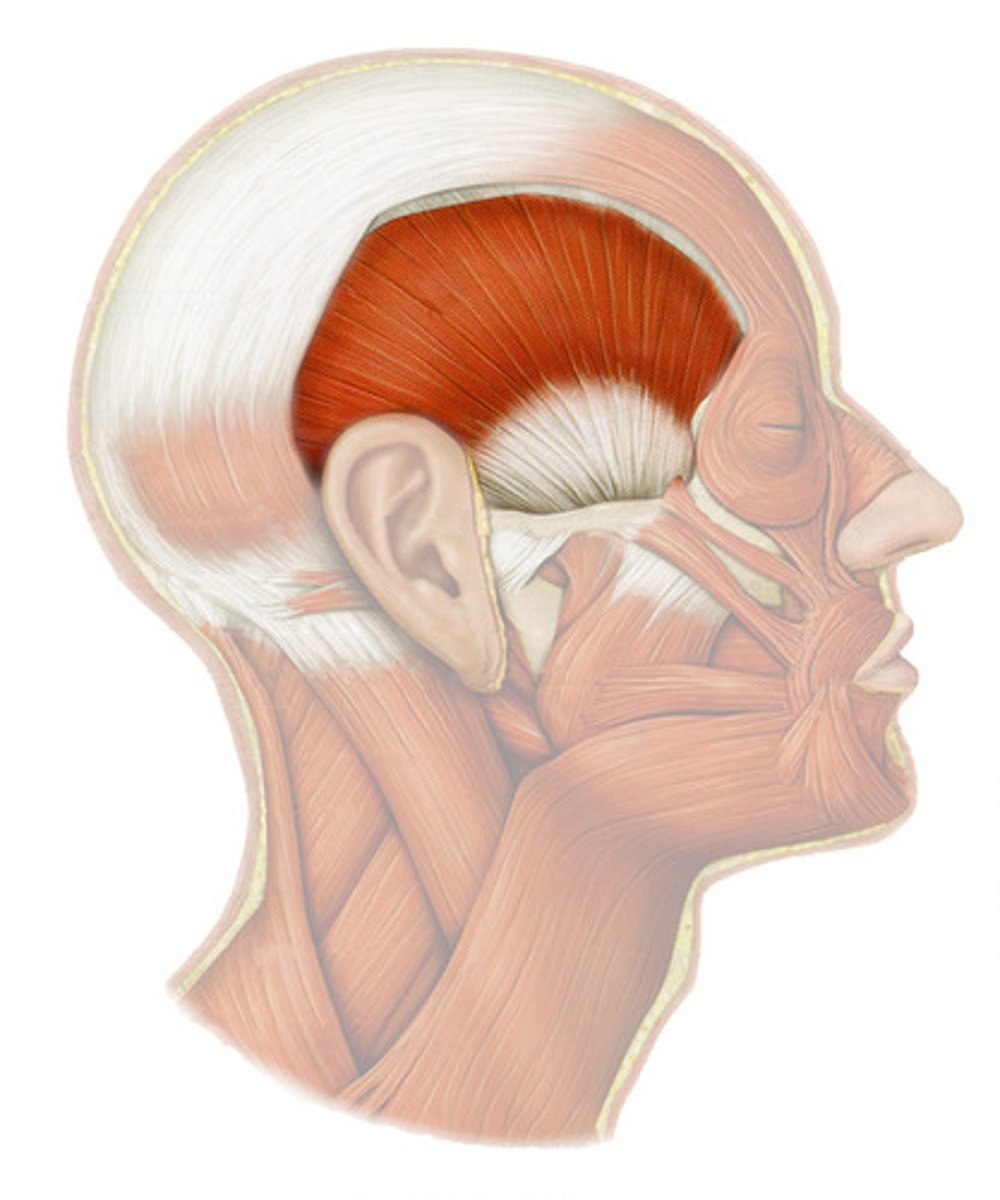
TEMORALIS
o: temporal, frontal, partietal bone
i: coronoid process of mandible
a: CLOSES JAW
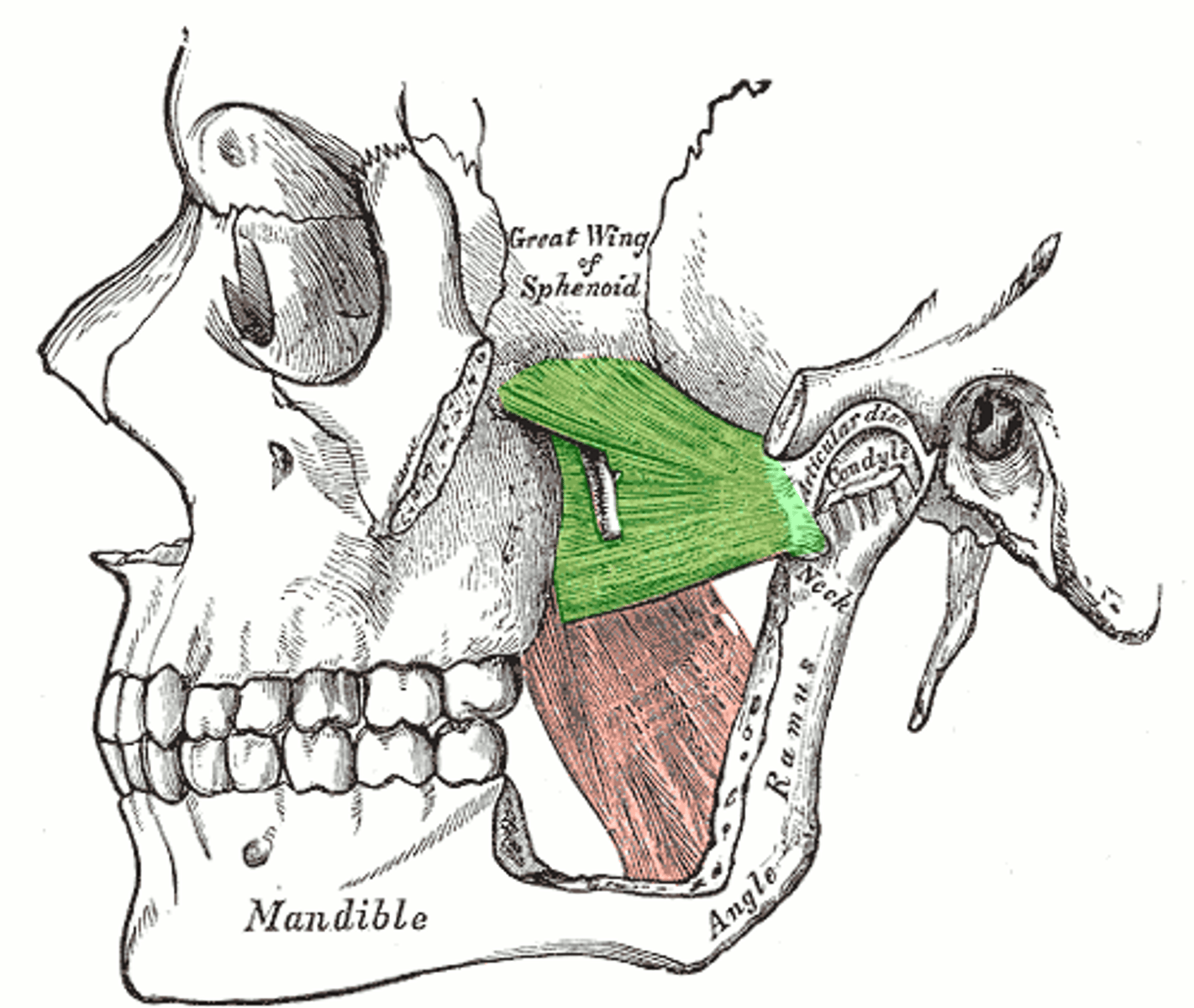
MEDIAL PTERYGOID
o: medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone, maxilla, and palatine bone
i: medial surface of mandible near its angle
a: PROTRACT MANDIBLE, SIDE TO SIDE MOVEMENTS
SYNERGIST of temporalis and masseter
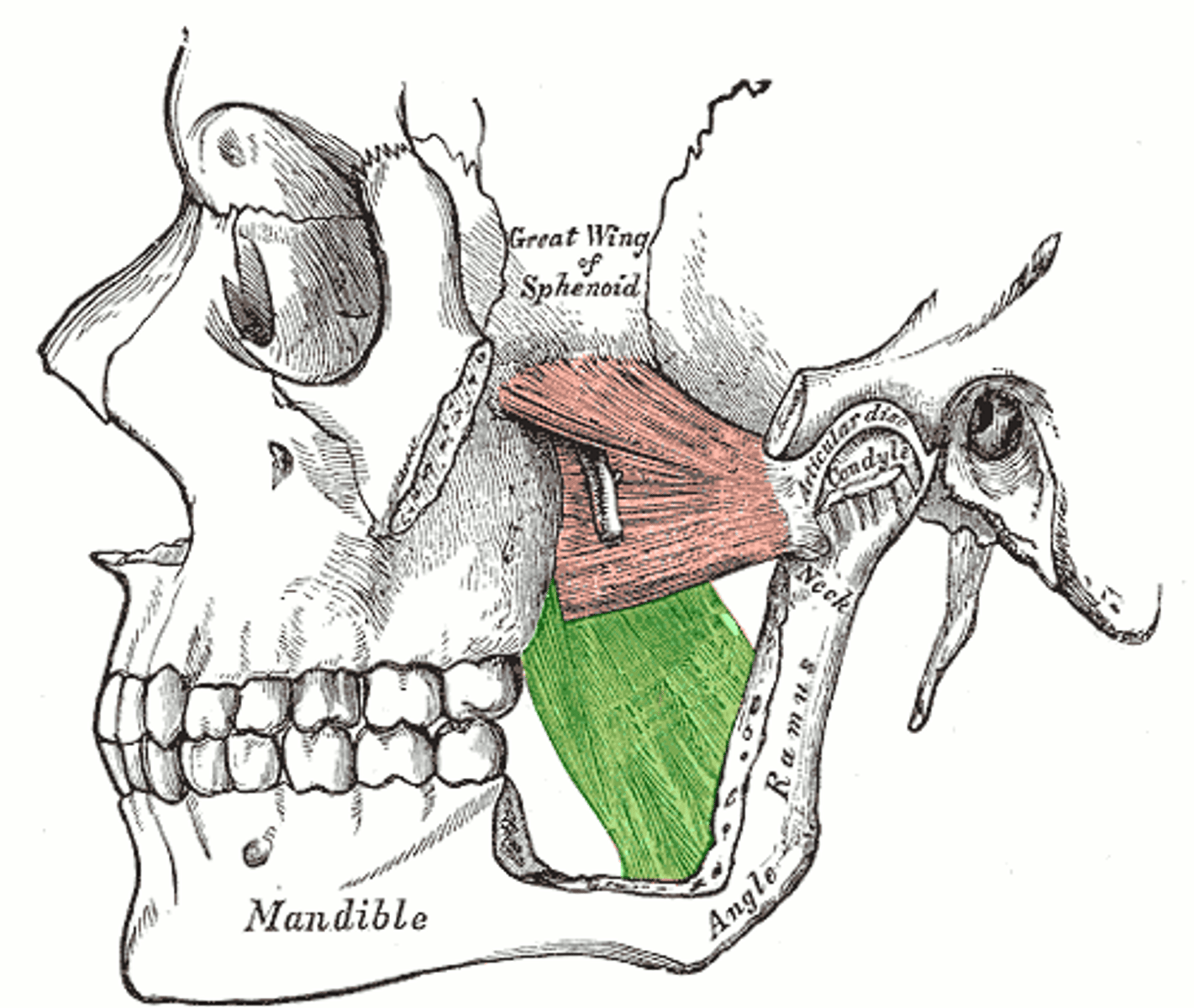
LATERAL PTERYGOID
lies superior to medial pterygoid muscle
o: greater wing and lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone
i: condyle of mandible and capsule of temporomandibular joint
a: FORWARD SLIDING AND SIDE TO SIDE GRINDING MOVEMENTS
DIGASTRIC
o: mandible (anterior belly)
mastoid process
(posterior belly)
i: by a connective tissue loop to hyoid bone
a: OPEN MOUTH AND DEPRESS MANDIBLE
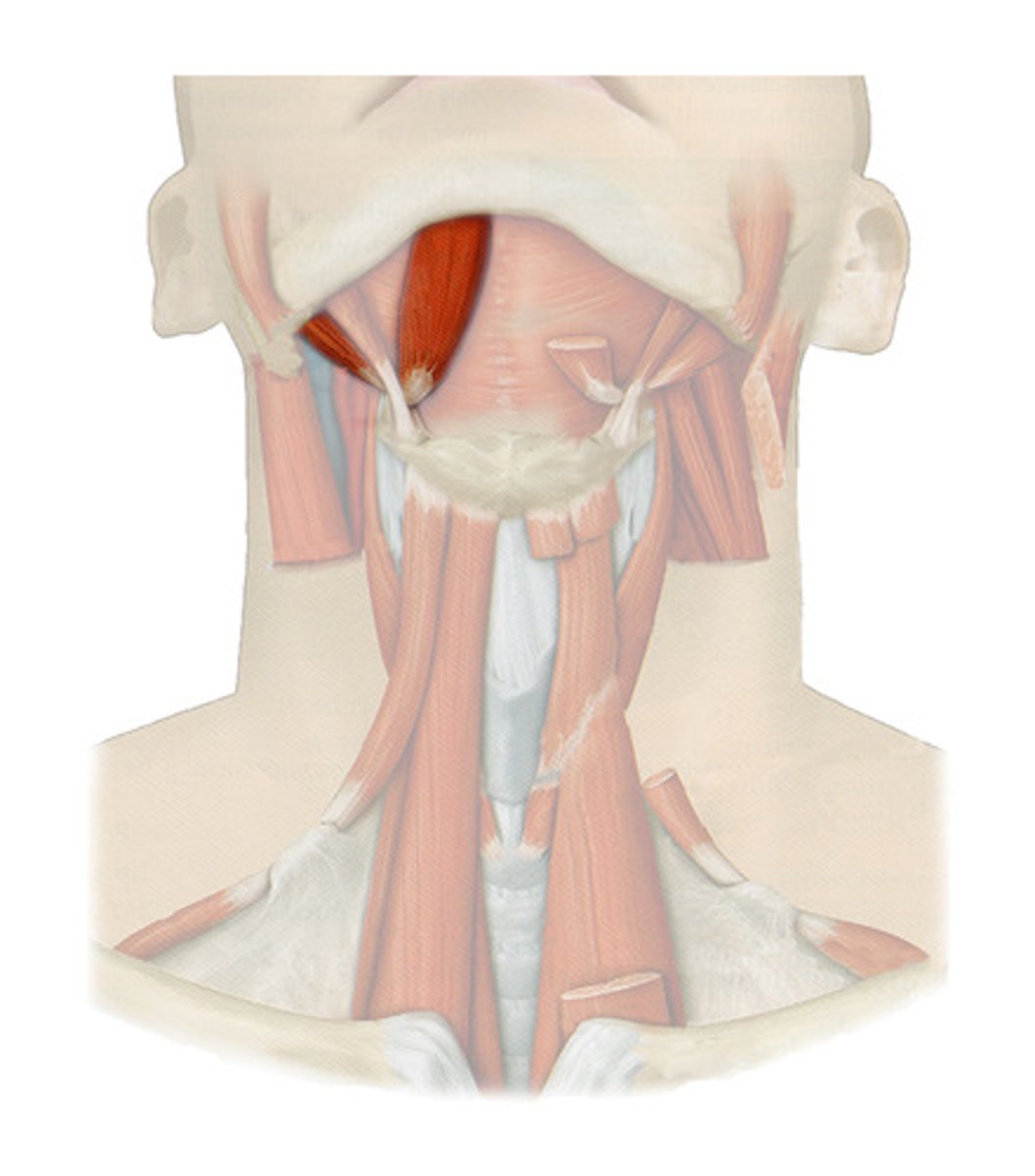
STYLOHYOID
parallels posterior belly of digastric muscle
o: styloid process
i: hyoid bone
a: ELEVATES & RETRACTS HYOID
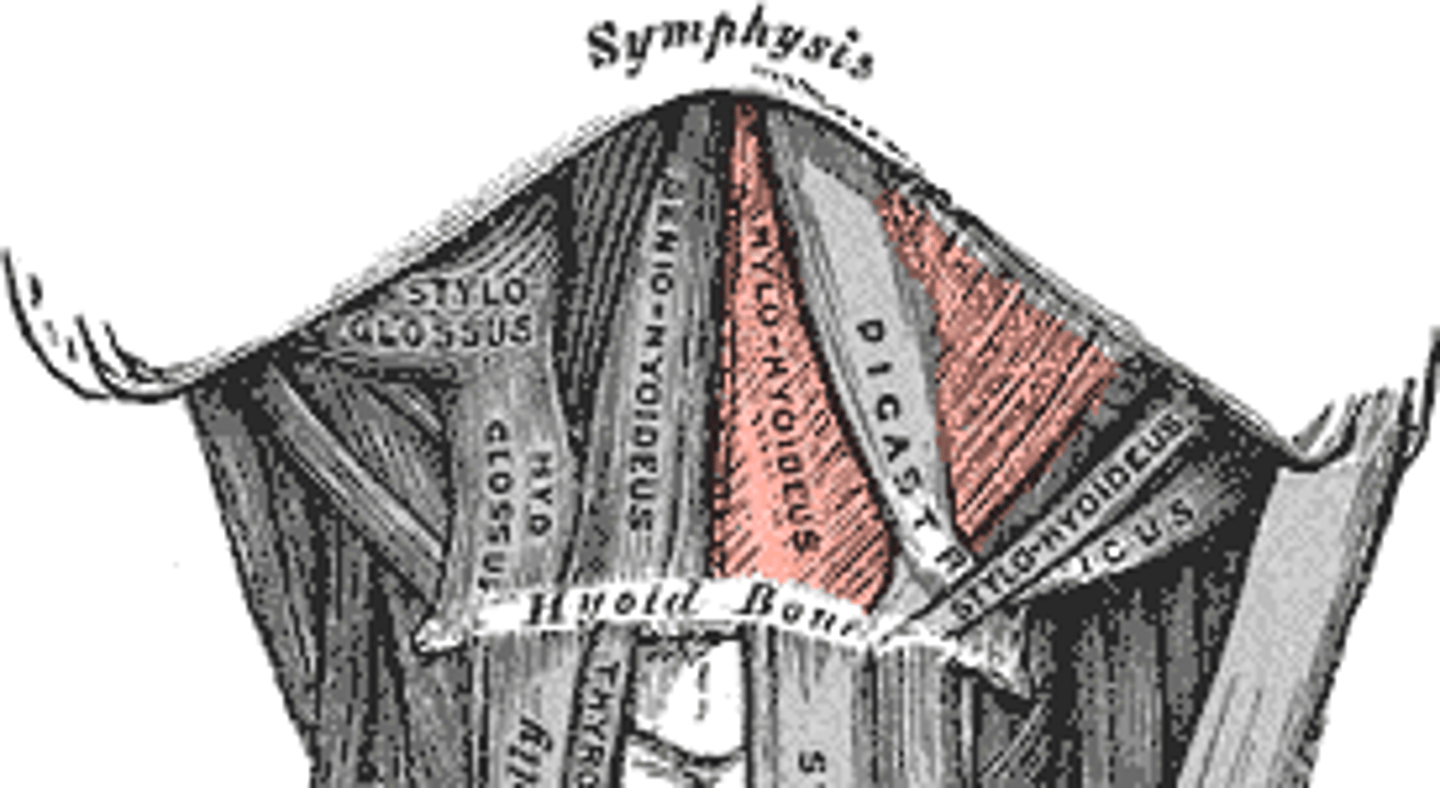
MYLOHYOID
deep to digastric muscle; floor of the anterior mouth
o: medial surface of mandible
i: hyoid bone
a: ELEVATES HYOID BONE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH
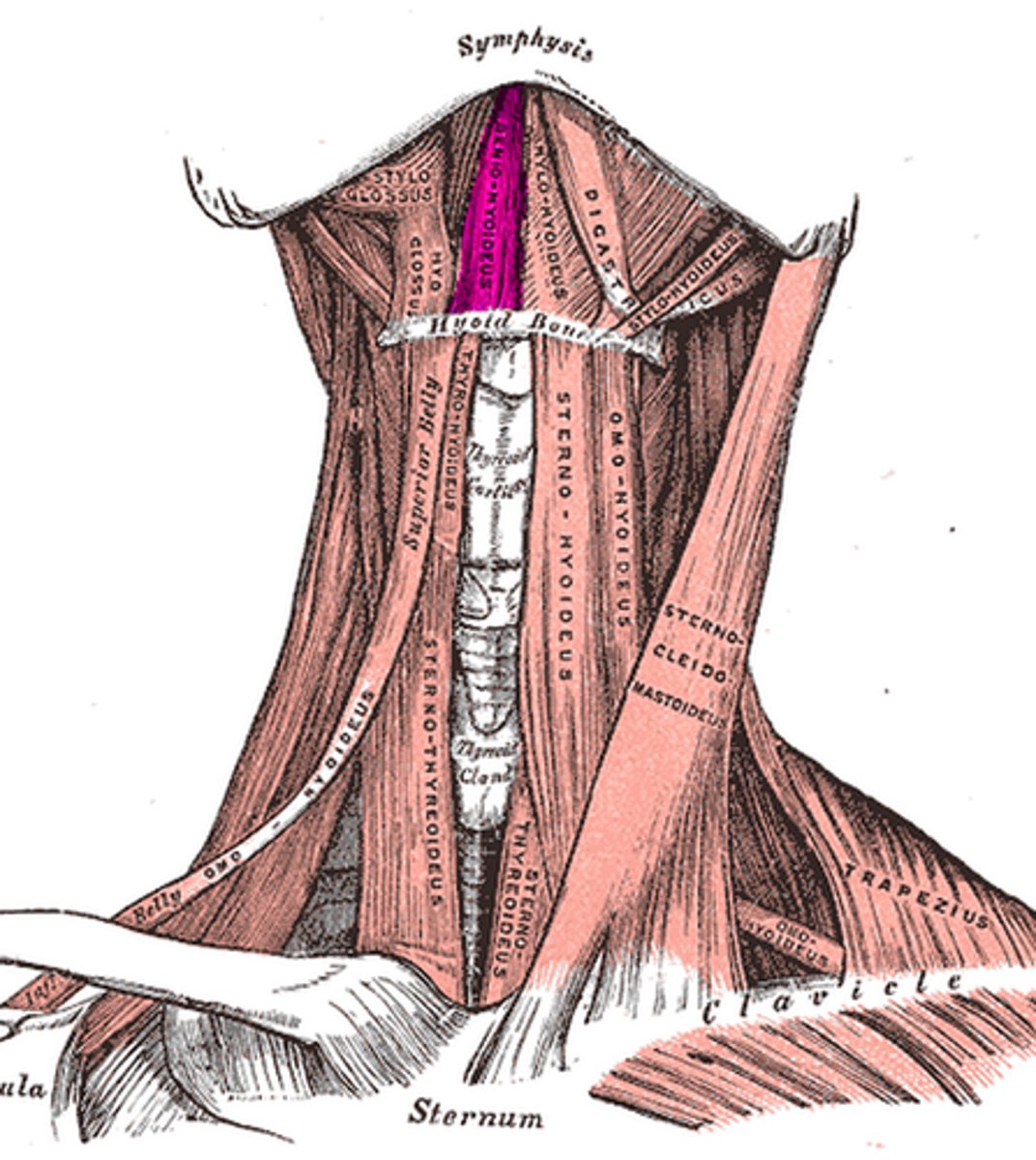
GENIOHYOID
deep to mylohyoid
o: inner surface of mandibular symphysis
i: hyoid bone
a: PULLS HYOID BONE SUPERIORLY & ANTERIORLY
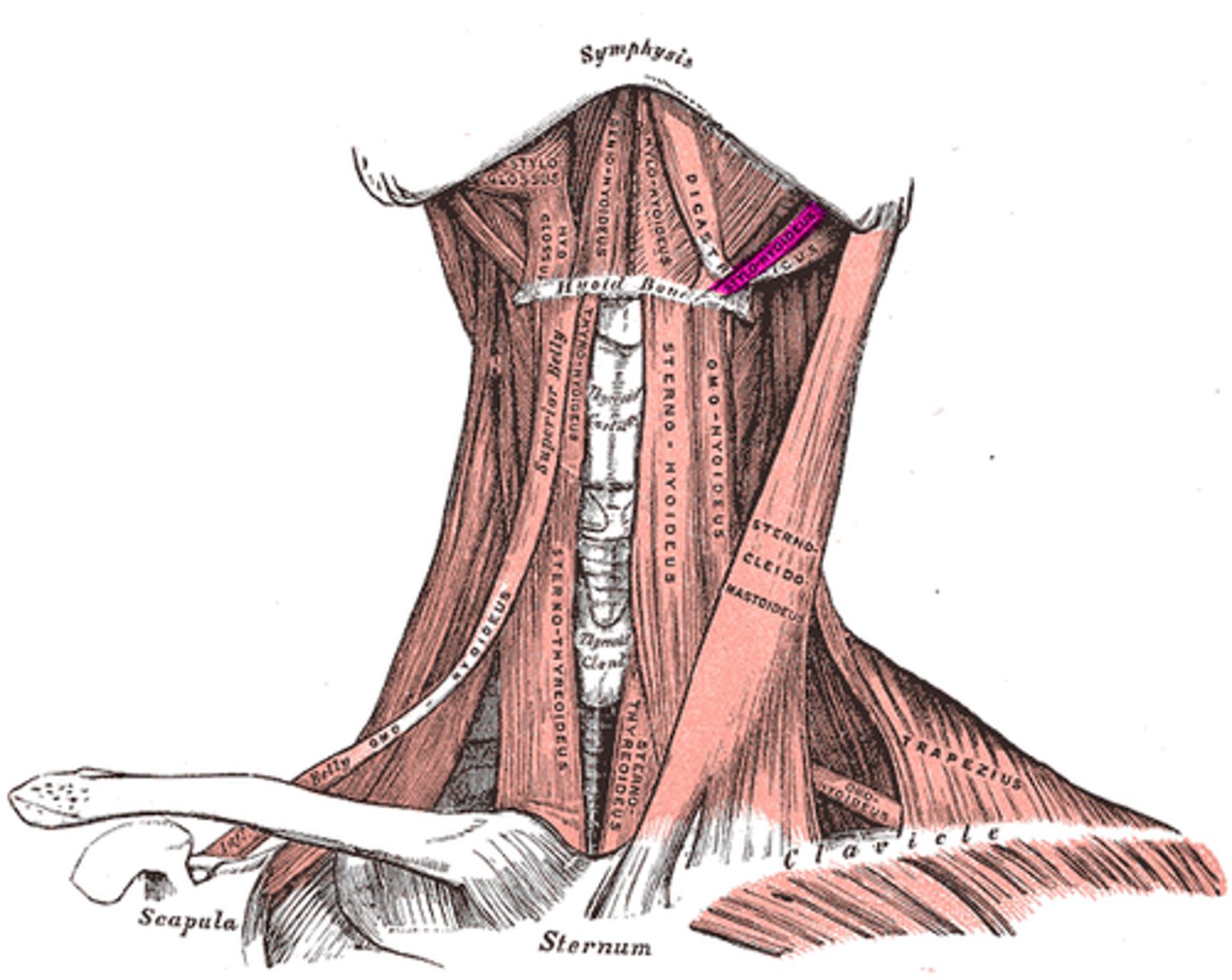
STERNOHYOID
most medial muscle of the neck; thin; superficial except inferiorly, where it is covered by the sternocleidomastoid muscle
o: manubrium and medial end of clavicle
i: lower margin of hyoid bone
a: DEPRESSES LARYNX AND HYOID BONE
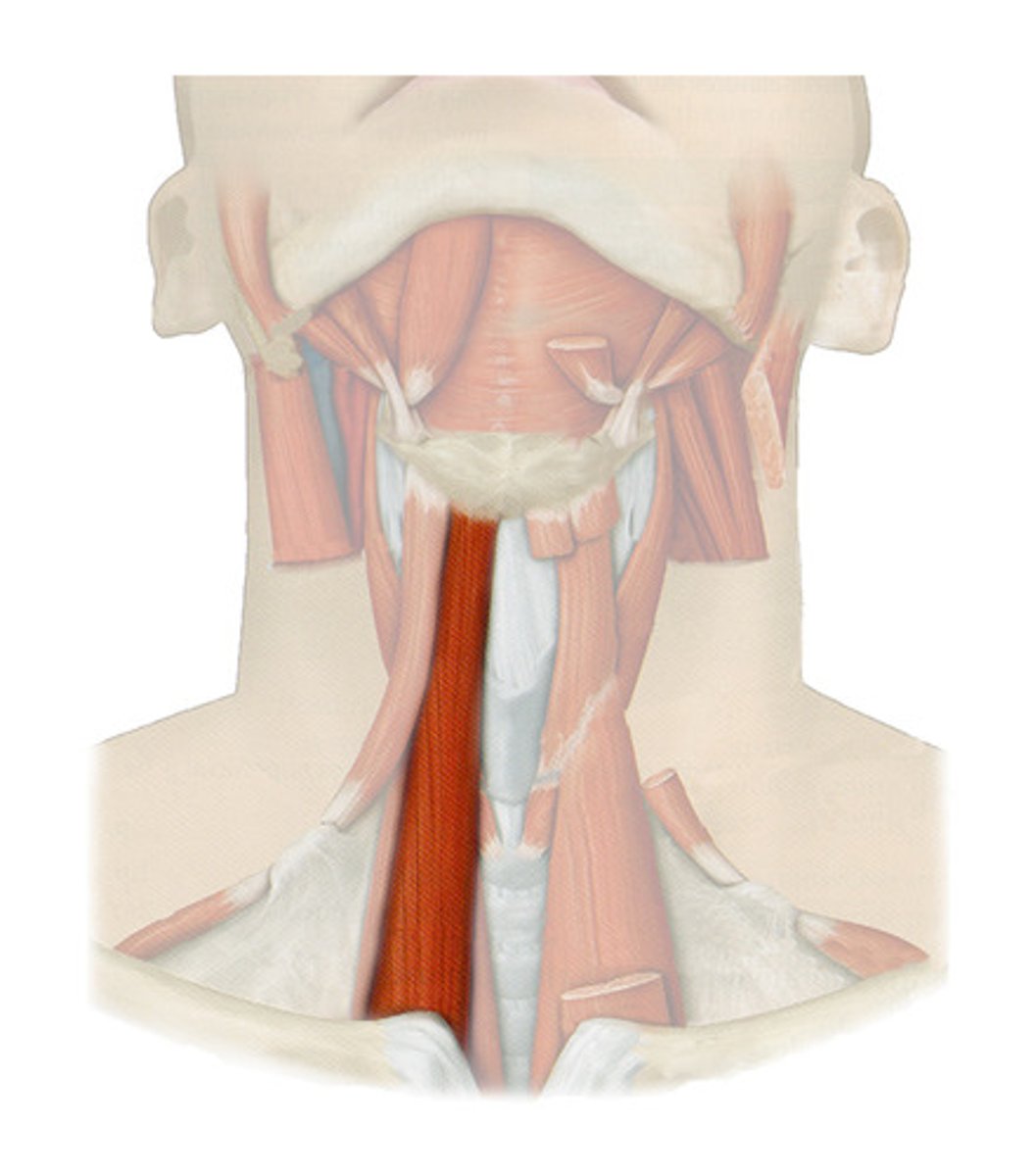
STERNOTHYROID
lateral and deep to sternohyoid
o: posterior surface of manubrium of sternum
i: thyroid cartilage
a: pulls larynx and hyoid bone inferiorly
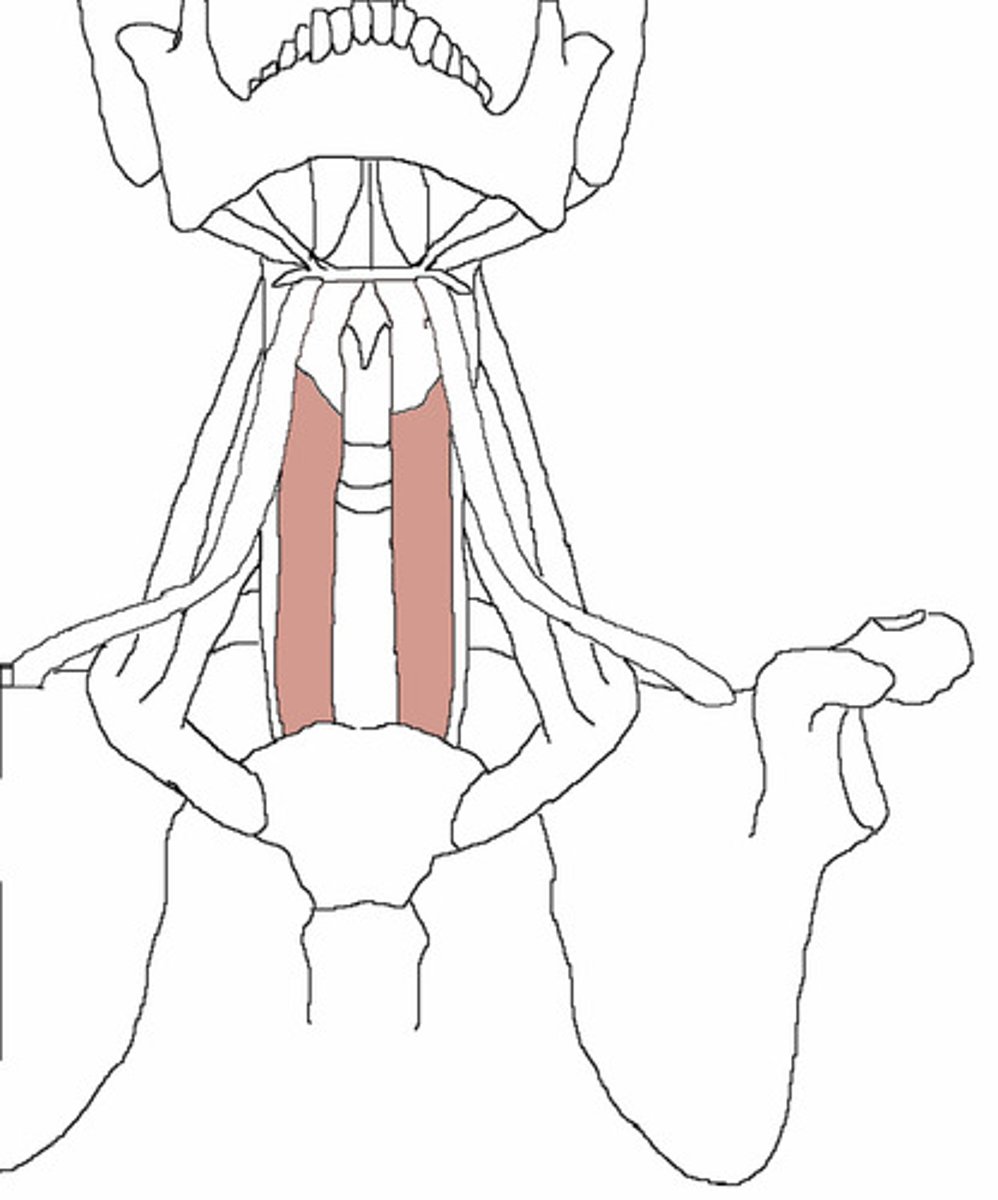
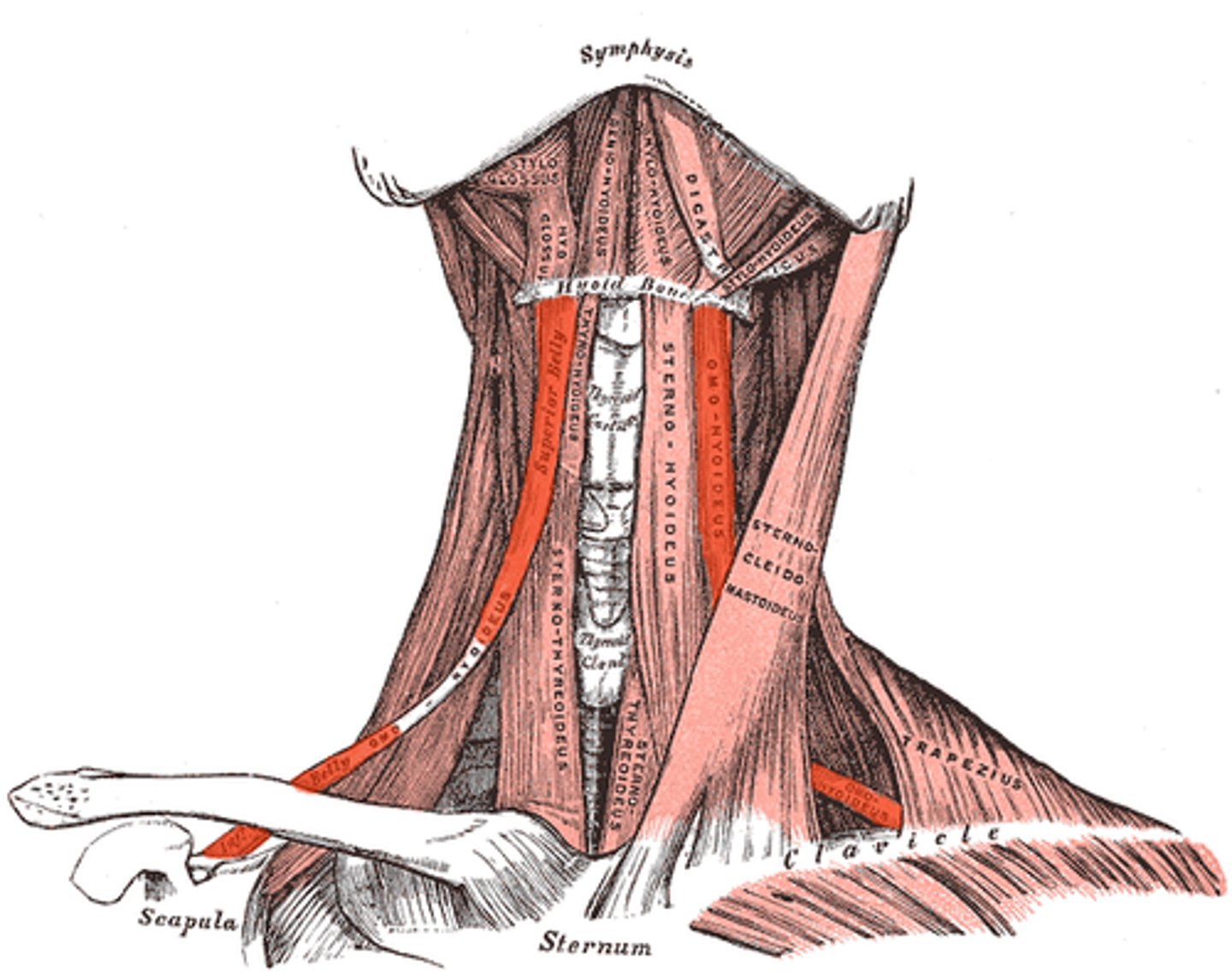
OMOHYOID
lateral to sternohyoid
o: superior surface of scapula
i: hyoid bone, lower border
a: depresses and retracts hyoid bone
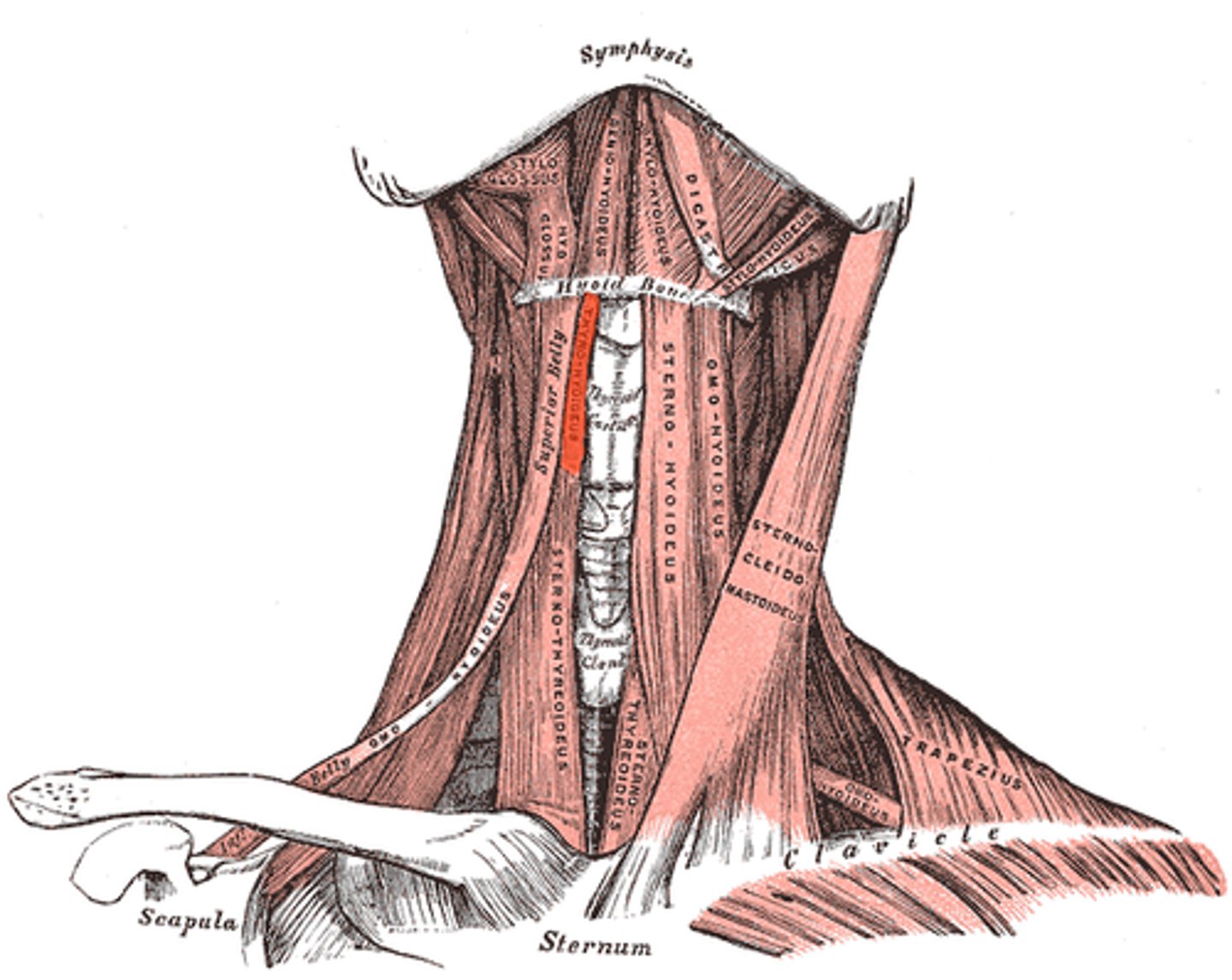
THYROHYOID
appears as a superior continuation of sternothyroid muscle
o: thyroid bone
i: hyoid bone
a: depresses hyoid bone or elevates larynx
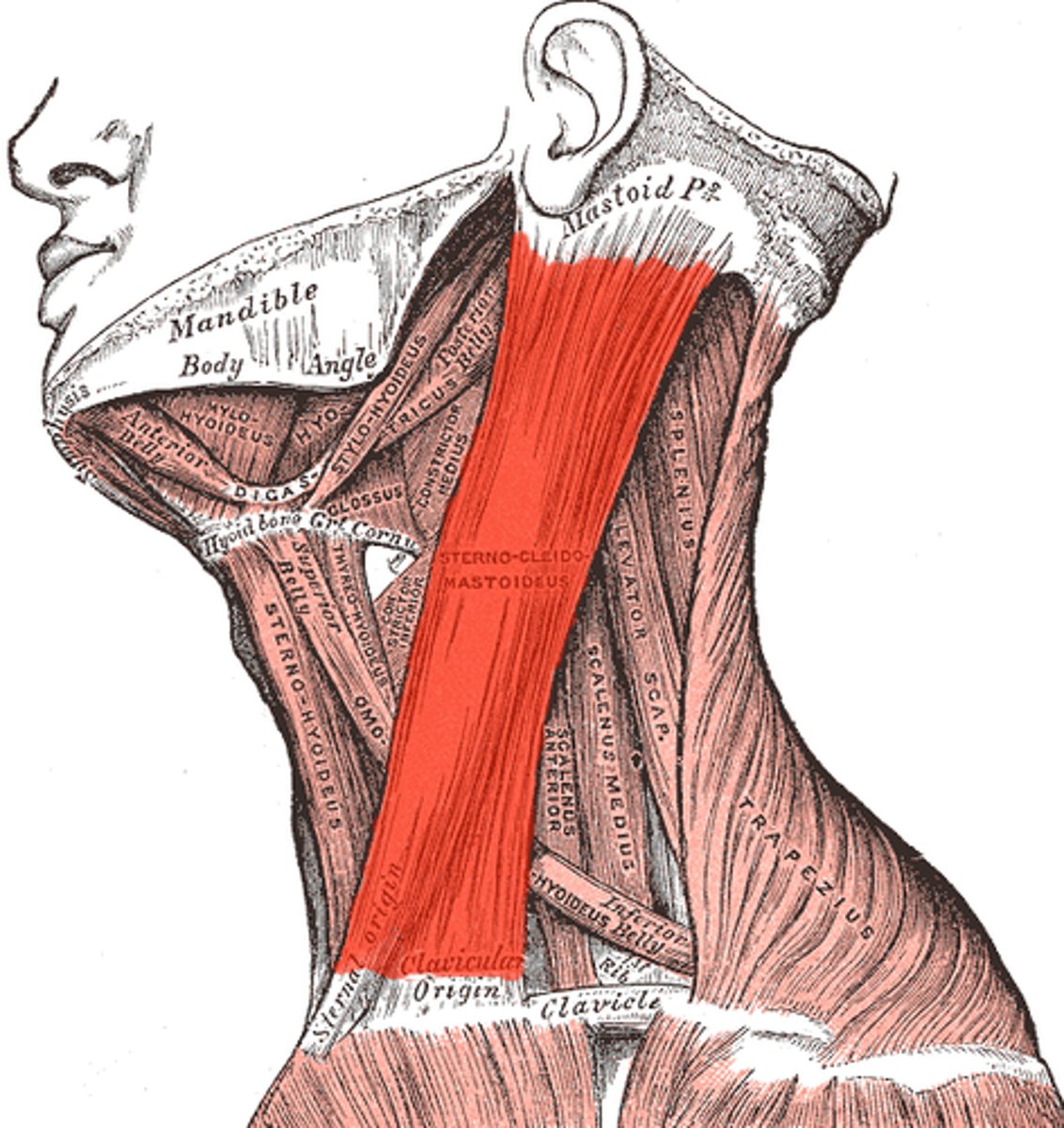
STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID
deep to platysma; key muscular landmark in neck
o: manubrium of sternum and medial portion of clavicle
i: mastoid process of temporal bone and superior nuchal line of occipital bone
a: FLEXES AND LATERALLY ROTATES HEAD
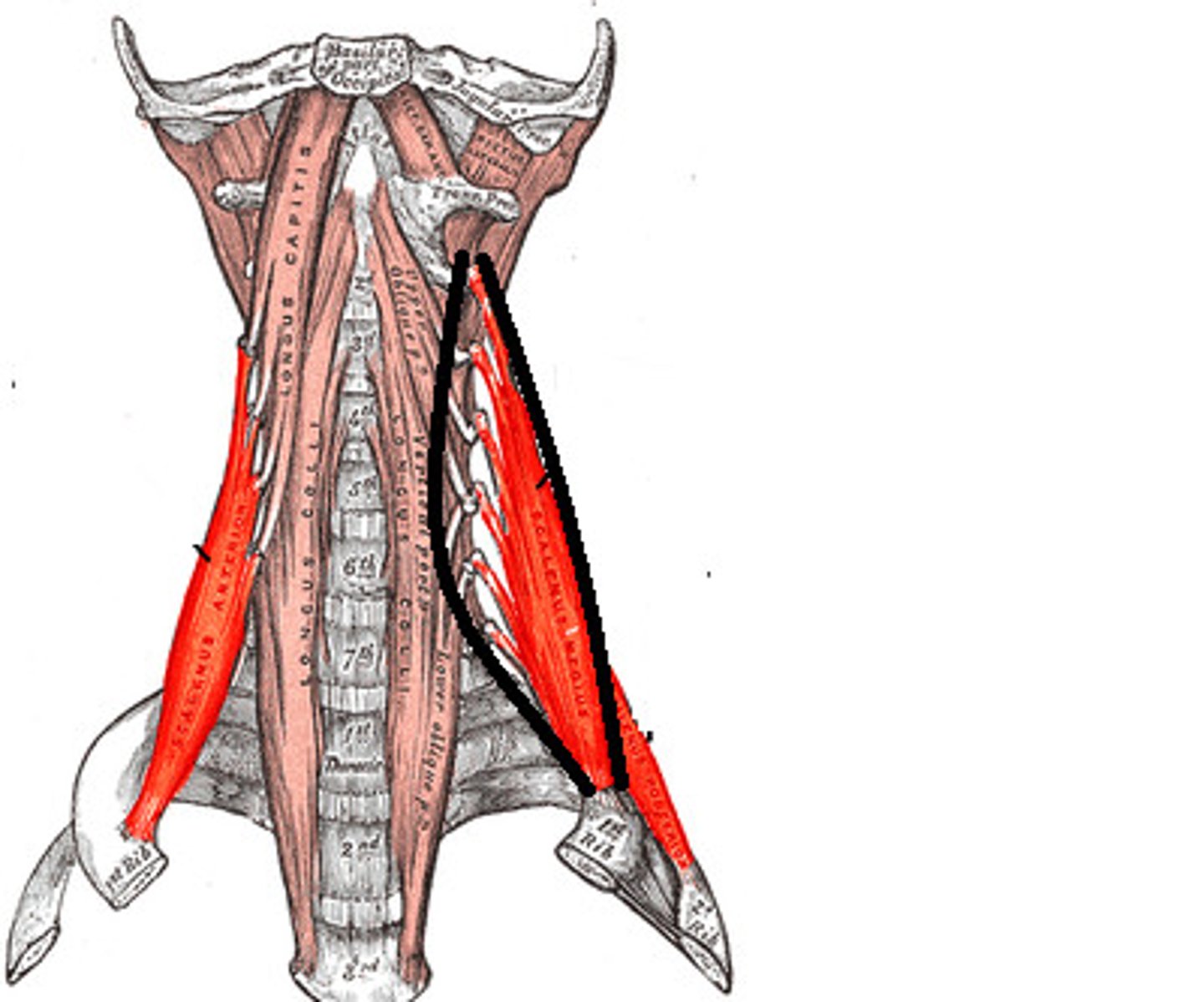
SCALENES
lateral / deep to platysma and sternocleidomastoid
o: transverse process of cervical vertebrae
i: anterolaterally on first two ribs
a: ELEVATES FIRST 2 RIBS
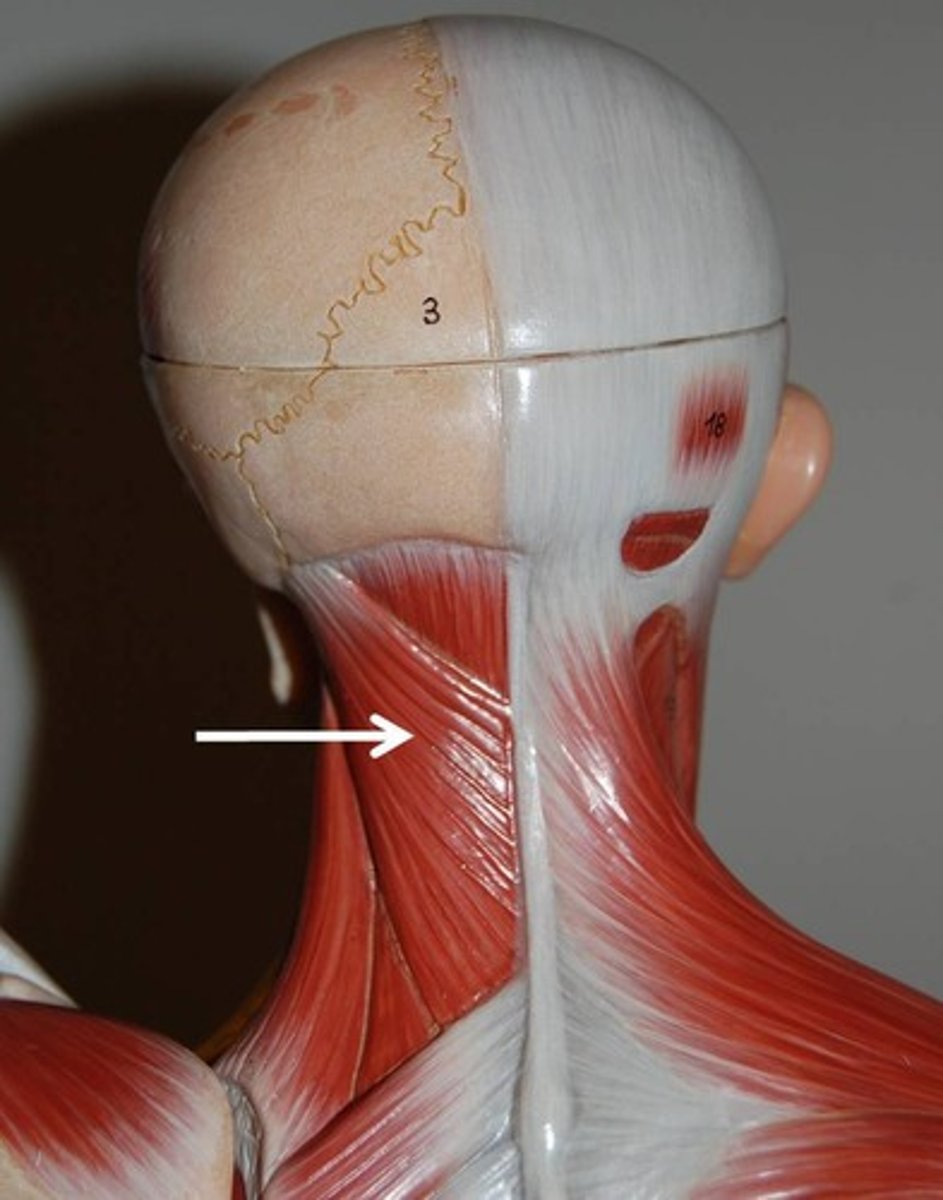
SPLENIUS
superficial muscle extending from upper thoracic vertebrae to skull
o: spinous procress of C7-T6
i: mastoid process of temporal bone and occipital bone; transverse process of C2-C4 vertebrae
a: EXTEND OR HYPEREXTEND HEAD
LATERAL TO MEDIAL
ILIOCOSTALIS, LONGISSIMUS, SPINALIS
PRIME MOVERS IN BACK EXTENSION
WHAT ARE THE ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES AND WHAT DO THEY DO?
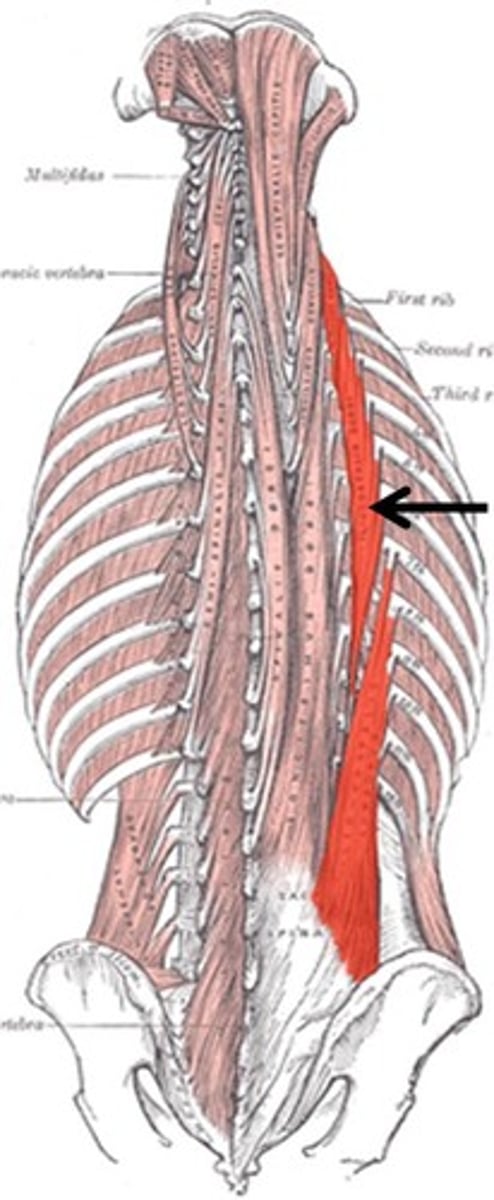
ILIOCOSTALIS
most lateral muscle group of erector spinae, extending from pelvis to neck
o:
iliac crests (lumborum)
inferior 6 ribs (thoracis)
ribs 3 to 6 (cervics)
i: angles of ribs
a: EXTENDS AND LATERALLY FLEX VERTEBRAL COLUMN
LONGISSIMUS
intermediate
o: transverse process of lumbar through cervical vertebrae
i: transverse process of T/C vertebrae and to ribs superior to origin; inserts into mastoid process of temporal bone
a: EXTENDS, LATERALLY FLEX VERTEBRAL COLUMN
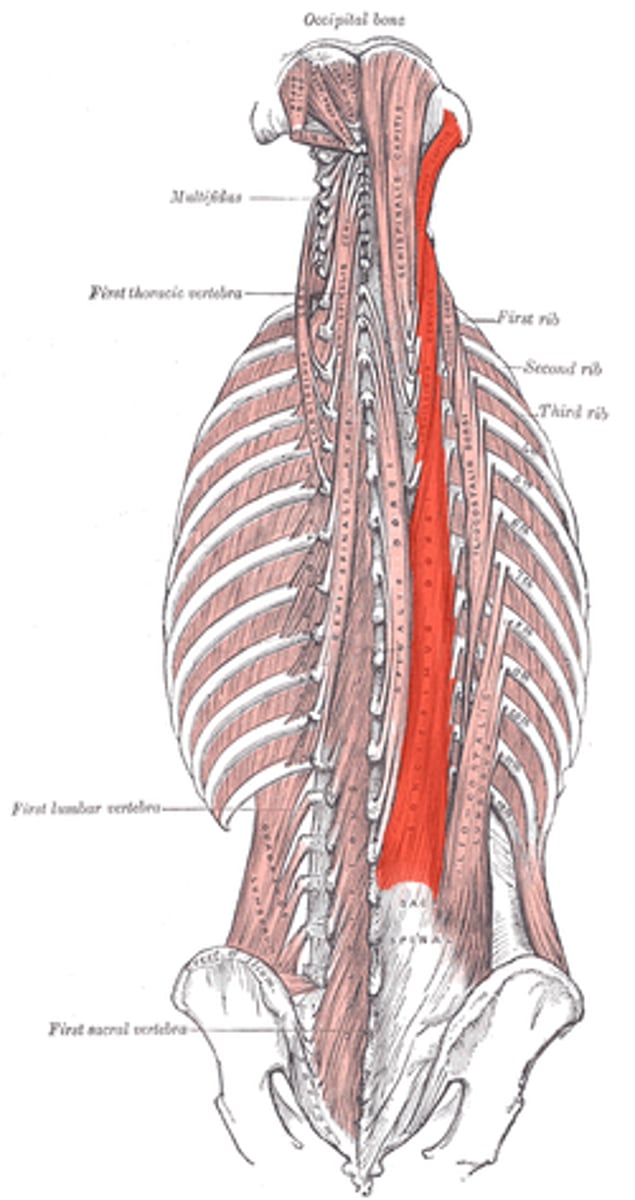
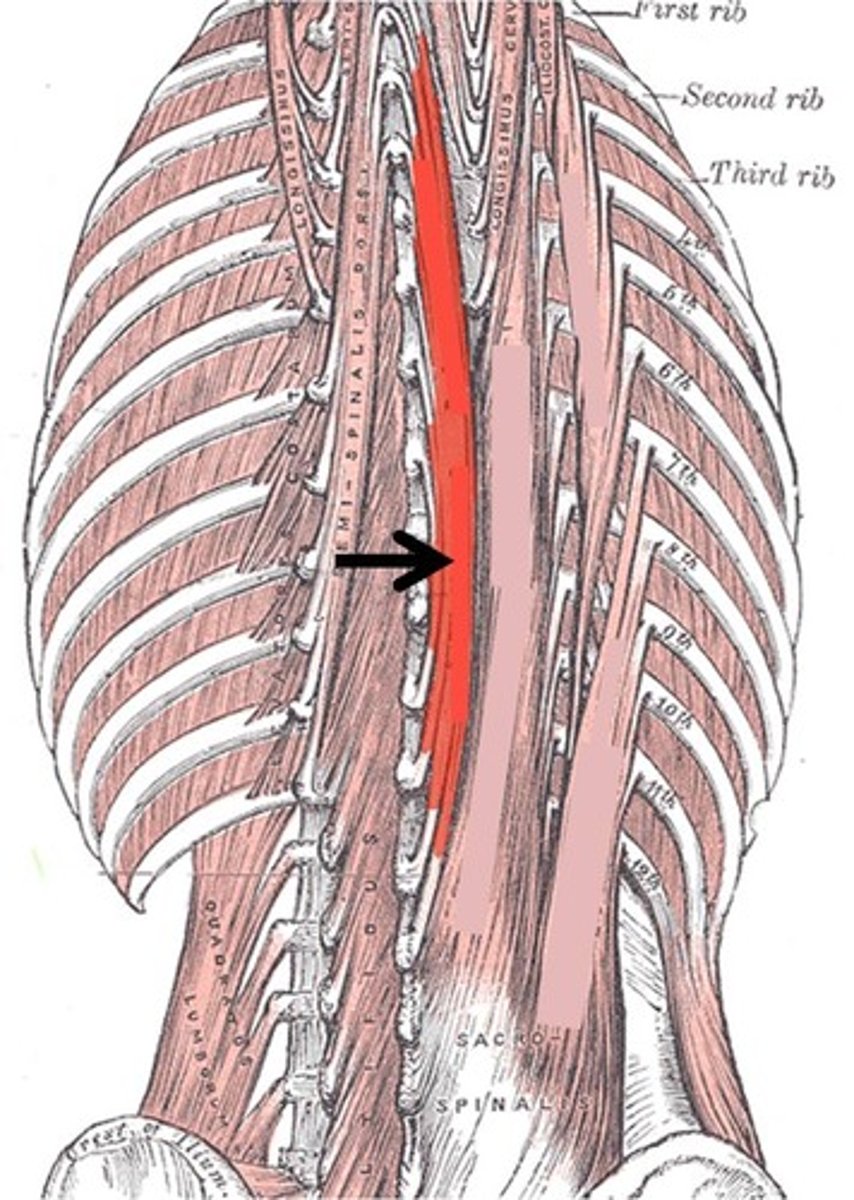
SPINALIS
most medial muscle of group
o: spines of upper lumbar and lower thoracic vertebrae
i: spines of upper thoracic and cervical vertebrae
a: EXTENDS VERTEBRAL COLUMN
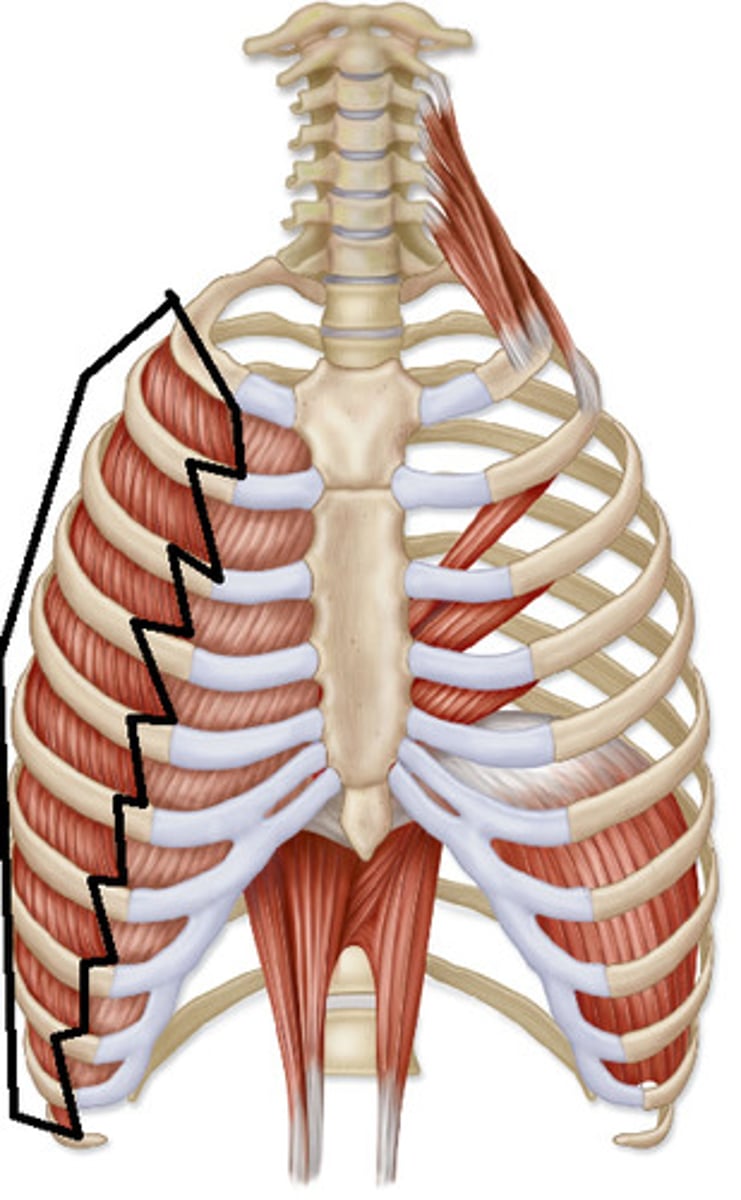
EXTERNAL INTERCOSTALS
11 PAIRS, short, in between ribs
o: inferior border of rib above
i: superior border of rib below
a: PULL RIBS TOWARD ONE ANOTHER, ELEVATES RIB CAGE
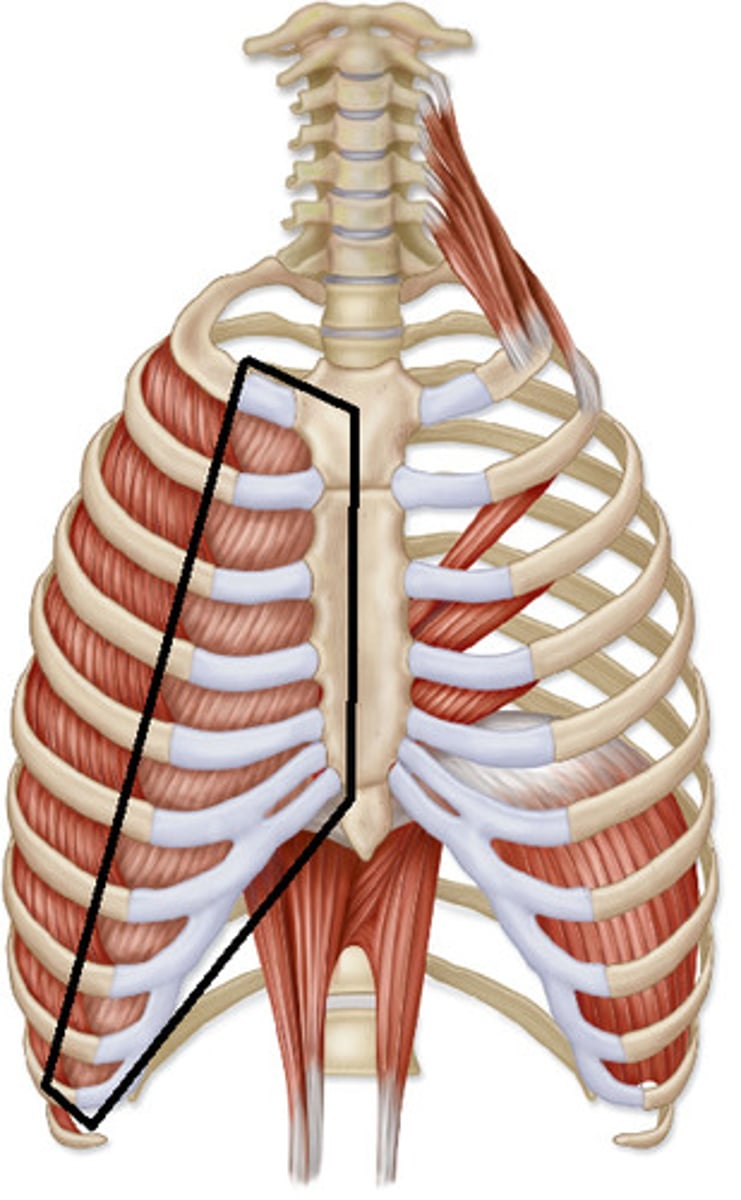
INTERNAL INTERCOSTALS
11 pairs lie between ribs
o: superior border of rib below
i: inferior border of rib above
a: DRAW RIBS TOGETHER, DEPRESS RIB CAGE
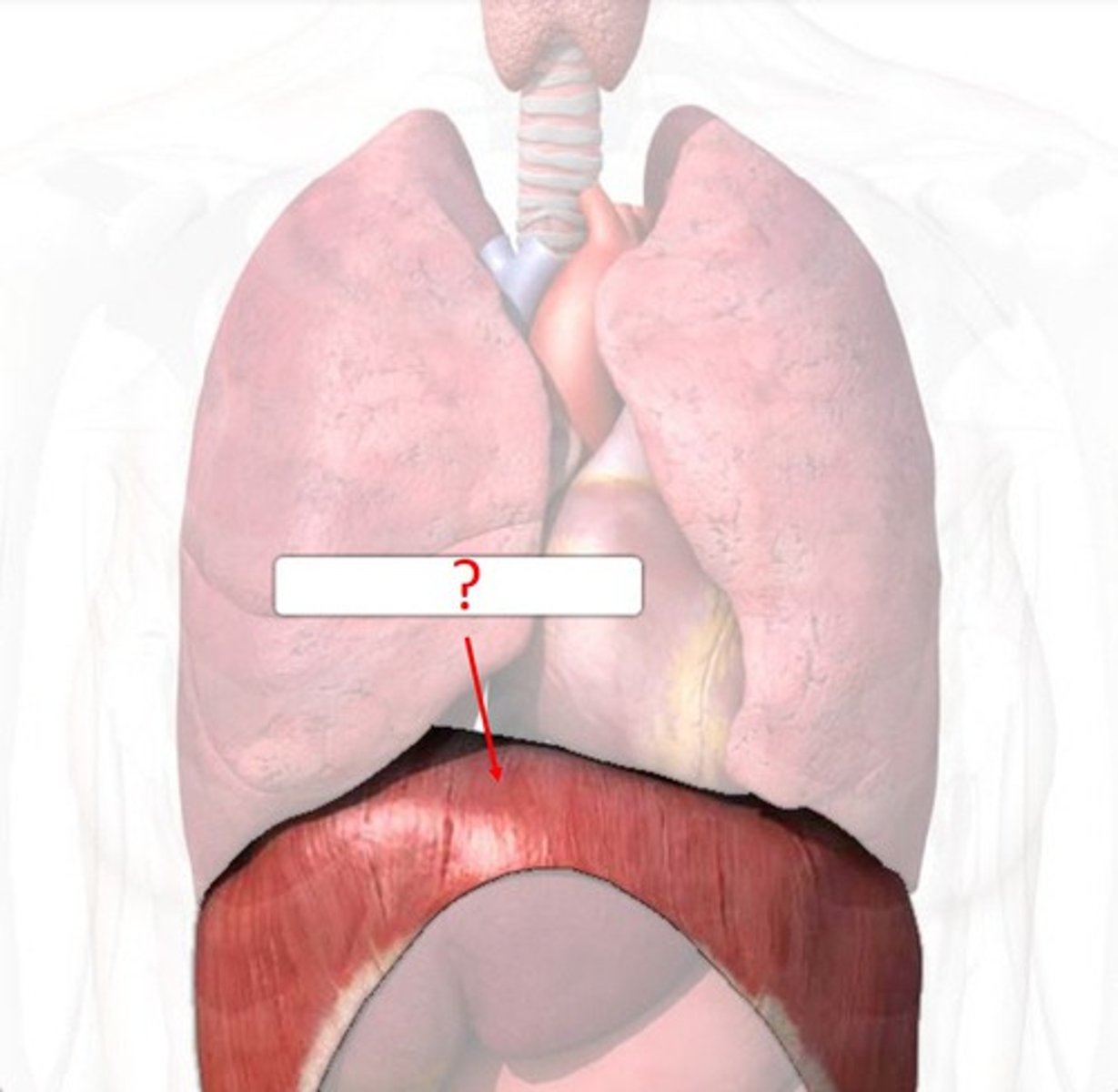
DIAPHRAGM
o: inferior internal surface of rib cage and sternum, costal cartilages of last six ribs, and lumbar vertebrae
i: central tendon
a: PRIME MOVER OF INSPIRATION; FLATTENS ON CONTRACTION
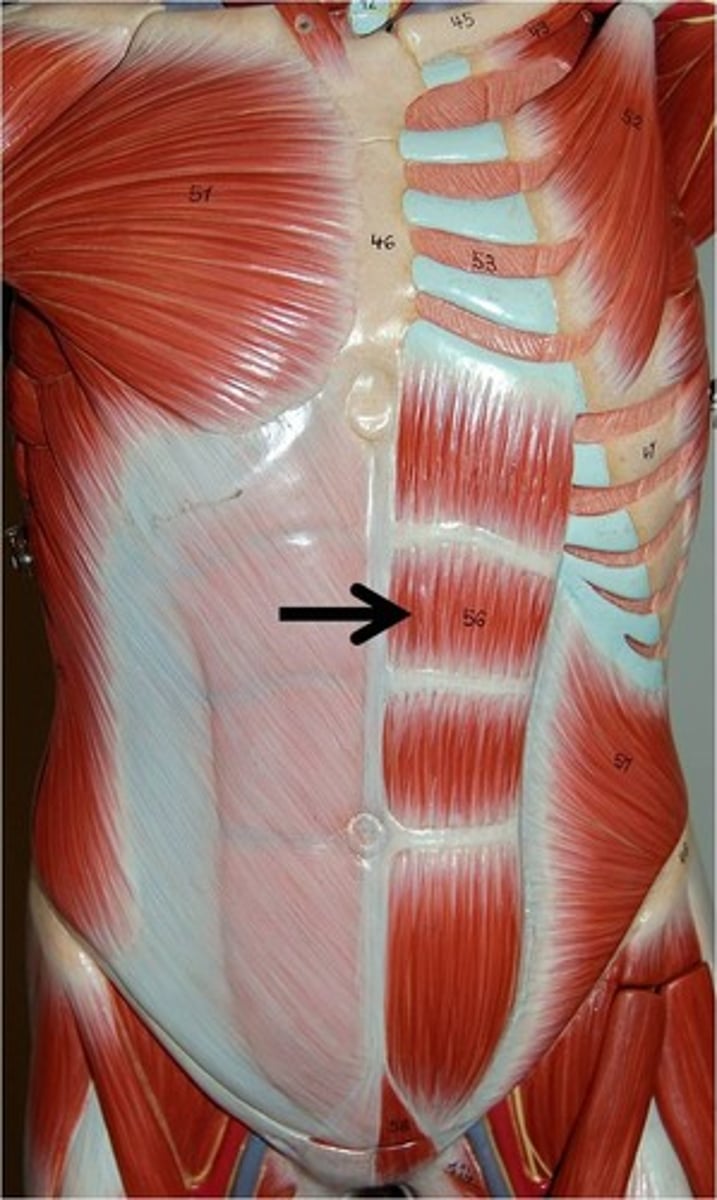
RECTUS ABDOMINIS
MEDIAL & SUPERFICIAL
o: pubic crest and symphysis
i: xiphoid process, costal cartilages of ribs 5-7
a: COMPRESSES ABDOMEN, FLEXES VERTEBRAL COLUMN
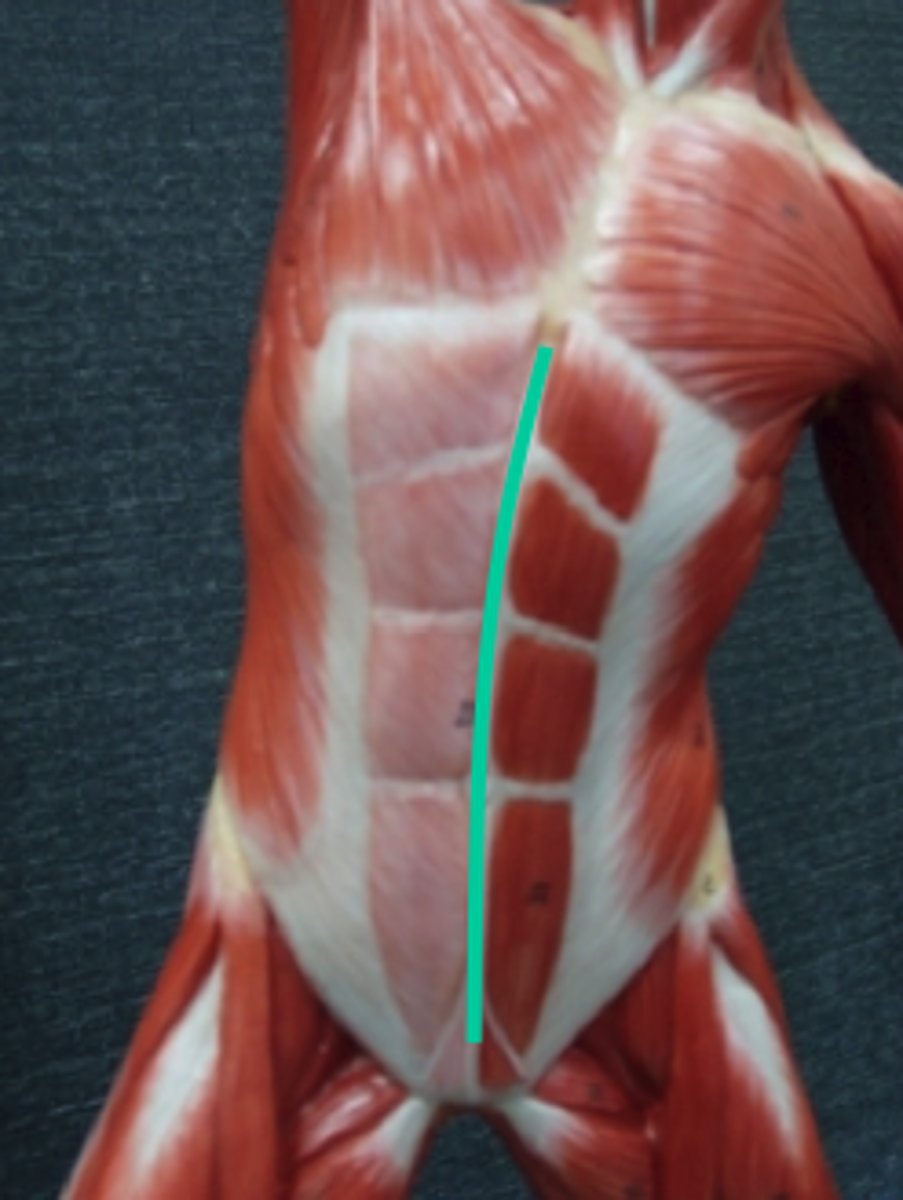
LINEA ALBA
The "white line:" the tendinous median line on the ventral abdominal wall between the two rectus muscles
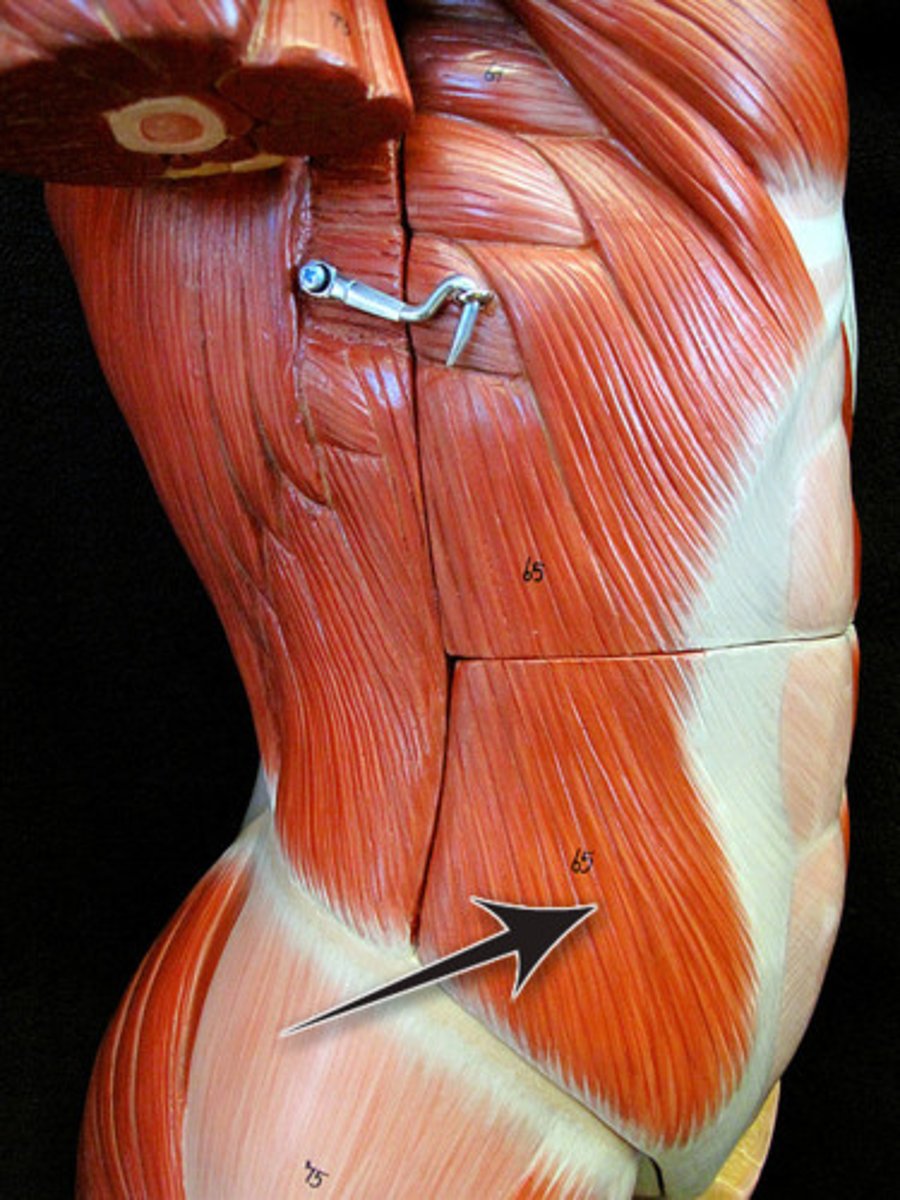
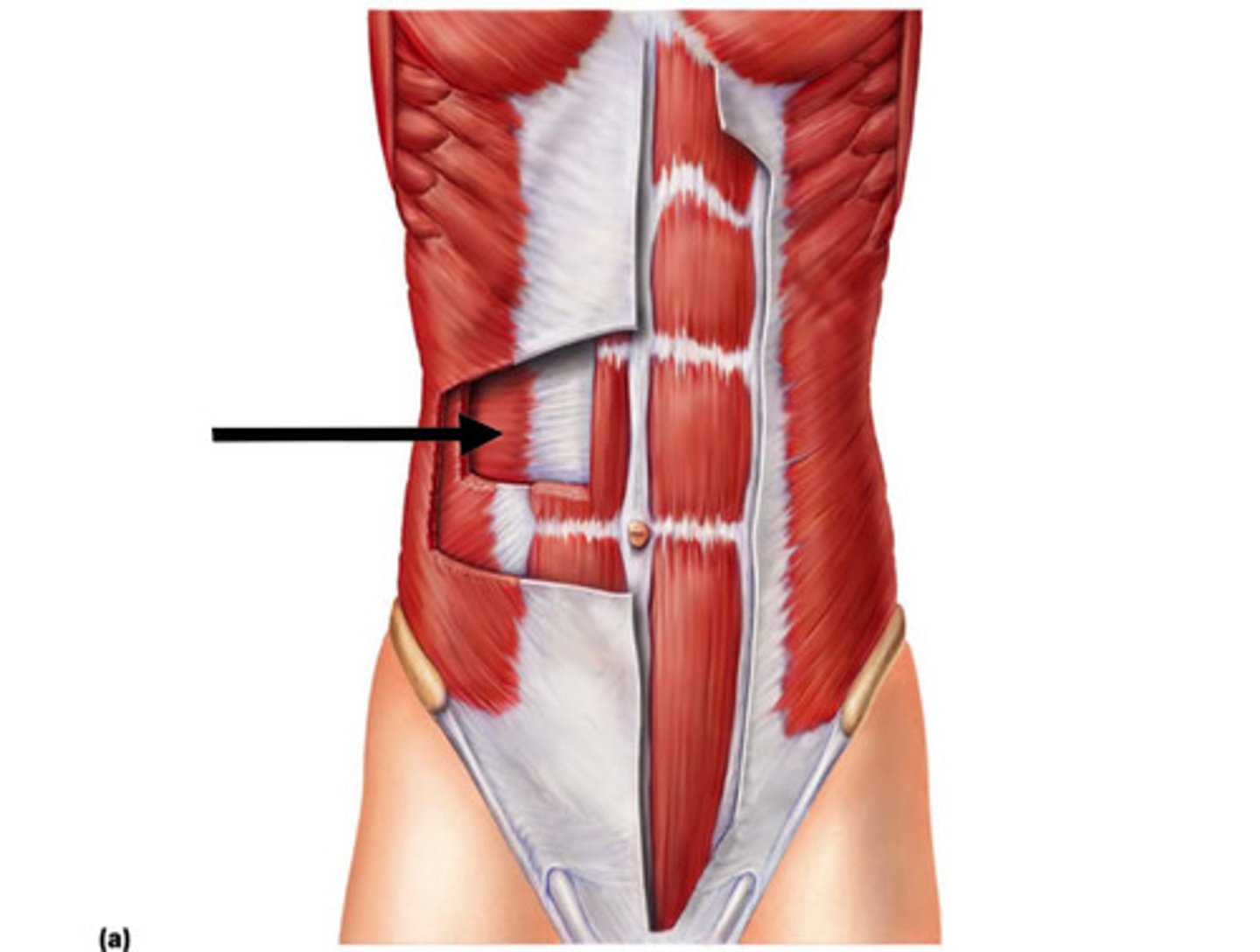
EXTERNAL OBLIQUE
(fibers run posterior and medially)
o: by fleshy strips from outer surfaces of lower eight ribs
i: most fibers insert into linea alba via a broad aponeurosis
a: FLEX VERTEBRAL COLUMN, COMPRESS ABDOMINAL WALL
INTERNAL OBLIQUE
fibers run superiorly and medially
o: lumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament
i: linea alba, pubic crest, last three or four ribs and costal margin
a: FLEX VERTEBRAL COLUMN, COMPRESS ABDOMINAL WALL
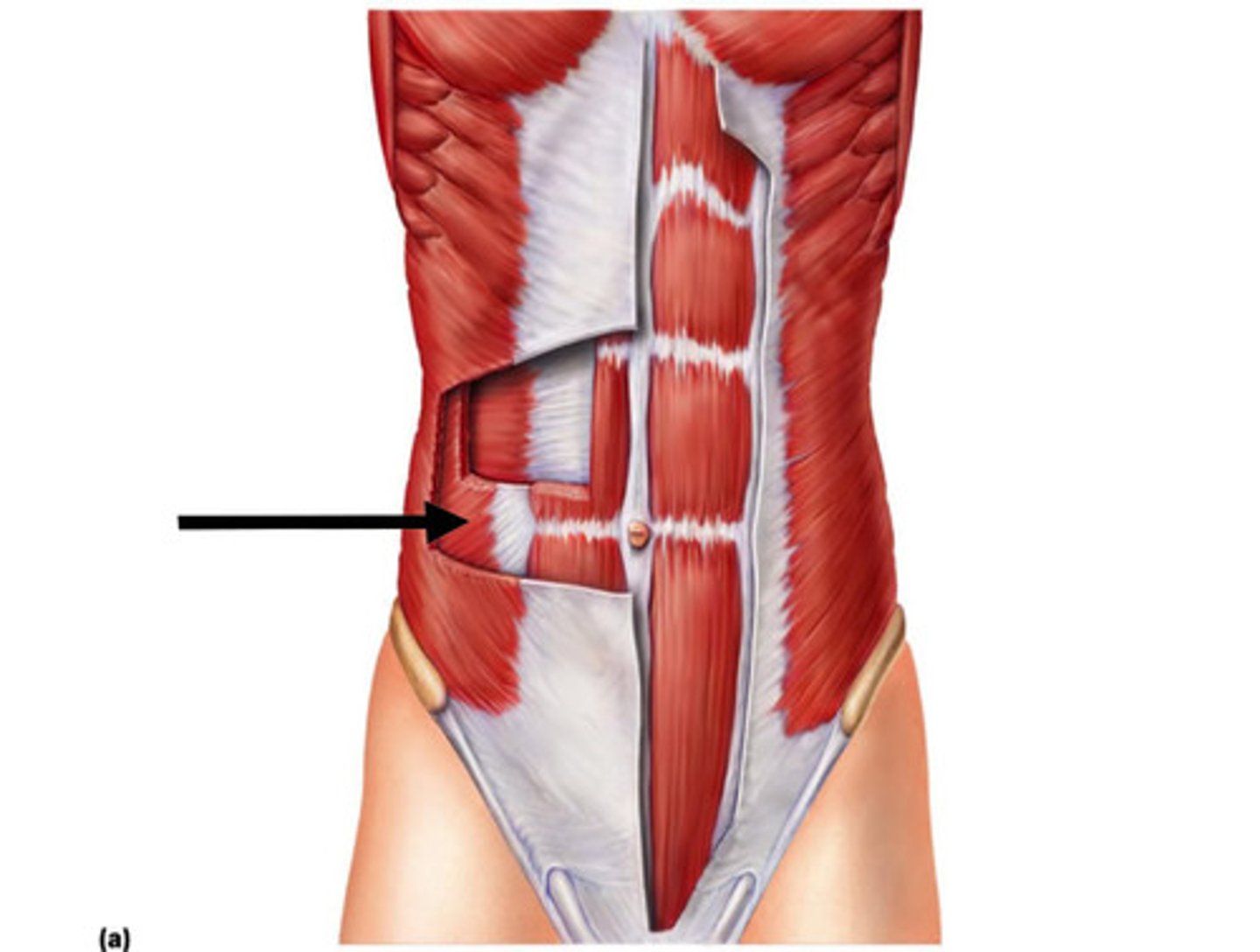
TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS
fibers run horizontally
o: inguinal ligament, lumbar fascia, cartilages of last six ribs; iliac crest
i: linea alba, pubic crest
a: COMPRESSES ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
The zygomatic arch is the origin of which muscle of mastication?
Masseter muscle
Which muscle of the neck elevates the floor of the mouth, elevates the hyoid bone, and/or depresses the mandible?
Mylohyoid muscle
The palatopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus, and stylopharyngeus muscles are all:
laryngeal elevators
Which of the following muscles elevates the upper lip?
Zygomaticus minor muscle
Which muscle closes the eye?
Orbicularis oculi muscle
Which term refers to the nerve supply to a particular structure or organ?
Innervation
Cranial nerve IV, the trochlear nerve, innervates which eye muscle?
Superior oblique muscle
hich of the following muscle(s) is/are required to roll the eye straight down?
Inferior rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle
Which muscle inserts into the side of the tongue, and depresses and retracts the tongue?
Hyoglossus muscle
Which eye muscle originates at the maxilla at the anterior portion of the orbit?
Inferior oblique muscle
What do the stylohyoid, thyrohyoid, geniohyoid, and omohyoid muscles have in common?
They all insert on the hyoid bone
Which of the following muscles is a muscle of the neck, that inserts on the mandible and skin of the cheek, and functions to tense the skin of the neck and depress the mandible?
Platysma
Which of the following muscles of mastication is innervated by the trigeminal nerve, and acts to elevate the mandible and close the jaw or to move the mandible side to side, but has no role in protraction or retraction of the jaw?
Medial pterygoid muscle
Which of the following statements is not true, concerning the oblique and rectus muscles?
The rectus muscles extend the vertebral column, assisting the action of the erector spinae muscles.
Which deep muscle of the spine inserts at the occipital bone between the nuchal lines?
Semispinalis capitis muscle
Which spinal flexor muscle originates at the iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament?
Quadratus lumborum muscle
Which of the following best describes the iliococcygeus muscle?
Its origins are the ischial spine and the pubis, and it elevates and retracts the anus.
Which of the following oblique muscles inserts on the external oblique aponeuroses, extending to linea alba and iliac crest?
External oblique muscle