DNA translation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is RNA processing?
When RNA is converted into different types of RNA to aid translation e.g., tRNA, mRNA and rRNA
What is the start codon?
AUG (methionine)
What is mRNA and which direction is it translated in?
The template for protein synthesis and is translated in the 5' to 3' direction.
Describe the structure of tRNA.
About 80 nucleotides long and has a clover leaf structure. It has an anticodon as well as a single stranded region at the 3' end that holds an amino acid.
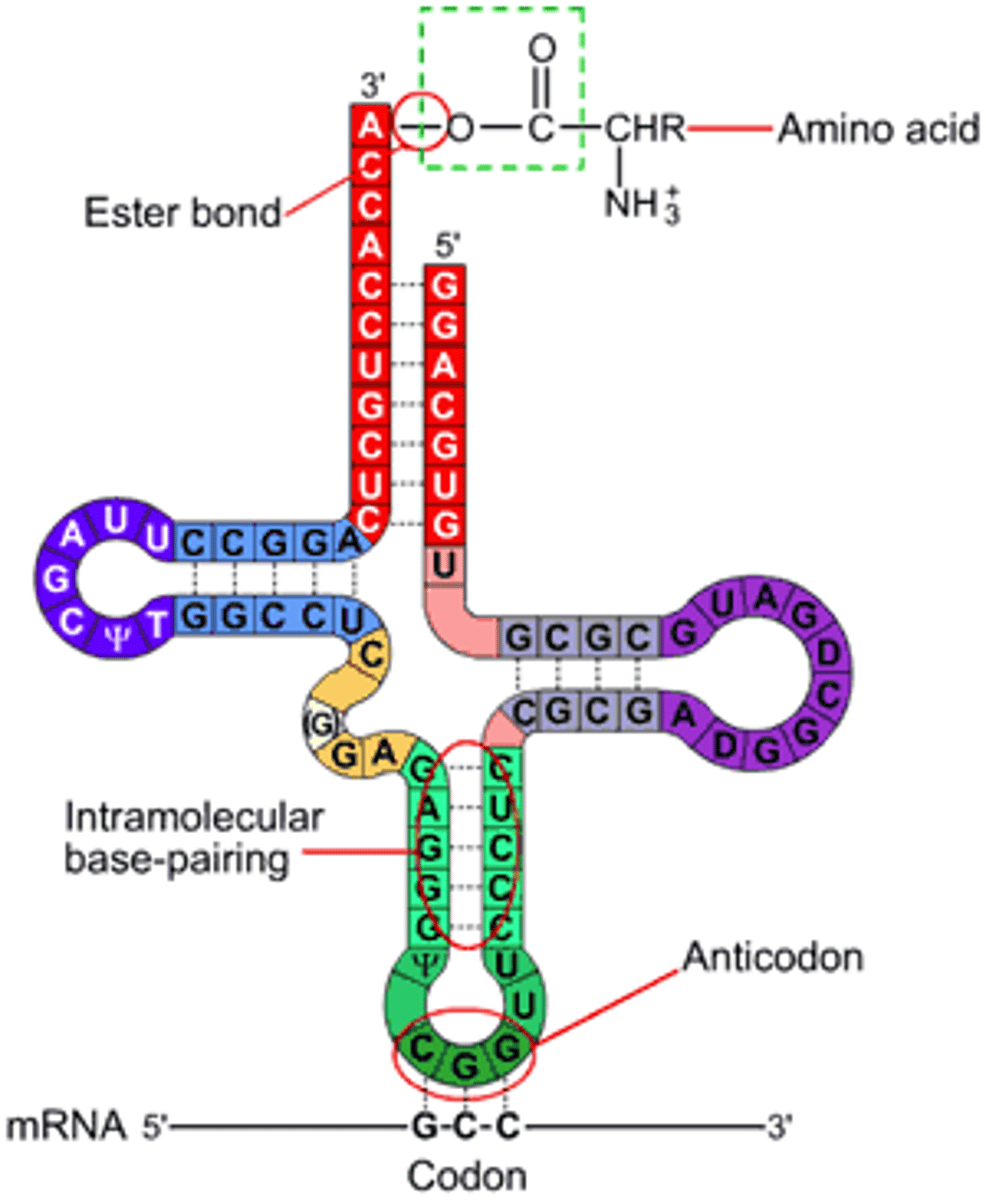
What is an anticodon?
An anticodon is the three unpaired bases on a tRNA that is complementary to the mRNA codon.
How does tRNA become charged?
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase adds the correct amino acid to the tRNA by forming an ester bond between the tRNA and amino acid.
where is ribosomal RNA (rRNA) produced?
The nucleolus from a DNA template.
What is the function of ribosomal RNA (rRNA)?
It is a major constituent in ribosomes as it it is combined with proteins to produce the large and small ribosomal units.
What are the three binding sites of a ribosome?
P (peptide) site, A (amino acid) site, E (exit) site
What is the initiation step in translation?
The small ribosomal subunit attaches to the mRNA start codon. The initiator tRNA (contains anticodon for start codon) attaches to the P site allowing the large sub unit to join.
What is the elongation step in translation?
Refers to growth in length of the polypeptide chain as tRNA molecules bring their amino acids to the ribosomes and involves translocation.
How does translocation occur?
The second tRNA approaches the A site and then replaces the initiator tRNA on the P site and a peptide bond forms between the amino acids and the spent initiator is moved to the E site and exits.
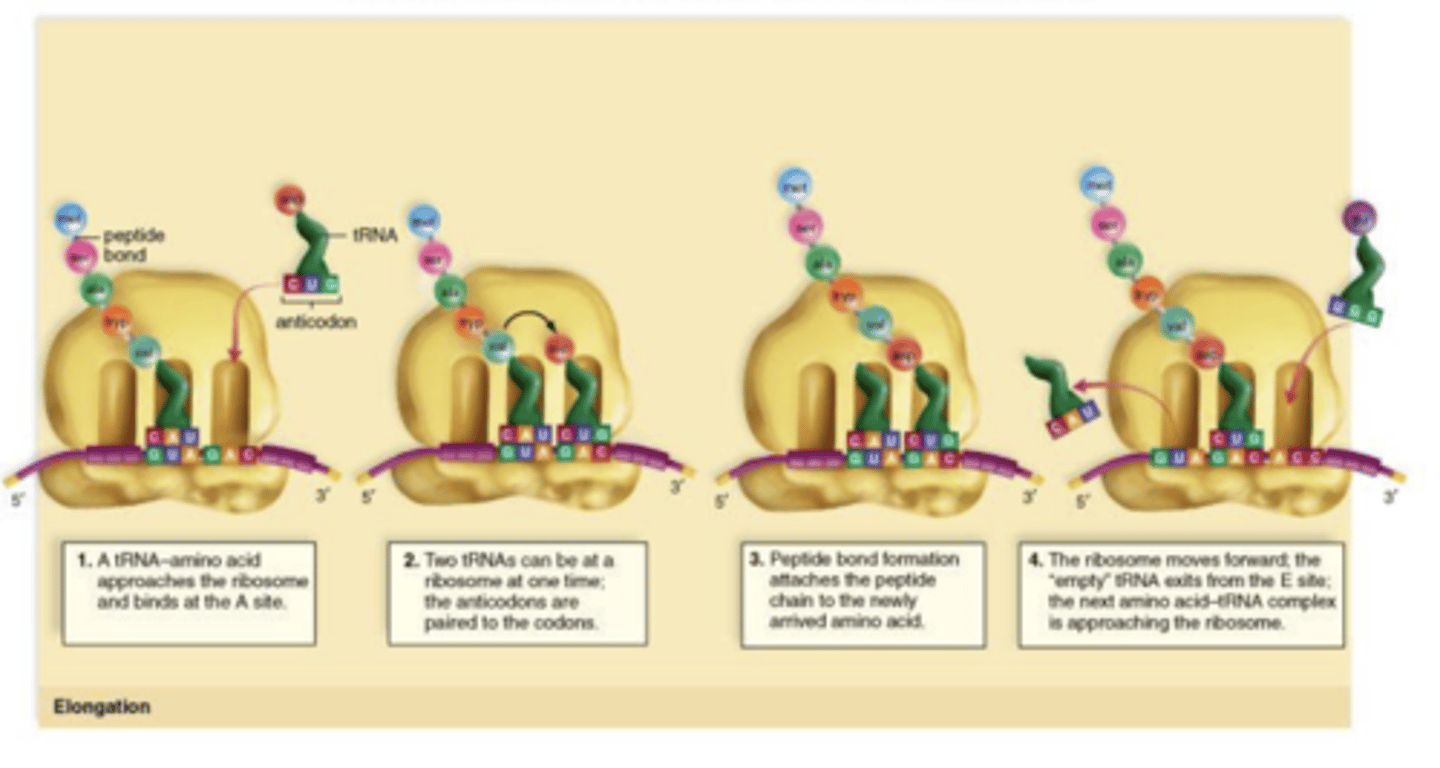
What is the termination step?
When ribosomes read the stop codon it then produces releasing factors. The mRNA is also dissociated into subunits and is read by another ribosome.
What are the three steps of translation?
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
What is the function of the large ribosomal unit?
Catalyses the formation of peptide bonds that link the amino acids together.
What is the function of the small ribosomal unit?
Matches the tRNAs to the codons of the mRNAs.
What is the function of releasing factors produced during termination?
- Hydrolyses bond between final tRNA and polypeptide chain.
- Causes release of ribosomal subunits, mRNA, polypeptide chain and tRNA's.
What post-translation modifications can occur when a protein is synthesised?
- Proteolysis
- Phosphorylation
- Insertion of cofactors e.g., heme into cytochrome C
- Glycosylation
- Formation of disulfide bonds
What is proteolysis?
The removal of signal sequences by hydrolysis of peptide bonds.
What is glycosylation?
The formation of glycoproteins via covalently binding oligosaccharides with amino acids.