TV4101 - Bovine - Toxic and Infectious Repro Loss
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Viral Diseases that can cause pregnancy loss include?
Most common one (put in bold)
I. Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus
II. Bovine Herpes-1 Virus
III. Akabane Virus
IV. Bluetongue Virus
V. FMD (Australia is free)
VI. Rinderpest
VII. Parainfluenza
VIII.Pseudorabies
Clinical manifestations by gestational stages
Trimester 1?
1. Early embryonic death (0-28 d)
2. Late embryonic death (28-42 d)
3. Regular or irregular return to oestrus
4. Abortion (> 42 – 90 d)
Clinical manifestations by gestational stages
Trimester 2?
1. Abortion
2. Mummification
3. Maceration
Clinical manifestations by gestational stages
Trimester 3?
1. Abortion
2. Mummification
3. Maceration
4. Abnormal foetus > Dystocia > Retained placenta > Metritis
Clinical manifestations by gestational stages
After trinester 3
1. Stillbirth
2. Weak neonates
3. Susceptible to diseases
4. Poor growth rate
5. Calf mortality
Factors Inducing Abortion?
Severe maternal illness
1. High fever
2. Hypoxia
3. Endotoxemia
Placentitis
1. Release of endometrial PGF
2. Low placental blood supply
3. Leads to foetal stress > foetal death or premature calving
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea in Australia
Agent?
Prevalence in AUS?
Forms of disease?
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus or Pestivirus
Widespread across AUS
Acute transient, persistently infected, mucosal disease
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea in Australia
Acute transient form features?
Animal will mount immune response after infection and clear virus in 10-14 days. (Fever and diarrhoea)
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea in Australia
PI form
How does it ocur?
Result?
Virus cross placenta of non-immune pregnant cows and infect foetus
Foetus may become PI calf that may or may not have any CX
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea in Australia
Mucosal Disease Form
How does it occur?
PI animals infected with non-cytopathogenic virus strain → spontaneously mutates into cytopathogenic form → mucosal disease
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea in Australia
Mucosal Disease Form
CX?
sero-mucoid nasal discharge,
severe erosive lesions in oral & intestinal mucosa, diarrhoea, and death
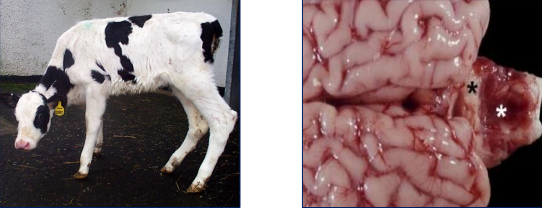
BVDV Gallery
What is each photo?
Left - incoordination (CNS birth defects in PI calf)
Right - cerebellar hypoplasia
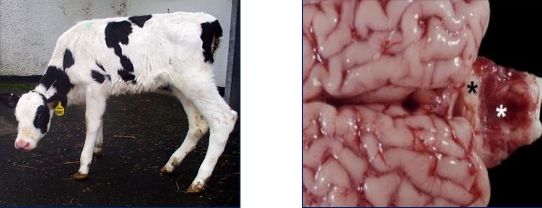

BVDV Gallery
What is each photo?
Left - aborted foetus
Right - Normal calf on left and PI calf on right
BVDV Routes of infection?
Route of infection: Inhalation, Ingestion, Venereal, Transplacental (nasal discharge, saliva, semen, urine, tears, and milk)
Impact of BVDV based on gestational stages
Around breeding?
40-120d gestation in naive cow
120-150d gest
>150 days gest
Around breeding
- Disrupted ovulation and fertilisation, EEL
40-120d
- LEL
- Abortions
- Birth of PI
- Ab -ve and virus positive
120-150d
- Abortions
- Congenital defects
AB +ve with or without virus
Cerebellar hypoplasia and hydrancephaly → prolonged gestation
>150
- Birth of normal calf which may be small and weak
- Has competent immune response
- Ab +ve and virus -ve

BVDV - infeced and born alive calves
Mortality?
Disease?
Growth?
Abnomalities?
1. Increase calf morbidity & mortality
2. Prone to respiratory diseases and profuse diarrhoea
3. May be born blind
4. Poor growth rates
5. Low weight at weaning / yearling
6. Die within < 2 years
7. Overall, reduced productiity and profitability
BVDV: Sampling & Tests
Aborted foetus?
1.Detection of BVDV Antigen
Foetal tissues – Antigen capture ELISA or PCR
2.Detection of BVDV Antibody
Pericardial fluid – ELISA
3.Gross pathology
Developmental defects
4.Histopathology
Mononuclear cell infiltration in skin, lymphoid, and cerebellar tissues
BVDV: Sampling & Tests
PI calves and cattle
Ear notch tissue sample
AG capture ELISA
PCR
Virus isolation
IHC
Blood – Serum / Plasma
AG capture ELIS
PCR
Virus isolation
BVDV: Sampling & Tests - Agar test and result features?
Agar Gel Immunodiffusion (AGID) Test: Determine recent exposure based on Ab titre
▪ 0: Negative
▪ +1 to +2: Exposed to BVDV, but not within last 12 months
▪ ≥ +3: Infection within last 3-9 months
▪ Won’t detect PI
▪ Won’t detect antibody post-vaccination
BVDV: Sampling & Tests - Milk test and results?
Bulk Tank Milk (BTM) Test – compare the BMT sample Ab against a known positive, resulting in a “sample to positive control” or S/P ratio.
▪ S/P = > 1.00: Active or recent PI exposure, likely lactating PI cattle
▪ S/P = 0.75 to 1.00: Relatively recent BVDV exposure
▪ S/P = 0.25 to 0.75 : Some random or historic BVDV exposure
▪ S/P = < 0.25: Naïve herd and likely free from BVDV
BVDV: Vaccination
Used on who?
Efficacy?
Cost?
Schedule of vax?
1.Whole herd / targeted groups
2.Not 100% effective
3.Approximately $5/dose
4.Requires 2 initial doses followed by annual boosters
BVDV: Prevention & Control
Management of animals
Environment
Closed herd management.
Test & quarantine all new introductions
Vaccinate cattle leaving but later returning to farm
Avoid mixing cattle from different groups
Avoid over the fence contact.
▪ Double fencing
▪ Keep pregnant animal away from
boundary fences
Screen and remove PI animals
Minimise BVDV transfer via fomites
▪ Clean cattle handling, transport, husbandry equipment and protective clothing between different properties / herds / groups of cattle.
BVDV: Prevention & Control
Repro aspects?
Use semen (for AI) form registered / certified
AI centres known to be BVDV free.
Use embryos (for ET) from registered /
certified suppliers known to be BVDV free
Test & confirm ET donors and recipients are
BVDV free.
Bacterial Diseases - Brucellosis in Australia
Agent?
Significance?
Brucella abortus
Zoonotic and notifiable in AUS (gain approval from chief veterinary officer for emergency testing of animal disease)

Brucellosis Gallery
Describe photo
Carpal hygromas

Brucellosis Gallery
Describe each photo
Aborted foetus
Ingesting aborted placenta
Placentitis – Cotyledonary & Intercotyledonary
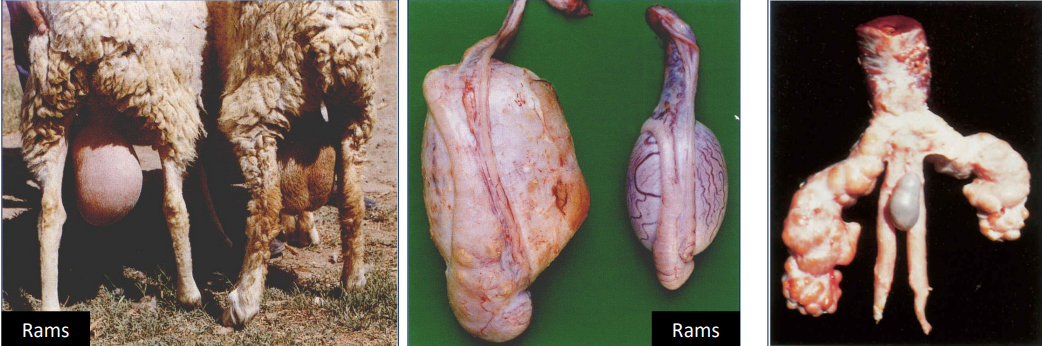
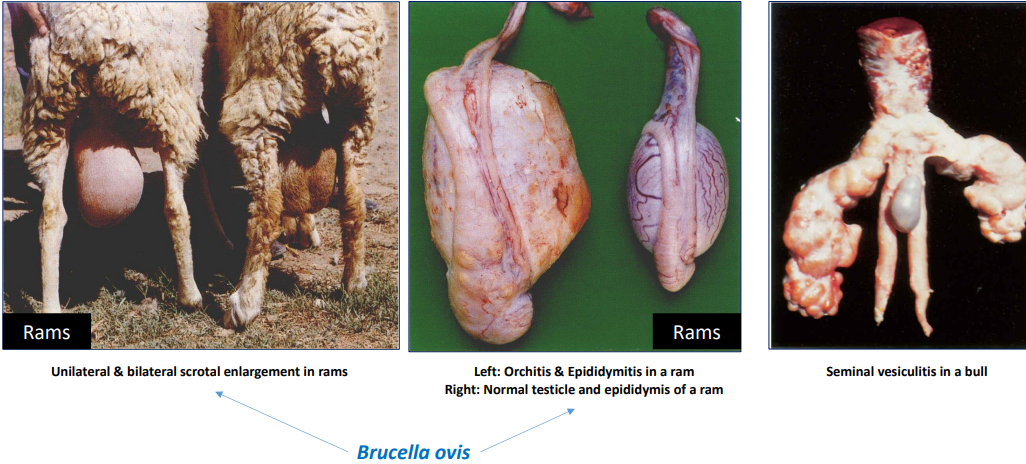
Brucellosis Gallery
Describe each photo
Unilateral & bilateral scrotal enlargement in rams
Middle - Left: Orchitis & Epididymitis in a ram Right: Normal testicle and epididymis of a ram
Seminal vesiculitis in a bull
First 2 photos technically have brucella ovis as the photos are from ovine species
Brucellosis – ROI
Oral - cont feed and water
Service from brucella infected bulls
AI from brucella infected bull semen
Brucella cont milk machines
Brucellosis - CX in Cows
I. Abortion (> 5 months of gestation)
II. Autolyzed foetus with no gross lesions
III. Still birth > Retained placenta > Metritis
IV. Weak calves (If born alive)
Brucellosis - CX in Bulls
I. Orchitis
II. Epididymitis
III. Seminal vesiculitis
IV. Carpal hygromas
Brucelllosis - Samples used for DX?
Foetal abomasal fluid and lung, placenta, uterine fluids, milk & serum samples
Brucelllosis - DX tests?
For brucella ABs
Rose bengal test
Complement fixation test
Standard agglutination test
Bacterial isolation & identification

Brucellosis - Prevention?
Live attenuated vax - Strain 19 or RB-51
Brucellosis - control
I. Closed herd approach
II. Testing & quarantine of new purchases
III. Bulk milk sample or repeated blood sampling to identify
& remove carriers
IV. Slaughter of positive animals
V. Quarantine during an outbreak
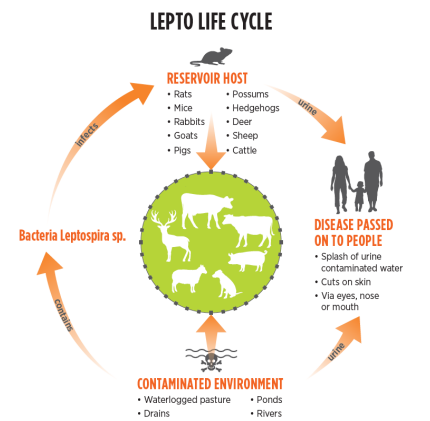
Leptospirosis in Australia
Agent?
Signficance?
*Leptospira hardjo or
Leptospira Pomona or L gryppotyphosa
Severe zoonoses and notifiable in humans in AUS

Leptospirosis in Australia
Shedding?
Environment for organism?
Cattle shed in urine when infected (even for life) or with aborted contents
Moist areas for months b4 infecting humans and cow (floodwaters make it worse)
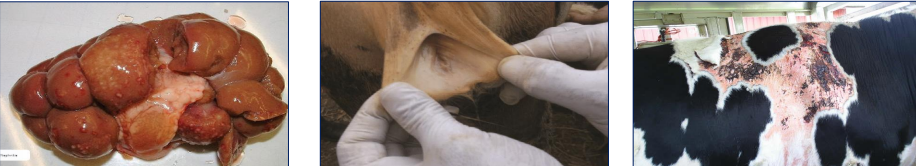
What can we see from left to right
Affliction?
Left - White spotted kidneys; non-pathognomic
Middle - Icteric mm from haemolysis
Right - Photosensitisation from liver damage
Leptospirosis

Describe each of these photos
Left - Leptospira bacteria under silver staining
Right - Urine contaminated stagnant water - the ideal environment for leptospirosis
Leptospirosis - ROI
Contact via intact mm (nose, eyes, and
mouth ) or abraded skin to..
Piss cont feed, pasture, soil, water
Aborted foetus cont environment
Leptospirosis - CS in cows?
Abortion storms >5 months gest
Mastitis → milk drop or agalactia
Photosensitisation

Leptospirosis - CS in calves?
I. High fever
II. Hemolytic anemia > Icteric mm
III. Hemoglobinuria > Reddish-brown urine
IV. High mortality rates
Leptospirosis - TX?
Oxytetracycline, Penicillin, Amoxycillin, Tilmicosin, or
Ceftiofur
Leptospirosis – Pathognomic lesions?
No pathognomic lesions - White spotted kidneys in infected cattle
Leptospirosis - samples for DX?
Urine
Serum
Whole aborted foetus and membranes
Fresh or fixed foetal brain, liver, spleen & kidney
Leptospirosis - DX tests?
I. Bacterial isolation & identification (Difficult)
II. Histopathology – Silver stains < foetal tissues
III. Dark filed microscopy < foetal fluids
IV. PCR or FAT or MAT > to detect Ag in foetal tissues
V. Maternal serology using MAT
Leptospirosis - Prevention and control?
Leptospira vaccine
I. Closed herd approach
II. Testing, Vaccinating & Quarantine of new purchases
III. Good biosecurity measures in place
IV. Bulk milk ELISA for screening
Listeriosis in Australia
Agent?
Significance?
Listeria monocytogenes
Zoonotic - serious illness in humans (mostly immunocompromised ones)

Listeriosis in Australia
Infect humans how?
Via raw milk or raw foods of plant origin that contaminated by manure from infected or shedding cattle
Listeriosis in Australia
Environment for oranism?
Soil, water, and animal faeces
Poorly fermented or spoiled silage is the breeding ground due to low acidity

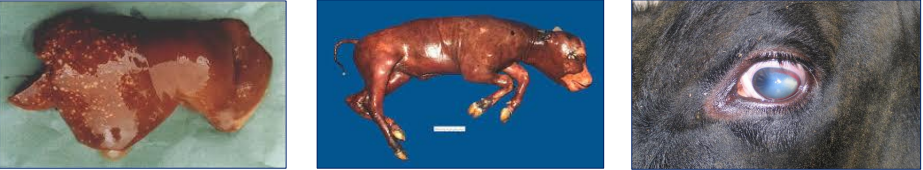
What can we see here?
Affliction?
Left - soiled silage (low acidity is breeding ground for Listeria)
Middle - Facial paralysis and head tilt → Encephalitis/Meningitis (Listeriosis)
Right - Loss of coordination and circling → Encephalitis / meningitis (Listeriosis)
LISTERIOSIS
What can we see here?
Affliction?
Left - foetal hepatitis (non-pathognomic) with white-yellow foci
Middle - aborted autolytic foetus (mostly 3rd trimester abortions)
Right - Corneal opacity (rare)
LISTERIOSIS
Listeriosis - ROI
Oral → contaminated silage (poorly fermented or spoiled) → bacteria to other organs inc brain (i.e. encephalitis)

Listeriosis - CX in cows
Sporadic abortions (>5 months)
Abortion storms/stillbirths (rare)
Neuro signs from encephalitis (rare)
Retained placenta → metritis → fever and anorexia
Septicaemia (rarE)
Listeriosis - CX - Neruo?
. Loss of coordination & circling
II. Head tilt & facial paralysis
III. Salivation & difficult to eat
IV. Depression and lethargy

Listeriosis - TX
Oxytetracycline or Penicillin
Listeriosis - Pathognomic Lesions?
No pathognomic lesions
Leads to suppurative placentitis
Pinpoint white to yellow foci (may present) in the liver
Listeriosis
Samples for DX?
CSF from affected cows
Whole aborted foetus and placenta
Fresh or fixed foetal brain, liver, spleen & kidney tissues
Listeriosis - DX tests
I. Bacterial isolation & identification – Gram staining
II. Immunohistochemistry – Using Listeria antibodies
III. Histopathology – look for placentitis & foetal hepatitis
IV. PCR – For Listeria antigens
Listeriosis - PX and control?
NO VACCINE
Avoid feeding poor quality silage

Campylobacteriosis Gallery
Describe each photo
Older bulls > deep preputial crypts > more bacteria
Preputial scrape or wash – sample collection
Early embryonic loss – no heartbeat + disintegrated

Campylobacteriosis (Vibriosis) in Australia
Agent?
Aka?
Bulls vs cows/heifers in infection
Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis
Also called Vibriosis
Bulls – Asymptomatic carriers
Cows/heifers – Acquire immunity following
infection but it lasts only for < 15 months
Campylobacteriosis – ROI
HX?
Transmission?
History of exposure to outside bulls/cows, recent introductions, shared grazing
Venereal transmission or AI using semen collected from
infected bulls or contaminated collection / AI tools
Campylobacteriosis - CX in cows
I. 10% perm infert – due to oviduct
obstruction after inf
II. EEL → may return to heat
III. Occasionally (4 - 7 months) abortions
IV. Develop immunity – may conceive later in the breeding
season
V. Inc interval from calving to conception
VI. Prolonged inter-calving interval
Campylobacteriosis - TX?
Oxytetracycline or Erythromycin

Campylobacteriosis - Samples for DX?
Cows/Heifers – Vaginal swab
Bulls – Preputial wash or scrape
Placenta – Intercotyledonary
Campylobacteriosis - DX tests?
I. Vaginal mucus
a. Bacterial culture & identification – IHC/DFM
b. IgA ELISA (Low specificity)
II. Preputial sample
a. PCR – 3 tests, one week apart for high sensitivity and
specificity
Campylobacteriosis - Prevention and Control?
Vax herd esp bulls - 2 doses, 4 wks apart
I. Closed herd approach
II. Test & cull older carrier bulls (> 5 Y old)
III. Purchase only younger & virgin bulls
IV. Avoid contact with stray bulls and cows
Vax new bulls b4 introducing for breeding
Protozoal Diseases
Includes? Put more common occuraances in bold and the ones that cause sporadic abortions occaionally in itlaics
I. Trichomoniasis
II. Neosporosis
III. Toxoplasmosis
IV. Theileriosis
Trichomoniasis (Trich) in Australia
Agent?
Aka?
Infections diffs in cow/heifer/bulls?
Tritrichomonas foetus
AKA trich
Bulls - Asympto carriers
Cows/Heifers - transient infection with acquired immunity <6 months

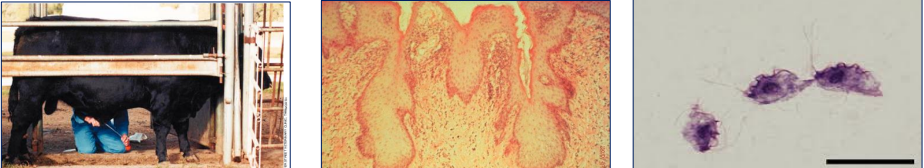
Describe photos from L-R
What is the affliction?
Left - preputial scrape/wash - sample collection
Middle - Epithelial crypts of preputial lining of 5Y bull
Right - Tritrichomonas foetus
Trichomoniasis
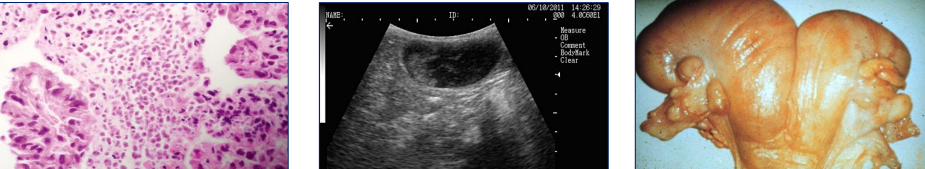
Describe photos from L-R
What is the affliction?
Left - Tritrichomonas foetus – Placentitis
Middle - Dead disintegrated foetus
Right - Post-coital pyometra
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis – ROI
HX?
Transmission?
History of exposure to outside bulls/cows, recent introductions, shared grazing
Venereal transmission or AI using semen collected
from infected bulls or contaminated collection / AI tools
Trichomoniasis - CX in cows
Abortions and Disease aspects?
I. Post-coital pyometra***
II. Early embryonic death
III. Occasionally (< 5 months) abortions + edematous
placenta (due to placentitis)
IV. Develop immunity – may conceive later in the
breeding season
Trichomoniasis - CX in cows
Interval and rates aspects?
CX in bulls?
V. Increased interval from calving to conception
VI. Prolonged inter-calving interval
VII. Reduced pregnancy & calving rates
Bulls asympto carriers
Trichomoniasis - TX?
NO Approved Rx available currently
Trichomoniasis - Samples used for DX?
Cows/Heifers – Vaginal swab
Pyometra cow – Uterine sample
Bulls – Preputial scrape or wash
Foetus – Abomasal fluid & Placenta
Trichomoniasis - DX tests?
I. Vaginal mucus / Uterine sample / Foetal abomosal
▪ Histology – H&E stain
▪ Immunofluorescent test (IFT)
▪ Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
II. Preputial sample
▪ PCR – 3 tests, one week apart for high sensitivity
and specificity
Trichomoniasis - Control?
I. Closed herd approach
II. Test & cull older carrier bulls (> 5 Y old)
III. Restrict breeding to bulls of < 5 Y old
IV. Purchase only young & virgin bulls
V. Avoid herd contact with stray bulls and cows
VI. Cull or segregate non-pregnant and aborted cows
VAXX not available in AUS
Neosporosis in Australia
Agent? Features?
Significance?
Neospora caninum - protozoa
Causes ~20-30% of abortions in both dairy and beef cattle in AUS
Neosporosis in Australia
ROI
Horizontal version
Ingestion of feed contaminated with dog faeces
that has Neospora oocysts
Neosporosis in Australia
ROI
Vertical Transmission features?
Most common more critical method
▪ Passing of Neospora oocysts from infected
pregnant cows to their foetus via placenta
▪ Maintain the infection in herd
Neosporosis - CS in cows
Abortion aspects
I. Sporadic or storm of abortions
II. Abortion is possible anytime during gestation but often
between 4-7 months
Neosporosis - CS in cows
Dam aspects that cause abortions
III. Seropositive dams 3-7 times higher risk of abortion
than seronegative dams
IV. Seropositive dams can abort during subsequent
pregnancies
V. Immunosuppressed dams can allow dormant Neospora
to be activated during pregnancy – leading to abortion
Neosporosis - CS in calves (from vertical transmission)
▪ Majority of infected calves show NO clinical signs
▪ If abnormalities present in calves, then:
▪ Underweight
▪ Unable to stand
▪ Flexed or hyper-extended limbs
▪ Lack of coordination
▪ Decrease sensory perception
▪ “Pop-eyed” (exophthalmos) & asymmetry eyes
▪ Birth defects like hydrocephalus
▪ None of these signs are pathognomic for neosporosis

Neosporosis
TX?
Prevention?
No approved TX available
Vax nt available in AUS
Neosporosis - DX
Samples used?
Dams – serum sample
Aborted foetal tissues & placenta (< placentitis)
Neosporosis - DX
Tests?
I. Serum sample – ▪ Positive Ab titres indicate exposure but not sufficient to confirm Neospora is the cause of abortion
II. Aborted foetal tissues and placenta
▪ Histopathology
▪ PCR or ELISA or Immunohistochemistry
Neosporosis - Control
Dogs?
Dog-to-cow transmission
▪ Reducing wild dog/fox population in extensive grazing farming
▪ Prevent contamination of pasture & feed by dog faeces
▪ Prevent farm dogs scavenging aborted foetuses
▪ Aborted foetuses, dead calves, placentas – buried or
burned or disposed properly
Neosporosis - Control
Calf?
Prevent cow-to-calf transmission
▪ Not including infected cows in the breeding herd
▪ Not breeding replacement heifers from infected cows
Blood test to determine infected cows or calves (for
culling but expensive) or as pre-purchase testing.

Toxoplasmosis
Agent?
Signficance?
How does it occur?
Toxoplasma gondii
Zoonoses (pregnant women)
Ingestion of feed contaminated with cat faeces that has
Toxoplasma oocysts

What is this?
Describe each photo
Toxoplasmosis
Pepperoni pizza like cotyledonitis – classical appearance due to Toxoplasma. (Intercotyledonary area is normal)
Cats transmit disease by shedding oocysts in faeces

Toxoplasmosis
DX?
Control?
Diagnosis based on histopathology or FAT on
aborted foetus & placenta
Control cat population in farms and avoid
cont of feed with cat faeces.
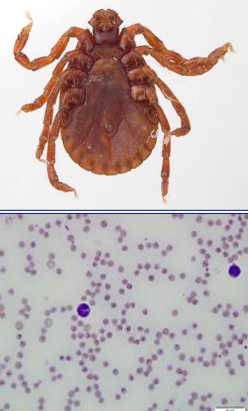
Describe each of these photos
What disease?
Top - Bush tick (Haemophysalis longicornis)
Bottom - Theileria orientalisorganism
Theileriosis
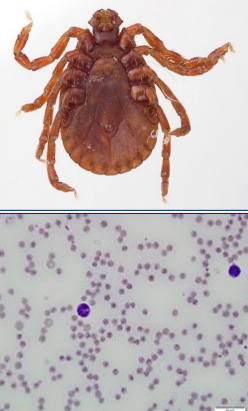
Theileriosis
Agent?
Significance?
Bovine Anaemia caused by the Theileria orientalis
Group (BATOG) - infects through the bite of Bush tick (Haemophysalis longicornis)
Getting more clinical important recently in AUS
Theileriosis
CX?
▪ Anaemia
▪ Red urine
▪ Jaundice
▪ Anorexia, lethargy & depression
▪ Pregnant animals may abort or premature birth due to high fever and anaemia

Theileriosis
Control & prevention
▪ Bush tick (Haemophysalis longicornis) control – by acaricides
▪ Quarantine of introductions for 30 days
▪ Avoid stress and stock movements during late term pregnancies
▪ Avoid moving non-exposed cattle to endemic areas
Toxic Causes include?
I. Mycotoxicosis
II. Ponderosa pine needle
III. Nitrate/Nitrite poisoning
Mycotoxicosis
Causative organisms?
Repro outcomes?
Control?
▪ Aspergillus sp.***
▪ Mucor sp. **
▪ Mortierella sp.
▪ Rhizopus sp.
▪ Candida sp.
▪ Absida sp.
Late term abortions, premature births, retarded growth in liveborn calves
▪ Good ventilation
▪ Avoidance or removal of mouldy feed
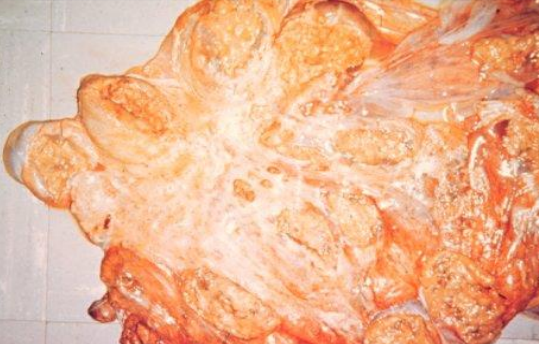
Describe photo
What is affliction?
Necrotic Placentitis – leads to asphyxia of the foetus
Mycotoxicosis