IMED1003 - Cholesterol Excretion and Summary (4)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Summary so Far
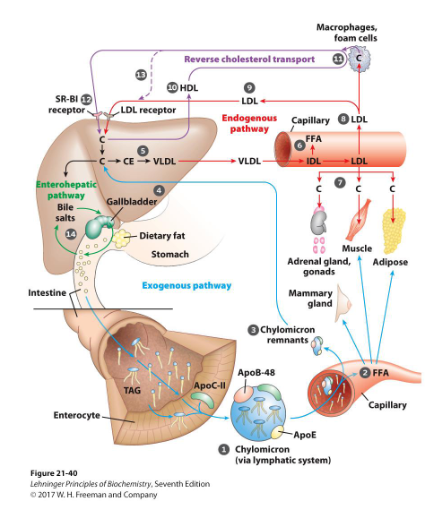
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 3
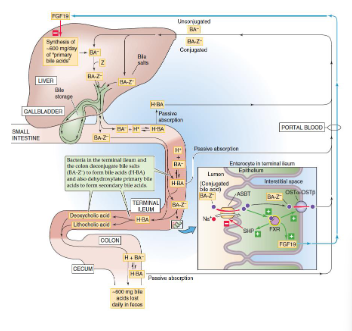
Enterohepatic circulation of bile acids: bile acids are reabsorbed
- bile acids/bile salts secreted by gall bladder into small intestine
- these bile salts are Passively reabsorbed throughout digestive tract
- they can also be Actively reabsorbed in ilium (apical sodium-dependent bile salt transporter (ABST)
- these bile salts are Returned to liver via portal vein
- 95% bile acids are reabsorbed
- this whole process is called enterohepatic circulation of bile acids
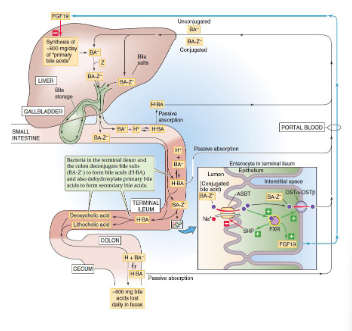
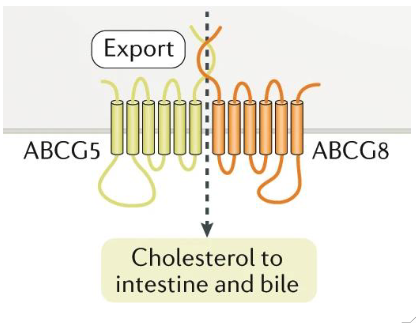
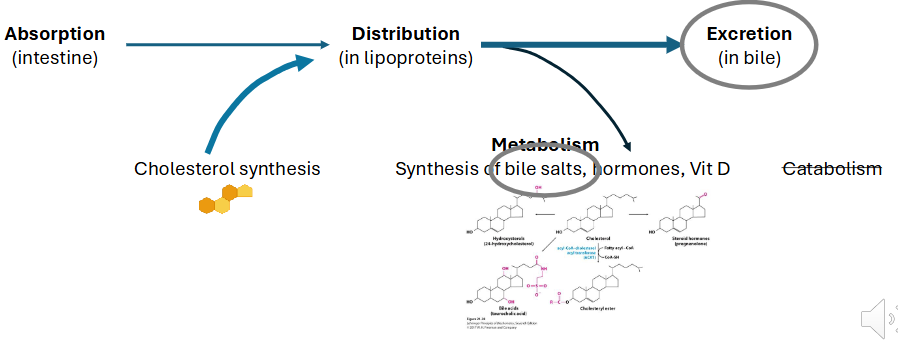
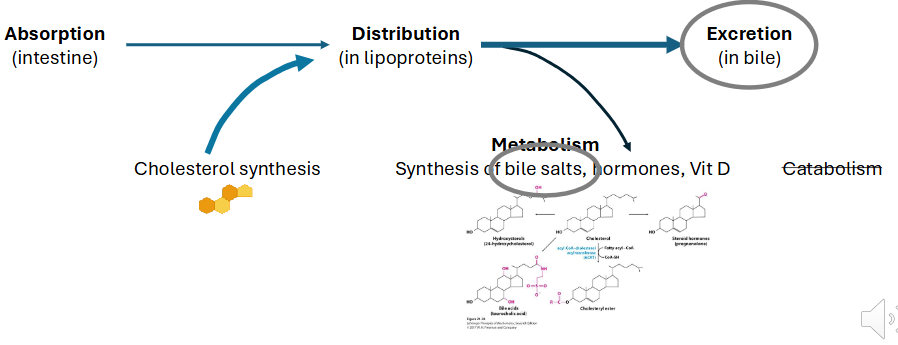
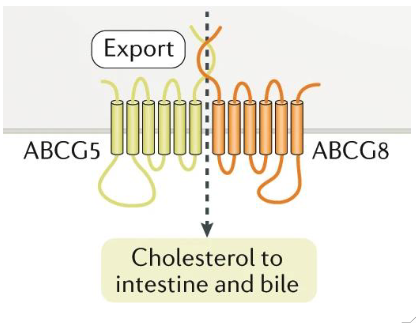
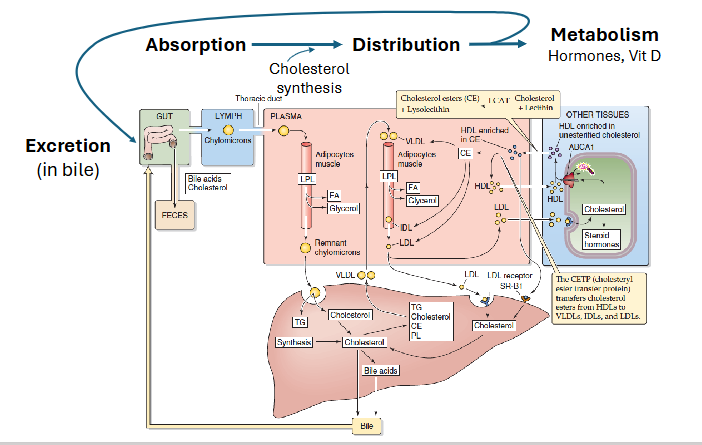
Excretion of Free Cholesterol in Bile
- major loss of cholesterol occurs through free excretion in bile
- Hepatocytes, enterocytes secrete excess free cholesterol directly into GI tract
- ABC transporters
- ABCG 5/8: apical side of enterocytes, hepatocytes
(basically bile moves from the blood into the small intestines)
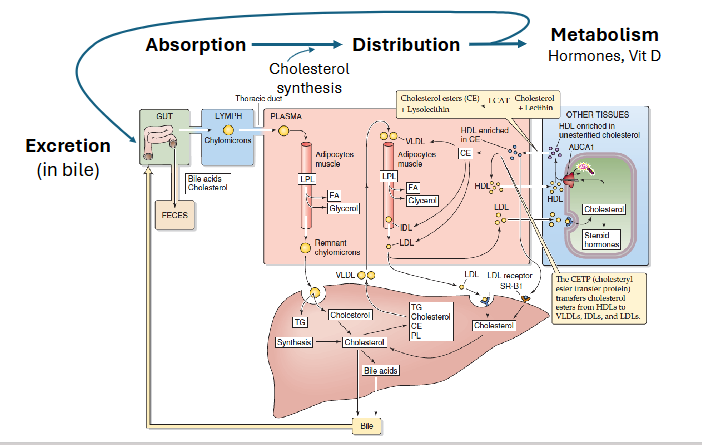
Cholesterol Homeostasis
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 7
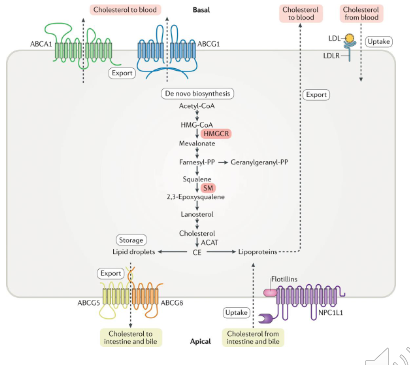
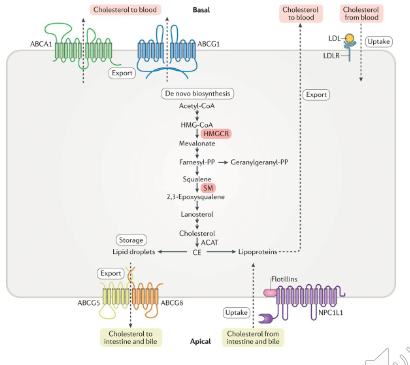
Cellular Regulation of Cholesterol: Points of Control
SYNTHESIS:
- HMG-CoA reductase:
- Post transcriptional modification
- transcriptional modification
- Proteolytic degredation
STORAGE:
- Cholesterol acetyltransferase (ACAT)
UPTAKE:
- Transcriptional regulation of LDL receptor
.
THIS NEXT THING IS FOR SYNTHESIS:
- when cholesterol levels are high, protein is tagged for degredation and proteolysis which means we dont have synthesis of cholesterol
- when intracellular levels of cholesteorl are low, HMG-CoA transcription is upregulated, whcih means we produce more of the enzyme
Genetic Disorders caused by disrupted cholesterol homeostasis
- genetic disorders: genes encoding metabolic enzymes, transporters, receptors required for cholesterol
- Synthesis
- Absorption
- Distribution (reverse cholesterol transport)
- Distribution (endogenous cholesterol transport pathway)
- Excretion
Synthesis: Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome
- cholesterol is required for signalling in embryonic development (establish positions of specialised cells, tissues, organs)
- Cholesterol availability: limiting prerequisite for myelin synthesis
- Brain: 20-25% cholesterol by mass
- Lipoproteins in blood cannot deliver cholesterol due to blood brain barrier
- Cholesterol synthesis crucial for CNS development
- Malformations of heart and kidney, cleft palate, mental and growth retardation
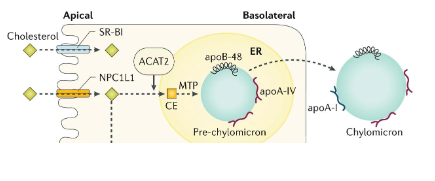
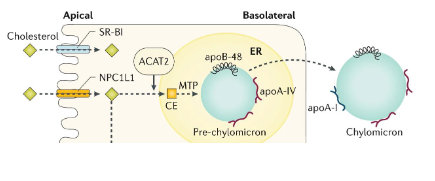
Absorption: Abetalipoporteinemia
- defective microsomal triglyceride transport protein (MTP)
- required for formation of CM (chylomicron) in enterocytes, VLDL in hepatocytes
- unable to absorb lipids, fat-soluble vitamins
- Severe deficiency in fat-soluble vitamins
- very rare
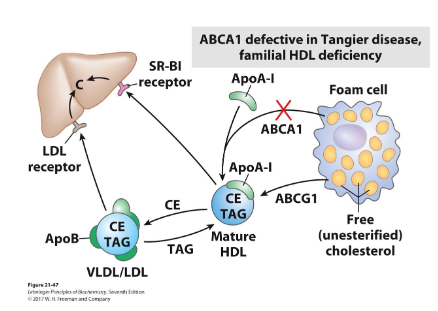
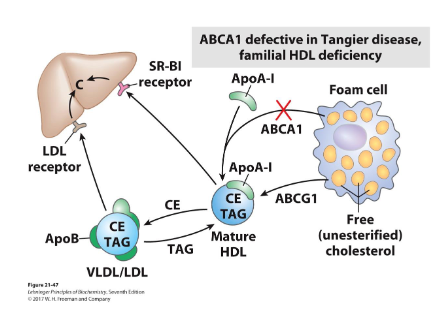
Reverse Cholesterol Transport: Tangier Disease
- defective ABCA1
- cholesterol can not be exported by many cells, including macropahges
- failure of reverse cholesterol transport leads
- severe and early cardiovascular diseases
.
Defective ABCA1 inhibits reverse cholesterol transport because it is the primary transporter responsible for moving cholesterol and phospholipids from inside cells, particularly macrophages, to the exterior. Without a functional ABCA1 transporter, cholesterol accumulates in the cell, preventing it from being loaded onto high-density lipoproteins (HDL) for transport back to the liver, which stops the reverse cholesterol transport pathway at its initial and rate-limiting step.
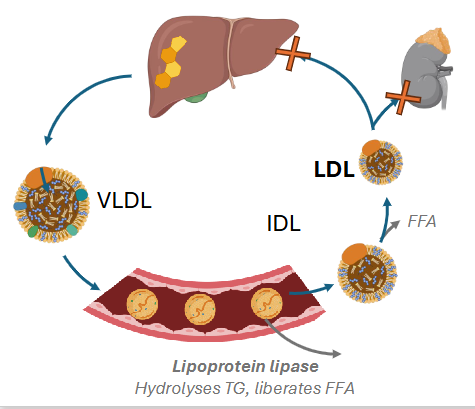
Endogenous Cholesterol Distribution: Familial Hypercholesterolemia
- defective LDL receptor
- LDL can not be absorbed by extrahepatic tissues or liver
- LDL accumulates
- [LDL] in plasma increases
- Early development of CVD
![<p>- defective LDL receptor</p><p>- LDL can not be absorbed by extrahepatic tissues or liver</p><p>- LDL accumulates</p><p>- [LDL] in plasma increases</p><p>- Early development of CVD</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e7a9d16e-a60f-4dba-8d32-bae60e4a36ce.png)
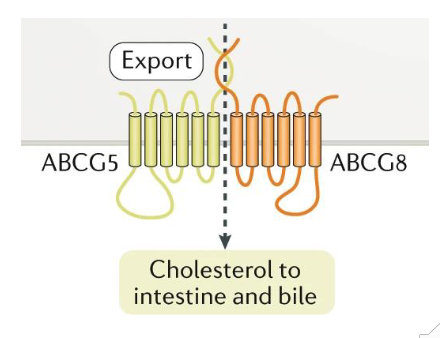
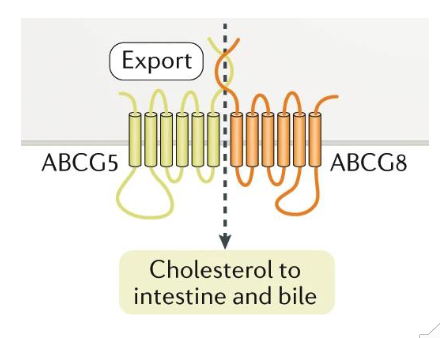
Excretion: Sitosterolaemia
- defective ABCG5/8
- elevated plasma, tissue cholesterol
- Xanthomas, premature cardiovascular disease
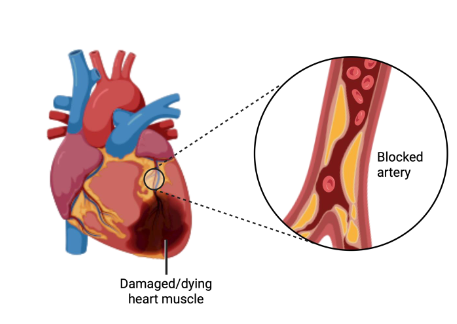
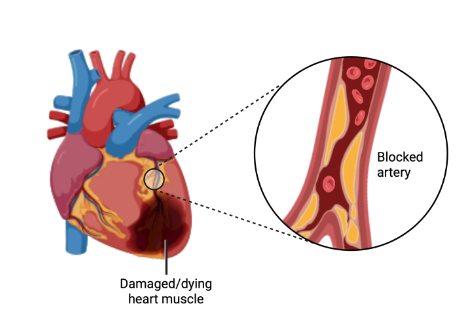
Excess plasma cholesterol causes cardiovascular disease
- Ratio of LDL:HDL essential for effective reverse cholesterol transport
- Cholesterol blood test: monitors concentrations of these lipoproteins
- Dietary absorption of cholesterol itself is poor, however some dietary patterns increase LDL
- LDL exceeds needs of tissues, overwhelms capacity for cholesterol scavenging by HDL
- Major cause of cardiovascular disease
- Pharmacological management - inhibit HMG CoA reductase with statins
.
- remember that HMG-CoA endogenously synthesises. We are limiting its natural syntrhesis becuase our diet has too much
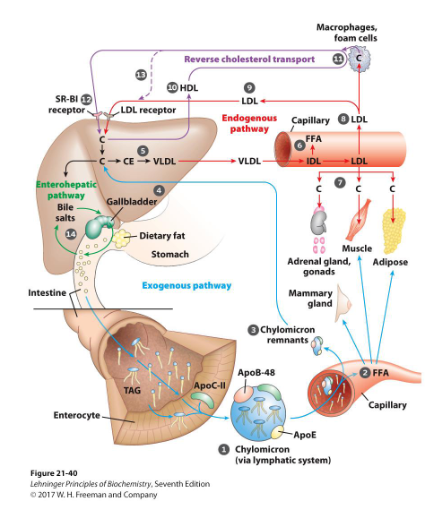
Summary
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 16