Pathophysiology Study Guide: Key Terms and Concepts
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
Normal vitals: O2 sat
>95% O2
Normal vitals: respiration rate
12-18 breaths/minute
Normal vitals: heart rate
60-100 bpm
Normal vitals: blood pressure
<120 mmHg SBP & <80 mmHg DBP
__________ BP: <120 mmHg SBP and <80 mmHg DBP
Normal
__________ BP: 120-129 mmHg SBP and <80 mmHG DBP
Elevated
__________ BP: 130-139 mmHg SBP OR 80-89 mmHg
Stage I Hypertension
__________ BP: >140 mmHg SBP OR >90 mmHg
Stage II Hypertension
List the dermatomes of the upper body.
C2 - suboccipital (behind the ears)
C3 - subclavicular fossa
C4 - upper trapezius (shoulders)
C5 - lateral antecubital fossa
C6 - thumb
C7 - 3rd digit
C8 - 5th digit
T1 - medial antecubital fossa
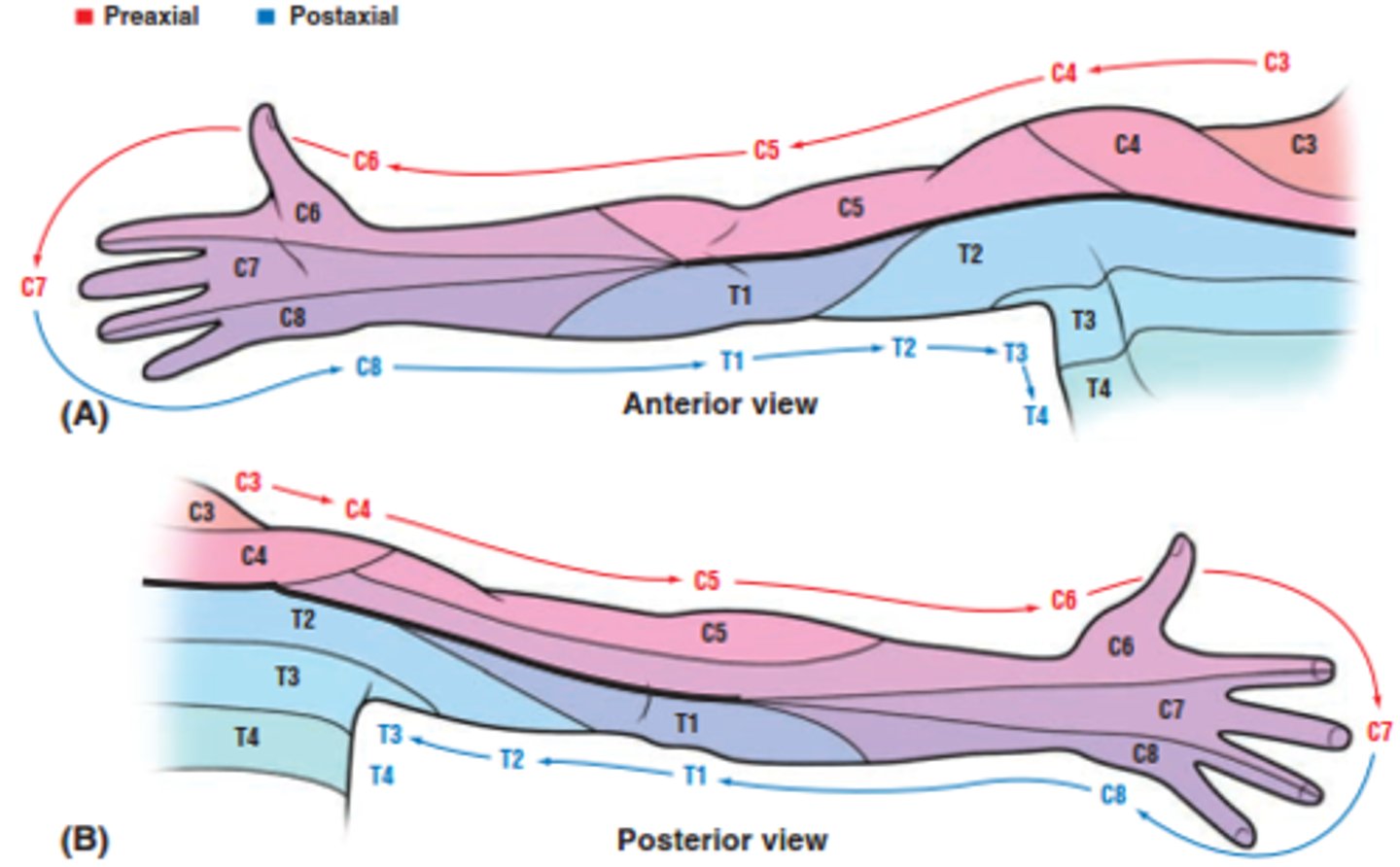
List the myotomes of the upper body.
C1-C2 - cervical flexion
C3 - cervical lateral flexion
C4 - shoulder elevation
C5 - shoulder abduction
C5/C6 - elbow flexion
C6 - wrist extension
C7 - elbow extension
C8 - thumb abduction or finger flexion
T1 - finger abduction
List the deep tendon reflexes of the upper body.
C5 - biceps (musculocutaneous)
C6 - brachioradialis (radial)
C7 - triceps (radial)
How do you grade deep tendon reflexes?
0 = absent
1+ = slight reflex (hypo-)
2+ = normal
3+ = brisk reflex (hyper-)
4+ = clonus
List the dermatomes of the lower body.
L1 - upper anterior thigh
L2 - mid anterior thigh
L3 - medial femoral condyle
L4 - medial malleolus
L5 - dorsum of great toe
S1 - lateral malleolus
S2 - popliteal fossa
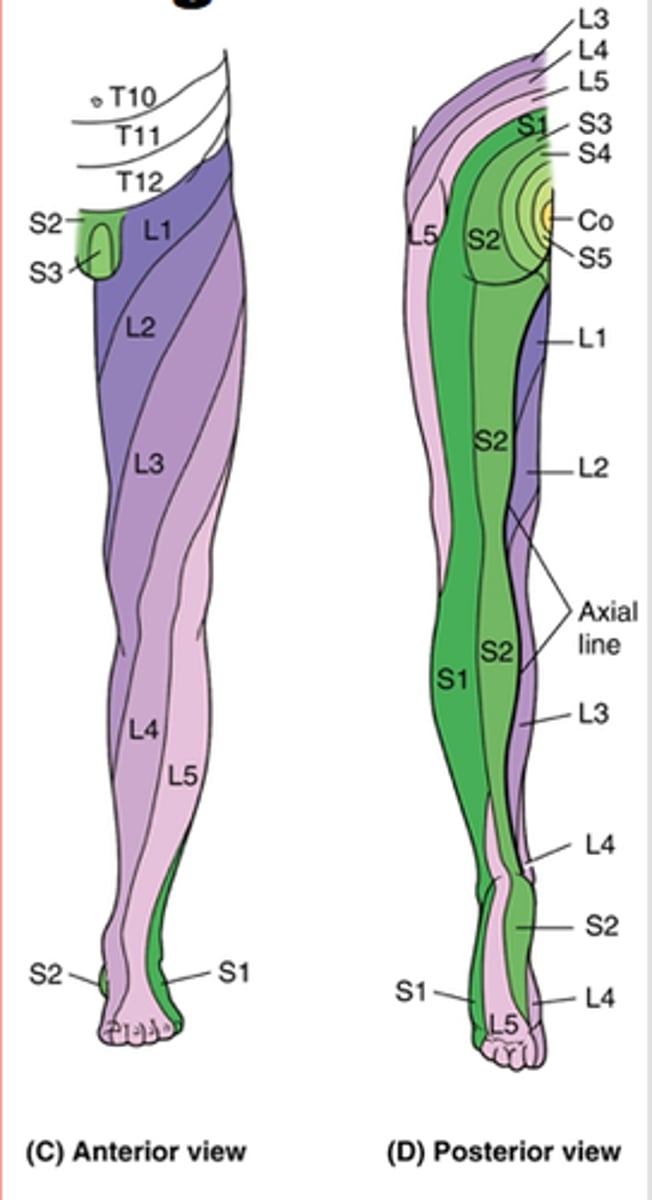
List the myotomes of the lower body.
L1-L2 - hip flexion
L3 - knee extension
L4 - ankle DF
L5 - great toe extension
L5-S1 - ankle PF
S1-S2 - ankle PF and eversion
List the deep tendon reflexes of the lower body.
L2-L4 - patellar (femoral)
S1-S2 - achilles (tibial)
What are the 5 cardinal signs of inflammation?
1. Erythema (redness)
2. Heat
3. Edema (swelling)
4. Pain
5. Decreased function
Overall goal: cellular responses of inflammation
Remove or eliminate injurious $ (by releasing enzymes and toxic substances that kill, inactivate, or degrade microbial agents, foreign antigens, or necrotic tissues)
What is the predominant leukocyte in acute inflammation? Chronic inflammation?
Neutrophils (acute); lymphocytes & macrophages (chronic)
What do leukocytes release to stimulate the healing process?
Growth factors
__________ is a short-lived, potent vasodilator that increases blood vessel permeability to promote vascular leakage
Histamine
___________ are chemical mediators of the inflammatory response that promote systemic inflammation (fever)
Cytokines
Overall goal: vascular changes during inflammation
Increase the movement of plasma proteins and circulating cells out of the intravascular space and into the site of injury
Vascular changes: immediate ____________ to stop blood loss --> _________ + increased capillary permeability --> platelets gather @ vascular injury site
Vasoconstriction -- vasodilation
What is the primary purpose of platelets during an inflammatory response?
Initial hemostatic plug
__________ (enzyme) converts fibrinogen --> fibrin to form the blood clot
Thrombin (component of the blood coagulation system)
What takes place in the fibrinolytic system to lyse the blood clot when it is no longer needed?
Plasminogen --> plasmin
____________: group of plasma proteins that normally lie dormant in the blood until activated by microorganisms or antigen-antibody complexes
Complement system
What are the primary functions of the complement system?
Vasodilation, chemotaxis of leukocytes
_____________ is a process within the complement system by which the surface of microbes are coated to make them vulnerable to phagocytosis
Opsonization
___________ function within the complement system to form channels in invading cells and cause cytolysis by rushing sodium inside to blow it up
Membrane attack complexes (MACs)
___________ (stage of tissue healing & repair): takes place hours after the event
Primary cellular activity: coagulation cascade begins, platelets form the initial hemostatic plug and release chemotaxins to attract inflammatory cells
Hemostasis and degeneration (stage 1 of healing)
___________ (stage of tissue healing & repair): takes place days after the event
Primary cellular activity: granulocytes protect and clean up the injury site + secrete GFs and cytokines; complement system activated
Inflammation (stage 2 of healing)
___________ (stage of tissue healing & repair): takes place weeks after the event
Primary cellular activity: inflammatory cell decline, angiogenesis, ongoing proliferation (fibroblasts and endothelial cells), fibroblasts synthesize collagen to produce the initial scar
Proliferation and migration (stage 3 of healing)
___________ (stage of tissue healing & repair): takes place months after the event
Primary cellular activity: scar tissue reduced and remodeled, fibroblasts and immune cells beginning degradation/apoptosis, myofibroblasts shrink ECM; healing achieved by regeneration and/or repair
Remodeling and maturation (stage 4 of healing)
During rapid vasodilation, endothelial cell shrinkage begins and allows _________ (process) of fluid, protein, and blood --> effusion, heat, and redness (stage 1 of healing)
Exudation
Loss of fluid --> high conc. of RBCs, increased blood viscosity, and slower blood flow (otherwise known as __________) (stage 1 of healing)
Hemostasis
Formation of a blood clot begins ___________ (stage 2 of healing)
Inflammation
Leukocytes and macrophages migrate to injury site through ____________ (stage 2 of healing)
Chemotaxis (via release of chemotaxins by platelets)
Fibroblasts, epithelial, and endothelial cells move into the wounded area to initiate formulation of ___________ (stage 2 of healing)
Granulation tissue
What is the general timeline for skeletal muscle healing?
6-8 weeks
- 1st stage (24-48 hrs) = hemostasis, hematoma, inflammation
- 2nd stage (6-8 weeks) = phagocytosis, satellite cells, and myofiber regeneration
- Final = remodeling of scar tissue and regeneration
What is the general timeline for bone healing?
8-12 weeks
- Blood vessel injury --> hematoma
- Inflammatory response --> vascular response and cellular proliferation
- Reparative phase --> neovascularization, initial fibrosis, and soft callus formation (2 wks)
- Regeneration and remodeling (no scar) --> endochondral ossification (6-12 wks)
What is the general timeline for tendons & ligaments?
3-4 months
- Hemostasis & inflammation (first 3-5 days)
- Proliferative phase (2-3 weeks)
- Maturation (begins week 3, 12-16 weeks until tendon safely able to be stressed)
- Remodeling (40-50 weeks BUT may not regain full tensile strength)
Unrelieved pressure --> ischemia --> __________ (pathology)
Pressure injuries
List several risk factors for pressure injuries.
Decreased sensation, impaired mobility, incontinence, impaired nutrition, altered cognition/consciousness
Excessive plantar pressure in the presence of sensory neuropathy and foot deformity --> __________ (pathology)
Diabetic/neuropathic ulcers
List several risk factors for diabetic/neuropathic ulcers.
Ill-fitting shoes, deformities, previous plantar ulceration, improper cleaning and lubrication of the feet, improper removal of corns or calluses, foot pressure
Muscle type: multi-nucleated w/ a large, cylindrical shape + striations (sarcomeres)
Skeletal
Muscle type: uni-nucleated w/ branching + striations (sarcomeres)
Cardiac
Muscle type: uni-nucleated w/ small, spindle shape + smooth
Smooth
Muscle type: somatic control via Ca2+ (from SR) and troponin -- fibers independent of one another
Skeletal
Muscle type: autonomic control via Ca2+ and calmodulin -- some fibers electrically linked via gap junctions, other independent
Smooth
Muscle type: autonomic control via Ca2+ (from ECF & SR) and troponin -- fibers electrically linked via gap junctions
Cardiac
Sliding filament theory: synaptic vessels in the presynaptic neuron are triggered by Ca2+ influx --> fuse w/ the presynaptic membrane --> release _________ via exocytosis
ACh
Sliding filament theory: _______________ (extensions of the sarcolemma that associate w/ terminal cisternae of the SR) bring AP to interior of cell
T-tubules
Sliding filament theory: Ca2+ released from _________
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sliding filament theory: Ca2+ binds to ___________ --> pulls away _________ to expose actin's binding sites
Troponin -- tropomyosin
Sliding filament theory: myosin utilizes _________ to generate power stroke
ATP
Skeletal muscle type: Type I, "red", slowest development of maximal tension BUT longest contraction duration
Slow-twitch oxidative
Skeletal muscle type: Type IIA, intermediate w/ short contraction duration
Fast-twitch oxidative-glycolytic
Skeletal muscle type: Type IIX, "white", fastest development of maximal tension BUT shortest contraction duration
Fast-twitch glycolytic
Skeletal muscle type: fatigue-resistant, most used--posture, first type to be recruited
Slow twitch oxidative (Type I)
Skeletal muscle type: fatigue-resistant, used in standing & walking, second type to be recruited
Fast twitch oxidative glycolytic (Type IIA)
Skeletal muscle type: fatigable, least used--jumping, quick, fine movements, third type to be recruited
Fast twitch glycolytic (Type IIX)
With _________ fibers, you are more likely to run out of oxygen w/ repeated contraction due to larger diameter, less myoglobin, and fewer blood vessels
Glycolytic
____________: contraction that creates force w/o movement due to series elastic elements helping to generate force w/o change in length
Isometric
___________: contraction that creates force WITH movement
Isotonic
The neurotransmitter of the somatic nervous system is ___________
ACh
Termination of neurotransmitter signaling via ACh occurs with which 3 methods?
1. Diffusion out of the synaptic cleft
2. Enzyme deactivation via AChE
3. Transport into adjacent cells or presynaptic cell for recycling
Myelin allows for ____________ (increased/decreased) contact of leaky ion channels w/ ECF, which prevents ion flow out of the cell
Decreased
__________ cells form myelin @ PNS
Schwann cells
___________ cells form myelin @ CNS
Oligodendrocytes
_____________: process that involves APs jumping from Nodes of Ranvier to avoid ion flow out of the cell
Saltatory conduction
What are 3 factors that contribute to faster AP conduction?
1. Larger diameter of the axon
2. *GREATER* resistance of the axon cell membrane to leakage out of the cell
3. Myelination
Neuron synapses of the somatic nervous system involve ______________ that are ALWAYS excitatory
Neuromuscular junctions
What is the most common disease @ NMJ? Hint: this disease involves a loss of ACh receptors.
Myasthenia gravis
Neuron synapses of the autonomic nervous system involve _____________, which include postganglionic axons that end in swollen areas called varicosities
Neuroeffector junctions
What is the hallmark characteristic of the autonomic nervous system?
Dynamic balance b/w the autonomic branches and their contrasting functions
True or false: the somatic and autonomic nervous systems include similar neurotransmitter release, which follows the same patter of depolarization --> Ca2+ influx --> exocytosis
TRUE!!
__________ (branch of the ANS): pre-ganglionic neurotransmitter = ACh @ nicotinic cholinergic receptors, post-ganglionic neurotransmitter = norephinephrine @ adrenergic receptors
Sympathetic
___________ (branch of the ANS): pre-ganglionic neurotransmitter = ACh @ nicotinic cholinergic receptors, post-ganglionic neurotransmitter = ACh @ muscarinic cholinergic receptors
Parasympathetic
PNS vs. SNS: dilates pupils & bronchioles
SNS
PNS vs. SNS: secretory to glands of bronchial tree
PNS
PNS vs. SNS: increases respiration, blood pressure, HR
SNS
PNS vs. SNS: vasodilation
PNS
PNS vs. SNS: inhibits digestion, decreases peristalsis
SNS
_________: proprioceptors that respond to changes in muscle TENSION @ junction of tendon and muscle fibers
Golgi tendon organs (GTOs)
_________: proprioceptors that respond to changes in muscle STRETCH to create a reflexive contraction of the muscle to prevent damage/injury from overstretching
Muscle spindles
_________: proprioceptors that allow for tonic activity -- resistance to stretch in relaxed muscle
Muscle spindles
What is the simplest reflex loop muscle spindles partake in?
Monosynaptic reflex loop
Which reflex type occurs ONLY in the somatic nervous system?
Monosynaptic
Which reflex type occurs in ALL autonomic reflex loops?
Polysynaptic (3+ neurons, 2+ synapses)
__________: simplest reflex in a myotatic unit (ex: patellar-tendon reflex)
Basic muscle stretch reflex
__________: relaxation of an antagonist muscle to allow unopposed contraction of the agonist muscle
Reciprocal inhibition
If all efferent motor neurons are excitatory, how does reciprocal inhibition occur?
Some branches of afferent sensory nerves synapse @ inhibitory interneurons that synapse @ motor neurons to suppress their activity
___________: reflex that results in pulling away from a noxious (painful) $
Flexion withdrawal reflex
____________: reflex that typically accompanies the flexion reflex to allow for rapid transfer of weight-bearing into the opposite leg
Crossed extensor reflex
How many pathways are required to ensure an effective crossed extensor reflex?
4 pathways
- Inhibitory to extensor muscle in limb w/ noxious $
- Inhibitory to flexor muscle in opposite limb
- Excitatory to flexor muscle in limb withdrawing from noxious $
- Excitatory to extensor muscle in contralateral limb to support weight
___________ is the MAIN $ of chemoreceptors in the blood --> increase ventilation, brochodilation
CO2
Diffusion of O2/CO2 in alveolus and capillaries is proportional to __________, _________, and ___________
Surface area, concentration gradient, barrier permeability
Diffusion of O2/CO2 in alveolus and capillaries is INVERSELY proportional to ____________
Diffusion distance^2