Human Biology Nervous System
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
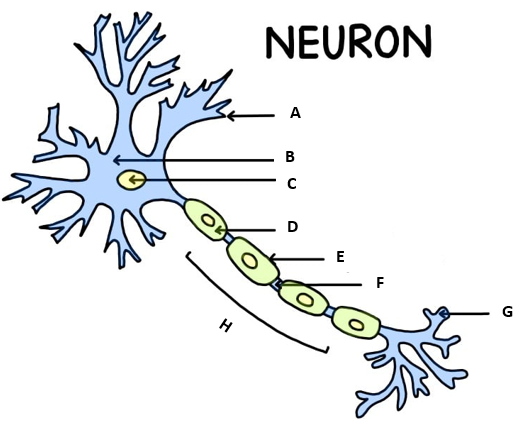
Identify the parts of the neuron in the diagram.
A- Dendrite
B- Cell Body
C- Nucleus
D- Schwann Cell
E- Myelin Sheath
F- Node of Ranvier
G- Axon Terminal
H- Axon
What are the functions of the Myelin Sheath?
For insulation
Speeds up the movement of nerve impulse along the axon.
Protects the axon.
What is the Neurilemma and what is its basic function?
It is the outermost coil of the Schwann cell, it helps in the repair of injured fibres.
The cells produce the Myelin Sheath?
Oligodendrocytes
What is white matter?
Myelinated fibres, grey matter are unmyelinated fibres.
What is the junction between two neurons called?
A synapse.
What transmit messages in the synaptic cleft?
Neurotransmitters.
What is a synapse between a neuron and a skeletal muscle cell called?
A neuromuscular junction.
What are the characteristics of Motor neurons, Sensory neurons, and Interneurons.?
Motor Neurons (Efferent)- CNS → Effector (e.g. muscles, glands).
→ Multipolar
Sensory Neurons (Afferent)- Sense organs → CNS.
→ Pseudounipolar
Interneurons- link between motor neurons and sensory neurons.
→ Multipolar
Where are Bipolar neurons found?
The eyes, nose, and ears.
Describe a Normal Nerve Pathway.
Receptor collects information (stimulated)
Sensory Neurons conduct signals from receptors to the CNS.
Interneurons (spinal cord → brain)
Brain processes information
Interneurons (brain → motor neuron)
Motor neuron conducts signals from CNS to an effector (e.g. muscle or gland)
Response triggered.
How does a Reflex Arc differ from a normal nerve pathway?
The information is not processed in the brain.
What are the steps to a Nerve Impulse?
Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
-70mV
maintained by sodium potassium pump and membrane permeability.
Depolarisation
All or none response (-55mV)
Voltage gated sodium channels open instantly.
till about (+30mV)
Repolarisation
Voltage gated sodium channels close instantly
Voltage gated potassium channels open
therefore, potassium exits cell
Hyperpolarisation
(-85mV)
Voltage gated Potassium channels slowly close
therefore, more potassium exits cell and the cell is more negative.
Refractory Period
Sodium potassium pump works to restore resting membrane potential (-70mV)
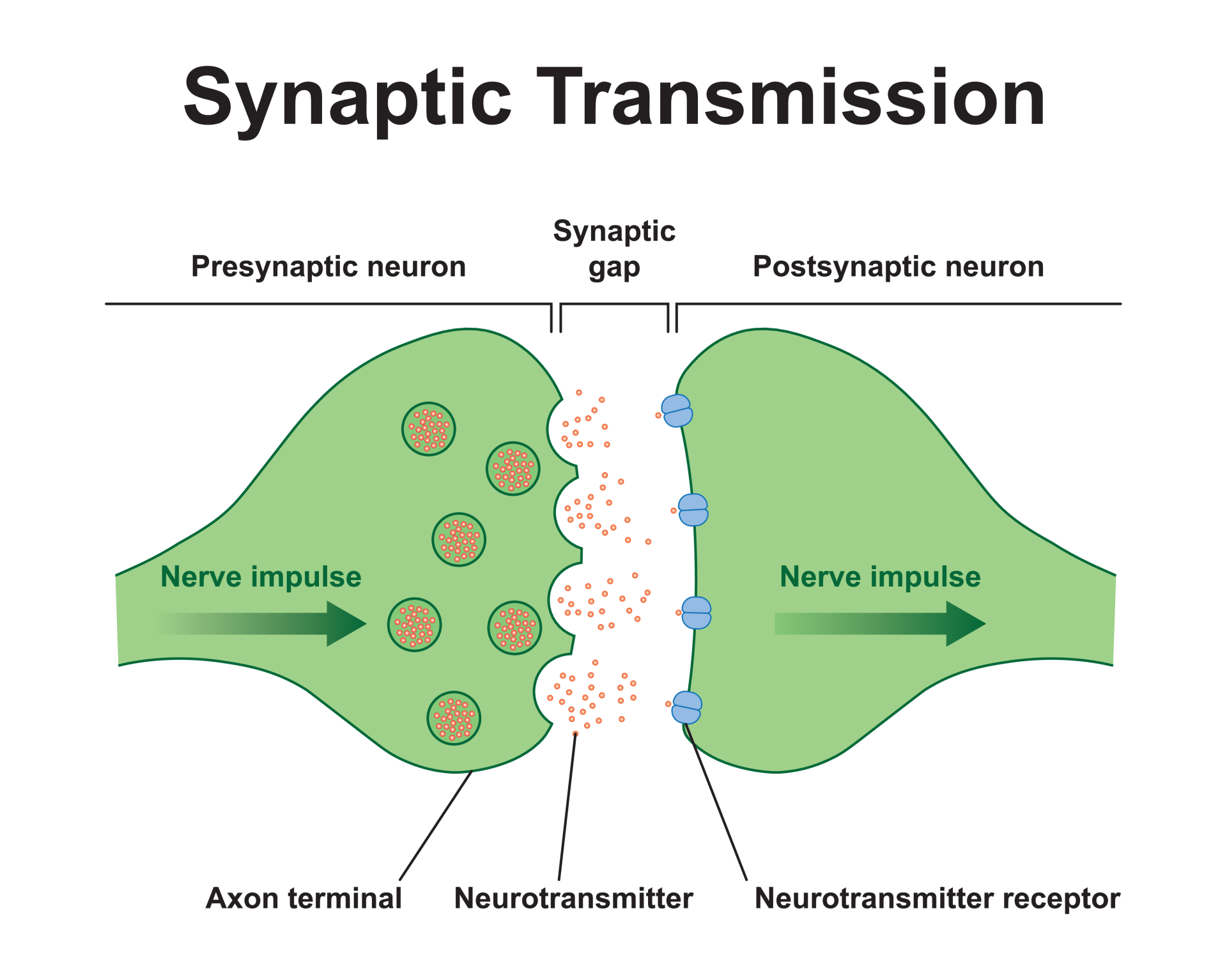
Describe how neurons communicate across a synapse.
Nerve impulse travels along presynaptic cleft
Voltage gated Calcium channels open
→ Calcium enters neuron
Vesicle is activated
→ exits neuron via exocytosis
Neurotransmitter released and diffuses across synaptic cleft.
Neurotransmitter binds to receptor on postsynaptic cleft.
Sodium channels open
→ carry across action potential
Enzyme breaks down neurotransmitter (recycled)
What does the Central Nervous System consist of?
The brain and the spinal cord.
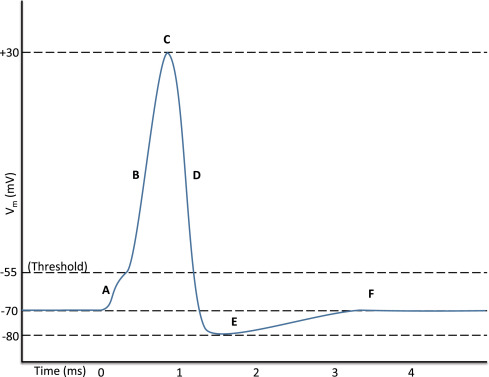
Identify the labels on the graph of Action Potential.
A- All or none response
B- Depolarisation
C- Peak Action Potential
D- Repolarisation
E- Refractory Period
F- Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
What differentiates the Autonomic division from the Somatic division
| Autonomic | Somatic |
Control | Involuntary | Voluntary |
Effector | Muscle, glands | Skeletal muscle |
Effect | Excitatory/ Inhibitory | Excitatory |
No. of Nerves | 2 (2nd Para, Sym) | 1 |
NT | Acetylcholine/ Noradrenaline | Acetylcholine |
Define the term ‘Ganglion”
a grouping of nerve cell bodies outside the brain or spinal cord.
Identify and outline the function of each lobe of the brain.
Frontal Lobe- Thinking, control of movement, emotions, personality, ect.
Parietal Lobe- Processing temperature, touch, taste pain, and movement (sense).
Temporal Lobe- Processing auditory information and memory.
Occipital Lobe- Vision.
Insula- Recognition of different senses and emotions, addiction, and psychiatric disorders.
What are the 3 structures that protect the CNS?
bone (cranium)
meninges
cerebrospinal fluid
What are the layers of the meninges?
Dura Mater (outer)
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater (inner)
What are the functions of the cerebrospinal fluid?
Protection- shock absorber
Support- suspension of the brain and spinal cord
Transport- nutrients + wastes (re-enter capillaries)
What are the folds (rounds) of the cerebral cortex called?
Gyri (convolutions)
What are the shallow downfolds of the cerebral cortex called?
Sulci
What are the deep downfolds of the cerebral cortex called and identify an important one of these downfolds that divides the two hemispheres of the brain?
Fissures, the longitudinal fissure
What are the bundles of nerve fibres called?
Tracts
What are the 3 functional areas of the cerebral cortex?
Sensory areas- interpret impulses from receptors.
Motor areas- control muscular movement
Association areas- concerned with intellectual and emotional processes.
State the relative location of each lobe of the brain.
Frontal lobe- anterior/ front of the head
Parietal lobe- superior/ top of the head
Temporal lobe- inferior/ besides the ear
Occipital lobe- posterior/ back of the head
Insula lobe- deeper within the brain
What structure of the brain connects the hemispheres of the brain?
Corpus callosum
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Exercising control over posture, balance, and fine coordination of movement.
What would movement be like without the cerebellum?
spasmodic, jerky, and uncontrolled.
What is the purpose of the hypothalamus, and give an example of one of it main functions.
Maintaining homeostasis, a constant internal environment.
regulation of the autonomic nervous system. e.g. heart rate, blood pressure, and the secretion of digestive juices, and the diameter of the pupil.
body temperature
Food and water intake
Patterns of waking and sleeping, etc.
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
cardiac centre- regulates rate and force of heartbeat.
respiratory centre- controls rate and depth of breathing.
vasomotor centre- regulates the diameter of blood vessels.
Other centres that regulate the reflexes of swallowing, sneezing, coughing, and vomiting.
Contrast the locations of grey and white matter in the brain and spinal cord.
Brain- grey matter surrounds 2-4mm the brain (cerebral cortex), white matter is then present within the brain with grey matter (basal ganglia).
Spinal cord- white matter surrounds the grey matter (white outside, grey inside)
What is the small space the runs down the spine called, which runs the length of the spinal cord.
The central canal.
Differentiate between the types of tracts.
Ascending tracts- sensory axons that carry impulses upwards, towards the brain.
Descending tracts- motor axons that conduct impulses downwards, away from the brain.
Differentiate between the types of Nerve fibres.
Sensory fibres- carry impulses into the CNS.
Motor fibres- carry impulses away from the CNS.
What types of fibres are located in the dorsal and ventral roots respectively?
Dorsal- Sensory fibres
Ventral- Motor fibres
The cell body of the sensory nerve entering the spinal cord is found in what structure?
The dorsal root ganglion.
What is the difference between the afferent division and the efferent division?
Afferent division- PNS → CNS
Efferent division- CNS → PNS
Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
CNS- brain and spinal cord
PNS- nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
Types of receptors?
Thermoreceptors- central receptors/ peripheral receptors
Osmoreceptors- in the hypothalamus
Chemoreceptors- central/ carotid and aortic
Touch/ mechanoreceptors- in the dermis
Pain receptors/ nociceptors- skin and mucus membranes.
Outline the action of a reflex arc.
A receptor reacts to a change in the environment by initiating a nerve impulse in the sensory nerve.
Sensory nerve carries impulse towards the spinal cord.
Interneuron carries nerve impulse to the motor nerve.
Motor nerve carries the nerve impulse to an effector.
Effector receives a nerve impulse and carries out appropriate response.

What are the properties of a reflex?
A stimulus is required to trigger a reflex- non-spontaneous
A reflex is involuntary
A reflex is rapid
A reflex response is stereotyped- occurs the same way each time.
Compare the nervous and endocrine systems.
Characteristics | Nervous | Endocrine |
nature of message | electrical impulses and neurotransmitters | hormones |
transport of message | along membrane of neurons | via bloodstream |
cells affected | muscles and glands; other neurons | all body cells |
types of response | specific | widespread |
time take to respond | rapid | slower |
duration of response | brief | longer lasting |
Define saltatory conduction.
When an action potential ‘jumps’ between the Nodes of Ranvier which results in a faster transmission of nerve impulse.
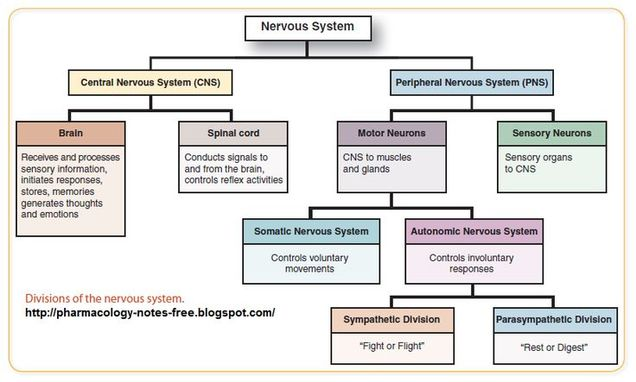
Identify the divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).