Lecture #1 Phys Prop of Seawater
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
specific heat/heat capacity
how much energy required to break hydrogen bonds(water has a high freezing and boiling point because of this) ALso Earth’s temp is moderated by oceans
surface tension/viscosity
measure of ‘stretch’ of the surface of a liquid, measure of resistance to motion/friction. H bonds help hold water particles together!
water density
D=M/V. Freshwater is densest at 3.98C, seawater densest at 0C
depth profile
salinity inc w depth, temp dec w depth
thermocline
layer of water where temp changes rapidly with depth
halocline
zone of salinity change where salinity is super different above and below
stratification and mixing
formation of different density layers due to temp or salinity. usually in lakes summer is most stratified because sun warms top layer and it become less dense(epilimnion). in fall surface waters cool and sink, causing mixing and weakening the thermocline.
photic zone
zone where photosynthesis can occur(sunlight still reaches!)
aphotic zone
zone where basically no sunlight reaches, can’t support photosynthesis
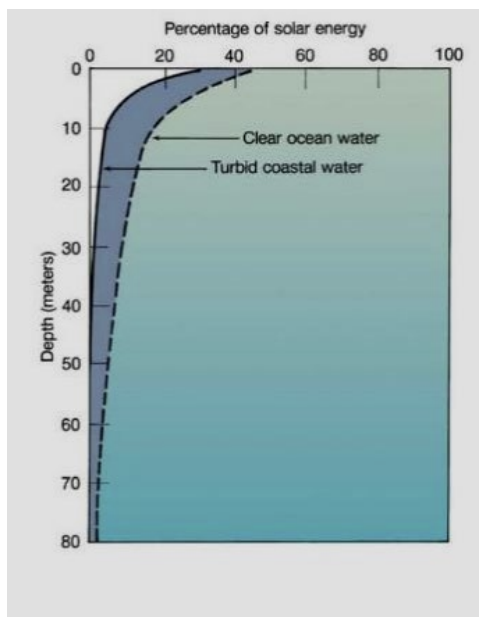
light attenuation
energy attenuates in water. most absorbed in first 3 meters, but turbid water isn’t as great
ROYGBV
red has longer wavelength and less energy, blue has shorter wavelength, more energy. this is why red stuff at the bottom of the ocean looks gray and blue color penetrates deeper
what affects density?
temperature dec D, salt conc inc D, pressure and D inc w depth
why is water unique and special?
high specific heat, high surface tension, moderate viscosity, ‘univeral solvent’
why does ice float?
it has this super cool lattice structure with fewer molecules per unit area than liquid water so it is lighter than water!!
why is thermal expansion of water important?
there are implications for sea level rise! at warmer temps, water expands in volume, causing overall SLR
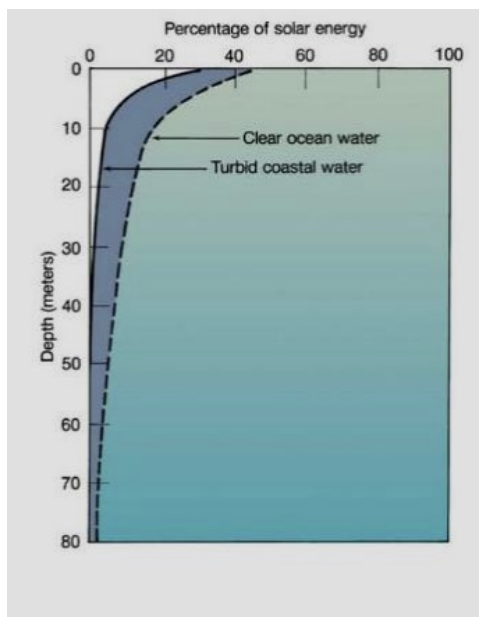
illustrate the attenuation of light in open ocean water and coastal water
open ocean water is a lot more clear so light can penetrate deeper. coastal water has a lot of particles and turbidity that absorbs light energy
what factors affect light attenuation in water
turbitidy, algae/sediment particles absorb light energy, coastal vs open ocean