A and P - chp 12 pt 2 - Development of Action Potentials (nerve impulses)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
definition of action potentials (nerve impulses)
an abrupt change in the electrical potential difference across the cell membrane which occurs after a stimulus
Where does an action potential begin?
axon hillock
what other set of channel proteins are involved?
voltage-gated sodium channels and voltage-gated potassium channels
they open and close in response to a change in transmembrane potential
what is the 1 step?
resting neuron
INSIDE = low Na+
OUTSIDE = high K+
-70 mV
what is 2nd step?
application of stimulus
localized change in resting membrane potential causes depolarization to threshold
-70mV → -60 mV
what is 3rd step?
Depolarization
voltage-gated sodium channel opens when threshold is reached
plasma membrane becomes permeable to Na+
Na+ quickly flows down its concentration gradiet
-60 mV → +10mV
what is the 4th step?
repolarization
voltage-gated sodium channels close at +30 mV = sodium channel inactivation
sodium permeability and sodium movement stops
voltage-gated potassium channels OPEN
plasma membrane becomes permeable to K+
K+ flows out of the cell down its concentration gradient +30 mV to -90mV ( hyperpolarization because K+ channels are slow to close) and then to resting -70 mV
PIC of graph for generation of action potential
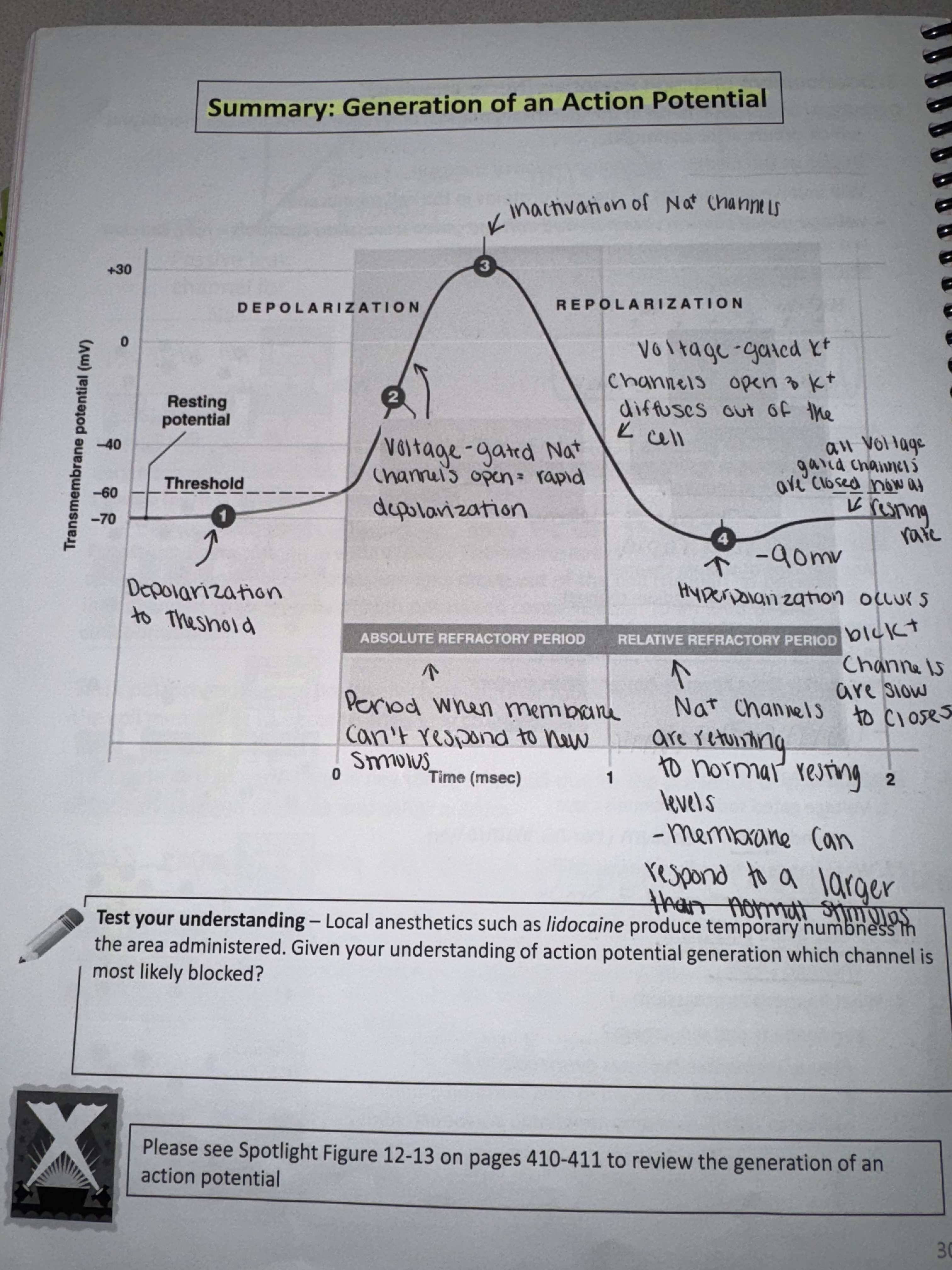
what is the absolute refractory period?
period when membrane cant respond to new stimulus
what is the relative refractory period?
Na+ channels are returning to normal resting levels - membrane can respond to normal than larger stimulus
What is the propagation of an action potential: “The wave” mean?
action potentials are relayed from one location to another in a series of steps
initiated at axon hillock
occurs in only one direction in unmyelinated axons - can only go forward
wave goes from resting → depolarizing → absolute refractory period