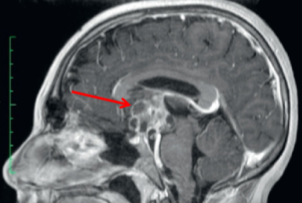
Optic Chiasm & Visual Pathway Lesions
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
25, 50
___% of brain tumors occur in the chiasmal area & ___% present w/ the initial complaint of visual loss
central/normal
orientation of chiasm: optic chiasm directly over pituitary gland
prefixed
orientation of chiasm: optic chiasm anteriorly over tuberculum sellae
postfixed
orientation of chiasm: optic chiasm posteriorly over dorsum sellae
bitemporal hemianopsia
what VF defect is produced w/ a chiasmal lesion if the pt has central/normal orientation?
unilateral monocular VF defect, junctional scotoma, bitemporal hemianopsia
what VF defects are produced w/ a chiasmal lesion if the pt has postfixed orientation?
bitemporal hemianopia, homonymous hemianopia
what VF defects are produced w/ a chiasmal lesion if the pt has prefixed orientation?
hemifield slide
w/ complete bitemporal hemianopia, pre-existing phorias may result in separation of the hemifields horizontally or vertically or double vision w/ overlap
temporal, ipsilateral
the nasal VF info is carried by ______ retinal fibers & project to the ________ optic tract
nasal, contralateral
the temporal VF info is carried by _______ retinal fibers & project to the ______ optic tract
inferior nasal, anterior
the superior temporal VF info is carried by the _______ retinal fibers in the ______ chiasm
superior nasal, posterior
the inferior temporal VF info is carried by the _______ retinal fibers in the ______ chiasm
benign
is a meningioma benign or malignant?
benign
is a pituitary adenoma benign or malignant?
benign
is a low grade I pilocytic astrocytoma benign or malignant?
malignant
is a grade II-IV astrocytoma benign or malignant?
malignant
is a oligodendroglioma benign or malignant?
malignant
is a ependymoma benign or malignant?
malignant
is a mixed glioma benign or malignant?
malignant
is a medulloblastoma benign or malignant?
lung
where is the most common site for secondary brain tumors to come from?
HA
seizure
neurological sx
nausea & vomiting
what are the s/sx of brain tumors?
pituitary tumor
craniopharyngioma
meningioma
glioma
aneurysm
what are the etiologies of chiasmal compression?
HA
blurry vision
VF defects
diplopia
females: amenorrhea, hirsutism
males: impotence, gynecomastia, libido loss
what are the s/sx of a pitutiary adenoma?
bitemporal (complete or incomplete), junctional scotoma, homonymous hemianopia (complete or incomplete)
what are the types of VF defects seen w/ pituitary adenomas?
nonfunctional (non-secreting) enlargement
type of pituitary adenoma: 25-33%, >70% of large adenomas causing visual loss
hormone hypersecretion (secreting)
type of pituitary adenoma: polactinomas, GH, ACTH, LH, FSH secreting tumors
<10
a microadenoma is ___mm
>10
a macroadenoma is ___mm
prolactinoma & non-secretory tumors
what pituitary adenomas are most likely to have suprasellar extension?
visual loss, hypopituitarism, cranial neuropathies
what s/sx are most common w/ nonfunctional enlargements?
snowman configuration
what is the classic MRI sign of a pituitary macroadenoma on MRI?
macroadenoma protruding into sphenoid sinus
bone of floor thin & sometimes non-existent
enlarged, asymmetric sella
erosion of dorsum sella
erosion of anterior clinoids
extension into cavernous sinus
what are the radiologic features of a pituitary adenoma?
bromocriptine
trans-sphenoidal surgery
radiation
what is the tx for a pituitary adenoma?
directly
the risk of recurrence of a pituitary adenoma is _______ proportional to tumor size
prolactin, TSH, GH, ACTH, LH, FSH, & MSH
what hormones are secreted by the pituitary?
prolactinoma
what is the most common pituitary adenoma?
amenorrhea, galactorrhea, infertility, can increase in size during pregnancy
what are the specific s/sx of a prolactinoma in women?
decreased libido, impotence, infertility, hypopituitarism, galactorrhea
what are the specific s/sx of prolactinoma in men?
micro
90% of females dx w/ a prolactinoma are _____
macro
60-80% of males dx w/ prolactinoma are ____
primary hypothyroidism → compensatory hyperplasia of TSH cells → enlarged pituitary
TSH secreting tumor → high T3 & T4
what are the 2 types of TSH-secreting adenoma?
acromegaly
GH secreting adenoma in adults
s/sx:
enlargement of hands/feet
enlargement of forehead, nose, chin, & lower jaw
coarsening of facial features
hyperthyroidism
diabetes
arthritis
VF defects
HA
gigantism
GH secreting adenoma in children
s/sx:
growth & height significantly above average
longitudinal bone growth still possible
ACTH-secreting adenoma
primarily seen in women of childbearing age
s/sx:
Cushing’s syndrome: truncal obesity, amenorrhea
pituitary apoplexy
spontaneous, rapid expansion of pituitary due to infarction or hemorrhage
neuro-ophthalmic emergency
s/sx:
HA sudden & severe
sudden VA decrease
diplopia due to ophthalmoplegia
loss of consciousness
tx:
surgery
corticosteroids
hormone replacement
meningioma
most common primary brain tumor
middle aged women >
pregnancy stimulates growth
slowly progressive
thought to arise from arachnoidal cap cells
s/sx:
asymmetric vision loss
nonspecific HA
proptosis
chemosis
engorgement of orbital vasculature
exophthalmos
disc: normal, edematous, or pale/atrophic
optociliary shunt vessels or collaterals at optic disc
what is the classic triad of an optic nerve sheath meningioma?
optic nerve sheath, tuberculum sellae, sphenoid wing, olfactory groove
what are the locations of a meningioma?
hyperostosis
no snowman on MRI
describe the appearance of a meningioma on imaging
glioma
primary astrocytic tumors
intrinsic tumor infiltrating parenchyma of ON, chiasm, optic tract & radiations, hypothalamus, or 3rd ventricle
grade I pilocytic astrocytoma
glioma seen in children
age of onset: 4-8yo
relatively benign, slowly progressive
link w/ NF type 1
s/sx:
decreased VA
unilateral axial proptosis
compressive ON atrophy
VF defects
hypothalamus dysfunction (growth retardation, diabetes, obesity)
tx:
observation
chemotherapy
radiation
surgery
grade II diffuse astrocytoma
glioma seen in young adults
age of onset: 20-40
infiltrating tumor, slow growing, poorly defined borders
grade III anaplastic astrocytoma or grade IV glioblastoma multiforme
malignant high grade gliomas seen in adults
M>F
middle aged
s/sx:
HA
rapid vision loss
retro-orbital pain
other intracranial signs
tx:
surgery
radiation
chemotherapy
poor prognosis
hypointense
how does a low grade glioma appear on MRI?
contrast enhancement on outside w/ necrosis on inside
how does a high grade glioma appear on MRI?
craniopharyngioma
slow growting benign tumors in suprasellar region
arise from remnants of Rathke’s pouch
benign, but locally aggressive
s/sx:
solid + cystic w/ calcification
erosion of dorsum sella
spreading of anterior & posterior clinoids
tx:
surgery
radiation
growth retardation
delayed sexual development
obesity
HA & visual difficulty
papilledema & hydrocephalus
what are the s/sx of craniopharyngioma in children?
diabetes
amenorrhea
galactorrhea
progressive vision loss
bitemporal hemianopsia or incongruous homonymous hemianopia
what are the s/sx of craniopharyngioma in adults?
anerysm
location: ICA, OA, ACA, PCA, circle of willis
rare cause of chiasmal compression
unilateral monocular VF defect
what kind of VF defect do you get from a lesion at the blue line?
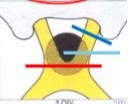
junctional scotoma
what kind of VF defect do you get from a lesion at the teal line?
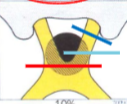
bitemporal hemianopia
what kind of VF defect do you get from a lesion at the red line?
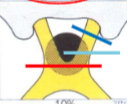
bitemporal hemianopia
what kind of VF defect do you get from a lesion at the blue line?
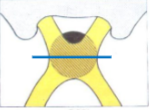
bitemporal hemianopia
what kind of VF defect do you get from a lesion at the blue line?
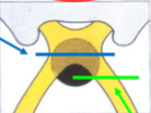
homonymous hemianopia
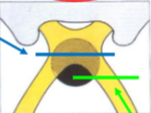
what kind of VF defect do you get from a lesion at the green line?
snowman (pituitary macroadenoma)
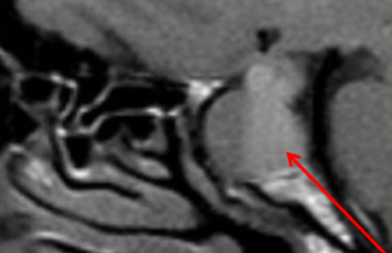
snowman (pituitary macroadenoma)
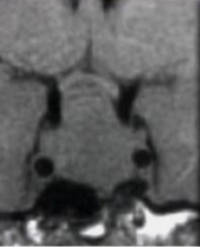
meningioma
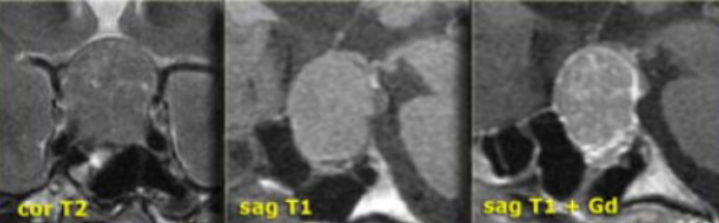
optic nerve sheath meningioma
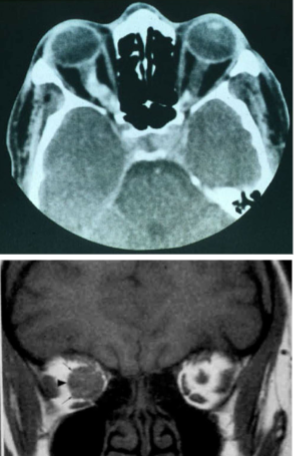
grade I pilocytic astrocytoma
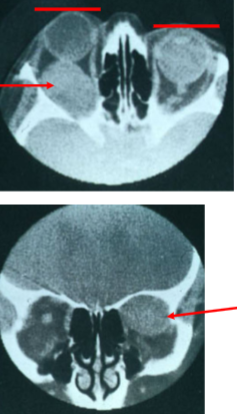
ON glioma
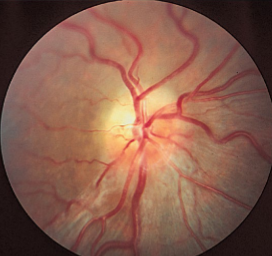
low grade glioma
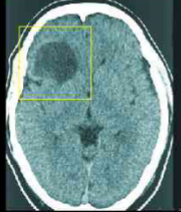
high grade glioma
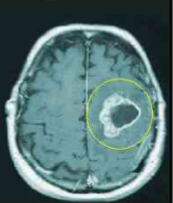
craniopharyngioma