Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Prokaryotes
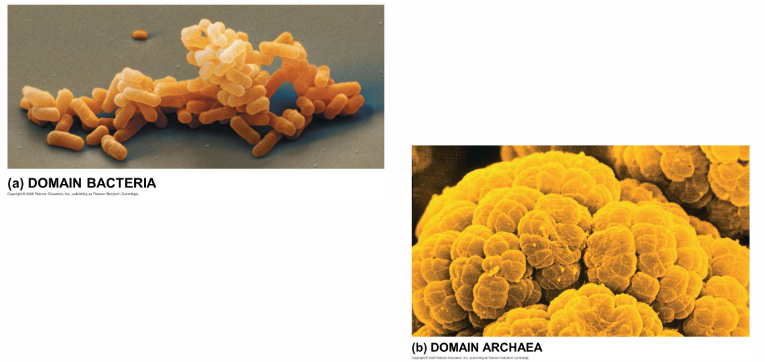
Domains Bacteria and Archaea; Ubiquitous; single-celled; microscopic
Some functions of prokaryotes
decomposers; add usable nitrogen to the environment; in our bodies
Domain Archaea: Kingdom Archaebacteria
cell walls (Polysaccharides & proteins), cell membranes; ribosomal RNA differ significantly from bacteria
Extremophiles
live where nothing else can; Extremozymes
Types of Archaebacteria
Extreme Thermophiles/Halophiles, Methanogens, Acidophiles
Greek Root ~Philos
Lover
Greek root ~Thermo
Heat
Greek root ~Halo
Salt
Types of Extreme thermophiles
Thermus aquaticus, Thermococcus litoralis, Pyrococcus
Types of Extreme halophiles
Halobacterium salinarum, Haloferax volcanii, Natronobacterium gregoryi
Types of Methanogens
Methanobacterium, Methanocaldococcus, Methanosarcina
Kingdom Eubacteria
all over our bodies; prokaryotic microorganisms; single-celled; lacks a nucleus; contains DNA in a single circular chromosome
Symbiosis
ecological relationship where two species live in close contact; larger host and smaller symbiont; prokaryotes often form symbiotic relationships with larger organisms
Mutualism
both symbiotic organisms benefit
Commensalism
one organism benefits while neither harming nor helping the other in any significant
Parasitism
an organism called a parasite harms but does not kill its host; pathogens
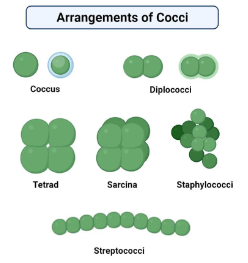
Cocci
spherical
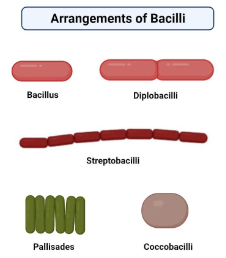
Bacilli
rod-shaped
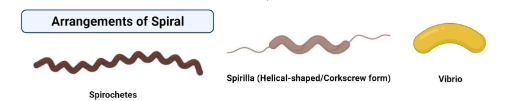
Spiral
spiral shape
Gram stain
can be Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on cell wall composition
Gram-negative bacteria
less peptidoglycan and an outer membrane that can be toxic; more likely to be antibiotic resistant; pink/red stain
Ex: Spirochetes, Chlamydia, Cyanobacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
thick cell wall made of peptidoglycan; purple stain
Ex: Bacillus anthacis, Clostridium botulinum
Key features of all bacteria
Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Plasma Membrane, Nucleoid containing DNA
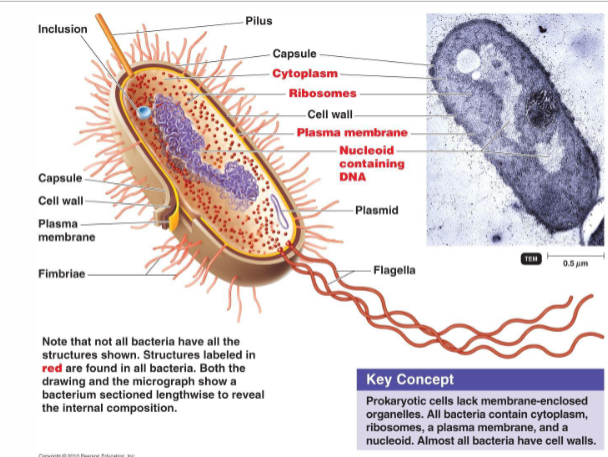
Bacterial cell wall
mantains cell shape, physical protection, prevents cell from bursting, contains peptidoglycan
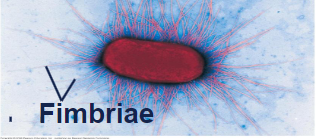
Fimbriae
allows bacteria to stick to their substrate or other individuals in a colony
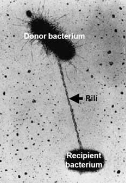
Pili
allows prokaryotes to exchange DNA and Conjugation
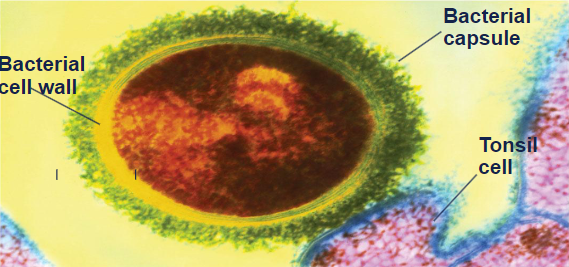
Capsule
made of Polysaccharides and Proteins; firmly attached to cell surface; prevents Phagocytosis; Virulence factor
Virulence Factor
any characteristic of bacteria that contributes to its ability to establish itself in the host and cause damage
Flagella
long, thread-like structures for movement; most motile bacteria propel themselves with this
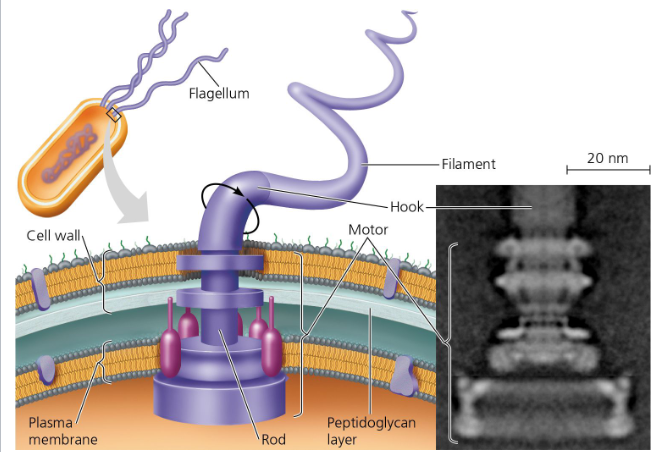
Chemotaxis
moving to or away from chemical nutrients
Phototaxis
moving to or away from light
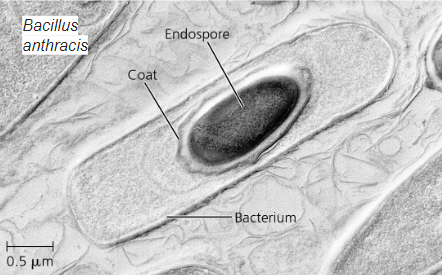
Endospores
dehydrated bacteria; withstand harsh conditions; resistant to high temps; can last for centuries
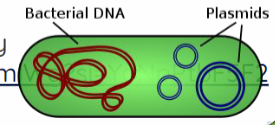
Genetic material in Bacteria
circular chromosome in nucleoid region
Plasmid
smaller, circular piece of DNA in addition to circular chromosome; R plasmids = antibiotic resistance. F plasmid = genes fertility
Bacterial Reproduction
Binary fission: divide every 1-3 hrs., Logarithmic growth, mutations can accumulate rapidly (rapid evolution of prokaryotes)
Transformation
new sequence introduced
Transduction
new sequence from Bacteriophage (viruses that infect bacteria)
Conjugation
new sequence from Plasmid exchange
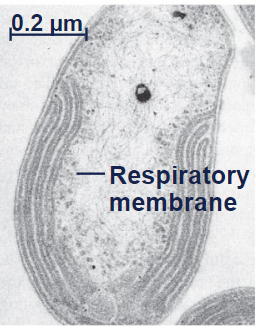
Aerobic prokaryote
respiratory membrane
Photosynthetic prokaryote
Thylakoid membrane
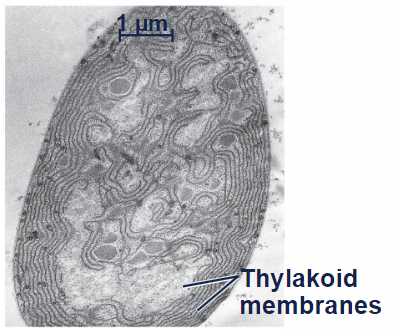
Phototrophs
obtain energy from light
Chemotrophs
obtain energy from chemicals
Autotrophs
require CO2 as a carbon source
Heterotrophs
require an organic nutrient to make organic compounds (consumers)
Obligate aerobes
require O2 for cellular respiration
Obligate anaerobes
poisoned O2 and use fermentation or anaerobic respiration
Facultative anaerobes
can survive with with or without O2
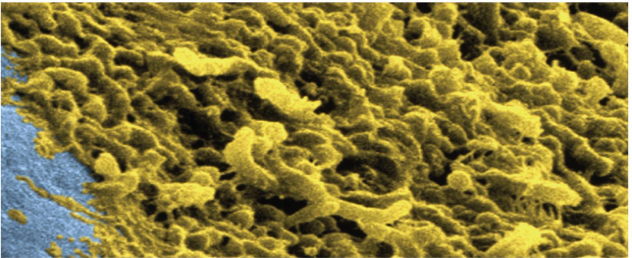
Biofilms
metabolic cooperation that occurs in surface-coating colonies
Exotoxins
cause disease even if prokaryotes that produce them are not present
Ex: Vibrio cholerae, Clostridium botulinum
Endotoxins
released only when bacteria die and their cell walls break down, Lipopolysaccharides from outer membrane of Gram-negative Bacteria
Ex: Salmonella typhi
Proteobacteria
Gram-negative; phototrophs, chemoautotrophs, and heterotrophs; aerobic or anaerobic
Ex: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Vibrio cholerae, Helicobacter pilori
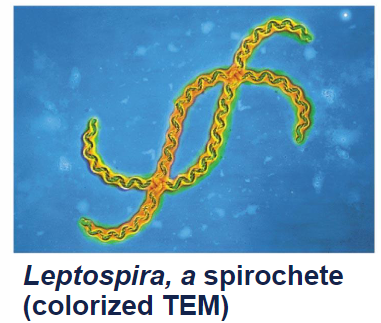
Spirochetes
helical heterotrophs, rotating internal flagella like filaments; Gram-negative, some free living, some parasites
Parasites: Treponema pallidum (syphilis), Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme Disease- caused by Deer ticks)
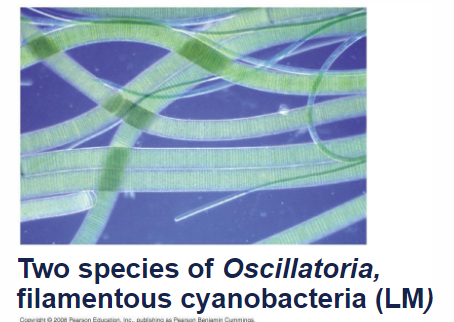
Cyanobacteria
photoautotrophs that generate O2, blue-green algae; Gram-negative
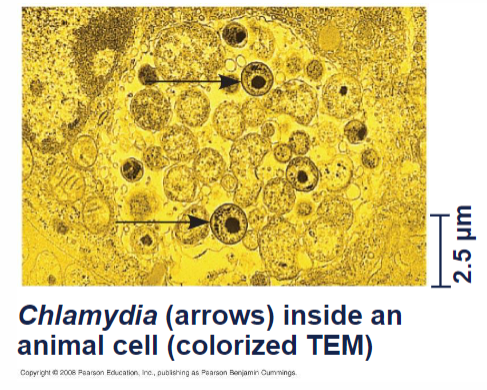
Chlamydias
parasites living in animal cells; Chlamydia trachomatis
Beneficial Prokaryotes
Bioremediation - decontamination of soil and water from industrial and human pollution
Recovery of metals from ores
Synthesis of vitamins
Production of antibiotics and hormones
Bioplastics
PCR Technology (Archaea)
CRISPR Gene editing technology