bio midterm
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i wish i was a dolphin so i wouldnt have to do this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
steps of scientific method
make an observation
form a hypothesis
must clearly establish an alt explanation
must generate testable prediction
devise a testable prediction
if, then
conduct a critical experiment
draw conclusions & make revisions
null hypothesis
negative statement proposing that there is NO RELATIONSHIP between 2 factors
treatment
any experimental condition applied to individuals
experimental group
a group of individuals who are EXPOSED to a particular treatment
EXPERIMENTED on
control group
a group of individuals who are treated identically to the experimental group w/ 1 exception
NOT EXPOSED to the treatment
NOT EXPERIMENTED on
experiment is flawed w/o them
variables
characteristics of an experimental system that are subject to change
independent or dependent
blind experimental design
experimental subjects do not know which treatment (if any) they are receiving
double-blind experimental design
neither the experimental subjects nor the experimenter knows which treatment the subjects are receiving
NO ONE KNOWS WE’RE ALL BLIND
randomized experimental design
experimental subjects are randomly assigned treatment
researchers do NOT give out treatments
replication def
process of repeating a study
increases confidence in results
isolates variables responsible for outcomes
hypothesis def
proposed explanation for a phenomenon
testable!
theory definition
exceptionally well supported hypotheses
repeatedly tested
unlikely to be altered
broad
independent variable
measurable entity that can be changed as required
x axis
dependent variable
created by process being observed
value cannot be controlled
y axis
positive correlation
when 1 variable increases, so does the other
characteristics of life
a complex, ordered organization (1 or more cells)
transforms energy to work
responds to external environment
homeostasis
growth, development, & reproduction
evolution
element def
a substance that cannot be broken down chemically into other substances
think periodic table! gold, carbon, & copper
smallest piece of gold (or any element) will still have all the same properties as a bigger piece
atom def
a bit of matter that cannot be divided any further w/o losing its essential properties
if you keep cutting the smallest piece of gold, you’ll start losing its essential properties
cannot be seen to the naked eye
nucleus of an atom
like the thing in the cell that holds genetic info!
electrons → negatively charged
protons → pos charged
atomic mass
made up of combined mass of protons & neutrons
NO ELECTRONS theyre too light
atomic number
number of protons found in the atom’s nucleus
isotopes
atoms w/ the same atomic number (number of protons) but diff mass
more or fewer neutrons
charge doesnt change
radioactive atoms
unstable nuclei
break down spontaneously
big 4 elements in your body
oxygen
carbon
hydrogen
nitrogen
unstable vs stable atoms
unstable → vacancies in electron shell, or the path electrons travel on
more likely to interact w/ other atoms
stable → all electron shells are filled to capacity!
versatility of carbon
can share its 4 valence (outermost) electrons w/ up to 4 other atoms
bons mostly w/ oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, & other carbons (4 elements in ur body)
ions def
charged atoms
atoms that have lost or gained electrons
lost → pos charge (bc theyre neg charged
gained → neg charge (bc theyre neg charged)
molecules def
groups of atoms held together by bonds
chemical reactions
forming & breaking of bonds
reactants → products
covalent bonds
2 atoms share electrons
like the atoms are holding hands <3
double bond → sharing 2 electrons
single bond → sharing 1 electron
ionic bonds
oppositely charged ions attract each other
hydrogen bonds
bond between slightly pos hydrogen atom (lost electrons) & a slightly neg atom (gained electrons)
weaker than covalent or ionic ☹
hydrogen atom + someone else
makes water cohesive!! thats why spiders can walk on water
hydrogen bonds gives water these cool things
cohesion
high heat capacity
low density when frozen
good solvent (things dissolve in water <3)
aciditi
amount of H+ (pos charged hydrogen ions) in a solution
measured in pH
acids!!!!!
pH lower than 7
more H+ than OH-
can donate H+ to other chems
very reactive
stomach acids, vinegar, cola (things that give u heartburn)
bases!!!
pH higher than 7
higher concentration of OH- than H+
tastes bitter, has a slippery/soapy feel
baking soda, bleach
pH buffers
quickly absorbs excess H+ ions (that element makes things acidic/high pH)
keeps solutions from becoming too acidic
can release H+ ions to counteract OH- increases (balancing things out)
blood pH
7.4
organic molecules that u eat
carbohydrates
lipids (fats)
proteins
nucleic acids
carbohydrates
includes macromolecules
primary fuel for cells!
forms much of the structure of cells in all organisms
mostly carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen
composed of monosaccharides (simple sugars)
glucose yay
most important carb
in bloodstream, can be used as energy or stored as glycogen for later use/converted to fat
disaccharide & polysaccharide
2 simple sugars (di) or multiple (poly) joined together
makes a complex carb
time-release stores of energy bc theyre harder to digest
what are complex carbs made of
disaccharides & polysaccharides
starch (primary form of energy in plants)
glycogen (important form of energy in animals)
indigestible carbs
chitin & cellulose
fiber yay! good 4 u
lipids
WAY MORE carbon & hydrogen bonds (C-H) than carbs
insoluble in water & greasy
hydrogen bonds! so they dont dissolve in water (insoluble)
hydrophobic vs hydrophilic
phobic → dont like water
philic → like water

saturated fat vs unsaturated fat
sat: each carbon in the C-H chain is bound to TWO (2) hydrogen atoms
contribute to heart disease & strokes ☹
animal fats, meat & eggs
unsat: at least 1 double bond between 2 carbon atoms in chain
crooked shape!
plants & fish
trans fat
partially hydrogenated vegetable oils
hydrogen atoms have been added to liquid, unsat fat to make it sat, but that gives it a weird shape & transes its gender
cholesterol
important for cell membranes
attach to blood vessel walls & makes them thicken (high chol bad)
cells in liver produce 90% of circulating chol
steriods! estrogen & testosterone!
LIPIDS BUT NOT FAT
proteins
made up of a unique combo of 20 amino acids
double string: 1 side always the same, other side unique
necessary for growth, repair, & replacement of tissue in living organisms
9 of 20 amino acids cant be made by the body so they have to be eaten munch munch
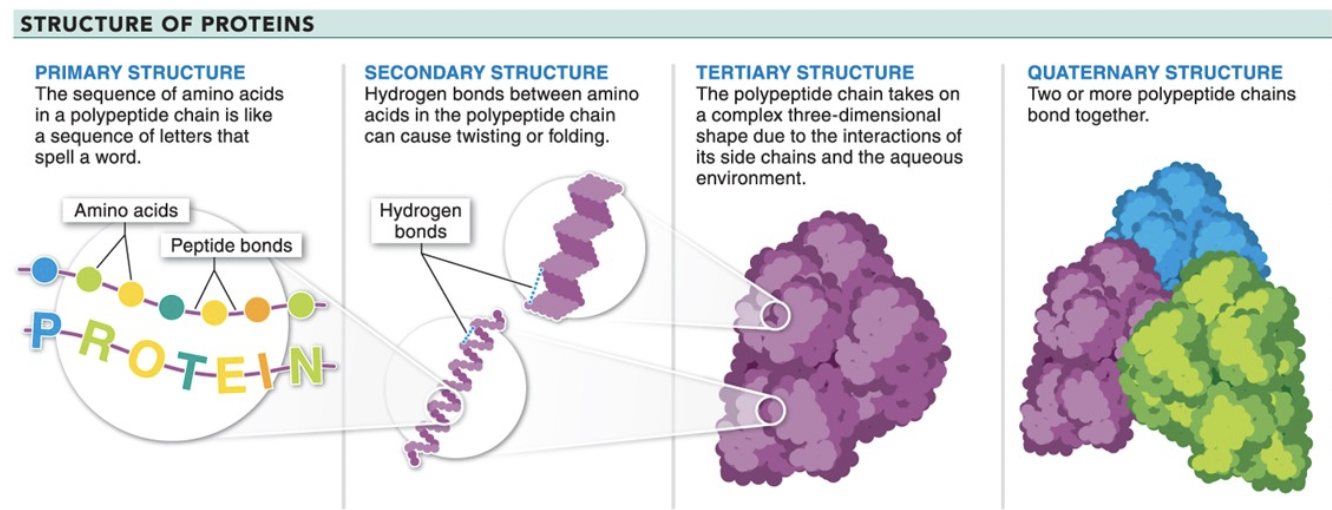
protein structure
primary
sequence of amino acids in the chain
secondary
distribution of folds & twists in the chain
tertiary
chain folds again into this shape
quaternary
2 or more chains bond together!
not all chains do this!
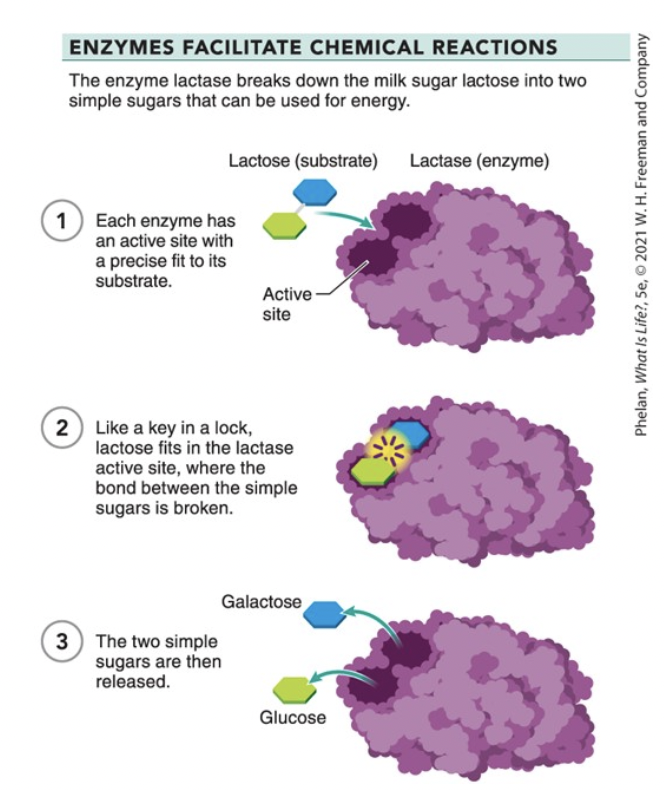
enzymes
initiate & accelerate chemical reactions in the body
has an active site to fit the substrate
substrate fits like key in lock, then bond is broken yay!
lactose is the substrate, lactase is the enzyme
activation energy
reactions need a push → yay activation energy
chemical reactions either release or consume energy
enzymes lower activation energy, yay a catalyst!
things that influence enzymes
enzyme & substrate concentration
enzymes & substrate can only increase up to the point where each is bound to another
temp
too high? reaction rate drops, enzymes lose their shape (aka denature)
pH
high rate close to optimal level, lowers farther you get
inhibitors or activators
inhibitors lower rate, activators rises
incorrect amino acid sequences
active site disruptions, cant work!
responsible for diseases & problems
nucleic acids
encode info on how to build & run a body
composed of nucleotides
sugar
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
carry genetic info (think like the nucleus)
yay dna
information is stored in dna sequence
A goes w/ T, C goes w/ G
THIS ALWAYS HAPPENS
double helix (strands)
yay rna
takes instructions from dna, moves to another part of cell, boom lets build!
A goes w/ U NOT T, C still goes w/ G
single strand
cell
smallest unit of life
functions independently & performs all necessary functions of life
complex
grow, develop, & reproduce
transforms energy to work
responds to external environment
evolves
homeostasis
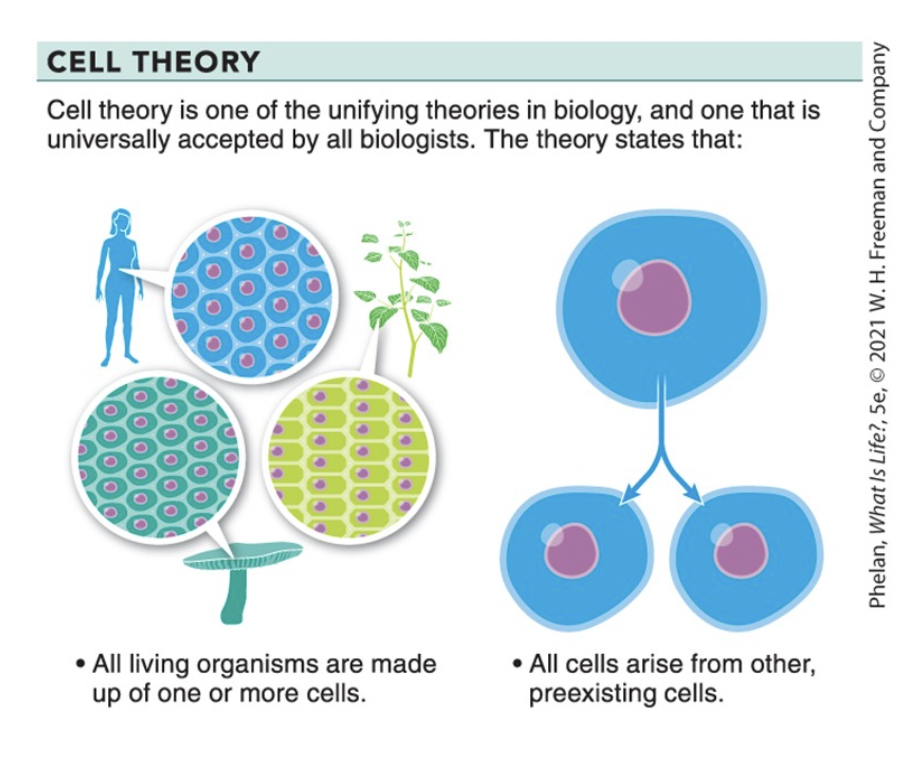
cell theory
all living organisms have 1 or more cells
cells arise from other, pre-existing cells (reproduction!)
eukaryotic cell vs prokaryotic cell
euk
nucleus holds cell’s dna
organelles
10k times bigger
pro
no nucleus, dna in cytoplasm
no organelles
tiny
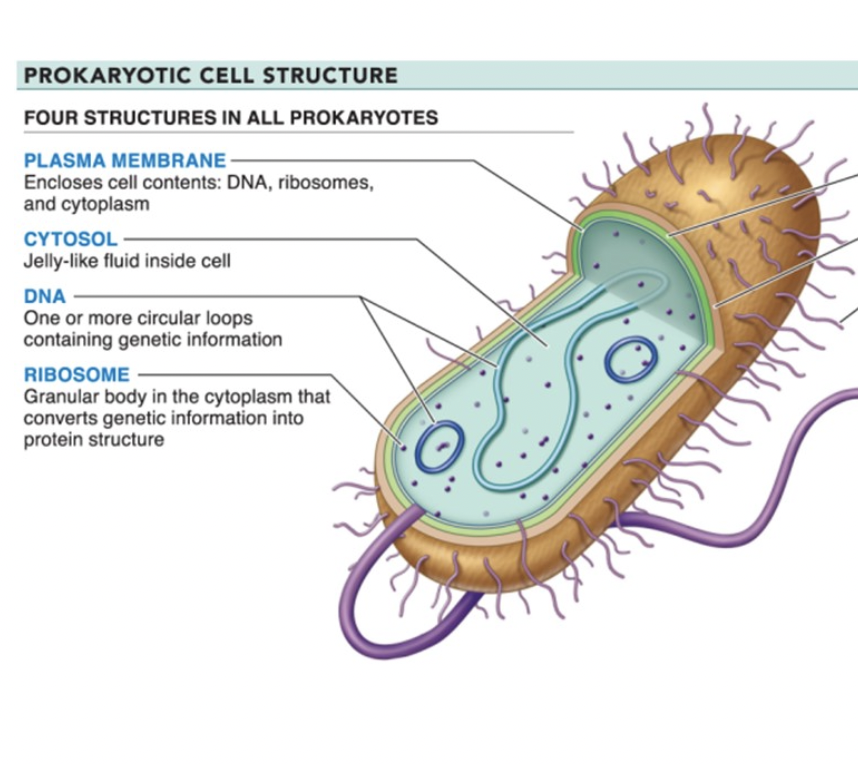
4 basic structural features of a prokaryote
plasma membrane
encloses cell contents
cytosol
jelly-like fluid inside cell
dna
circular loops
ribosome
converts genetic info (from dna) into protein structure
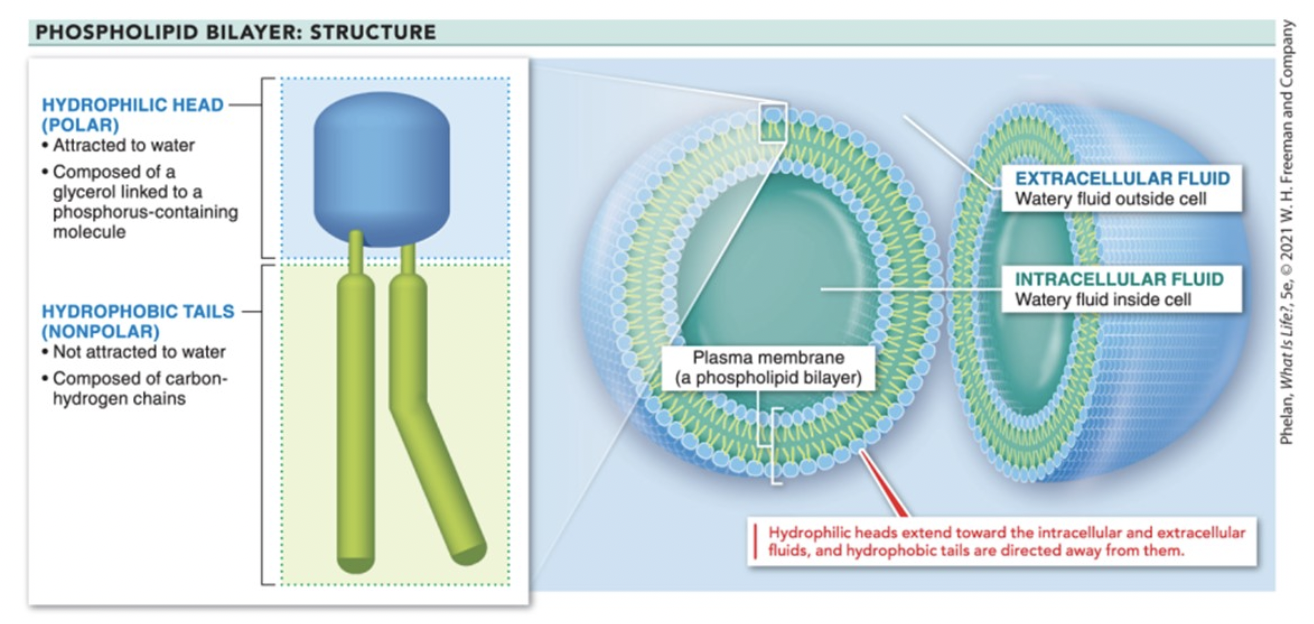
phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic head (polar & likes water) & hydrophobic tail (nonpolar & scared)
head is glycerol linked to phosphorus
tail is carbon-hydrogen chain
head face out, tails in touching each other
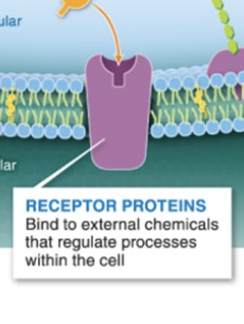
receptor proteins
bind to external chems that regulate processes in cell
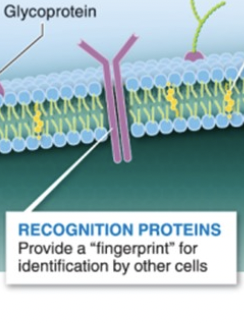
recognition proteins
provides a fingerprint for identification by other cells
helps immune system figure out which cells are from the body & which are harmful
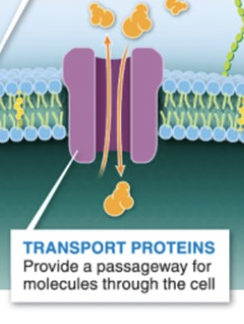
transport proteins
passageway for molecules to enter cell
little door <3
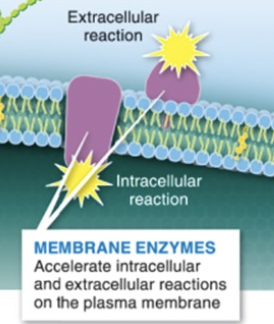
membrane enzymes
accelerates chem reactions in plasma membrane
passive transport
molecules spontaneously diffuse across a membrane
simple diffusion & facilitated diffusion
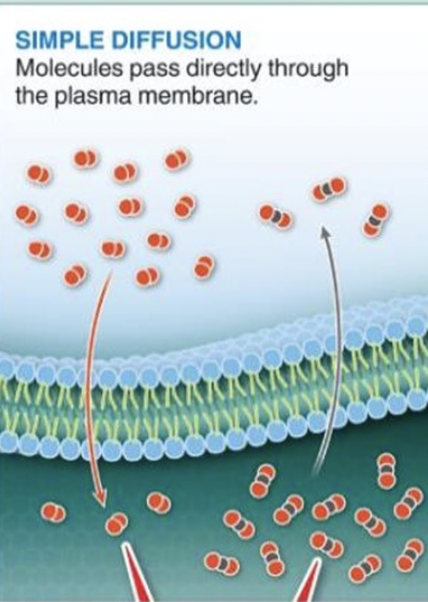
simple diffusion
molecules move DIRECTLY through plasma membrane
no help needed!
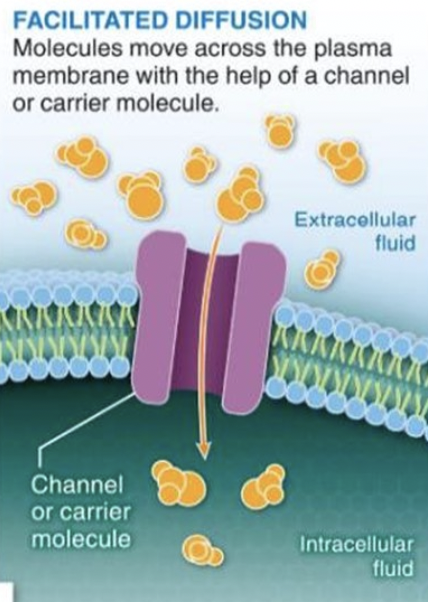
facilitated diffusion
molecules NEED HELP moving across plasma membrane!
transport proteins help
NO ATP SPENT thats the difference between this & active transport
osmosis
passive transport of water across membrane
water doesnt need help
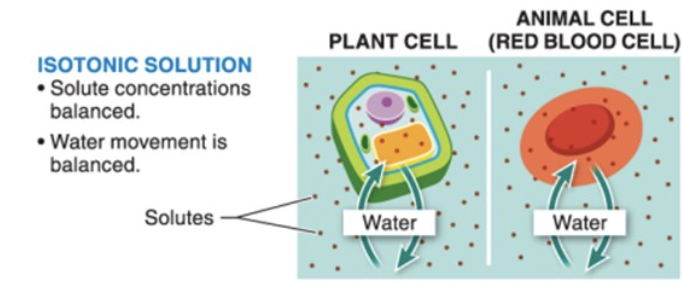
osmosis in an ISOtonic solution
concentration of solute & water is EQUAL yay!
water movement is balanced
cell retains shape
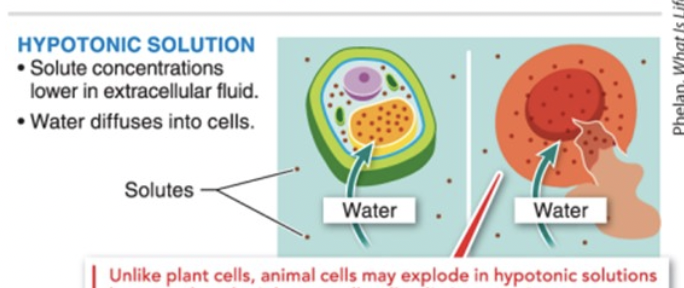
osmosis in a HYPOtonic solution
LOTS of water, not enough solute
water diffuses INTO cells
cell swells up, animal cell can EXPLODE
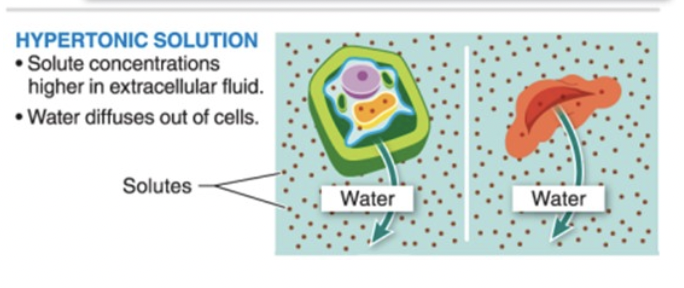
osmosis in a HYPERtonic solution
LITTLE water, more solute
water diffuses OUT of cells
cells shrivel up
active transport
using energy to transport molecules across a membrane
primary → uses atp directly
secondary → transport proteins get atp INDIRECTLY
endocytosis vs exocytosis
endo → INPUT large particles into cell
phagocytosis & pinocytosis
exo → EXPORT particles
vesicles enclose particle & then merge w/ membrane to release
phagocytosis vs pinocytosis
phag → cell membrane EATS large particle
pino → cells take in dissolved particles & liquids
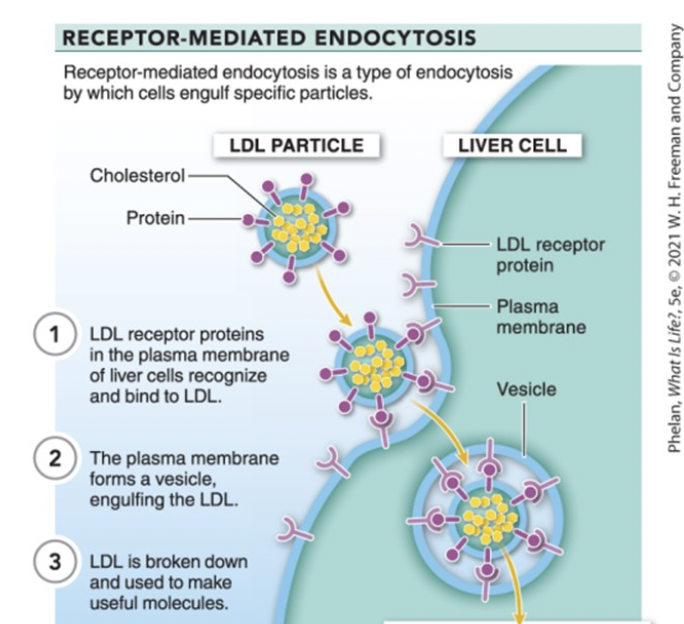
receptor-mediated endocytosis
INPUT large cells by engulfing specific particles
nucleus of a cell
genetic control center
stores hereditary info
nucleus structure (3)
nuclear membrane
chromatin → long, thin fibers that hold dna w/ some proteins attached
nucleolus → assembles ribosomes
cytoskeleton
inner scaffolding of cell (like my skeleton)
provides shape & support
controls traffic
movement!
cilia
short projections that beat swiftly to move FLUID along & past a cell
flagella
long tube structures that mov cells through ENVIRONMENT
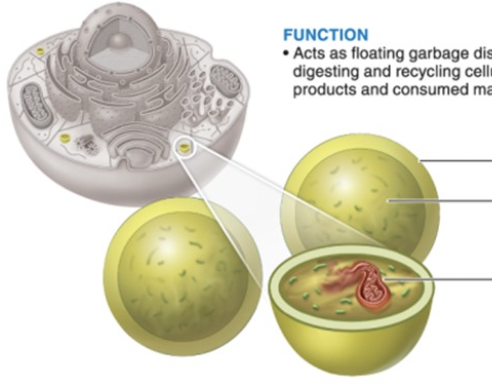
lysosomes
garbage disposals
digesting & recycling cellular waste
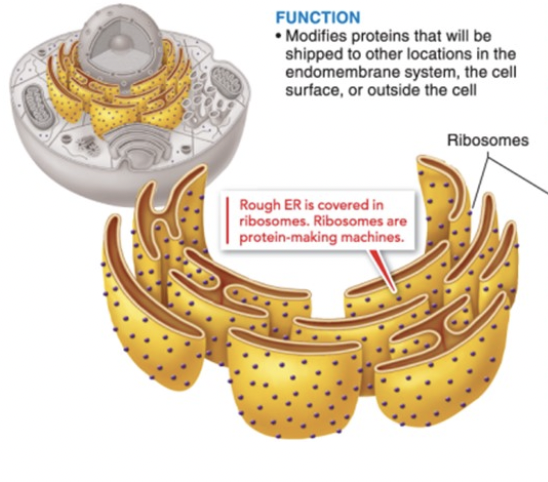
rough endoplasmic reticulum
modifies proteins that will be shipped out
covered in ribosomes, making them rough! ribosomes make proteins
wraps around nucleus
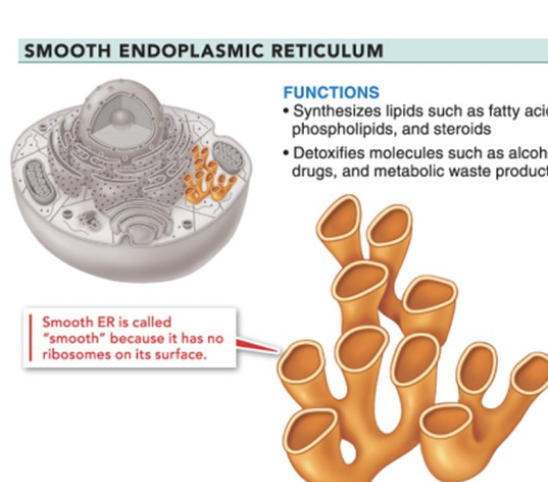
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes lipids
detoxifies molecules (drugs! alcohol!)
shaped like coral reefs
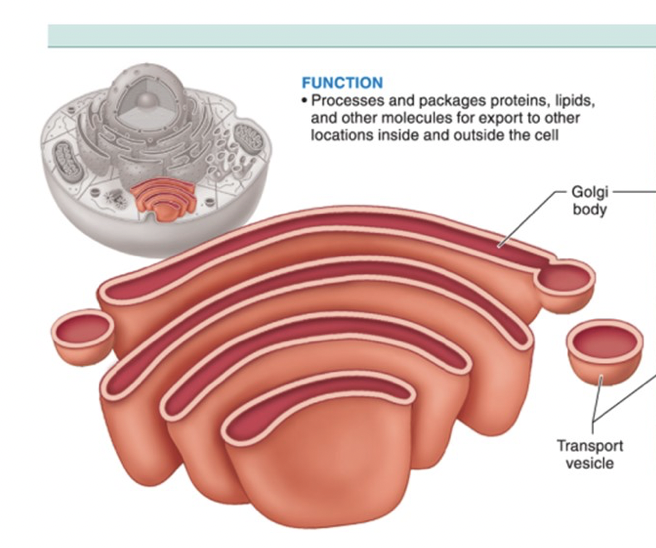
golgi apparatus
processes products for delivery
shaped like wifi signal
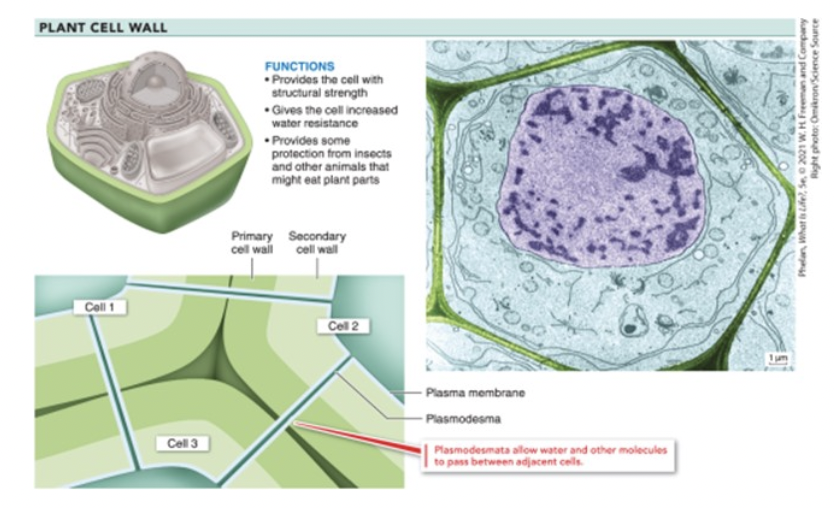
plasmodesmata
tube channels that connect plant cells to each other
sits on cell wall
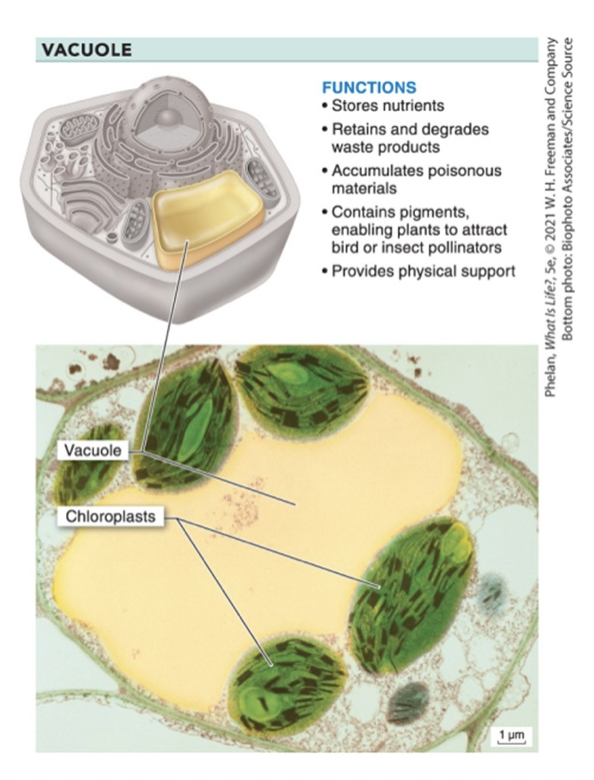
vacuoles
storage sacs!
nutrients
waste
also predator deterrence, repro, & physical support
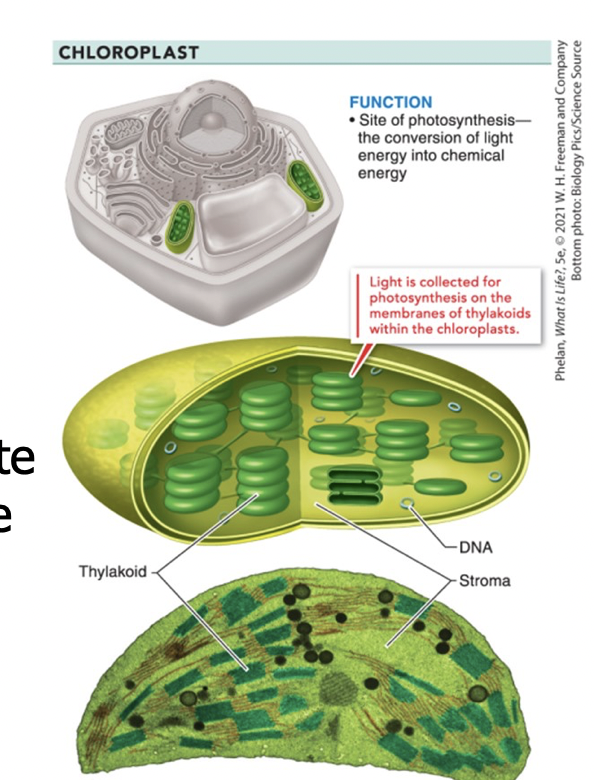
chloroplasts
do photosynthesis
CHAP 5
I WISH I WAS A FISH
what goes in & out of photosynthesis
in
sun
co2
water
out
sugar
oxygen
cellular respiration
PLANT CELLS WHO PHOTSYNTHESIZE
energy is released from chem bonds in food & stored in atp molecules to be used l8r
CHAP 15
IM GOING TO EXPLODE
microbe
organisms too small to see w/o magnification
grouped bc theyre small, not rlly bc theyre similar
most abundant organisms on earth
whats a bacteria
no organelles
classified by shape
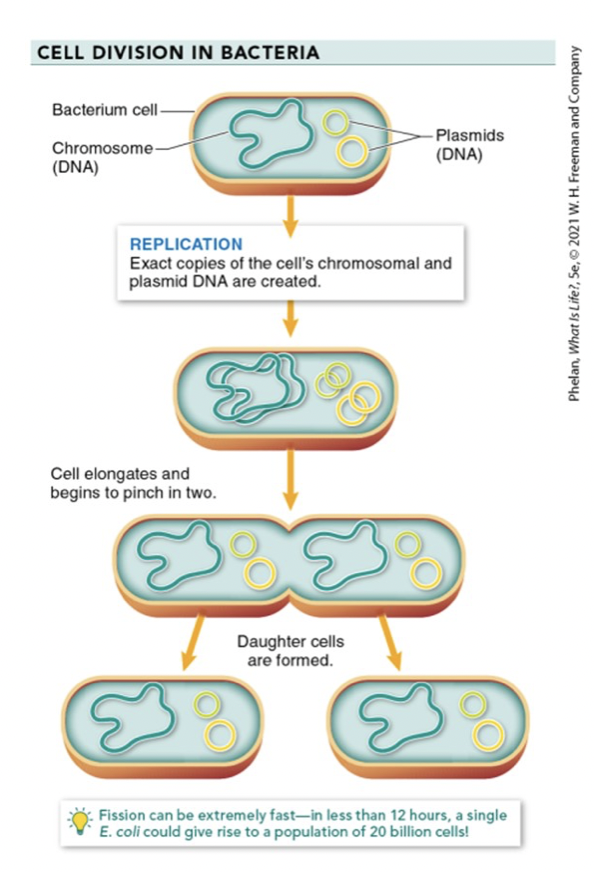
reproduce thru BINARY FISSION WOAH
how do you identify bacteria
appearance
gram strain
gram pos → glycoprotein layer on bacteria is on the outside of cell wall & can be stained w/ purple dye
neg → glycoprotein layer lies inside cell wall & membrane, cant be stained
binary fission
asexual cell division
produces 2 daughter cells who carry the exact same genetic info as parent
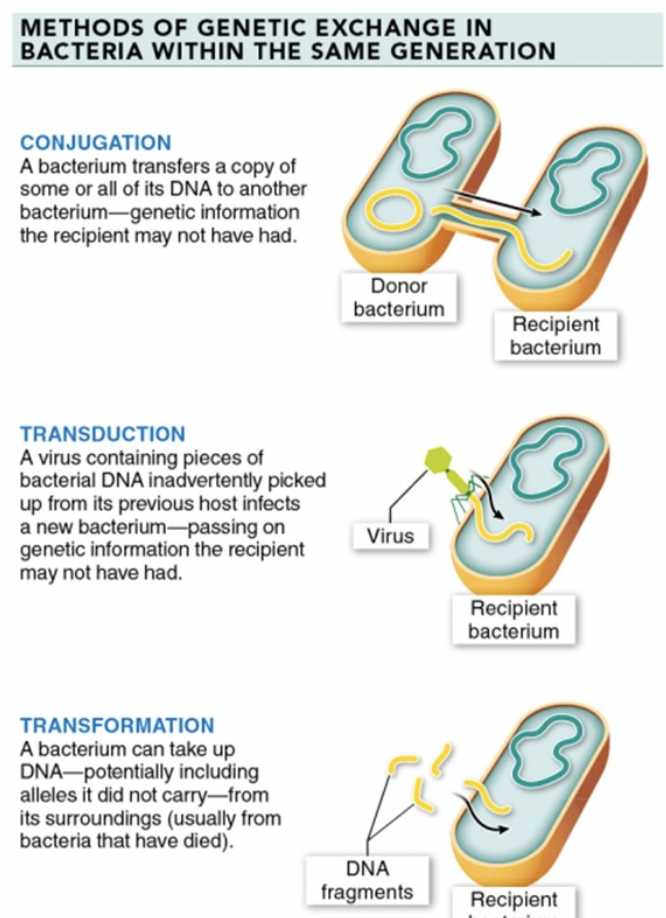
methods of genetic exchange
CONJUGATION
bacterium gives a copy of some or all of its dna to a friend <3
TRANSDUCTION
virus w/ pieces of bacterial dna infects a new bacterium, passing on genetic info
similar to passing of genetic info in conjugation
TRANSFORMATION
bacterium takes up dna from it’s surroundings
cyanobacteria & oxygen revolution
resemble 1st photosynthetic organisms 2.6 billion years ago
revolution: cyanobacteria release o2 through photosynthesis, yay it’s in the atmosphere now!