CIE IGCSE Business Studies - Unit 2 - People in Business
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
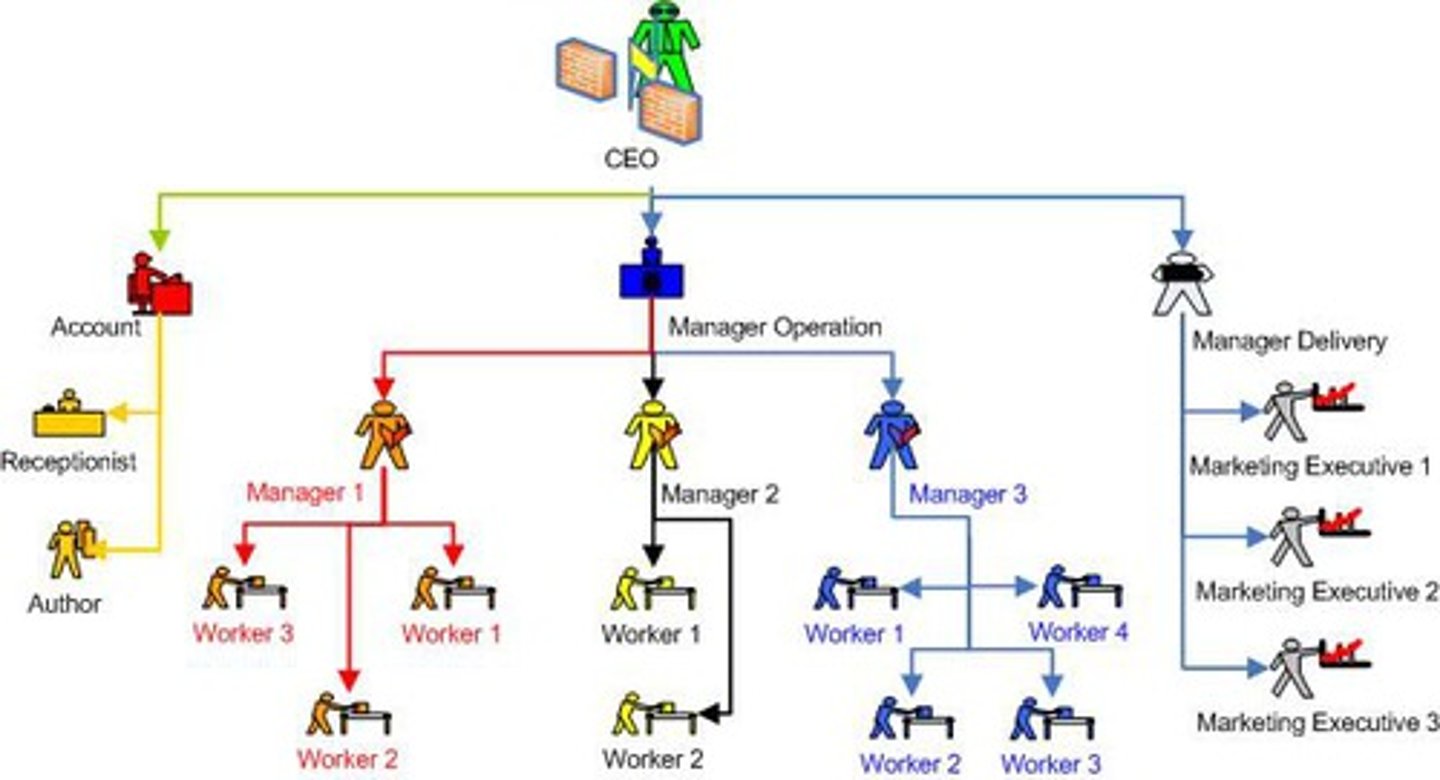
Organisation
The structure of a business, often split into 4 departments covering the main areas of business
Line Managers
Responsible for overseeing the work that other staff do
Tall Organisations
Have many levels of hierarchy. The span of control is narrow and there are opportunities for promotion. Lines of communication are long, making the firm unresponsive to change.
Flat Organisations
Have few levels of hierarchy. Lines of communication are short, making the firm responsive to change. A wide span of control means that tasks must be delegated and managers can feel overstretched.
Induction
Introducing a person to a business so they can know how to do their job properly
On-the-job Training
Where staff with a lot of experience explain the job
Off-the-job Training
Outside experts are paid to explain the job
Monetary (financial) factors
Being offered more money
Non-monetary (non-(financial) factors
Being offered incentives such as promotion or holidays
Time Rate
Payed for number of hours worked
Performance Related Pay
Bonus for meeting a certain target within the job
Empowerment
Staff are given more authority
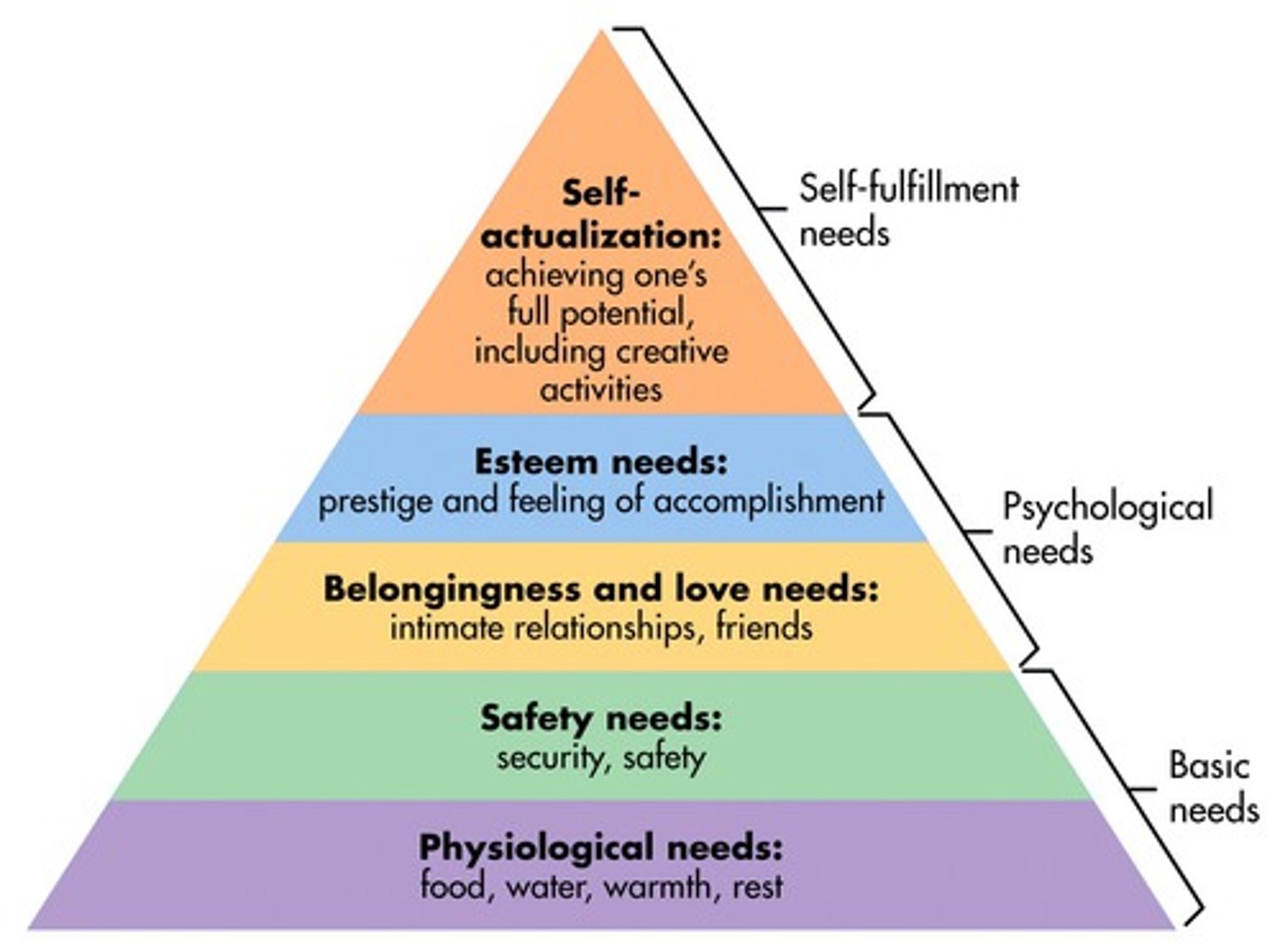
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Suggests that only once the needs at the base of the pyramid are met can the next step be achieved
Taylorism (Taylor's Theory)
Suggests that staff do not enjoy work and can only be motivated by threats and money
Employment Rights
Laws set by the government to prevent the unfair treatment of workers e.g Discrimination Act and EU Working Time Directive
Health and Safety
Laws put in place to prevent staff from being hurt or becoming ill due to work. All businesses are required to have a Health and Safety poster and do a Risk Assessment

Vertical Communication
Messages sent to staff at a different level of hierachy
Horizontal Communication
Messages sent between staff on the same level of hierachy
Wage
Payment to workers, usually paid weekly.
Salary
Payment to workers, usually paid monthly.
Commission
Payment related to the number of sales made.
Profit Sharing
Proportion of the company's profits is paid out to employees.
Bonus
Additional amount of payment above the employees wage/salary.
Performance-related pay
Payment related to the effectiveness of the employee where their output is easily measured.
Motivation
The reason why employees want to work hard and effectively for the business.
Share Ownership
Where the shares in the company are given to employees so they become part owners in the company.
Appraisal
Is a method of assessing the effectiveness of an employee.
Fringe Benefits
Are non-financial rewards given to employees.
Job Satisfaction
It's enjoyment from feeling that you have done a good job.
Job Rotation
Workers swapping round and doing each specific task for a limited time.
Job Enlargement
Where extra tasks of a similar level of work are added to a worker's job description.
Job Enrichment
Adding tasks that require more skill and/or on responsibility.
Self-actualisation
Succeeding to your full potential.
Teamworking
Involves using groups of workers and allocating specific tasks and responsibilities
Training
Is the process of improving a worker's skills
Promotion
Is the advancement of an employee in an organisation,for example, to a higher job
Esteem needs
Having status, recognition and achievement
Social Needs
Friendship, sense of belonging
Safety/Security Needs
Protection against danger.
Physiological Needs
Food, rest, shelter.
Motivators
Achievement, Personal growth, Recognition
Hygiene Factors
Status, Work conditions
Piece Rate
Payment depending on the quantity of products made.
Organisational structure
Refers to the level of management and division of responsibilities within an organisation
Organisational chart
Refers to a diagram that outlines the internal management structure
Hierarchy
Refers to the levels of management in any organisation, from the highest to the lowest
Level of hierarchy
Refers to managers/supervisors/other employees who are given a similar level of responsibility in an organisation.
Directors
Are senior managers who lead a particular department or division of a business
Supervisors
Are junior managers who have direct control over employees below them in the organisational chart
Chain of command
Structure in an organisation which allows instructions to be passed down from senior management to lower levels of management
Span of control
Number of subordinates working directly under a manager
Staff managers
Specialists who provide support, information and assistance to line managers
Line managers
Have direct responsibility over people below them in the hierarchy of an organisation
Delegation
Giving a subordinate the authority to perform particular tasks
Leadership styles
The different approaches to dealing with people when in a position of authority- autocratic, laissez-faire or democratic
Autocratic leadership
Where manager expects to be in charge of the business and to have their orders followed
Democratic leadership
Gets other employees involved in the decision-making process
Laissez-faire leadership
Makes the broad objectives of the business known to employees, but then they are left to make their own decisions and organise their own work
Trade union
Group of workers who have joined together to ensure their interests are protected
Closed shop
All employees must be a member of the same trade union
Recruitment
The process from identifying that the business needs to employ someone, to the point at which applications have arrived at the business.
Job (person) specification
A document which outlines the requirements, qualifications, expertise and physical characteristics for a specific job.
Internal recruitment
Is when a vacancy is filled by someone who is an existing employee of the business
External recruitment
Is when a vacancy is filled by someone who is not an existing employee of the business and will be new to the business.
Part time employee
A worker who works between 1-35 hours a week.
Full time employee
A worker who works 35+ hours a week.
Induction training
Is an introduction given to a new employee, explaining the business' activities, customs and procedures and introduces them to their fellow workers.
On-the-job training
Occurs by watching a more experienced worker doing the job.
Off-the-job training
Involves being trained away from the workplace, usually by specialist trainers.
Workforce planning
Establishing the workforce needed by the business for the foreseeable future in terms of the number and skills of employees required.
Redundancy
When an employee is no longer needed and so loses their job. It is not due to any aspect of their work being unsatisfactory.
Dismissal
Is when employment is ended against the will of the employee, usually for not working in accordance with the employment contract
Ethical decision
A decision taken by a manager or a company because of the moral code observed by the business.
Industrial tribunal
A legal meeting which considers workers' complaints of unfair dismissal or discrimination at work.
Contract of employment
A legal agreement between employer and employee listing the rights and responsibilities of workers.
Communication
Is the transferring of a message from the sender to the receiver, who understands the message.
Communication barriers
Are factors that stop effective communication of messages e.g poor explanations, poor spelling and grammar, incorrect language, technology issues, poor structuring of information, use of jargon, technical language or slang, lack of understanding.
Message
Is the information or instructions being passed by the sender to the receiver.
Medium of communication
Is the method used to send a message
Internal Communication
Between members of the same organisation.
External Communication
Between the organisation and other organisations or individuals.
One way communication
A message that doesn't call for or require for a response.
Two way communication
When the receiver gives a response to the message and there isn't a discussion about it.
Formal communication
When messages are sent through established channels using professional language.
Informal communication
When information is sent and received casually with the use of everyday language.
Feedback
Is the reply from the receiver which shows whether the message has arrived, been understood and, if necessary, acted upon.
Verbal communication
One to one talks, meetings, telephone conversations, video conferencing.
Written Communication
Business letters, memos , notices and faxes.
Visual Communication
Films, videos, posters, chart diagrams, photographs and cartoons.
Planning
determining organisational goals and a means for achieving them
Organising
the process of arranging resources and tasks to achieve objectives
Coordinating
Means bringing together
Commanding
Guiding, leading and supervising people to make sure they are keeping to targets and deadlines.
Controlling
Determines to what extent the business is accomplishing the goals it set out to reach in the planning stage