Concepts of bioavailability
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is a drug?
Substance that affects the structure or functioning of a living organism
Used for the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of disease or for the relief of symptoms
What is a medicine?
Drug delivery system
Used to administer drug to the body efficiently, safely, reproducibly and conveniently
What is a formulation?
Drug substance converted with excipients into a patient acceptable product
Makes a dosage form
What are the different dosage forms?
Liquids:
Solutions (mixtures, linctuses, gargles, lotions), suspensions, emulsions
Solids:
Powders, granules, capsules, tablets, suppositories, pessaries
Semi-solids:
Creams, ointments, gels, pastes
What is the therapeutic outcome of a drug is dependent on?
adequate concentration of drug reaching the site of action/target
Too high = overdose
Too little = no effect
drug concentration maintained for the required amount of time
What is drug concentration in the blood depends on?
• Relative amount of an administered dose reaching the systemic circulation
• Rate at which drug reaches systemic circulation
• Rate and extent of distribution of drug from systemic circulation to tissues and target site
• Rate of drug elimination from the body
Where does dynamic equilibrium happen for systemically acting drugs?
Exists between drug concentration at the site of action and concentration of drug in blood plasma
What's different about the type of blood plasma dynamic equilibrium exists between with systemic drugs?
It is plasma water so protein free
What part of the blood do drugs have to be dissolved in to be effective?
Drugs that are dissolved in plasma water can pass through the capillary endothelium and reach site of action
Why is measuring drug concentration at the target site complicated and how is it measured?
Drug conc in blood might not show accurately the conc at the target
Drug may bind to blood cells and plasma proteins
Clinically drug conc in plasma = drug conc at site of action
What is bioavailability?
The relative amount of an administered dose of a drug which reaches systemic circulation in a given time and the rate at which this occurs
What is the bioavailable dose?
The fraction of an administered dose of drug that reaches the systemic circulation in unchanged form
What is bioavailabilit important for?
Important in determining if a therapeutically effective concentration of the drug is achieved at the target site
What are the stages of oral delivery?
Drug must be completely released from the dosage form into solution in the gastro intestinal fluids
Drug must exhibit sufficient solubility in polar media
Drug must be stable in gastrointestinal fluids
Drug must then cross the gastro intestinal barrier into mesenteric circulation
Only drugs which exhibit a good balance between hydrophilicity and lipophilicity are absorbed
Finally, drug must pass into systemic circulation without being metabolised in the liver
What factors alter the rate and extent of absorptions?
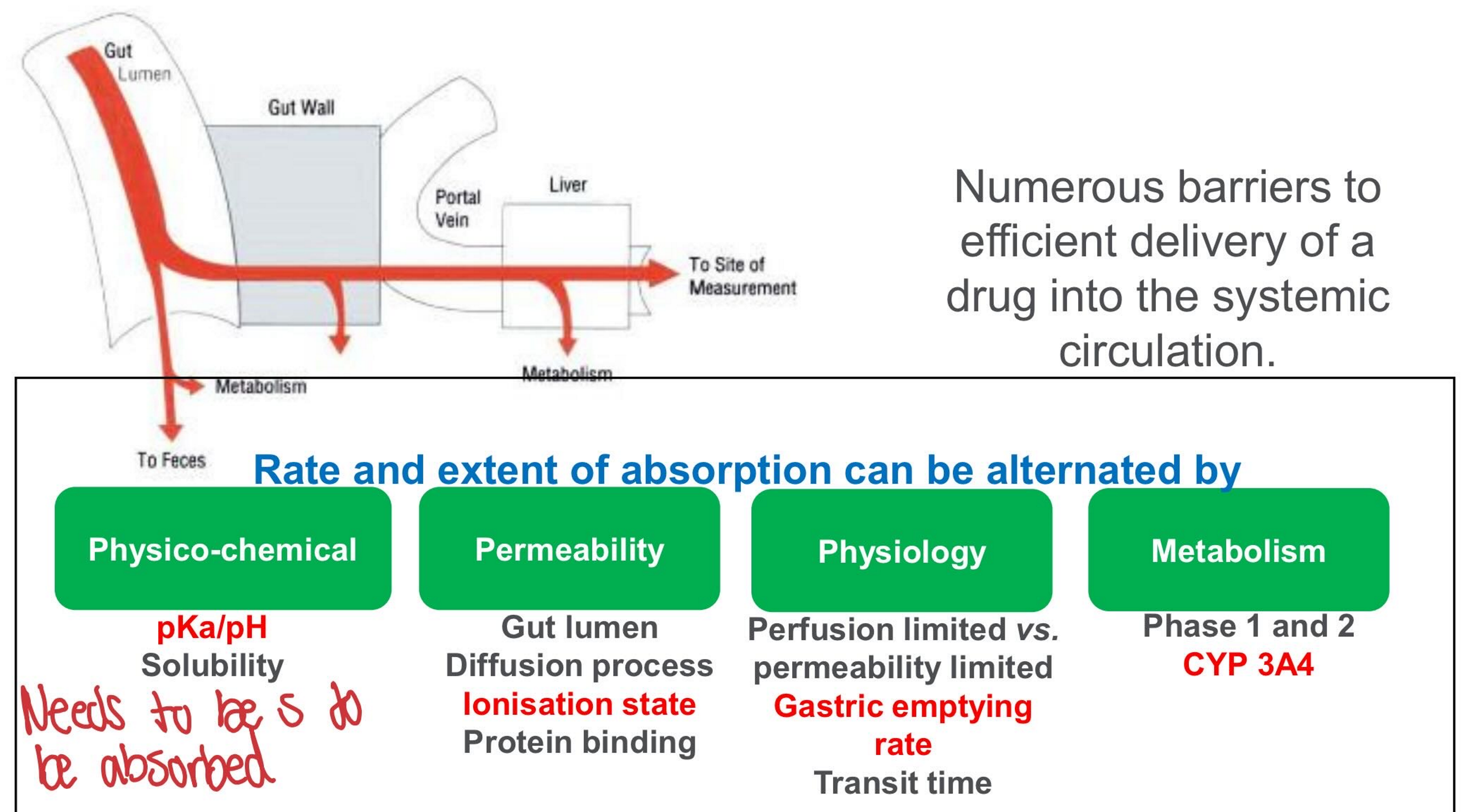
What is disintegration?
Rate of solubilism in a given time
What factors influence oral bioavailability?
Food
Age of the patient
Physico-chemical properties of the drug such as solubility, log P
Type of dosage form ( solids compared to liquids)
Composition of the dosage form (immediate release tablet versus sustained release)
Salt form of the drug (ibuprofen sodium when compared to ibuprofen lysinate)
Made to overcome solubility
What are the different paths of absorption?
Paracellular:
Passive
Very low molecular weight drugs pass through
Depends on drug properties
Lipid like membrane filter
Transcellular:
Diffusion
Hydrophobic drug particles
Conc dependent, pH and ionisation state
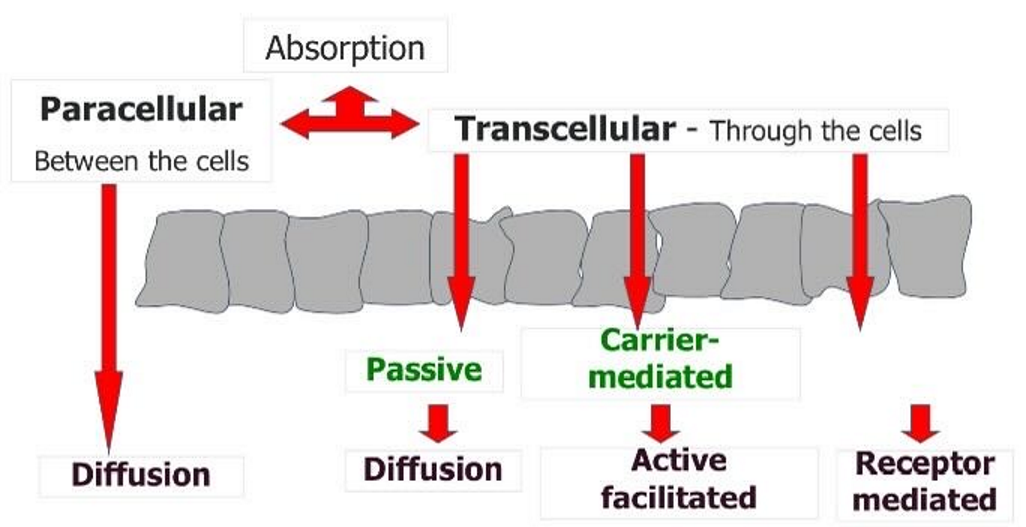
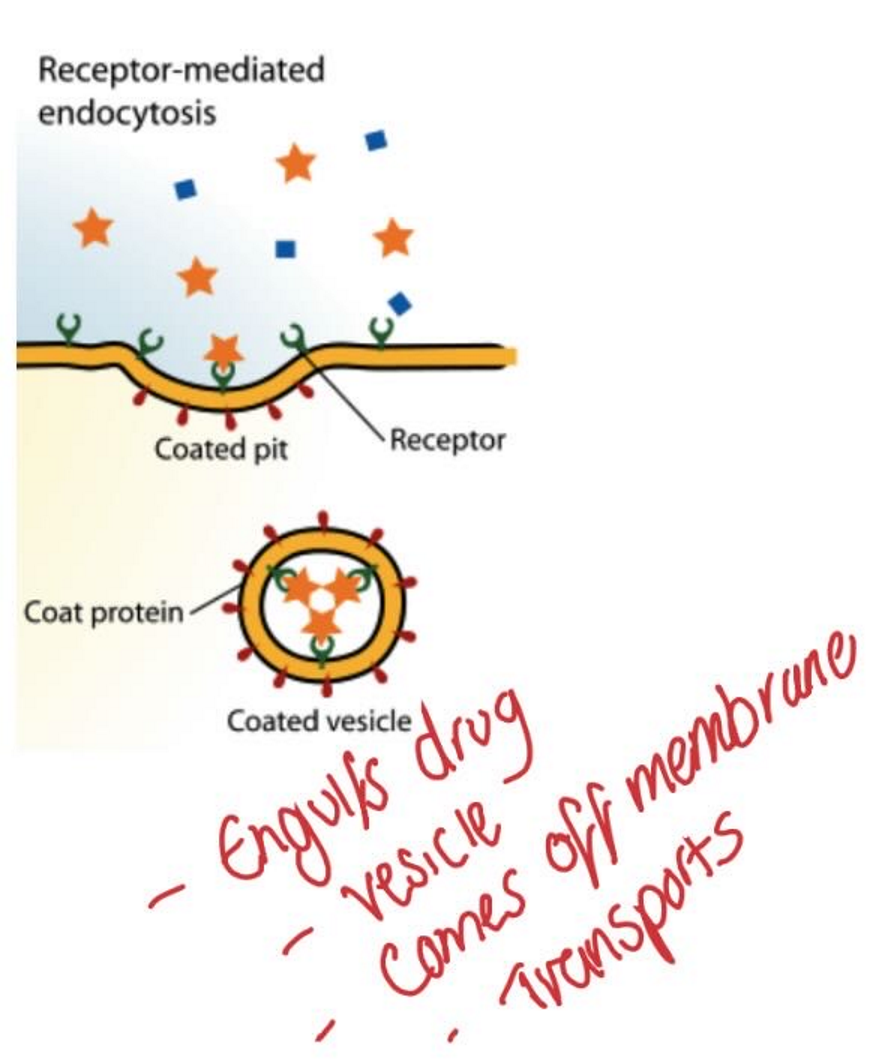
How do drugs get transported through cells?
Carrier-mediated system
Like a transporter pump
Requires energy (ATP)
Enzyme-therefore prone to saturation
System can exist in uptake (in) or efflux (out) state
Drug-drug interactions can compete for transporter
Specific transporters exist for endogenous substances in the body
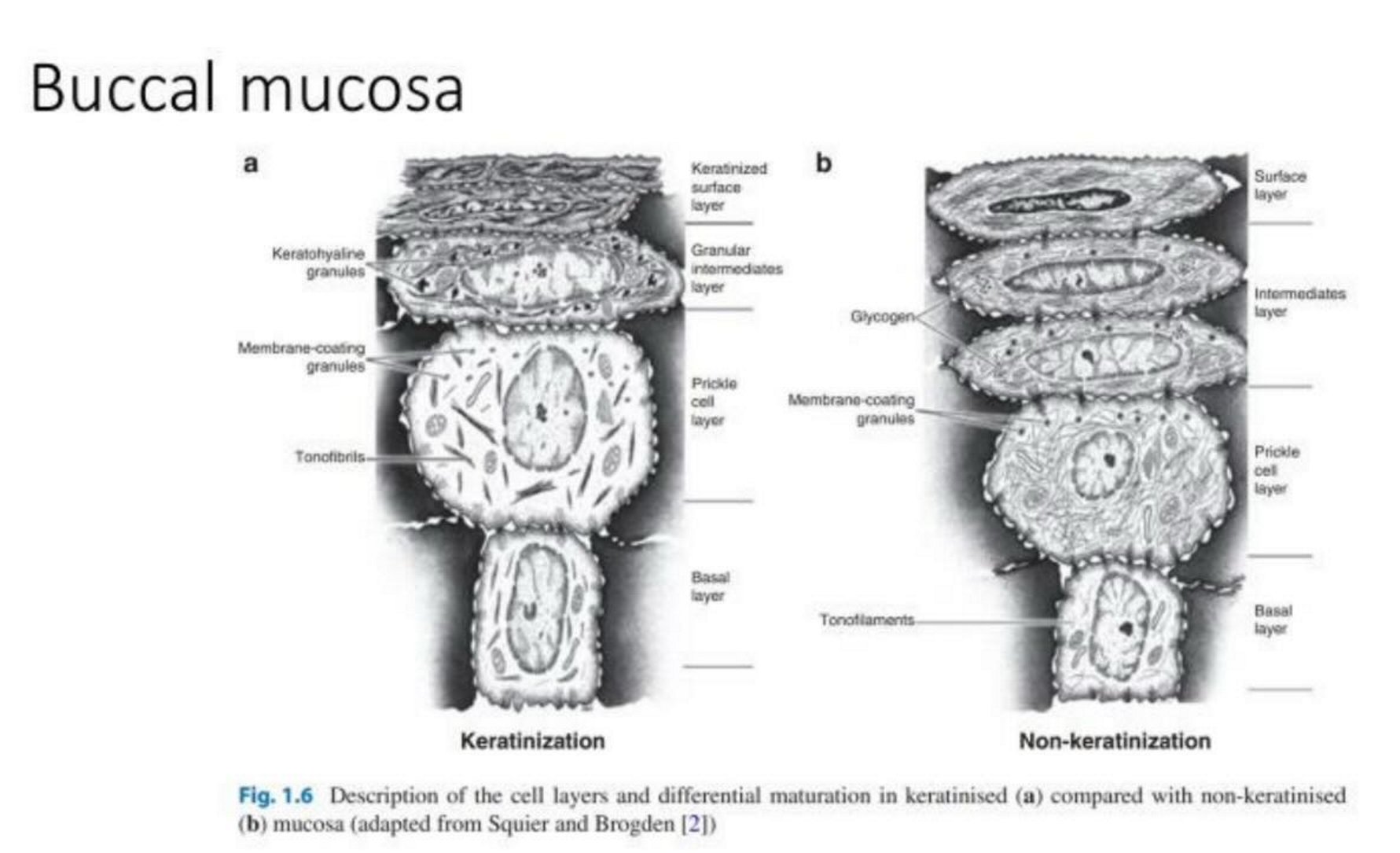
What is the oral mucosa?
First site of absorption encountered in oral delivery
Found at five sites in the cavity: buccal, sublingual, palatal, labial, and gingival
Buccal and sublingual are the most permeable so the main targets for drug delivery
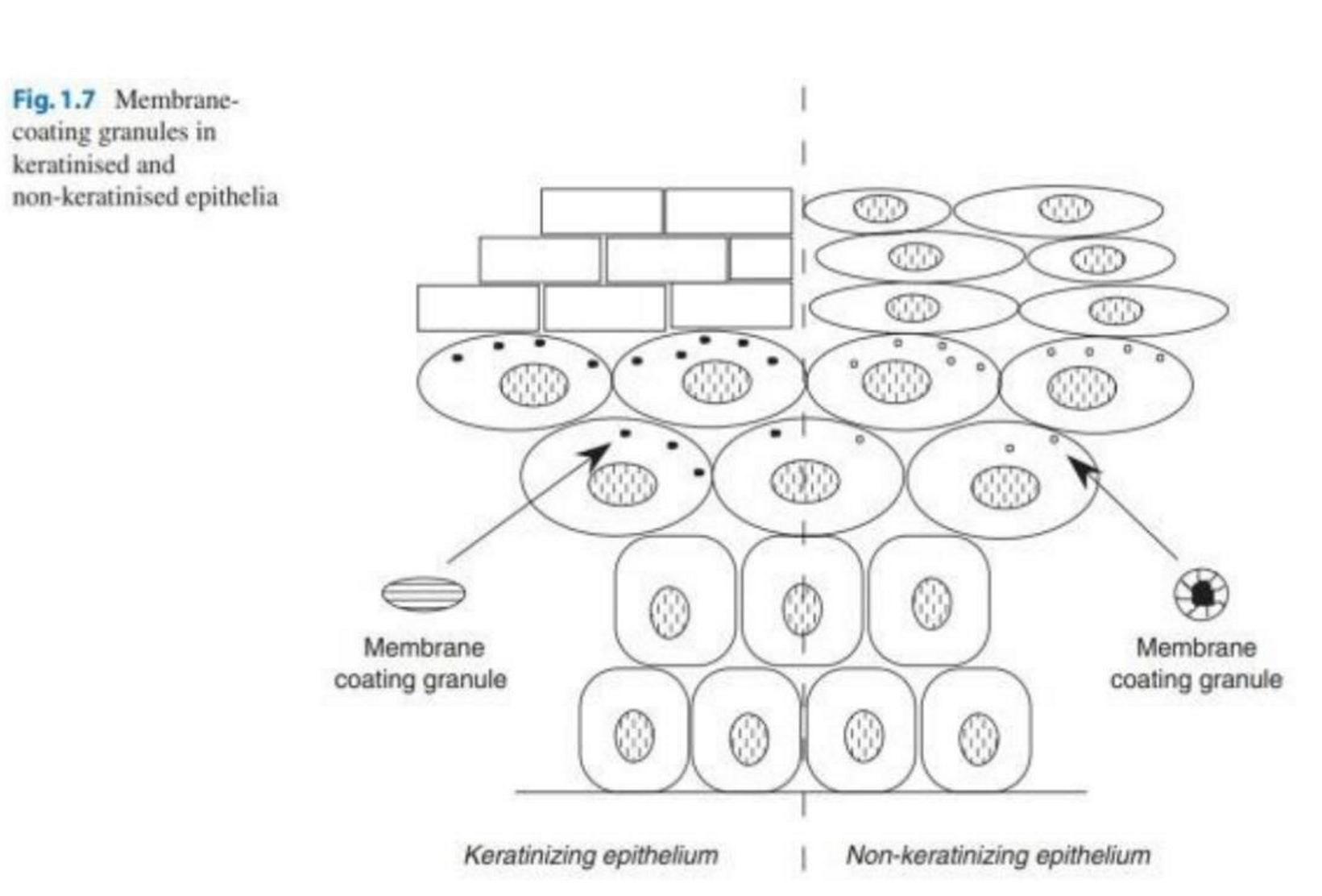
What is the oral mucosa divided into?
Subdivided into three types: lining mucosa, specialised mucosa, and masticatory mucosa (determined by location and historical properties)
Mucosa is highly vascularised, allowing for both mucosal (local) and transmucosal (systemic) effect