Infection Control & Sterile Technique: Microorganisms and Precautions
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What are bacteria commonly referred to as?
Germs
How do bacteria exist in the environment?
Bacteria are everywhere, both inside and outside of the body, and can live in a variety of environments.
What is the size range of viruses?
0.02 to 0.3μm, although some can be as large as 1μm.
What does the term 'virus' mean in Latin?
Slimy liquid or poison.
How are fungi classified in terms of biological kingdoms?
Fungi are classified in their own kingdom, separate from animals, plants, and bacteria.
What is a parasite?
An organism that lives in a host organism and gets its food from or at the expense of its host.
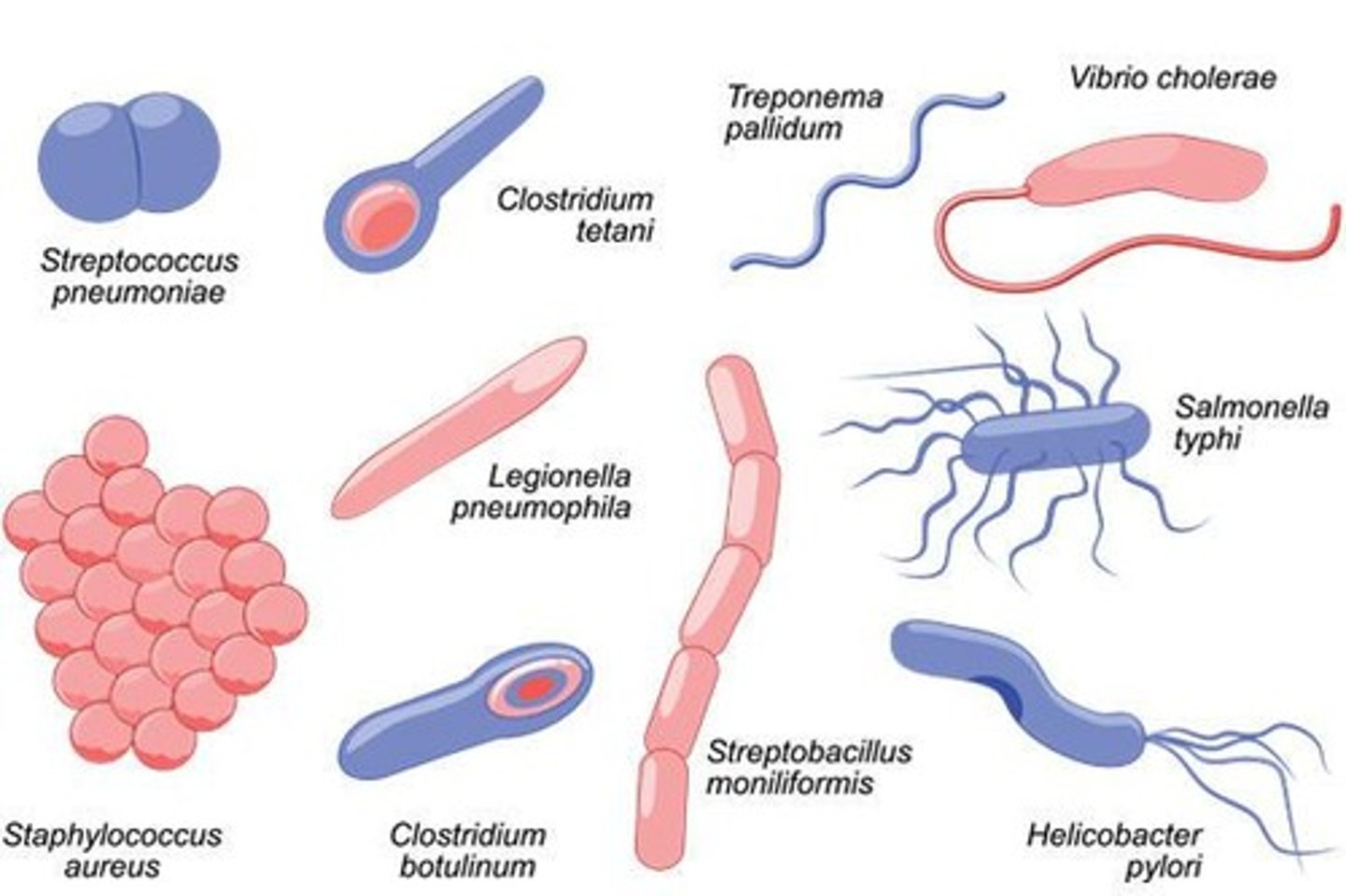
What are the four major categories of microorganisms that cause infection in humans?
Bacteria, Virus, Fungi, Parasite
What are the three main classes of parasites that can cause disease in humans?
Protozoa, Helminths, and Ectoparasites.
Define infection.
The invasion and multiplication of microorganisms that are not normally present within the body, which may cause symptoms or remain asymptomatic.
What is the difference between disease and illness?
Disease is a disorder of structure or function producing specific signs or symptoms, while illness is a personal experience of unhealthiness that may accompany disease.
What does 'asymptomatic' mean?
A condition where a person shows no symptoms of disease.
What does 'infectious' refer to?
A disease caused by microorganisms that may or may not be spread from one person to another.
What is a contagious disease?
An infectious disease that is easily spread from person to person through direct contact, droplets, airborne routes, or contaminated objects.
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that may cause disease.

What does immunocompromised mean?
A state where the immune system is weakened or not functioning properly, making a person more vulnerable to infections.
Define pathogenicity.
The ability of an organism to cause disease, which represents a genetic component of the pathogen.
What is asepsis?
The absence of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
What is medical asepsis?
Practices intended to confine a specific microorganism to a specific area, limiting its number, growth, and transmission.
What is surgical asepsis?
Practices that keep an area or object free of all microorganisms, including practices that destroy all microorganisms and spores.
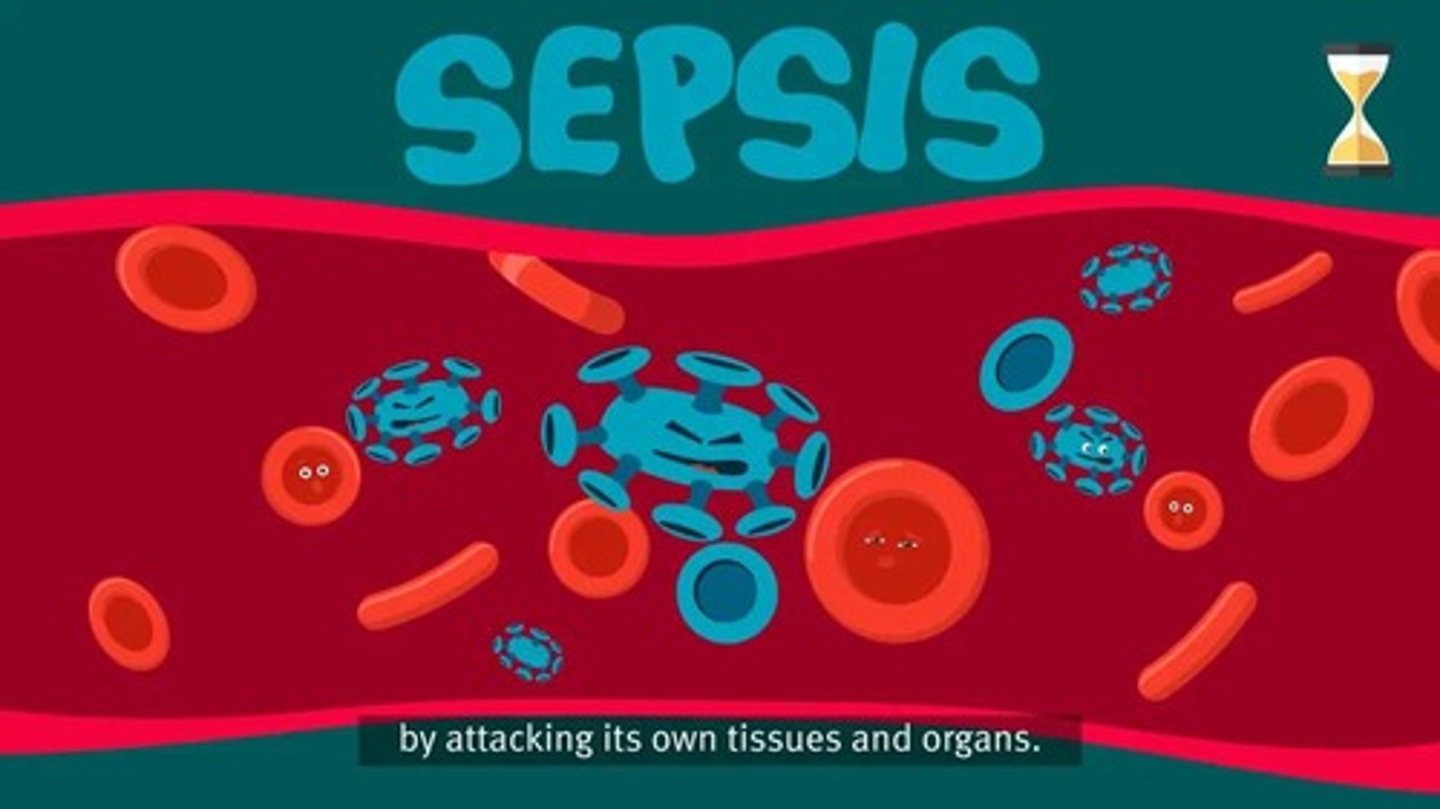
What is sepsis?
A potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection damages its own tissues.
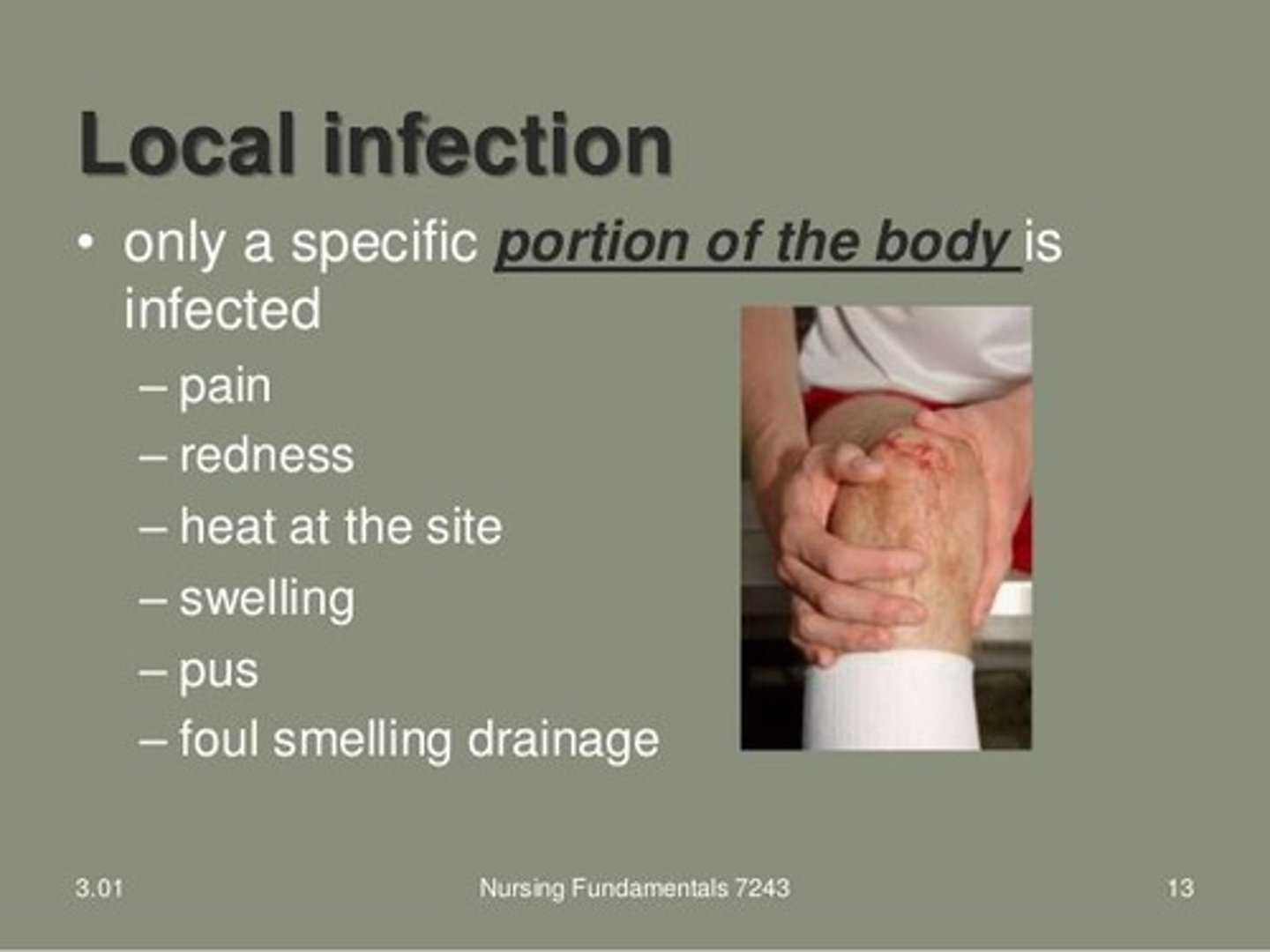
What is the difference between local and systemic infections?
Local infections are limited to a specific part of the body, while systemic infections spread throughout the systems of the body.
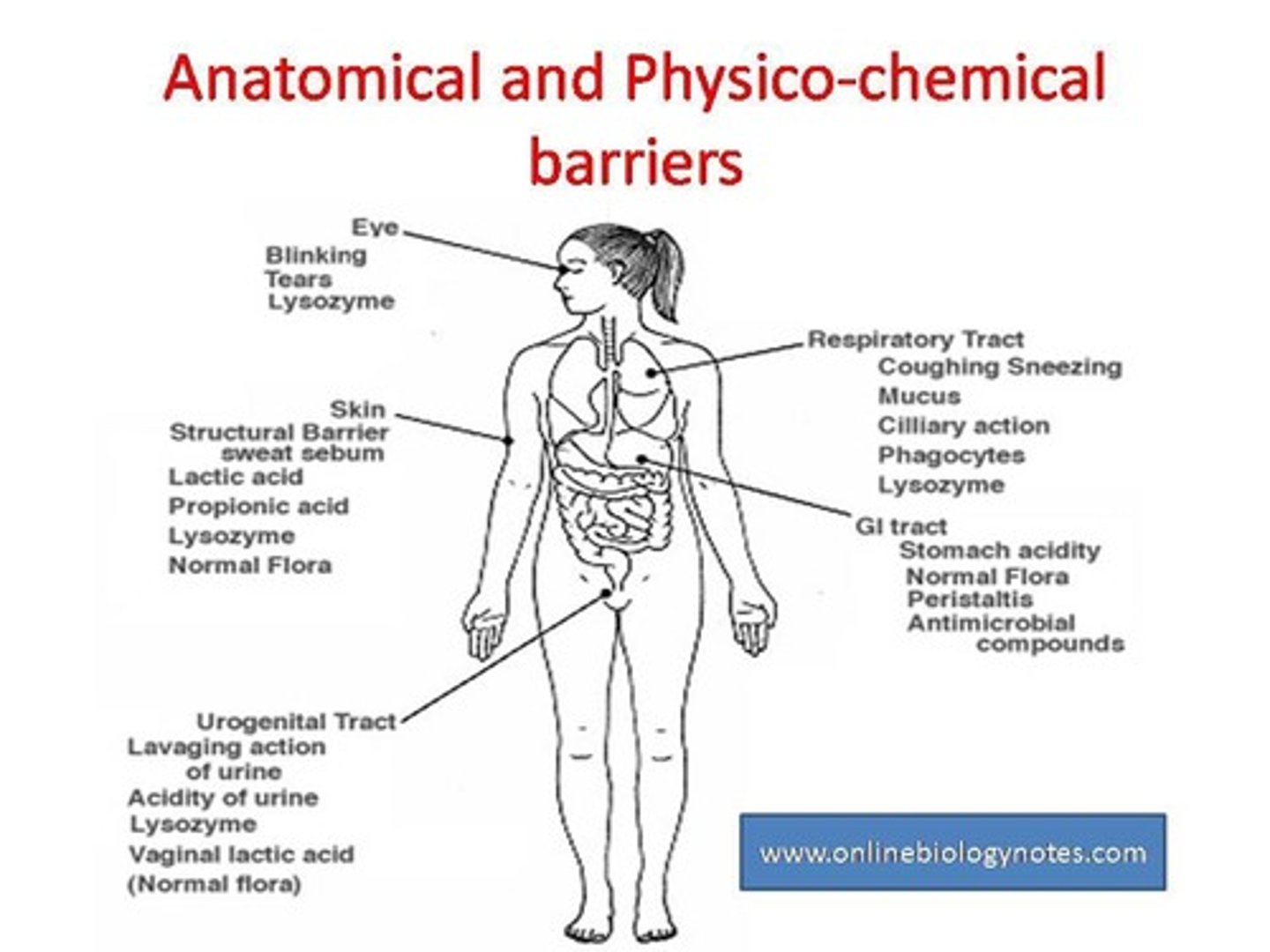
What are nonspecific defenses against infection?
Innate immunity mechanisms including anatomical barriers, chemical barriers, cellular defenses, inflammatory response, and fever.

What is the first line of defense in nonspecific defenses?
Anatomic and physiological barriers.
What is the role of antibodies in specific defenses?
Antibodies are part of adaptive or acquired immunity, produced by B cells.
What is a nosocomial infection?
An infection acquired in a hospital or healthcare facility.
What are some factors that increase susceptibility to infection?
Existing disease processes, nutritional status, emotional stressors, and recurrent infections.
What is the importance of assessment in nursing care for infections?
It helps to gather the client's history, conduct physical assessments, and collect laboratory data to identify infections.
What laboratory data indicate the presence of an infection?
Elevated leukocyte count, increases in specific leukocytes, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and positive cultures for pathogenic microorganisms.
What are the major goals for clients susceptible to infection?
Maintain or restore defenses, avoid the spread of infectious organisms, and reduce or alleviate problems associated with infection.
What is the primary goal of a nurse if infection cannot be prevented?
Prevent the spread of the infection within and between individuals and treat the existing infection.
What is direct contact transmission?
Transmission that requires physical contact between an infected person and a susceptible person, involving the transfer of microorganisms.
Give examples of direct contact transmission.
Kissing, sexual contact, contact with oral secretions, or contact with body lesions.
What is indirect contact transmission?
Infection from contact with a contaminated surface.
List some frequent touch surfaces that should be disinfected to reduce indirect contact transmission.
Door knobs, tables, washroom surfaces, medical instruments, and children's toys.
What is droplet contact transmission?
Transmission through droplets generated when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.
How can droplet transmission be reduced?
By using personal protective barriers such as face masks and goggles.
What is airborne transmission?
Transmission where droplet nuclei or dust particles containing microorganisms remain suspended in air for long periods.
Name diseases capable of airborne transmission.
Tuberculosis, chickenpox, and measles.
What is fecal-oral transmission?
Infection through ingestion of contaminated food and water.
How can fecal-oral transmission be reduced?
By proper food storage, thorough cooking, frequent handwashing, and adequate sewage treatment.
What is vector-borne transmission?
Transmission of diseases by animals, such as mosquitoes, which transfer disease through saliva.
What are standard precautions in infection control?
Using personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling blood, bodily fluids, and open skin.
What are transmission-based precautions?
Extra steps followed for illnesses caused by certain germs, in addition to standard precautions.
What are airborne precautions?
Precautions for germs that can float in the air and travel long distances, requiring special rooms and respirator masks.
What are contact precautions?
Precautions to prevent the spread of germs by touching, requiring gowns and gloves.
What are droplet precautions?
Precautions to prevent contact with mucus and secretions, requiring surgical masks.
What are the principles of surgical asepsis?
Strict adherence to aseptic practices to prevent infection during procedures.
What are core practices of medical asepsis?
Handwashing, cleaning the environment, wearing appropriate PPE, disinfecting articles, and using antiseptics.
How does medical asepsis protect clients?
It protects the client, environment, and healthcare providers from contamination or reinfection.
Still learning (6)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!