RP 3: Determination of g by a freefall method.
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the method used to determine the acceleration due to gravity using a free-fall method? (5)
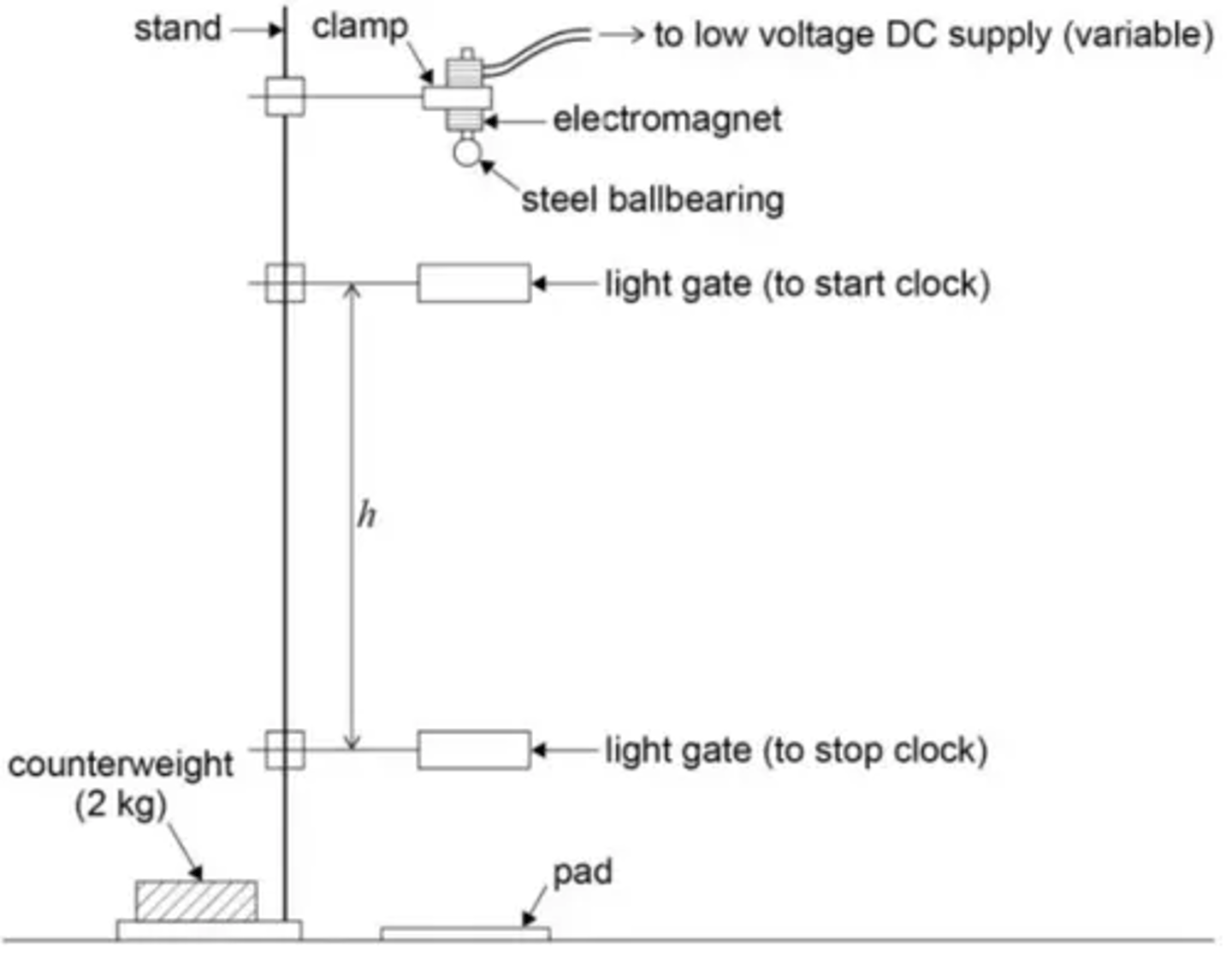
- Set up the apparatus so that a steel ball bearing is held in place by an electromagnet above two light gates.
- Adjust the height of the lower light gate so that the vertical distance (h) from the electromagnet is 0.500 m, measured using a metre ruler.
- Switch off the electromagnet to release the ball and use a stopwatch to record the time t for the ball to pass between the light gates.
- Repeat the measurement three times for each height and take the mean time. Reduce h by 0.050 m increments down to 0.250 m and repeat the entire process for each height.
- Repeat steps 1-4 two times and find the mean time for the ball to drop from each height for these three experiments carried out.
What equipment is required to determine the acceleration due to gravity using a free-fall method? (8)
- Stand and clamp.
- Metre rule.
- Electromagnet.
- Steel ball bearing.
- Light gate.
- Stopwatch.
- Pad.
- Counterweight.
What does a diagram of the setup used to determine the acceleration due to gravity using a free-fall method look like? (3)
What is the independent variable in the free-fall experiment? (1)
The independent variable is the height (h) from which the ball is released.
What is the dependent variable in the free-fall experiment? (1)
The dependent variable is the time (t) taken for the ball to pass between the light gates.
What are the controlled variables in the free-fall experiment? (3)
- Controlled variables include the initial speed of the ball.
- Another controlled variable is the vertical alignment of the apparatus.
- Another controlled variable is the type of ball bearing used.
What graph should be plotted to determine gravity (g) in the free-fall experiment? (1)
Plot a graph of 2h/t against t and draw a line of best fit.
What does a graph plotted to determine g in the free-fall experiment look like? (3)
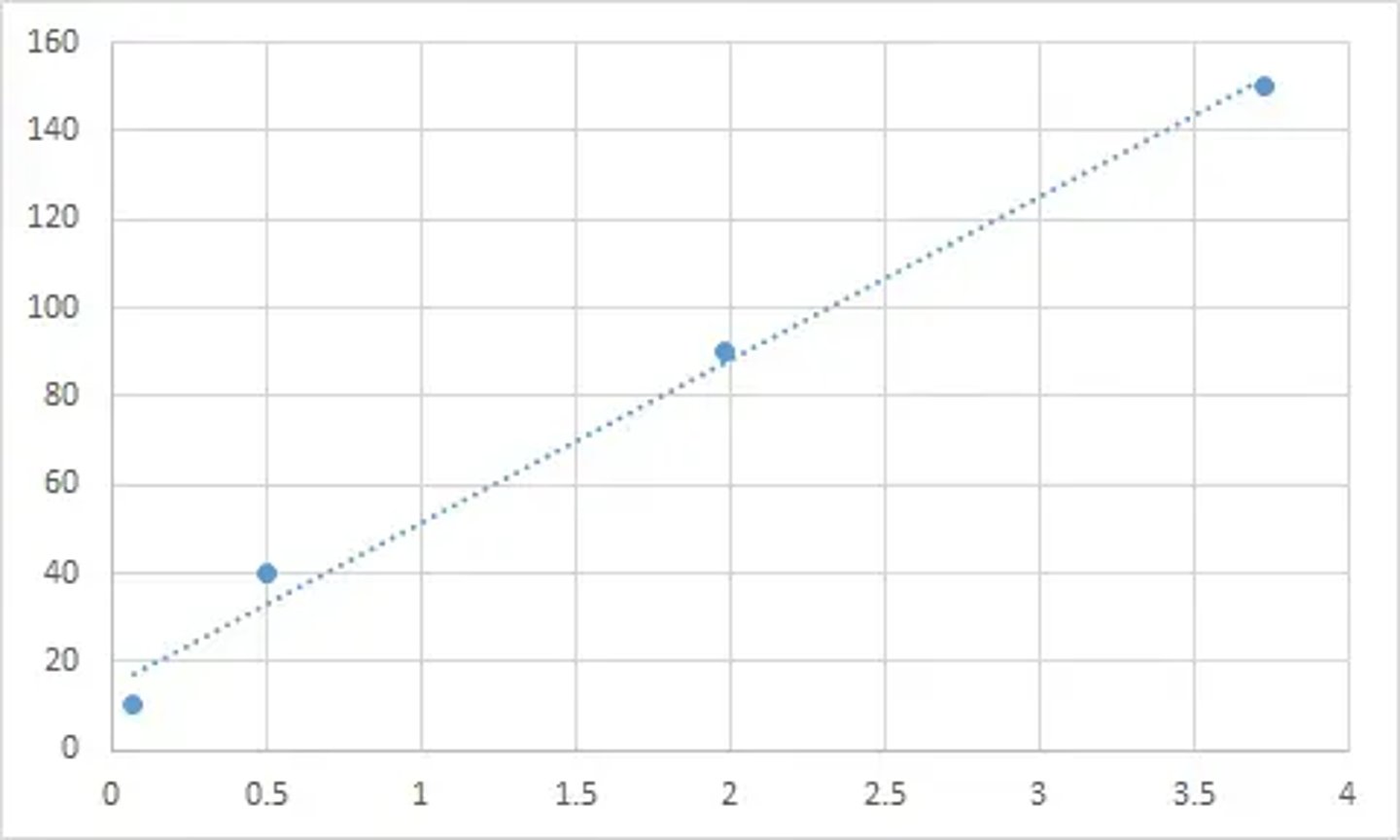
What does the gradient of the 2h/t vs t graph represent? (1)
The gradient of the graph is equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g).
Why does the graph 2h/t vs t give g as the gradient? (2)
- Based on s = ut + 1/2at² with u = 0 and a = g, s = h becomes 2h/t = gt.
- Therefore, the gradient of 2h/t vs t is g.
What is one safety precaution in the free-fall experiment? (2)
- A counterweight or clamp should be used to secure the stand so that it does not topple over during the experiment.
- This could cause injury.
How can consistency be improved in releasing the ball? (1)
Keep the height between the clamp and the upper light gate constant to ensure the ball always reaches the top light gate at the same speed.
How can the effect of air resistance be reduced in the free-fall experiment? (1)
Use a dense steel ball to minimise the effects of air resistance.
How can the experiment be made safer and reduce equipment damage? (1)
Cushion the ball using a soft pad at the bottom to prevent it from bouncing dangerously and reduce risk of damage.
How can height measurements be made more accurate in the free-fall experiment? (1)
Parallax error can be reduced by clamping the ruler directly next to the light gates so that height measurements can be taken at eye level.