B2 Retrieval Questions - Year 10 - CS
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Process required for growth in animals
Cell division and differentiation in animals
Processes necessary for growth in plants
Cell division, elongation, and differentiation in plants
Stem cells
undifferentiated Cells capable of forming various cell types
Three examples of stem cells
Embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, meristems
Advantages of embryonic stem cells
Easily extracted, can generate any cell type
Disadvantage of embryonic stem cells
Embryo destruction during cell extraction, can make tumour, moral issues , rejection
Risk with stem cells
Potential uncontrolled division leading to cancer
Advantage of stem cell treatment
Replacement of faulty cells with healthy ones
Advantages of using adult stem cells
No embryo destruction, minimal rejection risk
Disadvantage of adult stem cells
Limited cell type differentiation.
Embryonic stem cells source
Derived from early-stage embryos (8 cells)
Adult stem cells source
Obtained from bone marrow
Meristems location
Located in rapidly growing plant parts like root and shoot tips
Types of neurones in a reflex arc
Sensory, relay, motor neurones
myelin sheath
Part of a neurone that insulates it and speeds up the impulse
dendron
carry impulses towards the cell body
axon
Part of a neurone carrying impulses away from the cell body
Gap between 2 neurones
Synapse
Impulse travel across a synapse
impulse travels to end of neurone . triggers release of neurotransmitters which diffuse across synapse. the neurotransmitters stimulate an electric impulse in second neurone
cell differentiation
process by which cells become specialised
growth percentile charts
used to monitor growth of an organism by comparing its growth to usual trends for that particular organism
reflex arc
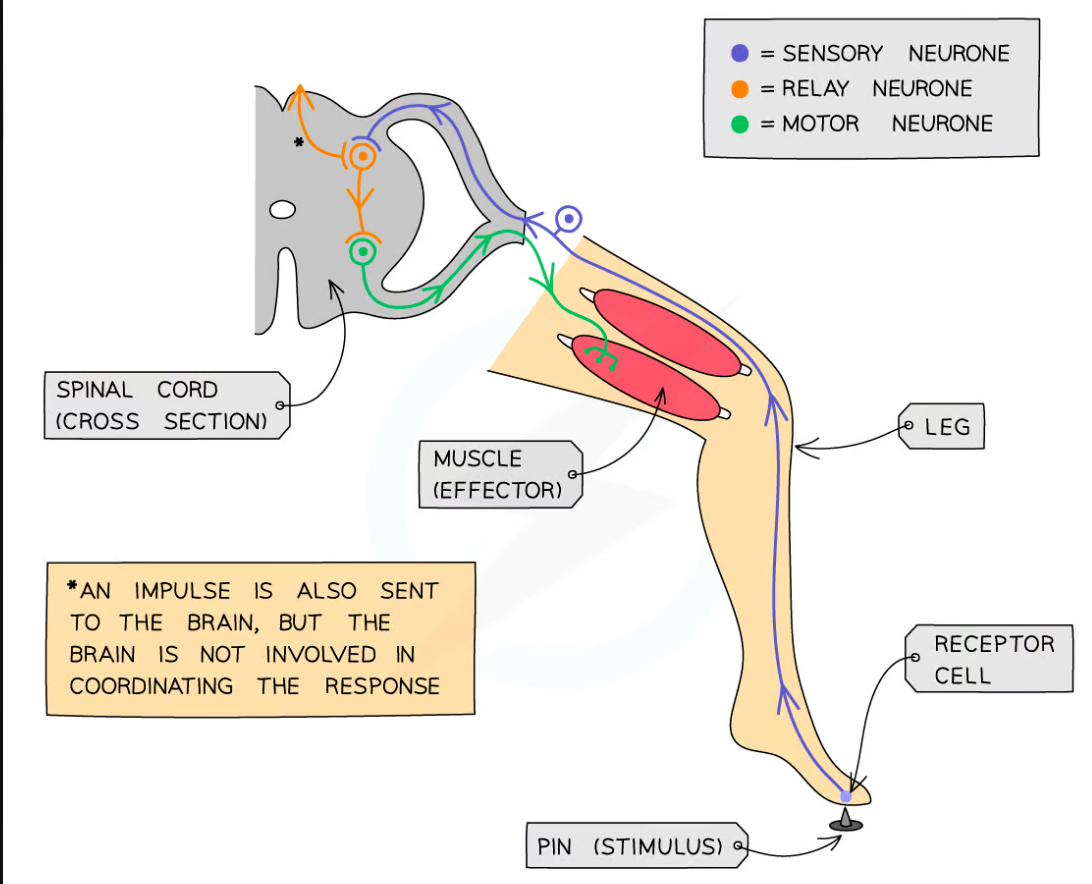
stimulus-receptor-sensory-relay-motor-effector-response
what are reflexes
fast, involuntary actions responding to a stimulus - keeps the body safe
What is the cell cycle?
The series of steps that take place as a cell grows and then divides
steps of the cell cycle
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
cytokinesis
the cytoplasm and cell membrane divides to form two identical daughter cells
4 stages of mitosis
prophase , metaphase, anaphase, telophase
prophase
chromosomes condense and nuclear envelope breaks down leaving the chromosomes free in the cytoplasm
metaphase
the chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell
anaphase
spindle fibres split the chromosomes down the centre and pull the chromatids to opposite ends of the cell
telophase
new membranes form around the chromosomes at either end of the cell . these become the nuclei of the two new cells
Which two structures make up the central nervous system (CNS)?
brain and spinal cord
What are the roles of the cerebral cortex?
interpreting senses , memory, consciousness, intelligence and language
What are the roles of the cerebellum?
balance, muscle coordination
role of medulla oblongata
coordinating unconscious activities like breathing rate
hypothalamus
regulates our body temperature
how can scientists study the brain apart from scans
study people with brain damage, electrically stimulate different parts of the brain
why is treatment of the CNS so difficult
some areas are difficult to access ,
its hard to repair damage as neurones don’t readily repair ,
risk of further damage leading to permanent effects
what 2 muscles make up the iris
circular muscles, radial muscles
rod cells
cells that are sensitive to light and more sensitive in dim light
cone cells
cells that are sensitive to different colours
Which two structures refract (bend) light entering the eye?
cornea, lens
When light passes into the eye, where on the retina should the light be focused?
The fovea
what lens is used to correct long-sightedness
convex
what lens is used to correct short-sightedness
concave
what does a CT scan do
uses X-rays to produce an image of the brain. shows main structures not functions.
what does a PET scan do
use radioactive chemicals to show brain activity. can show both functions and structures in real time
iris
controls how much light enters the pupil
lens
transparent disc that refracts light, focussing it on the retina
cornea
transparent lens that refracts light into eye
retina
where light is detected , has light receptor cells
how do you focus on distant objects
ciliary muscle relaxes but suspensory ligaments pull tight. lens is less rounded so less light is refracted
how do you focus on nearby objects
ciliary muscle contracts but suspensory ligaments slacken. lens is more rounded so more light is refracted
causes of long sightedness
short eyeball or lens not curved enough meaning it doesn’t refract enough light
long sightedness problem
light from near objects is brought to focus behind the retina
causes of short sightedness
long eyeball or lens being too curved meaning it refracts too much light
short sightedness problem
light from distant objects is brought to focus infront of the retina
red-green colour blind problem
red or green cones don’t work
cataracts
cloudy patch on the lens which means less light reaches retina
cure for cataracts
replacing faulty lens with artificial lens
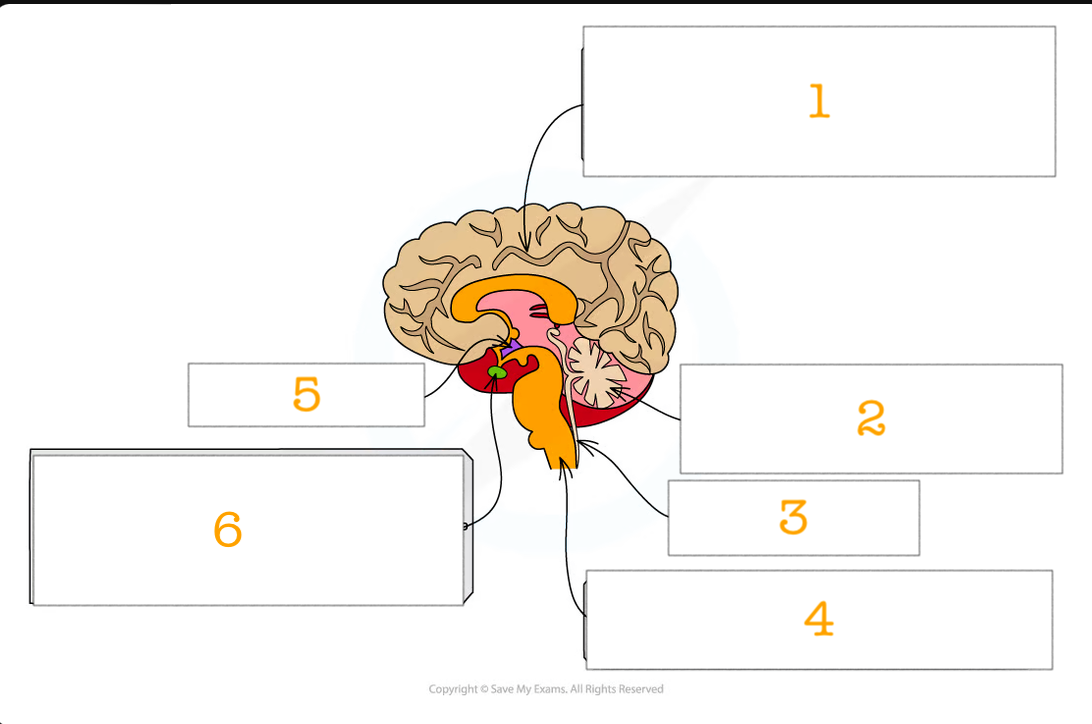
label the brain 1-6
cerebral cortex
cerebellum
spinal cord
medulla oblongata
pituitary gland
hypothalamus
optic nerve
sensory nuerone that carries impulses between the eye and the brain
pupil
hole that allows light to enter the eye
ciliary muscle
a ring of muscle that contracts and relaxes to change the shape of the lens
suspensory ligaments
ligaments that connect the ciliary muscle to the lens
label the eye 1-9
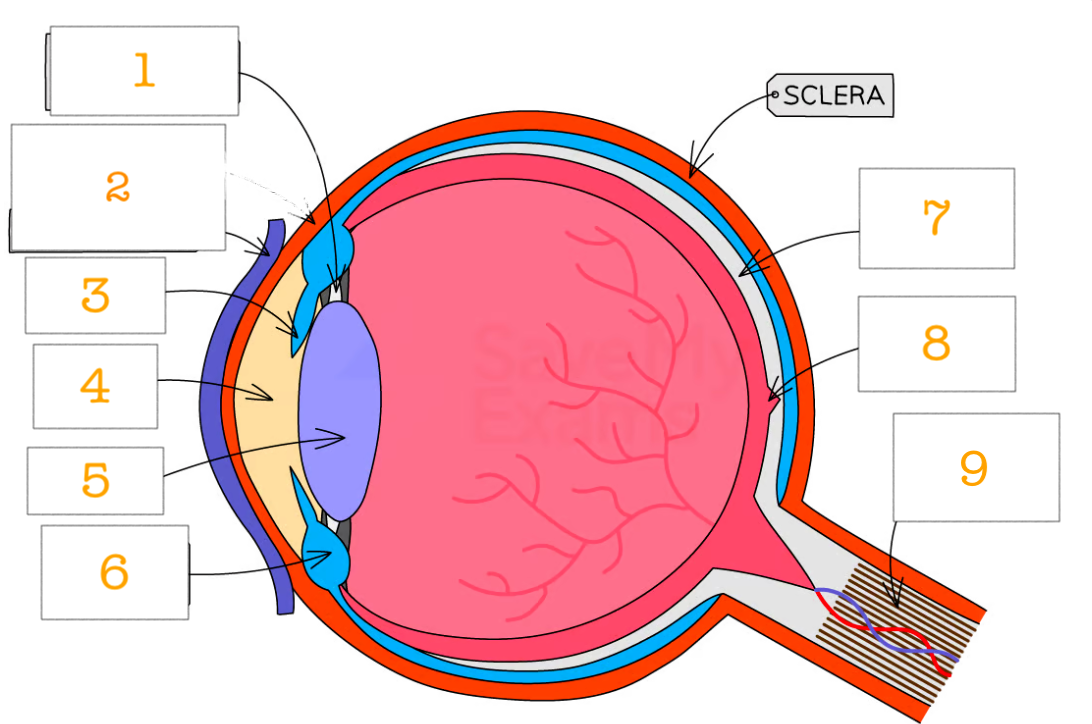
suspensory ligaments
cornea
iris
pupil
lens
ciliary muscles
retina
fovea
optic nerve
label which neurone in which
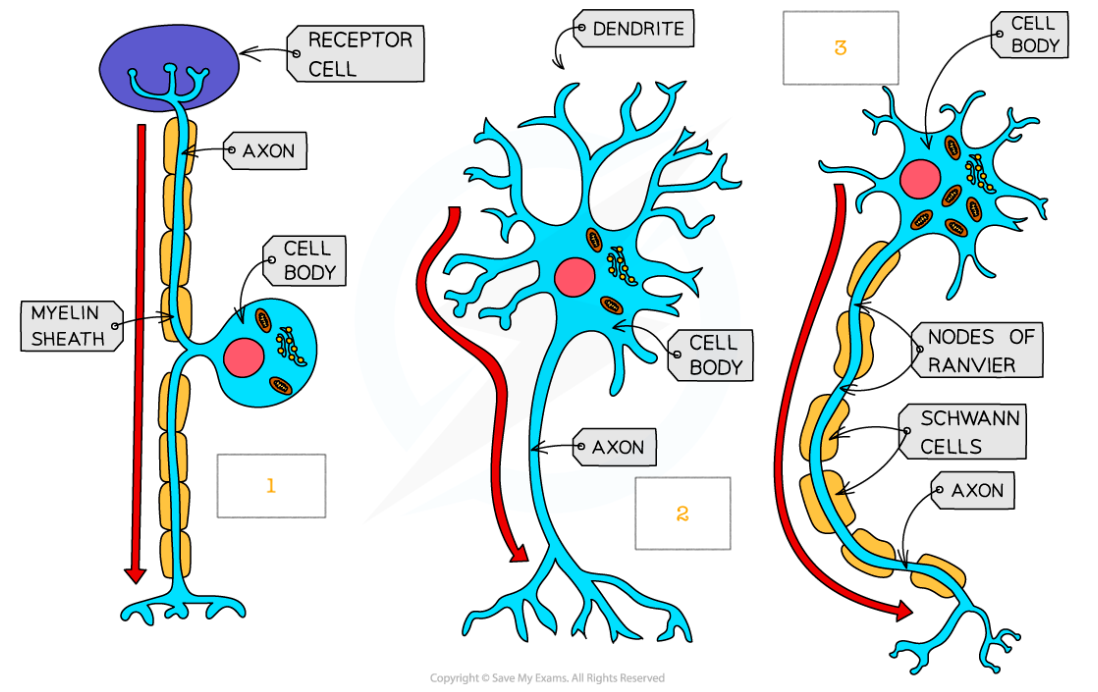
sensory
relay
motor
2 main parts of human nervous system
Central nervous system , peripheral nervous system
function of sensory neurone
carries impulse from sense organs to CNS
2 features of a processed response and reflex response
processed requires a conscious decision and is slower
why do motor nuerone’s have myelin sheaths
they travel great distance
reflex arc definition
the pathway of a reflex response
growth
permanent increase in size and mass
why is using percentile charts to compare baby growth important
to identify health issues like malnutrition and obesity
what causes uncontrolled cell division
genes that control cell division mutate
similarity and difference of benign and malignant tumours
both form a lump, malignant tumours are cancerous and dangerous as they invade surrounding cells
why in a growing root does only one daughter cell from cell division become differentiated
the other daughter cell stays a meristem for future growth
cell elongation
when hormones such as auxin cause cells to grow longer in response to stimuli like sunlight
how are growth percentile charts used
compares growth of a baby by historical data of children the same age
how is growth measured in babies
mass, height, head circumference
what does it mean if a baby is on the 25th percentile for mass
they are lighter than 75% of children their age but heavier than 25%
why is differentiation important
to allow formation of specialised cells with structural adaptations which allow them to perform specific functions
cell differentiation in plants
meristem can divide and differentiate into any cell type for as long as the plant lives
adult stem cell usage
replace damaged cells or produce new cells for growth
cell differentiation in animal cells
animals lose the ability to differentiate and divide into any cell type after the early stages. only adult stem cells remain
disadvantages of stem cell treatment
tumour development, disease transmission, rejection
adult stem cell usage in medicine
used to replace faulty cells
How are embryonic stem cells used in medicine
They differentiate into cell type . The healthy cells replace the faulty cells .
How can stem cells be used to cure diabetes
The stem cells differentiate into insulin producing pancreatic cells
How can stem cells be used to cure paralysis
Stem cells differentiate into nerve cells to replace damaged neurones
what is the brain made of
billions of interconnected neurones
spinal chord
long column of neurones that run from the base of the brain down to the spine
what does the spinal chord do
relay information between the brain and the body
what 2 types of scans are used to investigate the brain and understand it
CT scans, PET scans
how can a CT scan be used to identify function of an area
if that area is damaged and the patient has lost a particular function - the function of that part can be figured out
what is PET scanner good for studying
disorders that change the brains activity
sensory neurone structure
cell body in the middle. long dendron. short axon
relay neurone structure
small cell body at one end with many short dendrites branching off, axon
motor neurone structure
cell body at one end with long dendrites , an axon and a myelin sheath
adaptations of nuerone’s
myelin sheath, longer axon