Carbon Cycle
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
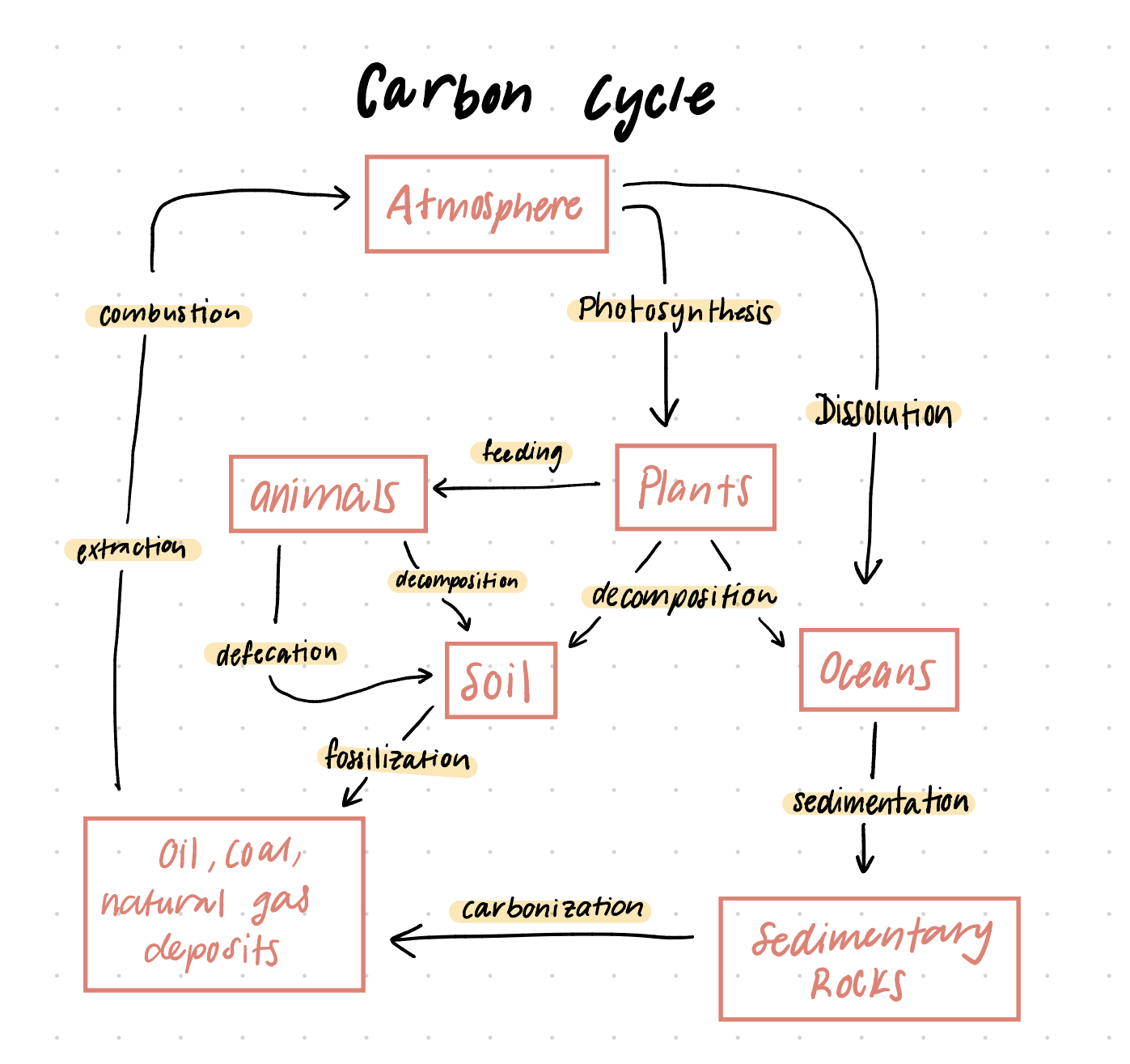
Carbon Stores
an area where carbon accumulates over time through carbon sequestration — capturing gaseous and atmospheric carbon dioxide and storing it in a solid/liquid form
examples: atmosphere, ocean, organisms, soil, coal deposits, sedimentary rock
Carbon Sink
when the carbon inflow to a carbon store is greater than the carbon outflow
examples:
1) forests — sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide into sugars simple sugars like glucose and carbon through photosynthesis
2) ocean — carbon dioxide is used by phytoplankton to make their own food, which feeds the entire marine ecosystem
Carbon Source
when the carbon outflow is greater than the carbon inflow of a carbon store
examples:
1) animals — through cellular respiration, they produce CO2 as they exhale
2) burned/deforested fore
Photosynthesis
Storages:
from atmosphere to plants
Process:
plants transform carbon dioxide. and water into glucose and oxygen
Cellular Respiration
storages:
from plants and animals to the atmosphere
process:
plants and animals transform glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water
Feed/Consumption
storages:
from plants/animals to animals
process:
plants transfer carbon to animals, and those animals transfer carbon to other animals when they are eaten
defecation
storages:
from animals to soil
process:
animals transfer their feces to soil surfaces
decomposition
storages:
from plants/animals to soil and atmosphere
process:
decomposers transform dead organic substances and feces from organisms into soils/sea bed — carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere
dissolution
storages:
from atmosphere to ocean
process:
atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves in ocean water
fossilization
storages:
from soil to coal/oil/natural gas deposits
process:
organic matter under pressure transforms into coal/oil/natural gas deposits
sedimentation
storages:
from aquatic environments to coal/oil/natural gas deposits
process:
organic matter settles to the floor, forming sediment. Under pressure, this transforms into coal/oil/natural gas deposits
extraction
storages:
from coal/oil/natural gas deposits to energy technologies
process:
humans transfer coal/oil/natural gas deposits to energy production technologies (power plants, refineries, car engines)
combustion
storages:
from energy technologies to atmosphere
process:
humans transform coal/oil/natural gas by burning, releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
draw the carbon cycle