ESS - Unit 1
1/54
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Ecologist
believe that the planet has limited resources and that people should not use them for personal gain. Believes humans have to adapt and find a way to live in harmony with the Earth.
Cornucopians
believe the complete opposite of an Ecologist. They think the planet has endless resources that should be manipulated to benefit humankind.
inputs
Everything around us affects our opinions, the decisions we make and how we live our lives.
culture, education, science, media, etc.
Processes
Once we have the inputs we can start processing them. assimilation of knowledge, thinking and evaluating.
output
Once the inputs are there and the information has been processed the answers are available, the choices and decisions can be made, and perspectives and viewpoints can be formed
Preservationists
An individual who advocates for the preservation of land, and its resources in pristine untouched conditions.
John Muir
founded the Sierra Club. A major preservation organization that focused on reducing pollution and protecting natural beautiful spaces, by creating National Parks.
Henry David Thoreau
published the book Walden, which was based on his experience of a simplistic lifestyle. He was living “intimately with nature”
Conservationists
They weren’t conserving the environment for its intrinsic value, rather they worked on the value of the goods and services it could provide.
Emphasized the sustainable use of the environment and the management of its resources to allow further development
Intrinsic value
the idea that something can be of value in and of itself and not because it is of any use to humanity.
Instrumental value:
Something is valued because it is a means to an end, it gives you something tangible.
Ecocentric
Propose self-reliance, self-restraint and minimal disturbance of the natural processes to achieve sustainability for the whole earth. (Nature-Centered)
Deep ecologist
someone who is a deep ecologist is Ecocentric and believes that nature has intrinsic values in and of itself. (No development)
Self-reliance soft ecologist
Small-scale development Community identity that keeps development in check. (mostly ecocentric but has some anthropocentric aspects)
Anthropocentric
approach in which people manage their environment and themselves with the help of independent regulatory authorities.
Environmental managers
Natural resources and human population need to be managed. (mostly anthropocentric but has some technocentric aspects)
Technocentric
Science will find alternative resources and the market economy can continue unheeded. Therefore, they believe that they can use, and destroy the environment.
Cornucopians
believe that they can carry on with development because technology will solve any problems that arise.
Holistic worldview
there should be minimal disturbances of natural processes, and that bio-rights (of animals or the environment) should be respected
Ecocentric society
is where humans are part of nature rather than in control of it. Form global citizenship where there is sustainability for the whole earth
Systems
Set of interrelated parts and the connection between them that unites them to form a complex whole and produces emergent properties
Ecological systems
Biological community consisting of all living organisms, with non-living components interacting with each other
Social systems:
Man-maid systems
what are the 2 types of systems
open, closed and isolated
Open System
exchanges matter and energy with its surroundings
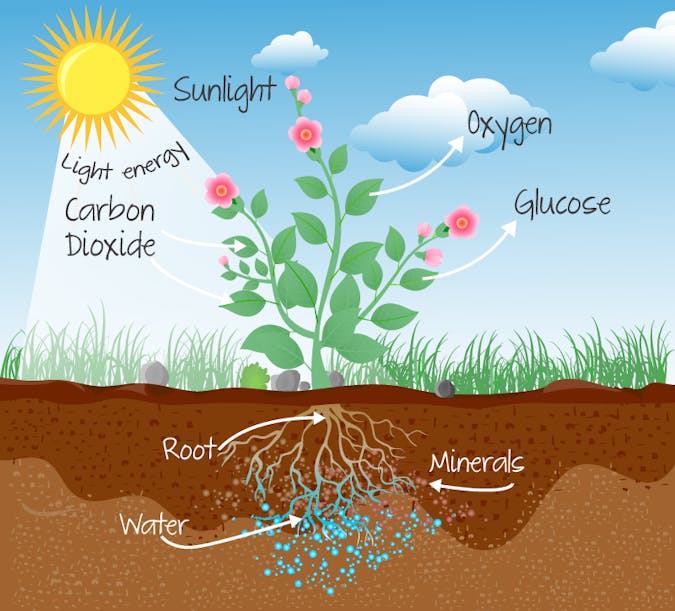
Closed systems
Exchanges energy but doesn’t exchange matter with its surroundings
Isolated Systems
exchanges neither energy nor matter with its surroundings (imaginary construct since nothing in nature is completely isolated)
Store of matter
Plants, and animals—> store energy and matter
Store of Energy
Carbon bonds = energy storage
Transfer
moves energy or matter from one place to another with 0 change
Transformations
moves energy and matter causing change in the process
Model
a simplified version of reality that tells a story about what happens in the natural world
Simulations
shows a model in action and provides information about how something will respond over time
Advatages of model
Can study things that are either too small or too large for researchers to deal with
A simplified version of the real-world example
Helps illustrate complex concepts and formulates hypotheses
Disadvantages of a model
Maybe misleading and affect our understanding
Lack of detail → predicts may not be accurate
maybe oversimplified
Thermodynamics
Branch of physics that studies heat and temperature and how that relates to energy and work
first law of thermodynamics
States that energy can’t be created or destroyed
second law of thermodynamics
the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant in any spontaneous process; it never decreases.
Bioaccumulation
process of collecting chemicals in an organism that happens if the rate of intake exceeds the rate of excretion
Trophic levels
levels that a species occupies in the food web
Entropy
a measure of the disorder of a system which describes how much energy is not available to do work.
negative feedback
promotes stability in a system. It reverses the change and returns the system to its original state
positive feedback
amplifies change in system + keeps it going in the same direction
Equilibria
if everything is in balance (equilibrium)
Static state
system remains constant over a long period of time
Steady state
has many small changes over a shorter period of time
Stability
the ability of an ecosystem to remain balanced
Resistance
An ecosystem continues to function during disturbance
Resilience
the ability to recover after a disturbance
Renewable
replaced as fast as it's used
Natural capital
natural resources that produce natural income of goods and services
Goods
marketable commodities that can be exploited by humans
Services
natural processes that provide benefits for humans