Trauma/Burns
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
LeFort Fractures
-three types of fractures that escalate in amount of damage done to bones in the face
-requires an extensive amount of force to obtain
-causes a lot of bleeding
-airway (SALAD technique)
-OG tube
MAP goal for trauma patients with s/s of hypovolemia
60 mmHg
pale/white feet and ankles
What is an ominous sign in a trauma patient?
blood loss of 30-40%
Class III blood loss
HR/SBP
shock index calculation
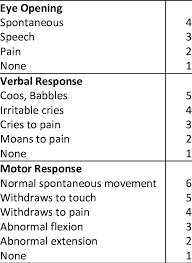
GCS Adult

GCS Child
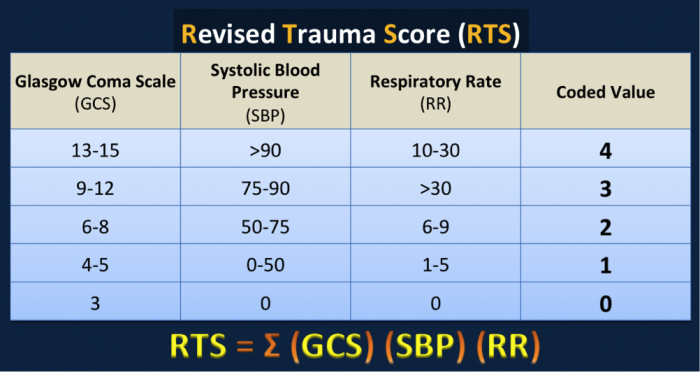
Revised Trauma Score
Penetrating Trauma
-stab wounds (what type of knife?)
-gun shot wound (what type of gun and caliber?)
leading cause of death in 15-25 yr olds
-permissive hypotension
Cardiac Tamponade
-Beck’s Triad
-confirmation via ultrasound
tx:
supportive measures
pericardiocentesis
Beck’s Triad
narrow pulse pressures
JVD
muffled heart tones
Pericardiocentesis
Equipment:
10-60 cc syringe
spinal needle
identify xiphoid process
point the spinal needle toward the left shoulder at a 45 degree angle
placed pressure on xiphoid, advance the catheter slowly while pulling back on the syringe
once you have blood return, evacuate the volume & reassess your patient
Tension Pneumothorax
severe respiratory distress
decrease or absent breath sounds
tracheal shift = late finding
subcutaneous air
High plateau pressure [Pplat]
Hemothorax
decreased breath sounds
midline/shifting trachea
flat neck veins
decreased LOC
Tx:
chest tube
fluid replacement/PRBC/FFP
chest rube should be clamped @ 1500 cc initial output to avoid reexpansion pulmonary edema
Chest Tube Procedure
4-5th intercostal space
incision over 5th rib
grab Kelly clamp, hold your fingers 2-3 cm from the distral end of the kelly clamp prior to insertion into the chest cavity
slide the kelly clamp over the top of the rib, pushing into he pleural space, while maintaining your index finger at the 2-3 cm mark on the kelly clamp
remove finger, spread incision site, replace finger, retract kelly clamp, confirm placement in the chest cavity with finger
clamp the distal end of the chest tube with the kelly clamp, the blunt end of the kelly clamp is extended past the distal end of the chest tube
Size = ETT size x 4
Suture in place
connect heimlich valve
reassess
Flail Chest
paradoxical movement
respiratory distress
tachypnea
grunting
accessory muscle use
chest pain
Tx:
self-splinting
intubation
placed injured site down
be aggressive w/ pain management
Pelvic Trauma
stable
unstable
ant/post compression
lateral compression
vertical shear (often fatal)
disrupted pelvis can hold 4000 cc or 80% of blood volume
Tx:
compression of pelvis (pelvic binder)
check for blood @ the meatus
have them lift their leg up
can do it = no pelvic fracture
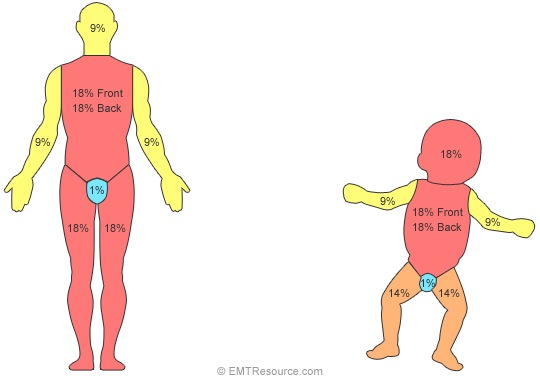
Rule of 9s
Escharotomy
gently run scalpel across skin in ‘w’ pattern across chest
skin will ‘pop’
patient will not feel this and no bleeding
kg x TBSA x 4 mL
Parkland Formula
½ of it
How much of the parkland formula should be given within the first 8 hours?
all of it
How much of the Parkland formula should be given within 24 hours?
0.5 mL/kg adults and 1 mL/kg Peds
What is the target urine output for a burn patient?
Phase 1: 0-36 hours
electrolyte imbalance after burns
hyponatremia & hyperkalemia
intravascular loss
increased vascular permeability
cellular edema
interstitial osmotic pressure increase
Phase 2: 3-7 days
electrolyte imbalance after burns
hypernatremia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, hypomagnesmia, & hypocalcemia
reabsorption of cellular edema
urinary retention - stimulation of ADH
Rhabdomyolysis
extensive muscle damage often causes myoglobinuria
if left untreated, results in acute tubular necrosis & renal failure
Tx:
fluid! fluid! MORE fluid!
monitor urine output (1-2 mL/kg/hr)
NaHCO3- to alkalinize the urine
mannitol
diuretic (lasix)
Damage control resuscitation
-concept of treating hemorrhagic shock
-early transfusion of PRBCs, plasma, and platelets (1:1:1) or whole blood
-restricting crystalloids to a SBP of 90-100
-while also preventing/correcting hypothermia and coagulopathy
Linear
Most skull fractures are:
Diastatic Skull fracture
separation of the bones at the suture line or a marked separation of bone fragments
facial fractures play a role in this
Basilar Skull Fracture
-occurs from direct injury to the base of the skull and/or extension of fractures of the calvaria
-s/s:
Battle sign
hemotypanum
CSF leaking from the nose or ears
raccoon eyes (1-2 days after injury)
Pneumocephalus
-air in the cranial vault
-think of how this affects the patient during flight due to Boyle’s law
Subdural Hematoma
collection of blood in the potential space between the arachnoid mater and the dura mater
crescent shaped appearance on the CT
acute = high morbidity and mortality
often associated with cerebral contusion and edema
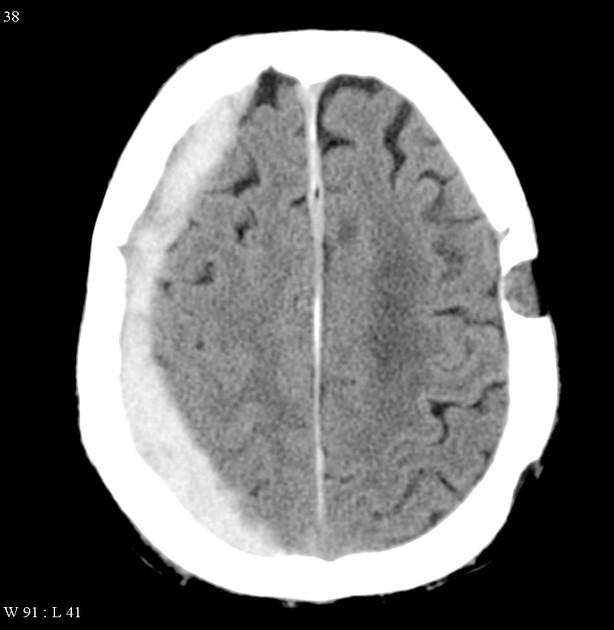
Epidural Hematoma
-collection of blood between the skull and the outer layer of the dura
-often caused by disruption of the branch of the middle meningeal artery
s/s:
transient LOC
recovery with lucid period
secondary onset of headache
decreasing LOC again
maybe fully unconscious or never unconscious
Peds: only warning may be bradycardia or early papilledema
dilation of ipsilateral pupil
Cheyne-stokes respirations
bradycardia
death
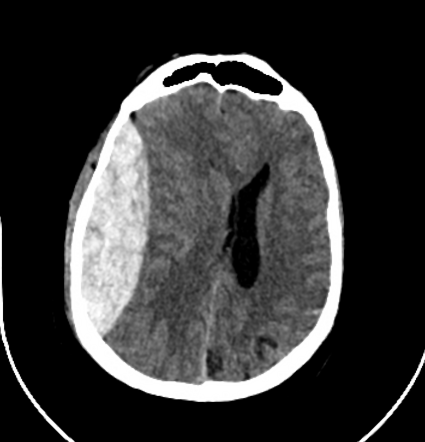
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
-blood collecting between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater
-identified in 30-40% of TBIs
-increased risk for seizures and cerebral vasospasm
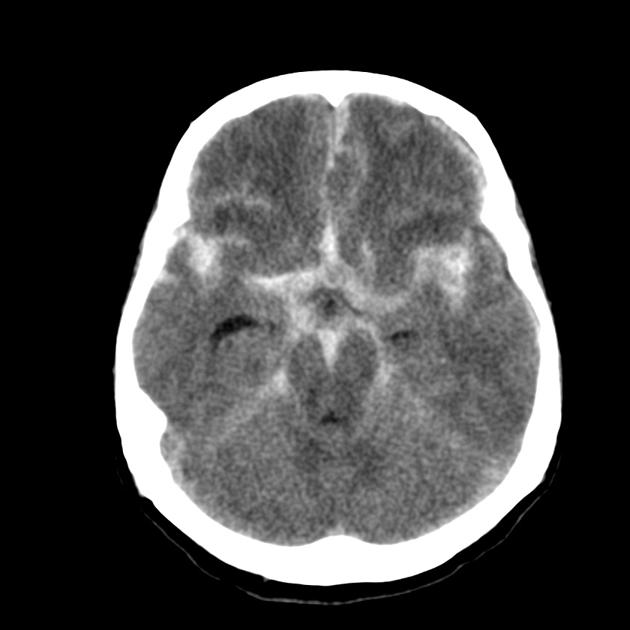
Diffuse Axonal Injuries
occurs when the delicate axons of the brain are stretched and damaged as a result of rapid movement of the brain
multiple neurological deficits
range from headache to respiratory compromise
HIGH mortality rate
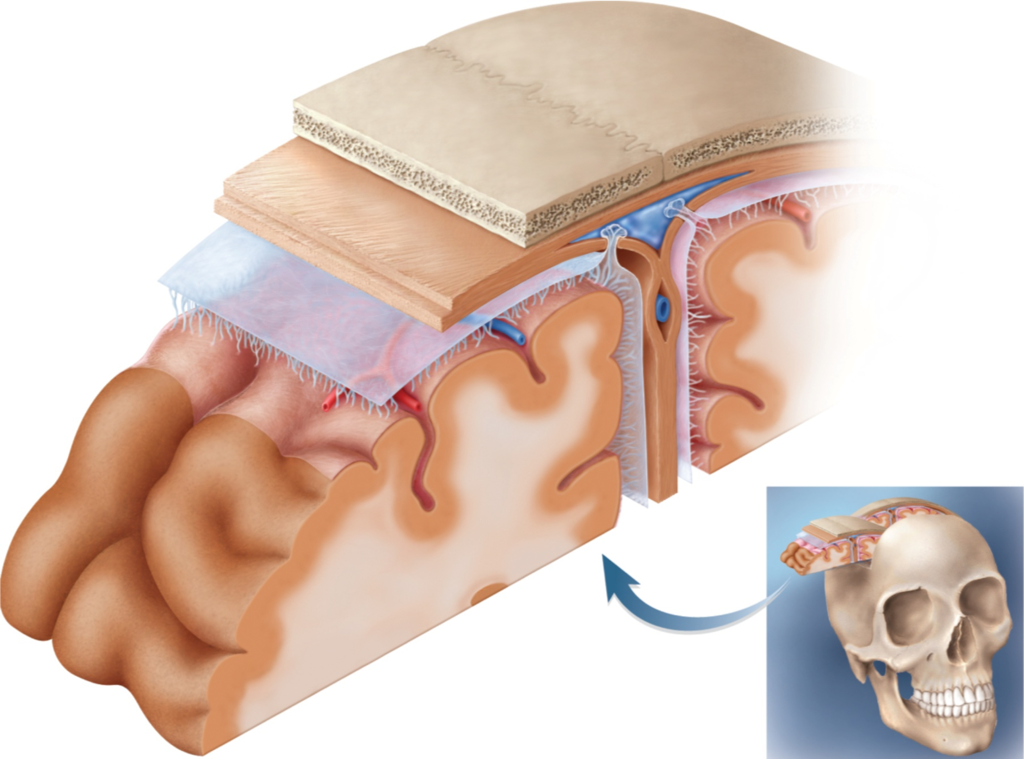
dura mater, subdural space, arachnoid mater, subarachnoid space, pia mater
Name the layers of the brain starting from the skull down