Chapter 13: Sexual Problems and Therapy
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:01 PM on 5/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
Individual Differences and Relationship Conflicts - Expectations for Men
goal-oriented
2
New cards
Individual Differences and Relationship Conflicts - Expectations for Women
partner-oriented
3
New cards
with masturbation, men use ___ approach while women use ---
1 approach
different techniques
different techniques
4
New cards
Relationship conflicts
Many couples (50%) have had, or eventually will have, sexual problems at some time in their relationship
5
New cards
Relationship solutions
\
* Working together and talking about differences
* Choosing properly trained and certified Marriage and Family Therapist
* Working together and talking about differences
* Choosing properly trained and certified Marriage and Family Therapist
6
New cards
Sexual Therapy Techniques - Medical History
possible organic causes
7
New cards
Sexual Therapy Techniques - Sexual History
attitudes, behaviors, and partner reactions and involvement
8
New cards
Four types of sexual therapy
1. psychoanalysis
2. medical model
3. cognitive-behavior therapy
4. biopsychosocial approach
9
New cards
Psychoanalysis therapy
Long-term, intensive exploration of childhood causes for adult problems. Not commonly used today.
10
New cards
cognitive-behavioral therapy
Short-term, focusing on attitudes, beliefs and how they affect our behaviors.
11
New cards
psychosexual therapy
Insight into causes of the problems; successful with sexual aversion and low sexual desire.
12
New cards
medical model therapy
Looking for and treating organic causes for sexual problems
13
New cards
Sexuality __educator__
Teaches and trains about a range of topics related to sexual health, anatomy, etc
14
New cards
Sexuality __counselor__
Variety of professions ranging from medicine to clergy
15
New cards
sex __therapist__
Licensed mental health professions
16
New cards
ICD-10 Sexual Disorder
a clinically recognizable set of symptoms or behavior associated ... with distress and with interference with personal functions
17
New cards
APA Sexual Disorder
A heterogeneous group of disorders that are typically characterized by a clinically significant disturbance in a person’s ability to respond sexually or to experience sexual pleasure
18
New cards
Sexual problem criteria
1. one time occurrence
2. stress of life
3. common
4. most have problem at some point
5. problem with firsts
6. communication can help if it’s couple-related
19
New cards
Sexual disorder criteria
1. if the individual considers it to be one
2. some amounts of time (usually at least 6 months)
3. not the result of some other personal or interpersonal problem (depression)
4. issue occurs majority of the time
20
New cards
two views of dysfunction
1. medical
2. psychological
21
New cards
According to the DSM-5, Male Erectile Disorder will manifest at least one of three symptoms 75% to 100% of the time during sexual activity:
* Marked difficulty in obtaining an erection during sexual activity
* Marked difficulty in maintaining an erection until the completion of sexual activity
* Marked decrease in erection rigidity
* Persisted for approximately at least 6 months
* Cause clinically significant distress in the individual
* Marked difficulty in maintaining an erection until the completion of sexual activity
* Marked decrease in erection rigidity
* Persisted for approximately at least 6 months
* Cause clinically significant distress in the individual
22
New cards
Medicalization of sexuality with viagra
originally used to treat heart issues, realized giving erection, now used for ED
23
New cards
sexual health
* a state of physical, emotional, mental, and social well-being in relation to sexuality
* positive and respectful approach to sexuality
* free from coercion, discrimination, and violence
* positive and respectful approach to sexuality
* free from coercion, discrimination, and violence
24
New cards
feelings toward ___ can affect sexual health
* body
* sexual anatomy
* expression of sexual feelings
* orgasm
* masturbation
* sexual intercourse
* desire, arousal
* sexual anatomy
* expression of sexual feelings
* orgasm
* masturbation
* sexual intercourse
* desire, arousal
25
New cards
Sexual problems you have heard from college students - ==Women==
1. hard time orgasming
2. pain - lack of lubrication
3. inexperience
26
New cards
Sexual problems you have heard from college students - ^^Men^^
1. Ejaculating too quickly - No lube
2. Inexperienced
3. No clit knowledge
4. No condom knowledge
5. Alcohol and erections
6. Erection
27
New cards
Sexual disorders in ^^men^^
1. hypoactive sexual desire
2. erectile disorder
3. premature ejaculation
4. male orgasmic disorder
5. sexual pain disorder
28
New cards
Sexual disorders in ==women==
1. Female Sexual Interest/Arousal Disorder
2. Female Orgasmic Disorder
3. Sexual Pain Disorders
29
New cards
causes of sexual disorders
1. organic/medical
2. psychological
3. sociocultural (relationship)
30
New cards
hypoactive sexual desire (lack of interest for 6 months)
1. primary: never had sexual interest
2. secondary or acquired
\
* **causes**: organic (low T) or psychological (more common)
* **treatment**: common reason for entering therapy but difficult to treat
* medical vs biopsychosocial model
31
New cards
Causes of erectile dysfunction
1. 80% are physical, do REM sleep test
1. circulatory problems, neurological disorders, prostrate surgery, low T, groin injuries
2. 25% due to medications prescribed for other conditions (antidepressants and beta-blockers)
3. Smokers and drinkers
4. being overweight
32
New cards
What is erectile dysfunction?
* persistent or recurrent inability to get or maintain erection adequate for satisfactory sexual performance
* APA diagnostic criteria includes persistent (6months or more), causing distress or interpersonal relationship problems
* APA diagnostic criteria includes persistent (6months or more), causing distress or interpersonal relationship problems
33
New cards
nocturnal penile tumescence test
* measures force and duration
* several nights
* several nights
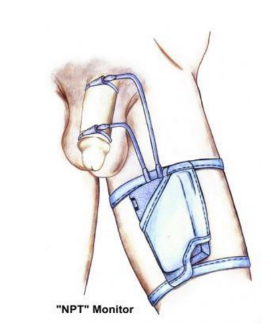
34
New cards
sensate focus
* non-demand mutual pleasure technique
* couple learns how to touch and be touched
* without worrying about performing or reaching a goal
* couple learns how to touch and be touched
* without worrying about performing or reaching a goal

35
New cards
premature ejaculation
* Absence of reasonable voluntary control of ejaculation resulting in personal distress
* Organic or psychological causes
* Organic or psychological causes
36
New cards
solutions to premature ejaculation
1. masturbating several hours before intercourse
2. pause-squeeze technique
3. pelvic floor exercises
4. condoms or analgesic cream to reduce stimulation
5. other medications
6. counseling
37
New cards
male orgasmic disorder
* delay or absence of orgasm following what is typically a normal sexual excitation phase
* most common causes are psychological (fear, guilt, etc.)
* most common causes are psychological (fear, guilt, etc.)
38
New cards
bridge manuever
man masturbates alone and w/partner; partner stimulates to orgasm then quickly puts penis into vagina
39
New cards
dyspareunia
* infections
* peyronie’s disease
* peyronie’s disease
40
New cards
priapism
prolonged erection
41
New cards
benign coital cephalalgia
sex headache at start/after orgasm, usually in men
42
New cards
Four categories of sexual problems in ==women==
1. sociocultural, political, economic factors
2. partner and relationship factors
3. psychological factors
4. medical factors
43
New cards
sexual interest/arousal disorder (most common for women)
* persistent or recurrent deficiency of sexual fantasies/thoughts and/or desire for or receptivity to sexual activity, which causes personal distress
* 1/3 women
* 1/3 women
44
New cards
sexual aversion disorder
* more severe
* not in DSM-5
* not in DSM-5
45
New cards
psychological and/or organic causes (women)
Sexually repressive upbringing, past sexual traumas, depression, some medications (esp. antidepressants), low testosterone (not common),coexisting sexual problem (such as painful coitus)
46
New cards
relationship issues (women)
Betrayal, dislike, fear of partner, partner’s abuse, partner’s negative patterns of communication, insufficient emotional intimacy
47
New cards
Treatments for desire
* most difficult to treat and lowest success rate
* self-help
* communication, sex goals, novelty, non-sexual intimacy
* self-help
* communication, sex goals, novelty, non-sexual intimacy
48
New cards
self-expansion
* broadening sense of self with your partner
* engaging in new activity (going to a lecture, new site, exploring something new)
* engaging in new activity (going to a lecture, new site, exploring something new)
49
New cards
persistent sexual arousal disorder
* Characterized by unrelenting, spontaneous, and uncontainable genital arousal, mostly in females.
* Can experience spontaneous orgasms that do not resolve arousal. The person's arousal is not linked to sexual desire.
* Can lead to on going physical pain, stress, and psychological difficulties due to an inability to carry out everyday tasks.
* Sexual syndrome that takes joy out of life
* Can experience spontaneous orgasms that do not resolve arousal. The person's arousal is not linked to sexual desire.
* Can lead to on going physical pain, stress, and psychological difficulties due to an inability to carry out everyday tasks.
* Sexual syndrome that takes joy out of life
50
New cards
Female orgasmic disorder
* persistent or recurrent inability of a woman to have an orgasm (climax or sexual release) after adequate sexual arousal, and sexual stimulation, which causes personal distress
* Associated with older women, less assertive women, can be primary, secondary, or situational (partner-or action based)
* Only half of women are distressed by failure to orgasm
* Associated with older women, less assertive women, can be primary, secondary, or situational (partner-or action based)
* Only half of women are distressed by failure to orgasm
51
New cards
genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorders
1. dyspareunia (pain during sex)
2. vaginismus (involuntary spasms of muscles surrounding vagina cause full/partial closure)
3. noncoital pain disorder
52
New cards
postcoital dysphoria
* sadness, irritability, and anxiety after sex
* 33% women, 12-34% men
* 33% women, 12-34% men
53
New cards
Cross-cultural perspectives on sexual therapy
* western, middle-class values
* sex for physical pleasure
* men and women are equal partners
* sex for physical pleasure
* men and women are equal partners
54
New cards
Northern Africa and Middle East sexual attitudes
restrictive, patriarchal, sexual attitudes
55
New cards
Latin countries sexual attitudes
male-oriented sexual regimehi
56
New cards
Hindu and Buddhist sexual attitudes
emphasize unity, harmony, and spiritual growth
57
New cards
female genital mutilation
* any procedure involving partial removal or total removal or deliberate injury to the female genitals for non-medial reasons
* NO HEALTH BENEFITS
* CULTUAL CUSTOM based on limiting female sexual behavior
* illegal in the US still routinely performed in some African countries
* NO HEALTH BENEFITS
* CULTUAL CUSTOM based on limiting female sexual behavior
* illegal in the US still routinely performed in some African countries
58
New cards
Where does FGM occur?
* 300 million women
* 0-4 years, almost always before 15 years
* 1/2 population live in Indonesia, Egypt, and Ethiopia
* 84.5% report complications
* 0-4 years, almost always before 15 years
* 1/2 population live in Indonesia, Egypt, and Ethiopia
* 84.5% report complications
59
New cards
hypersexuality
* No DSM-5 category
* Sexual compulsion aka sexual addiction
* Recurrent failure to control the behavior and/or continuation of behavior despite significant harmful consequences
* Engage in sex (or masturbation) compulsively to reduce anxiety; usually finding little or no emotional satisfaction
* Sexual compulsion aka sexual addiction
* Recurrent failure to control the behavior and/or continuation of behavior despite significant harmful consequences
* Engage in sex (or masturbation) compulsively to reduce anxiety; usually finding little or no emotional satisfaction
60
New cards
compulsive sexual behavior
* a disorder in which the individual experiences intense sexually arousing fantasies, urges, and associated sexual behavior
* Not in DSM – 5
* 3-5% - hypersexuality
* 3% - 20 or more hours per week online sex
* ICD – 11 (International Classification of Diseases)
* Classified as an impulse control behavior like gambling and kleptomania
* Not in DSM – 5
* 3-5% - hypersexuality
* 3% - 20 or more hours per week online sex
* ICD – 11 (International Classification of Diseases)
* Classified as an impulse control behavior like gambling and kleptomania
61
New cards
Types of treatment
* therapy
* cognitive behavioral therapy
* acceptance and commitment therapy
* medications
* support groups
* 12 step programs
* sex addicts anonymous
* sexaholics anonymous
* NoFap - online community
* cognitive behavioral therapy
* acceptance and commitment therapy
* medications
* support groups
* 12 step programs
* sex addicts anonymous
* sexaholics anonymous
* NoFap - online community
62
New cards
Porn addiction
* An addiction model of compulsive sexual activity with concurrent use of pornographic material, despite negative consequences to one's physical, mental, social, or financial well-being.
* Neither the DSM-5 nor the ICD-11 classify pornography as a mental disorder or addiction.
* Neither the DSM-5 nor the ICD-11 classify pornography as a mental disorder or addiction.
63
New cards
problematic internet pornography viewing
viewing of Internet pornography that is problematic for an individual due to personal or social reasons, including excessive time spent viewing pornography instead of interacting with others.
64
New cards
sexual dysfunction in younger men ( < 40Y)
* Sharp increase
* 10 – 20% organic
* More often psychological
* Increased rise in ED, orgasmic disorder, low sexual arousal
* Porn-Induced Erectile Dysfunction
* 10 – 20% organic
* More often psychological
* Increased rise in ED, orgasmic disorder, low sexual arousal
* Porn-Induced Erectile Dysfunction
65
New cards
gender differences in porn (==women==)
* often watch with partner
* watch soft porn; couples porn
* report higher levels of intimacy
* watch soft porn; couples porn
* report higher levels of intimacy
66
New cards
gender differences in porn (^^men^^)
* often watch alone
* watch sex acts without context
* report lower levels of intimacy
* watch sex acts without context
* report lower levels of intimacy
67
New cards
associative learning
* When a user has conditioned his sexual arousal to Internet pornography, sex with desired real partners may register as “not meeting expectations” (negative reward prediction) resulting in a corresponding decline in dopamine.
* Combined with the inability to click to more stimulation, this unmet prediction may reinforce an impression that partnered sex is less salient than Internet pornography use.
* It is possible that if a susceptible Internet pornography user reinforces the association between arousal and watching other people have sex on screens while he is highly aroused, his association between arousal and real-life partnered sexual encounters may weaken.
* Combined with the inability to click to more stimulation, this unmet prediction may reinforce an impression that partnered sex is less salient than Internet pornography use.
* It is possible that if a susceptible Internet pornography user reinforces the association between arousal and watching other people have sex on screens while he is highly aroused, his association between arousal and real-life partnered sexual encounters may weaken.
68
New cards
Treatments by Many Different Types of Professionals
* medical doctors
* family practitioners
* OB-GYNS
* psychotherapists
* marriage-family
* cognitive-behavioral
* sex therapists
* family practitioners
* OB-GYNS
* psychotherapists
* marriage-family
* cognitive-behavioral
* sex therapists
69
New cards
O-shot
* Marketed as the orgasm shot, or O-Shot, treatment involves injecting the clitoris, labia, and G-spot with platelets — a substance in your blood that contains healing proteins called growth factors —extracted from your own blood.
* There’s currently very little research on the O-Shot, and no scientifically proven evidence that it can improve your sex life.
* There’s currently very little research on the O-Shot, and no scientifically proven evidence that it can improve your sex life.
70
New cards
sex surrogate
* **A sex surrogate is a person who helps others over come social and sexual issues through hands-on intimacy**
* The surrogate engages with the client in a physical, intimate way to build their sexual confidence and make them more comfortable with emotional and physical intimacy
* The legal status of surrogate partners is undefined in most of the United States and most countries around the world, according to the IPSA. This means that there are generally no laws regulating the profession.
* The surrogate engages with the client in a physical, intimate way to build their sexual confidence and make them more comfortable with emotional and physical intimacy
* The legal status of surrogate partners is undefined in most of the United States and most countries around the world, according to the IPSA. This means that there are generally no laws regulating the profession.
71
New cards
sex surrogacy experiment
* (1985), director Kirby Dick weaves a fascinating study of the curious role of a sex surrogate in the then-new discipline of sexual therapy.
* Maureen Sullivan and two of her clients agreed to have the entire progression of their therapy taped.
* Newly divorced man
* 25 year old grad student
* Maureen Sullivan and two of her clients agreed to have the entire progression of their therapy taped.
* Newly divorced man
* 25 year old grad student