A&P Module 9: Diarthrosis
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
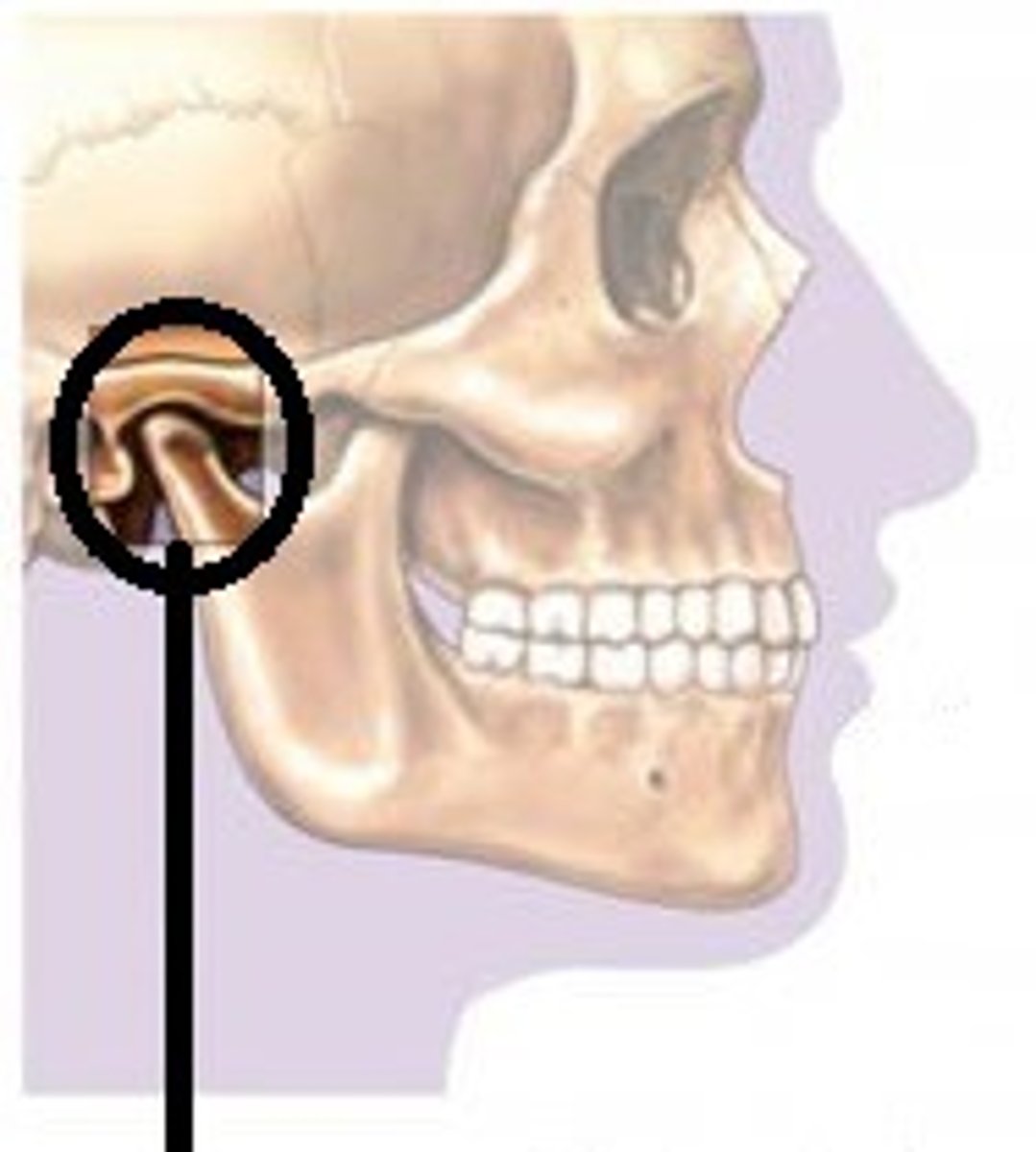
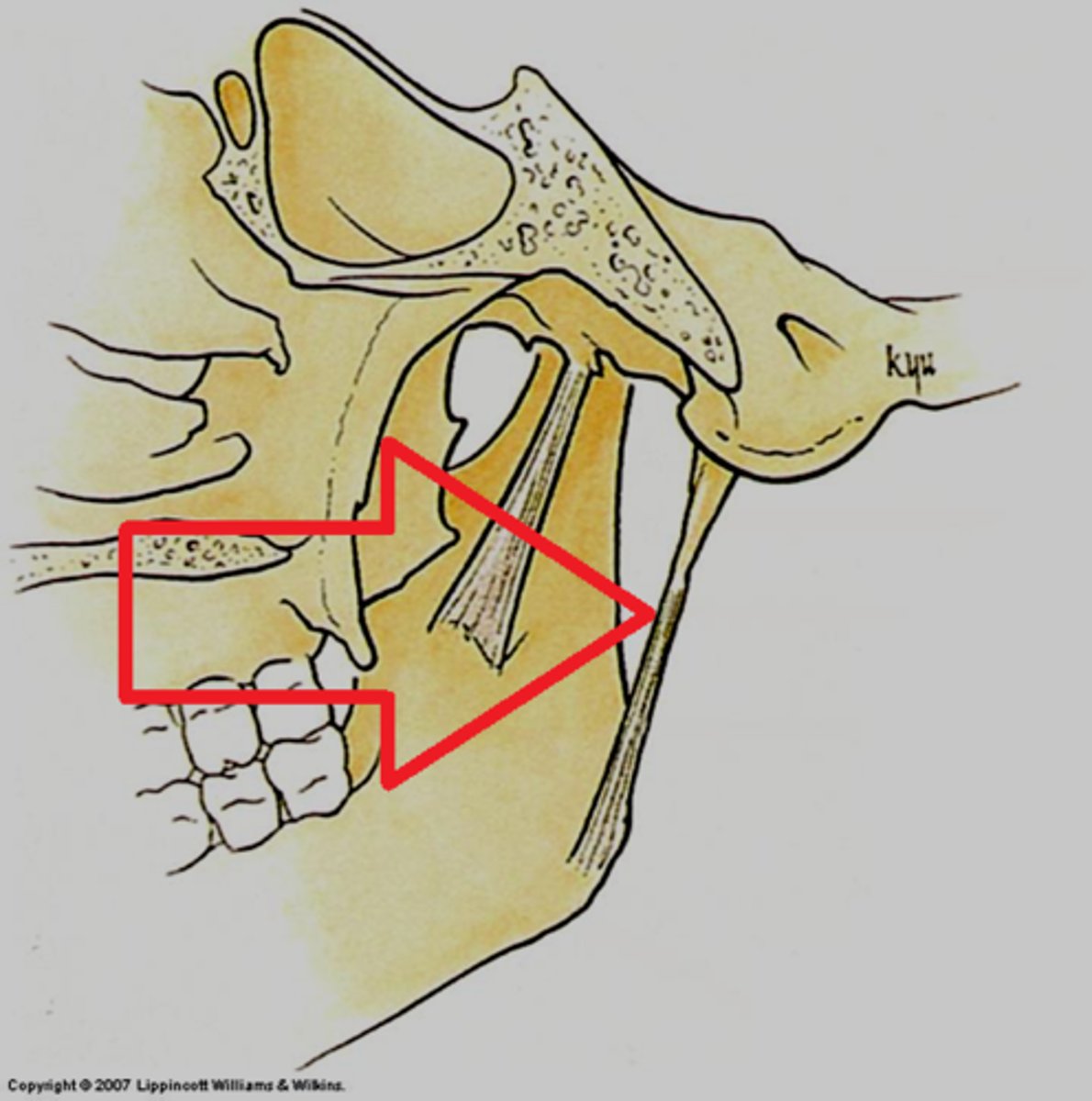
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
The articulation of the condyle of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone.
Lateral ligament of the mandible
Prevents posterior displacement of the mandible.
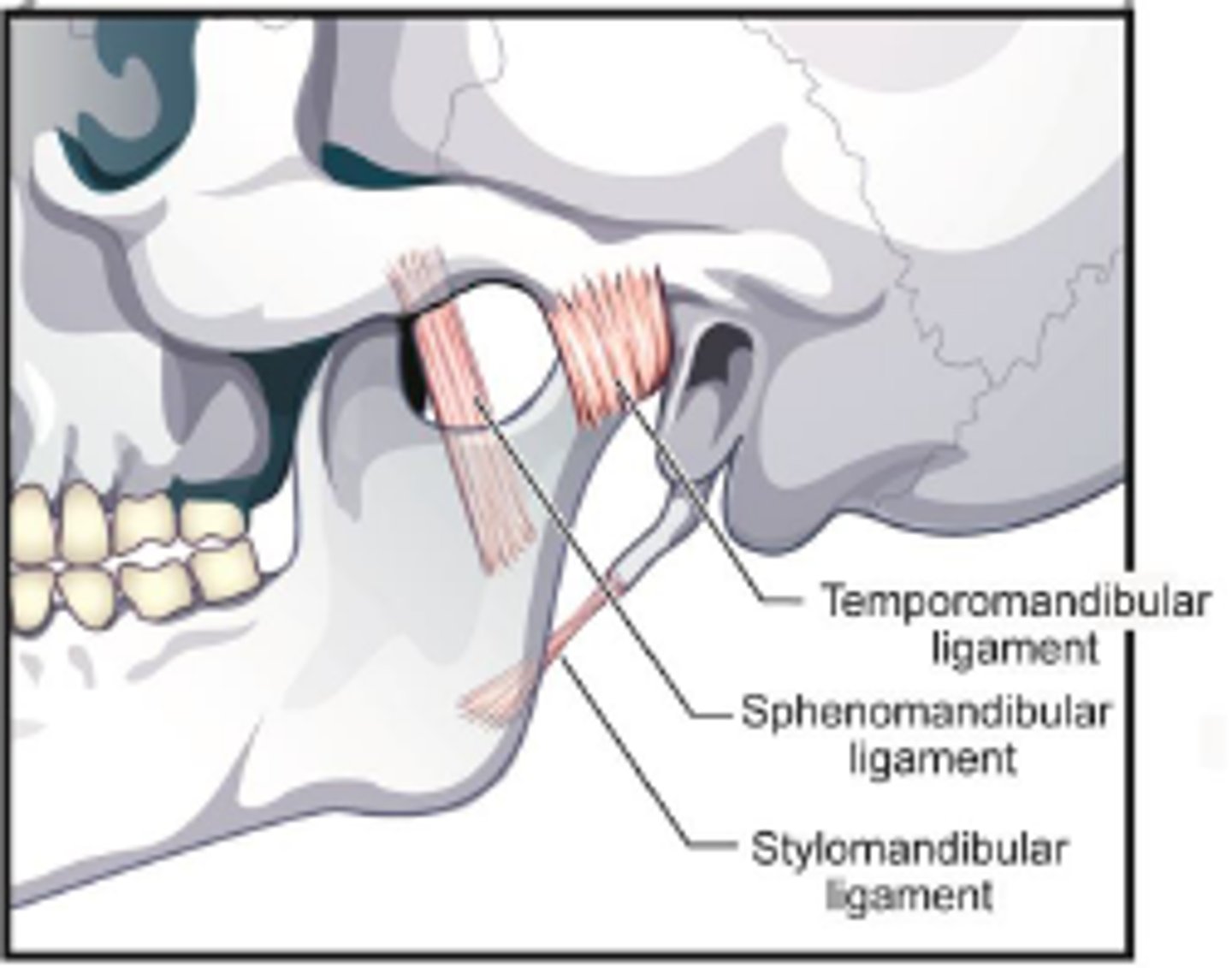
Sphenomandibular ligament
Ligament running from the sphenoid bone to the ramus of the mandible.
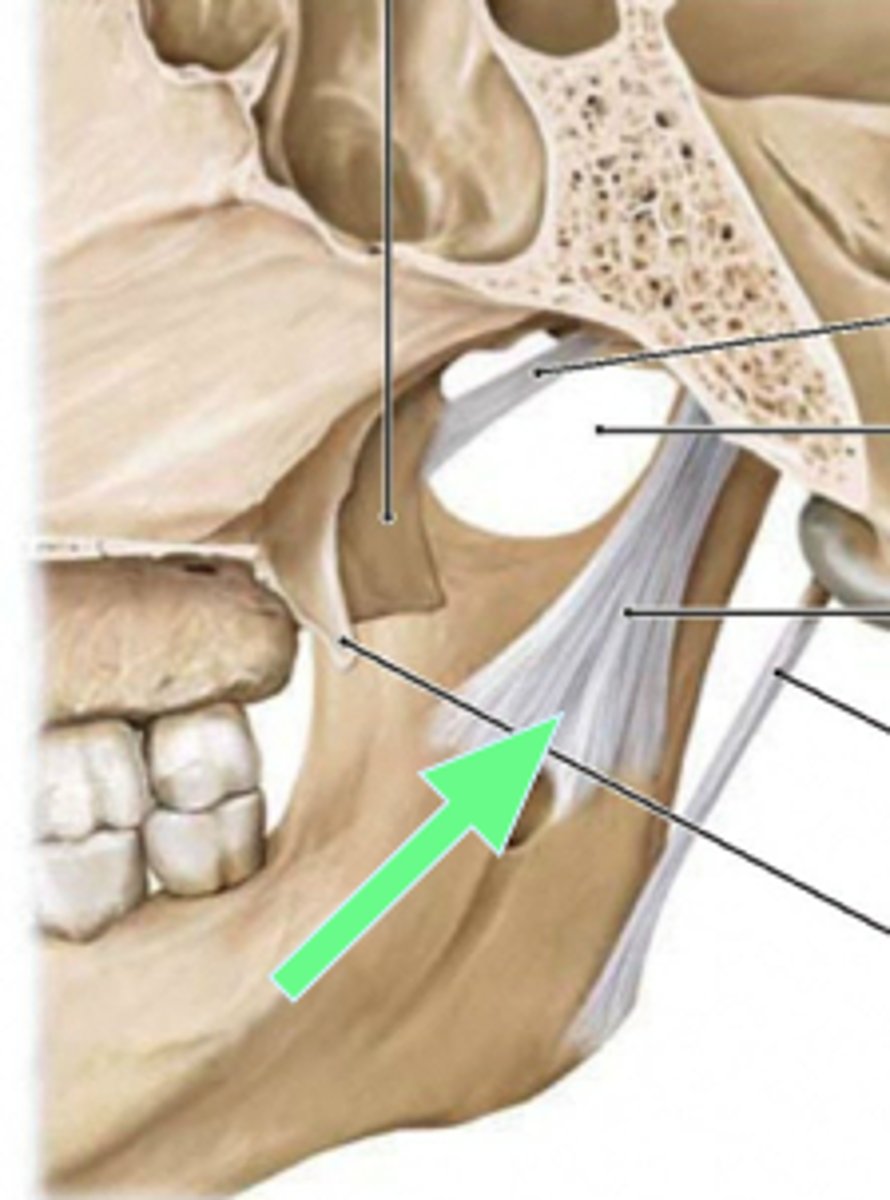
Stylomandibular ligament
Ligament running from the styloid process to the angle of the mandible.
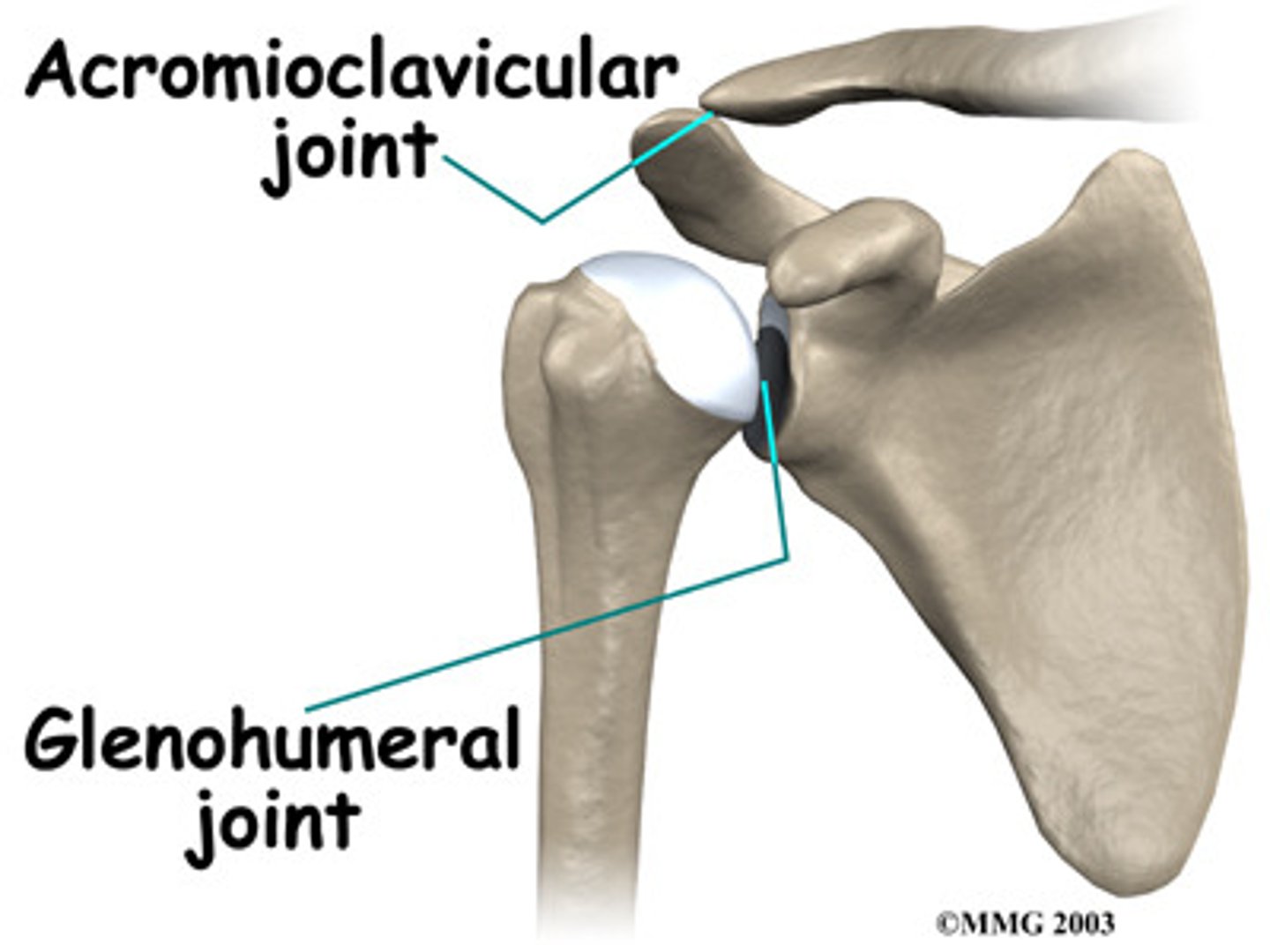
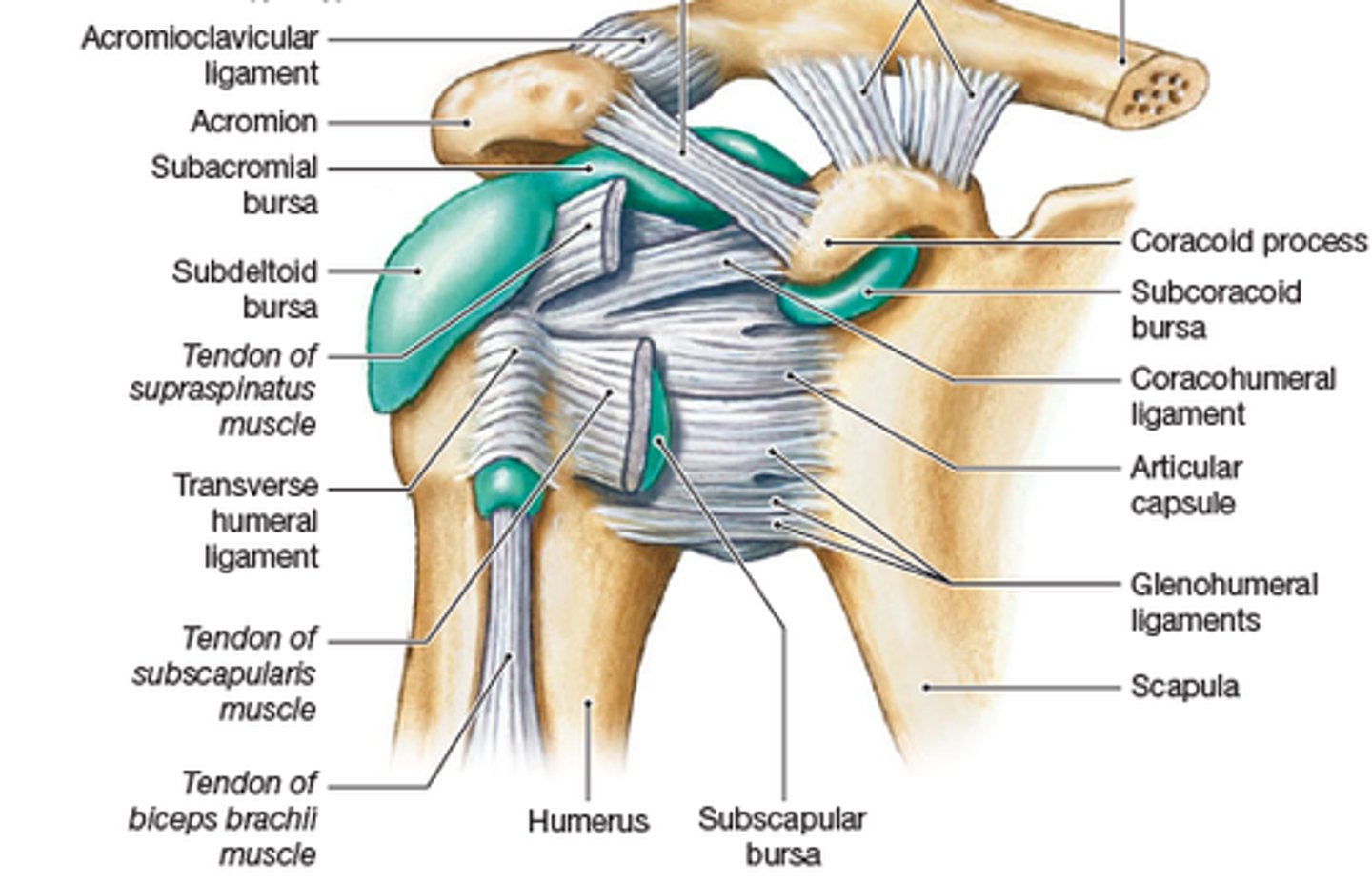
Glenohumeral joint
The synovial ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder; where the head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
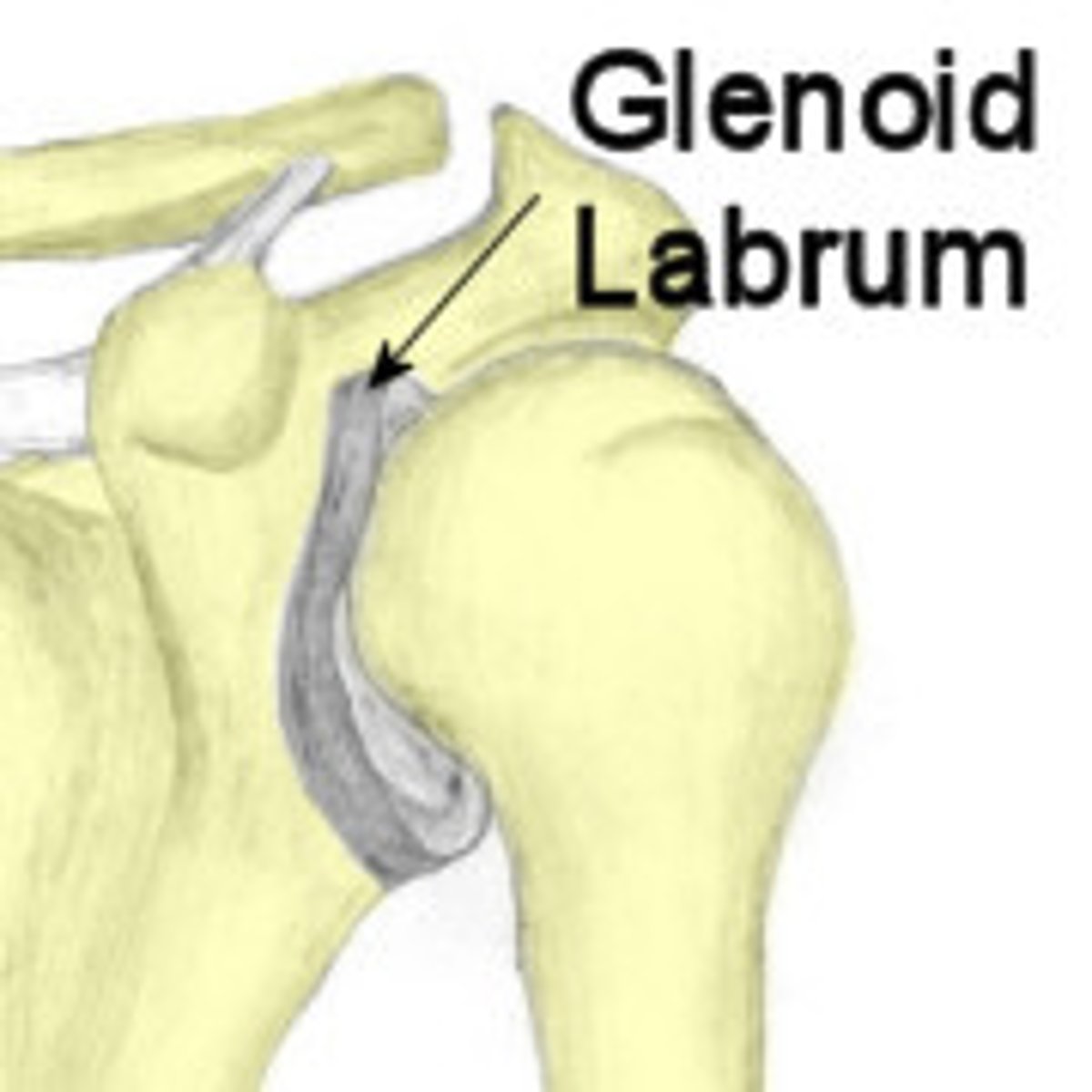
Glenoid labrum
A ring of cartilage attached to the margin of the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
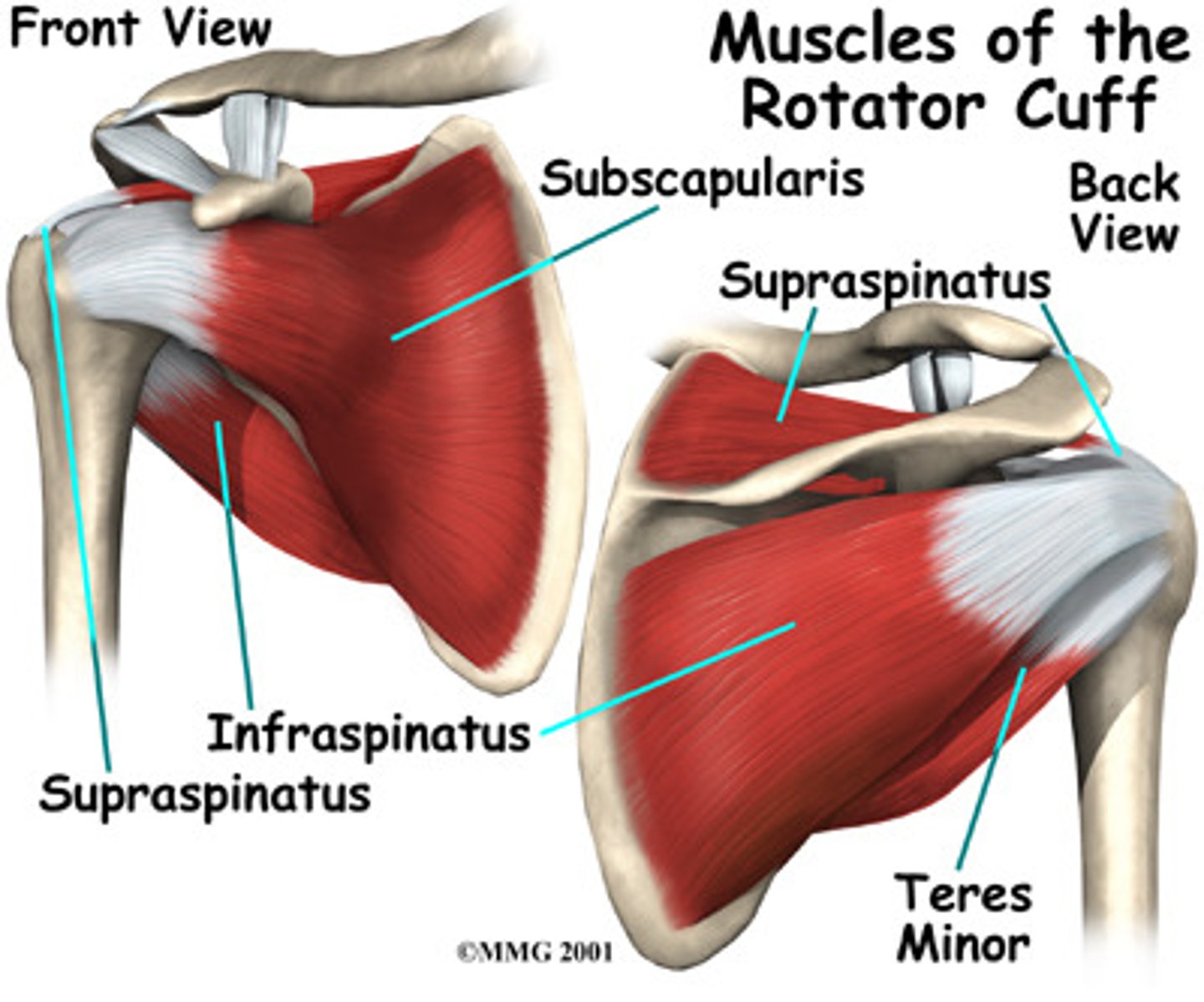
What is the function of the rotator cuff?
To hold the head of the humerus securely in place as it rotates within the shoulder joint
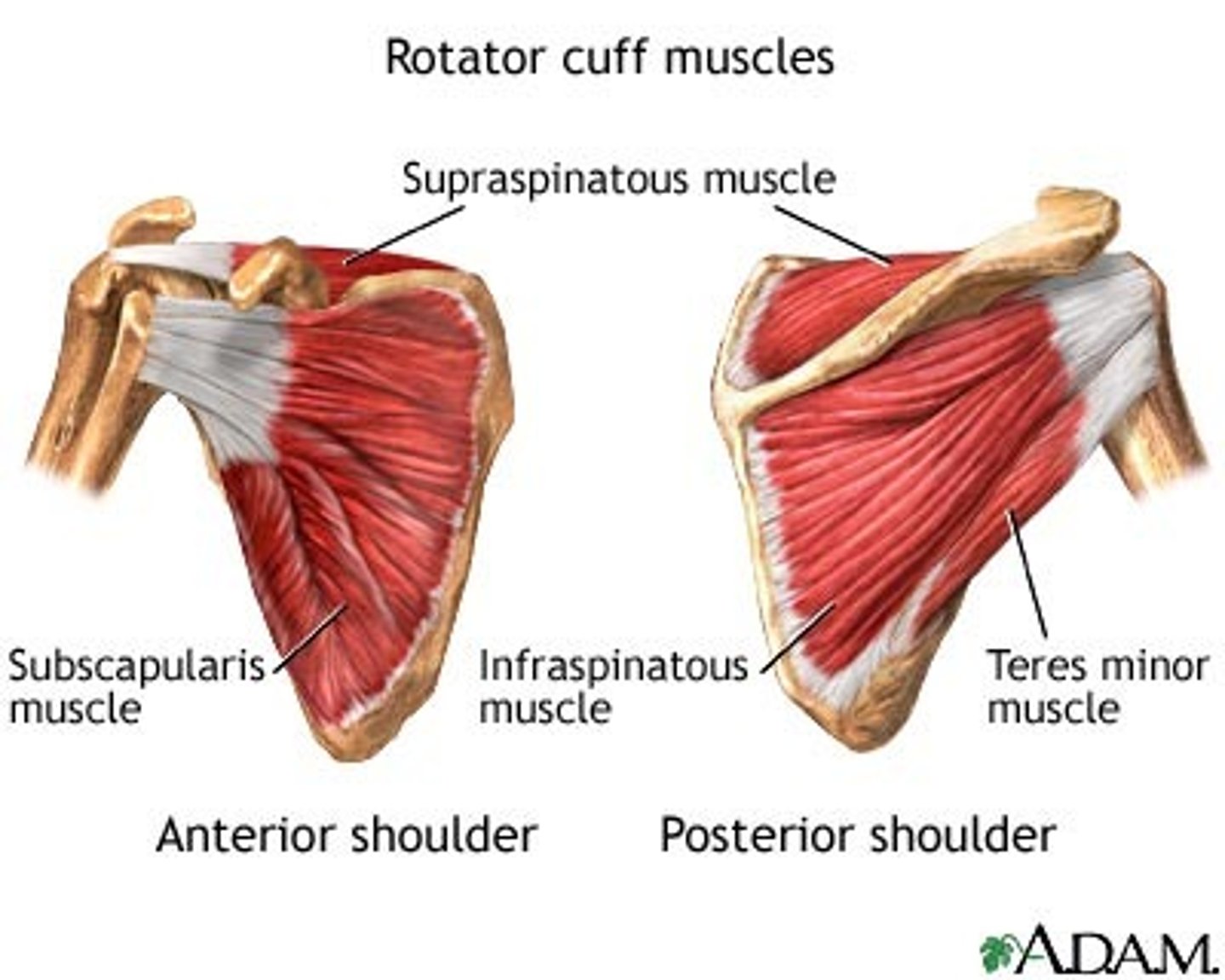
Name the muscles of the rotator cuff.
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis
Glenohumeral ligaments
Supports the shoulder joint; relatively weak and sometimes absent.
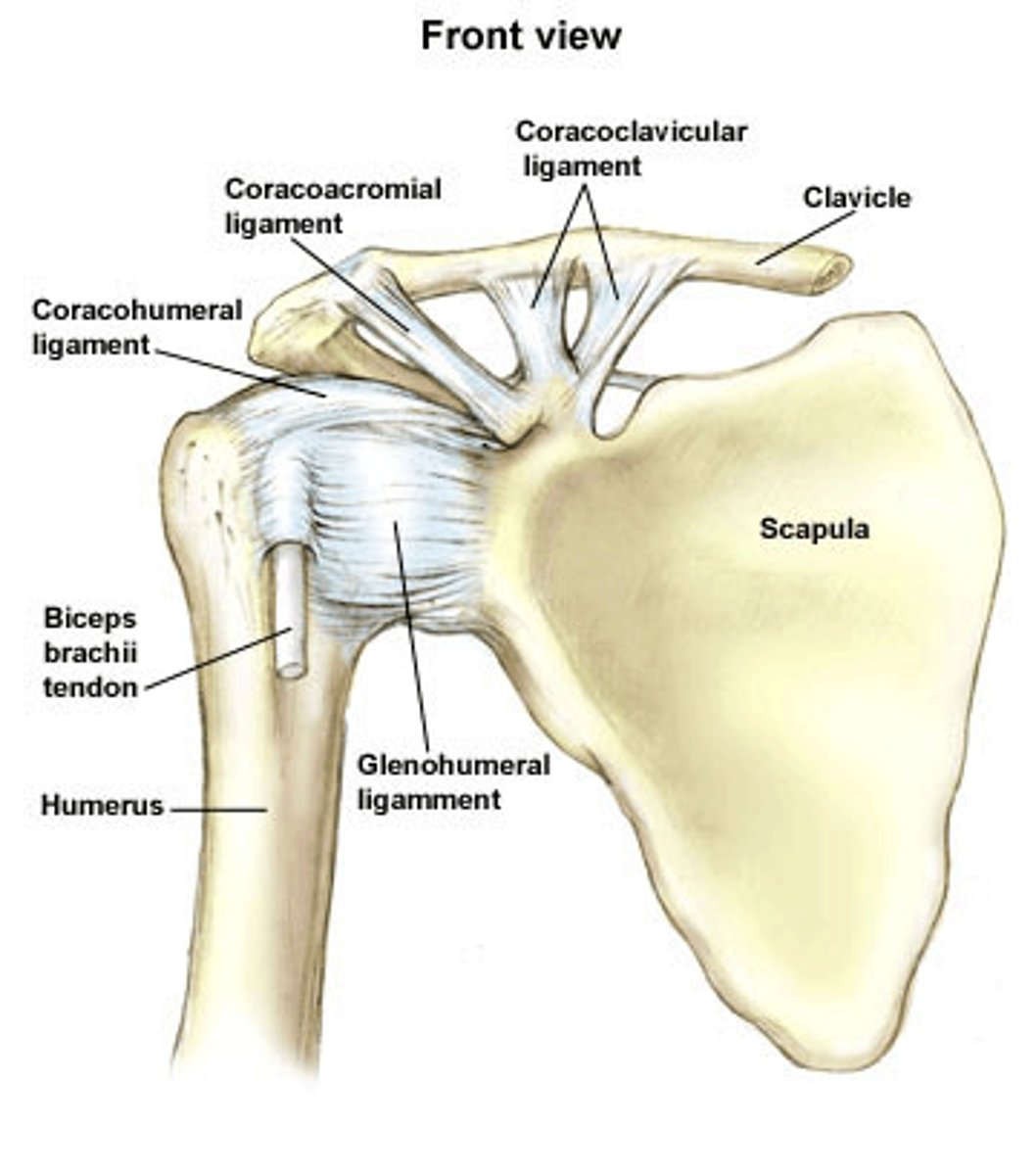
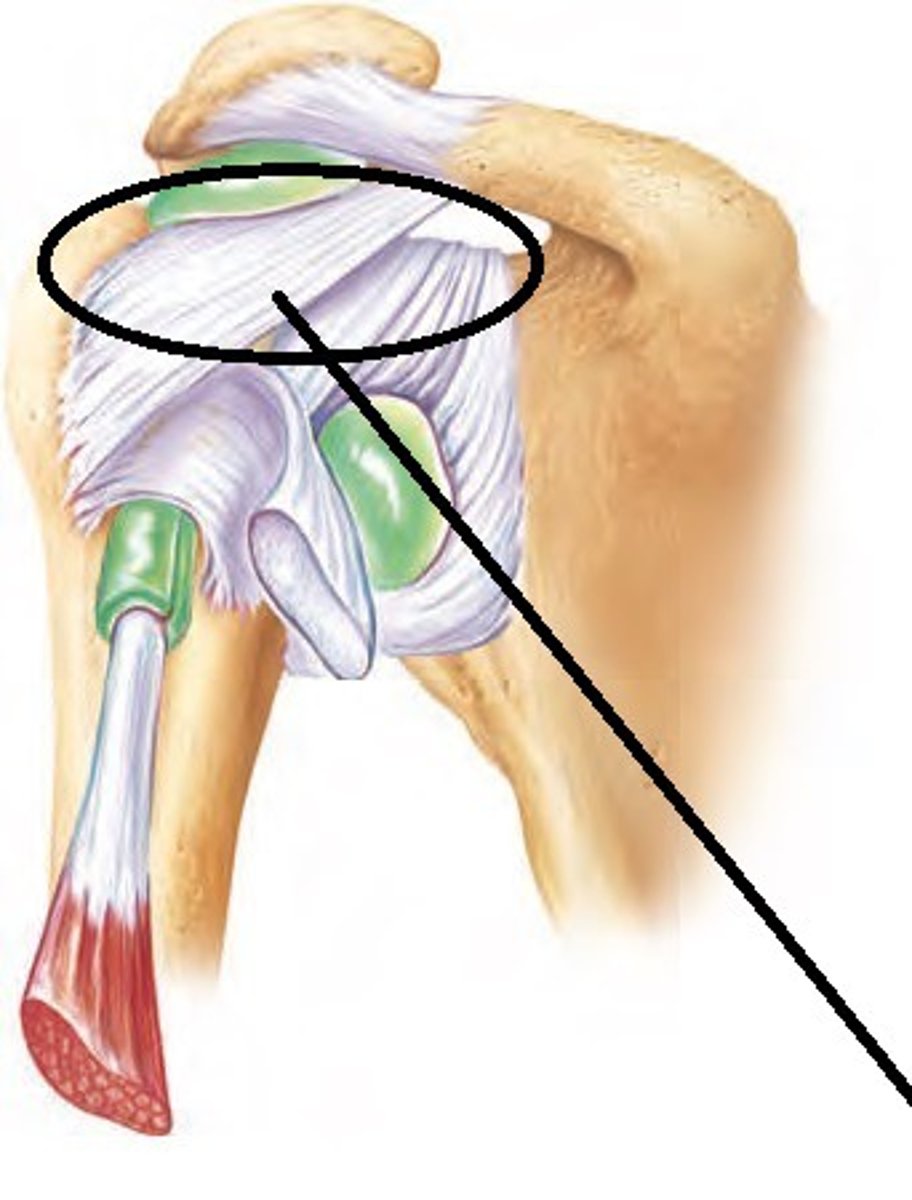
Coracohumeral ligament
Extends from the coracoid process of the scapula to the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Transverse humeral ligament
Extends from the greater to the lesser tubercle of the humerus and forms a tunnel housing the tendon from the long head of the biceps.
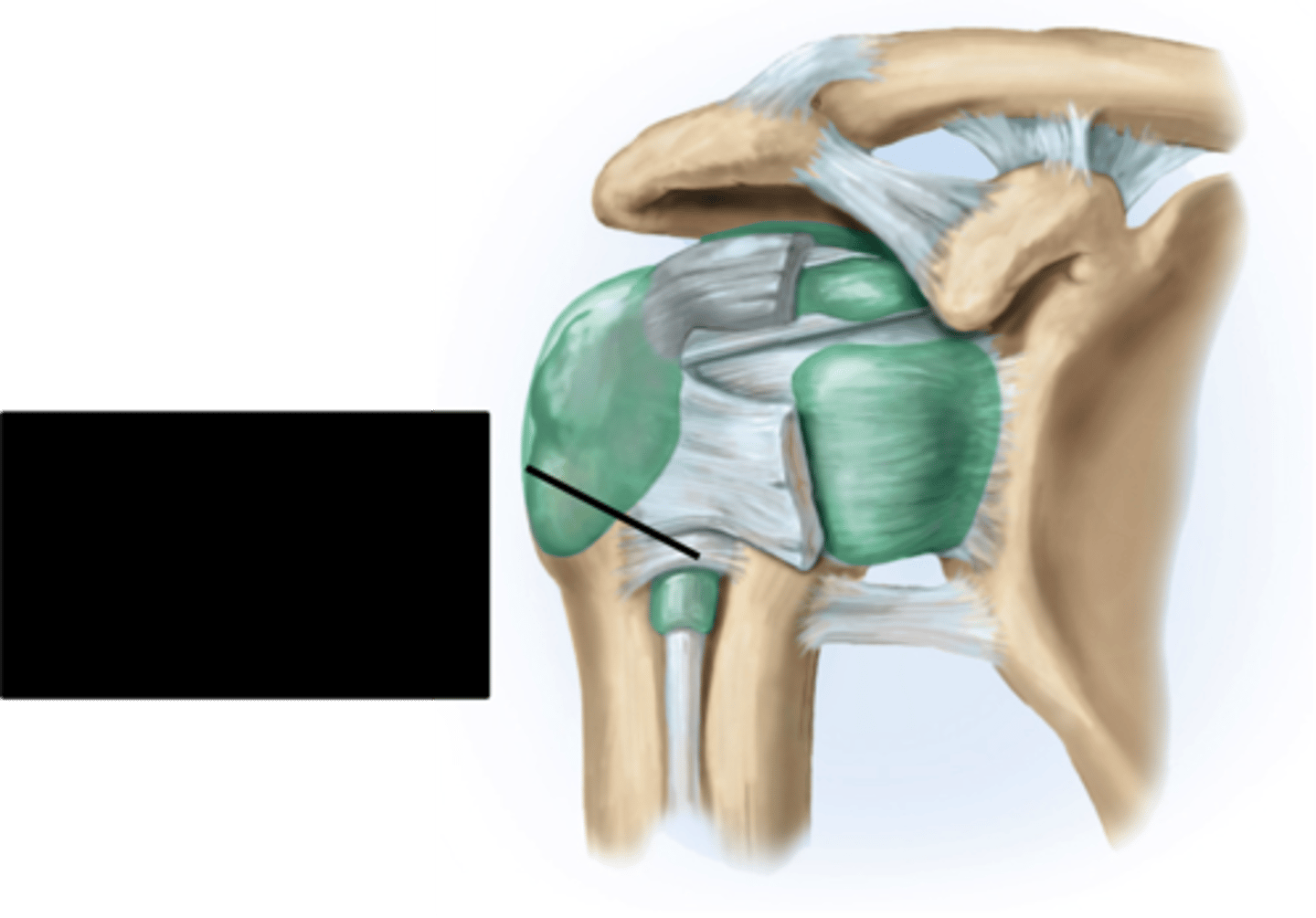
What are the four bursae at the shoulder?
Subdeltoid, subacromial, subcoracoid, and subscapular bursae.
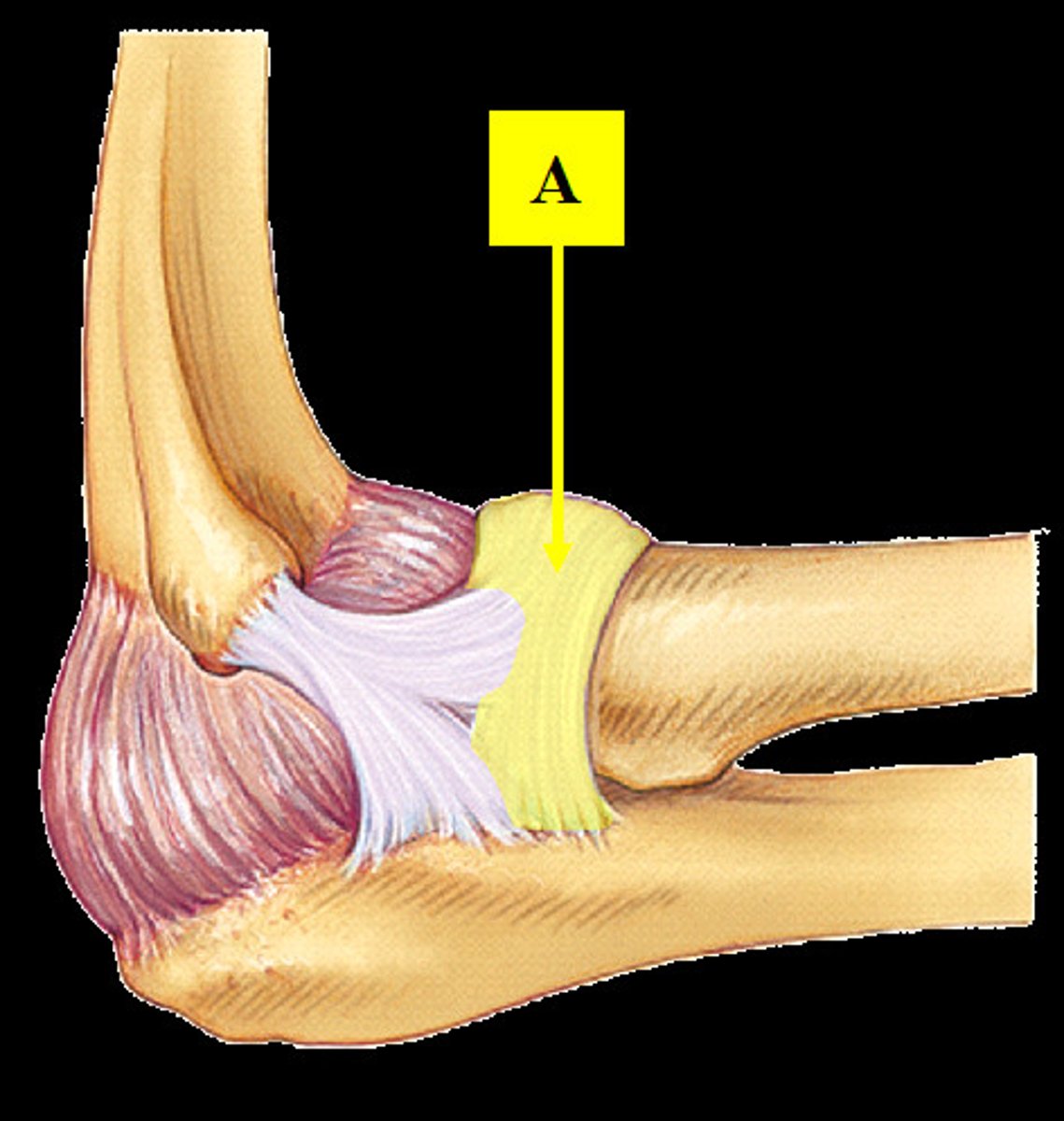
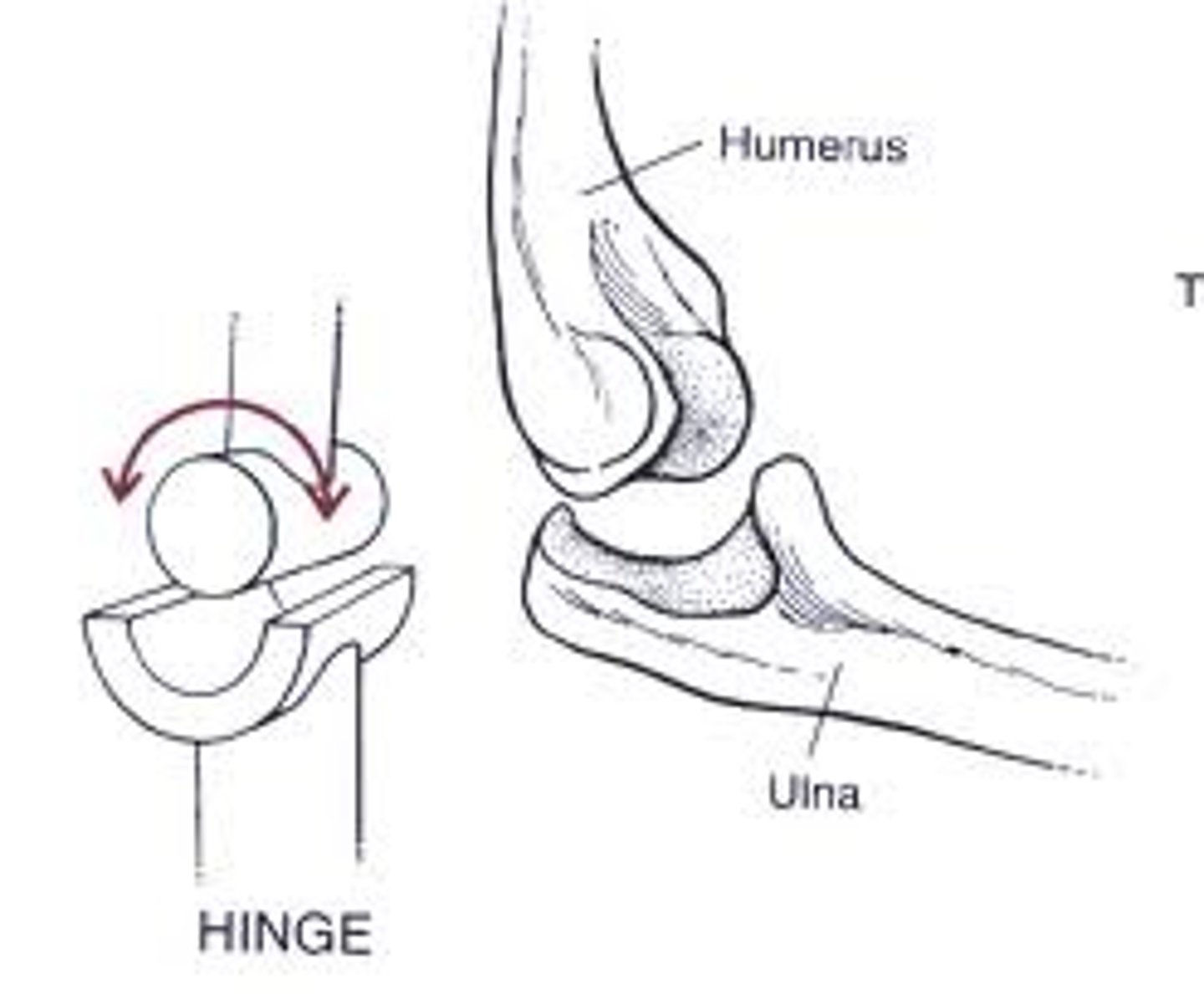
Humeroulnar joint
Makes up one of the two articulations of the elbow joint; where the trochlea of the humerus joins the trochlear notch of the ulna.
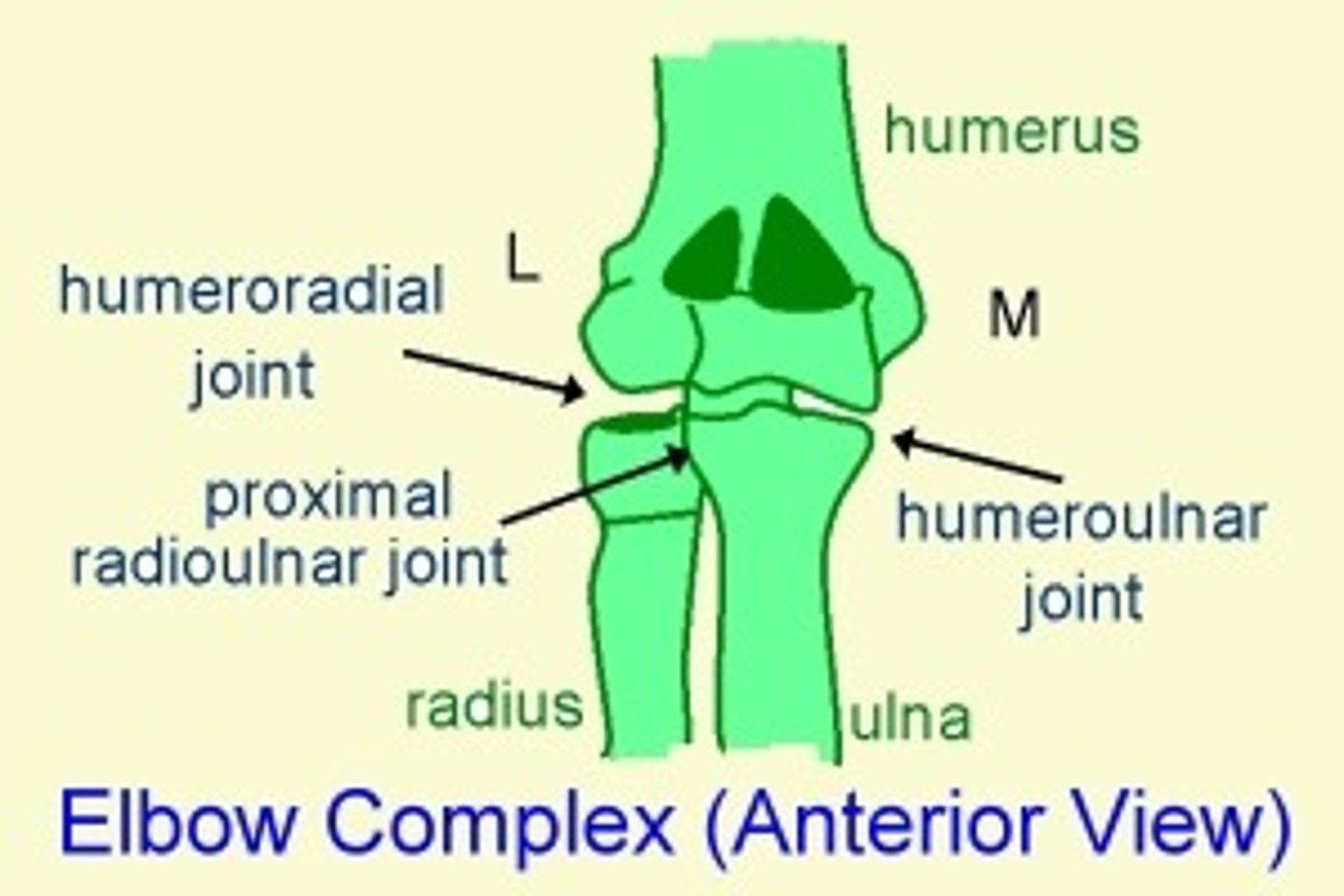
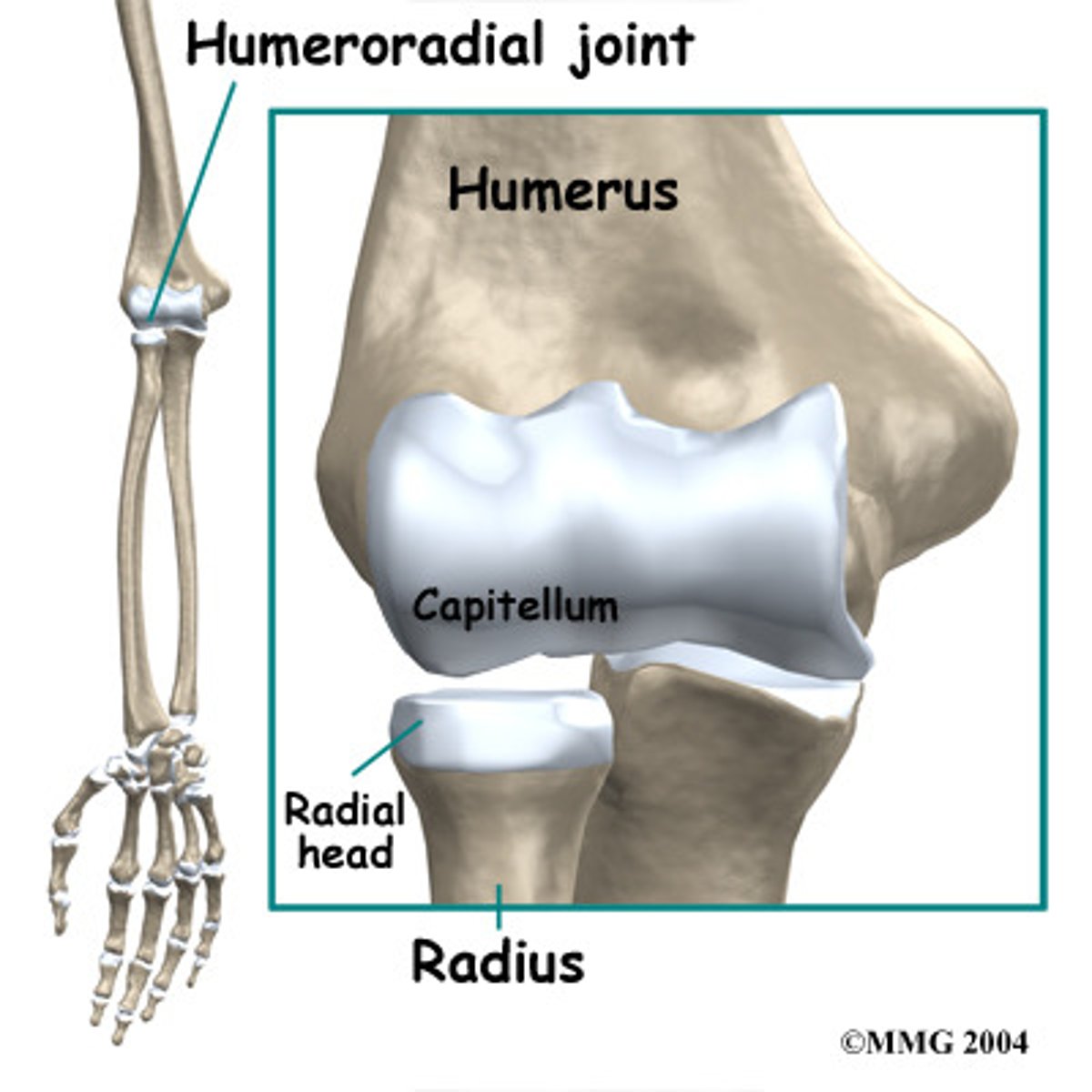
Humeroradial joint
Articulation between the capitulum of the humerus and head of the radius; makes up part of the elbow joint.
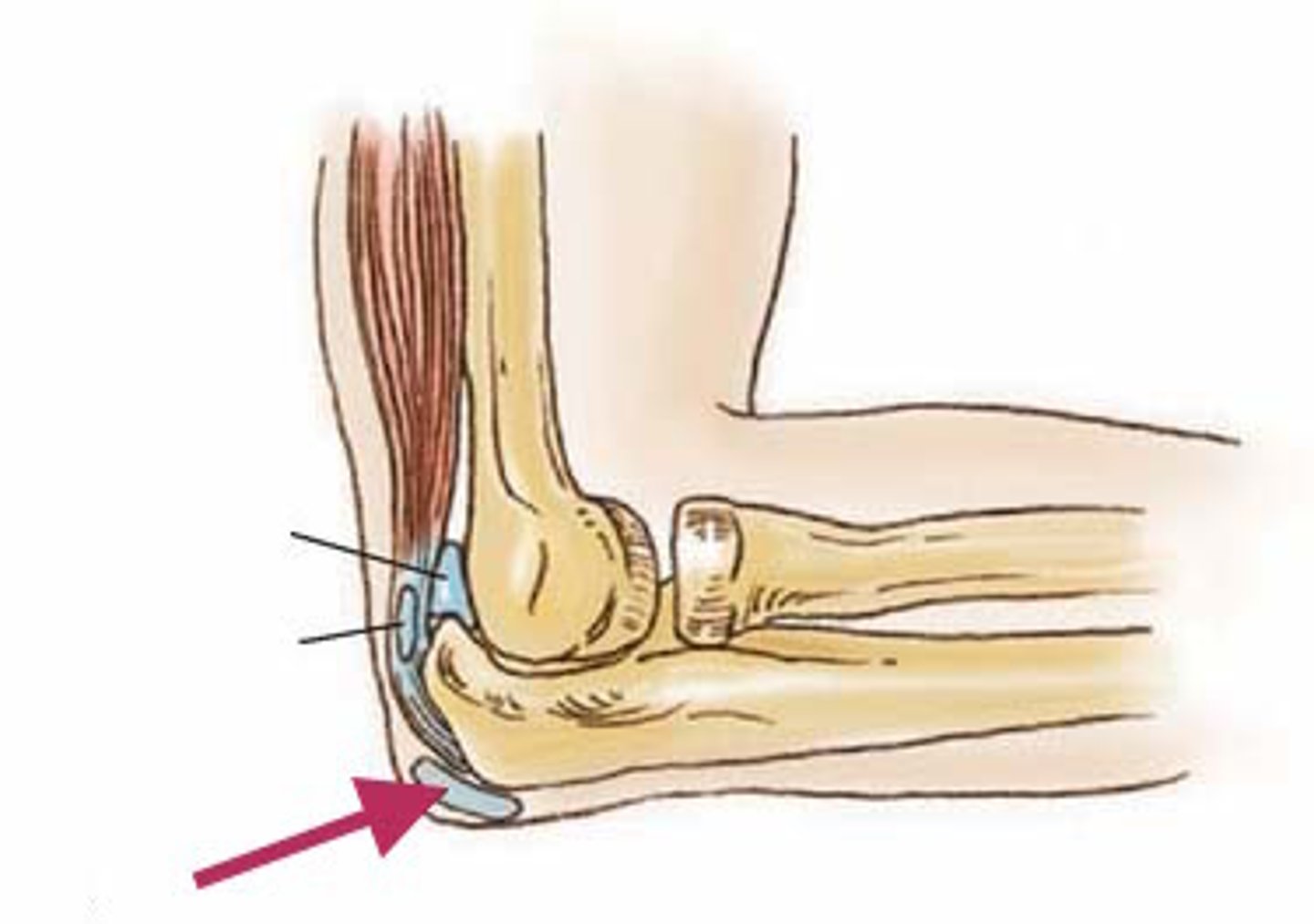
Olecranon bursa
Located on the posterior side of the elbow and eases the movement of tendons over the joint.
Radial (lateral) collateral ligament
Responsible for stabilizing the joint at its lateral surface; restricts side to side motions of the elbow joint.
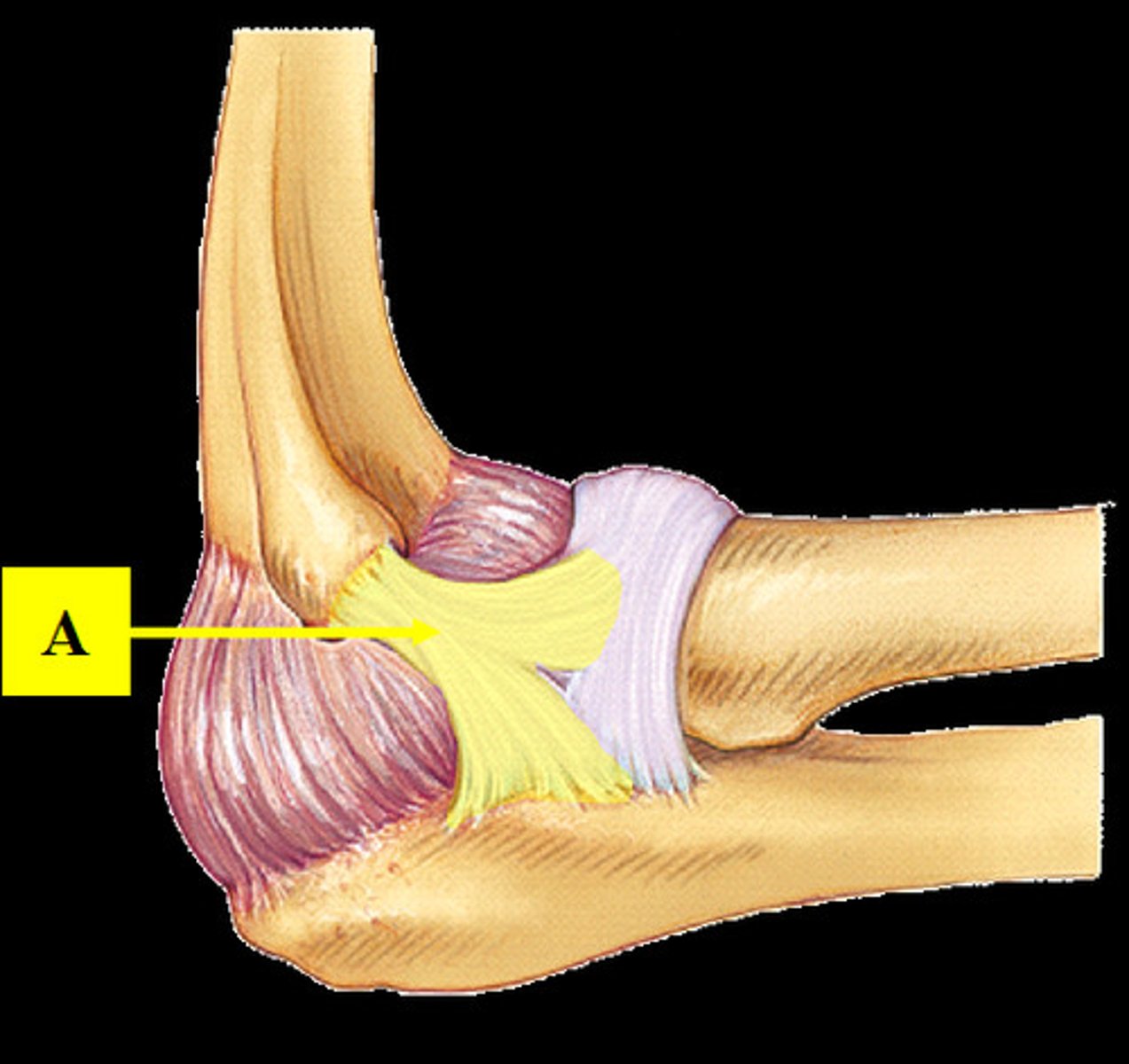
Ulnar (medial) collateral ligament
Stabilizes the medial side of the elbow joint; restricts side to side motions of the elbow joint.
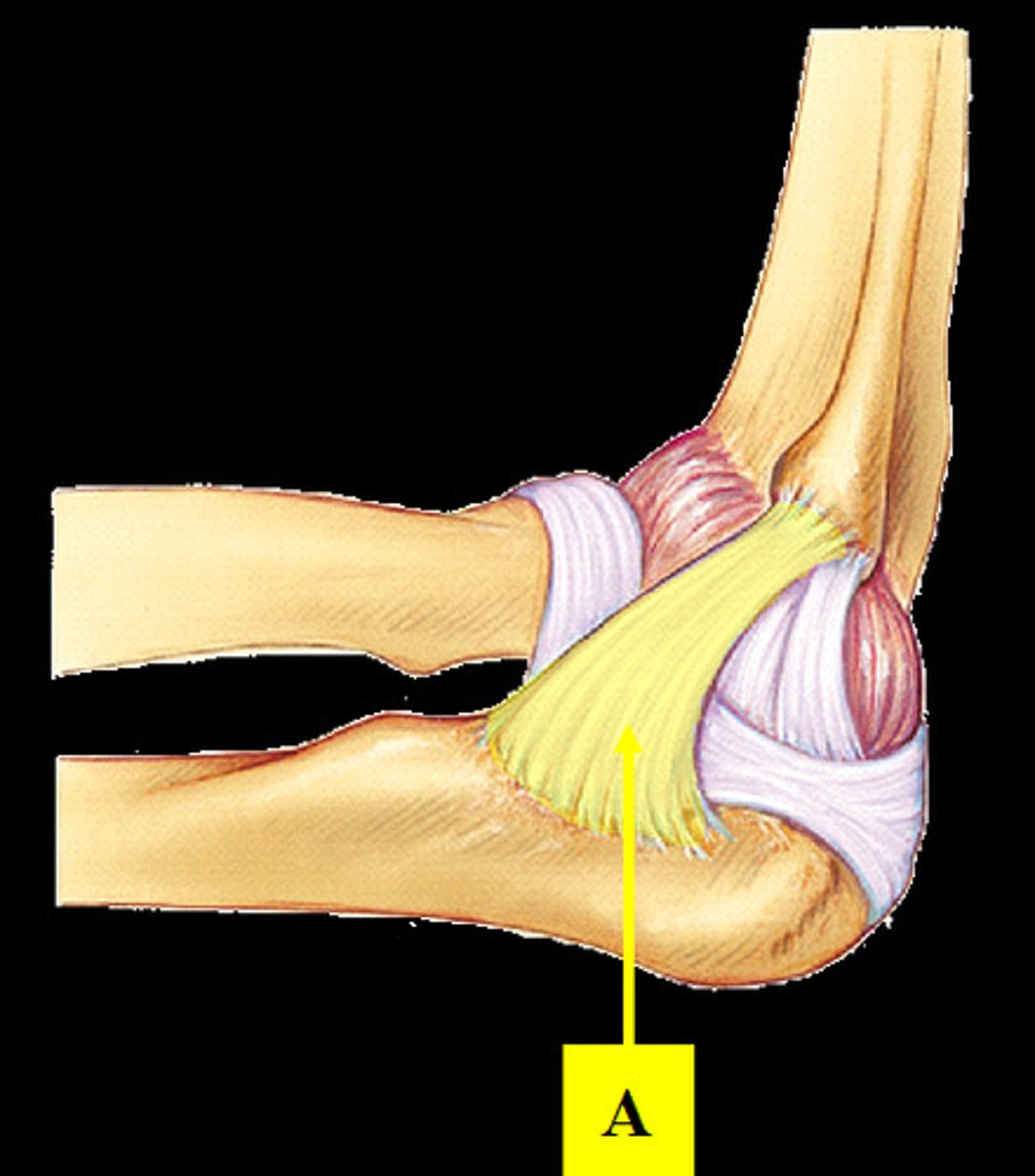
Proximal radioulnar joint
Articulation between head of radius and radial notch of ulna; uniaxial pivot joint that allows for rotation of radius during pronation/supination of forearm.

Anular ligament
Ring-shaped band of connective tissue below the elbow joint that encircles the head of the radius.
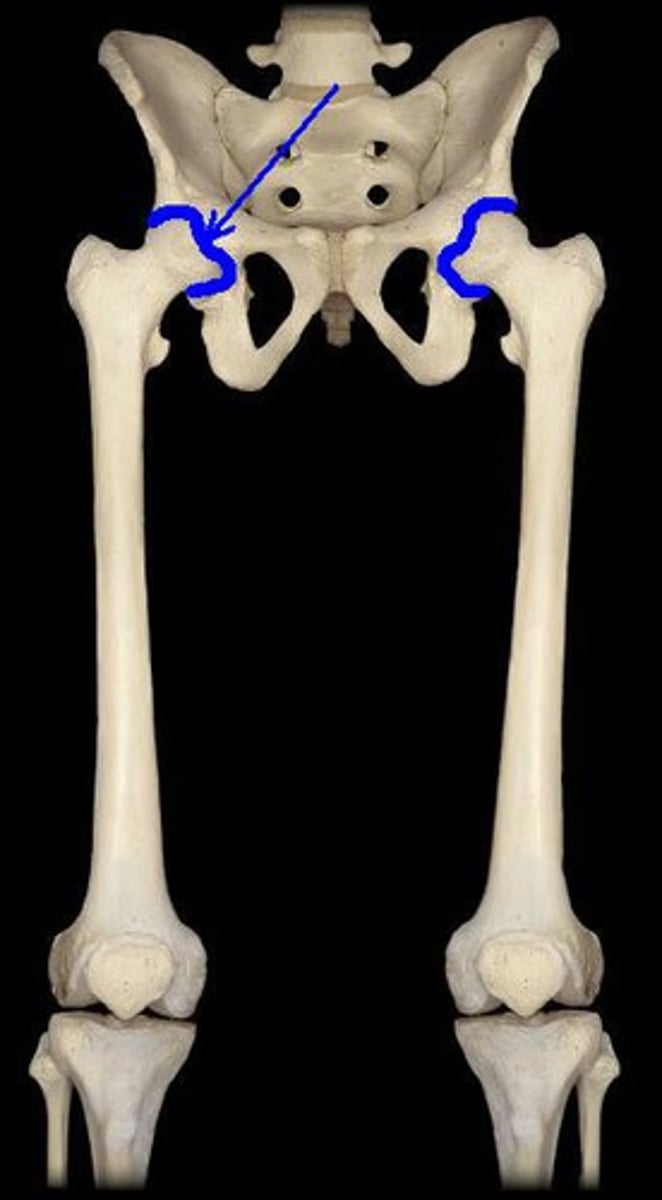
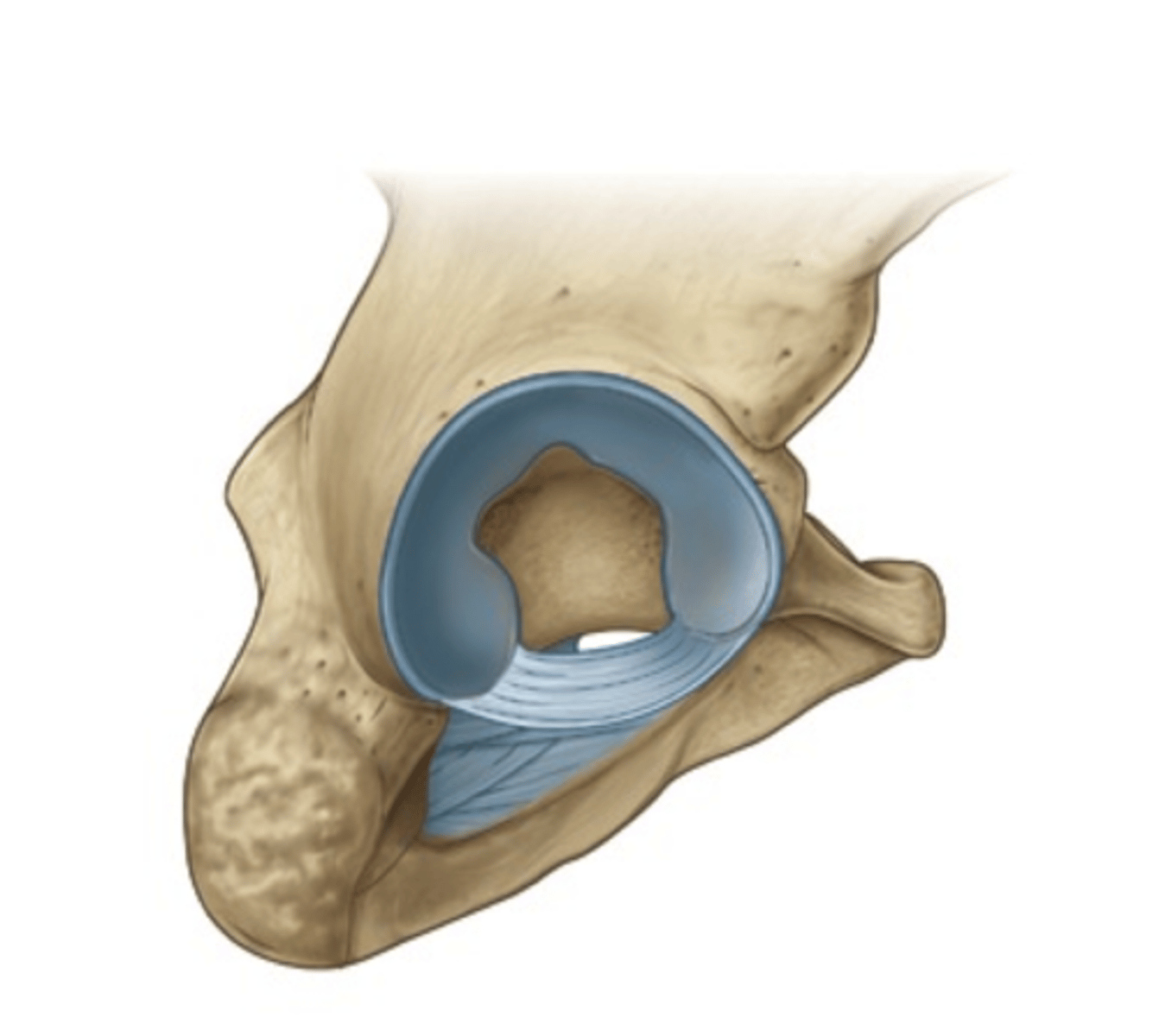
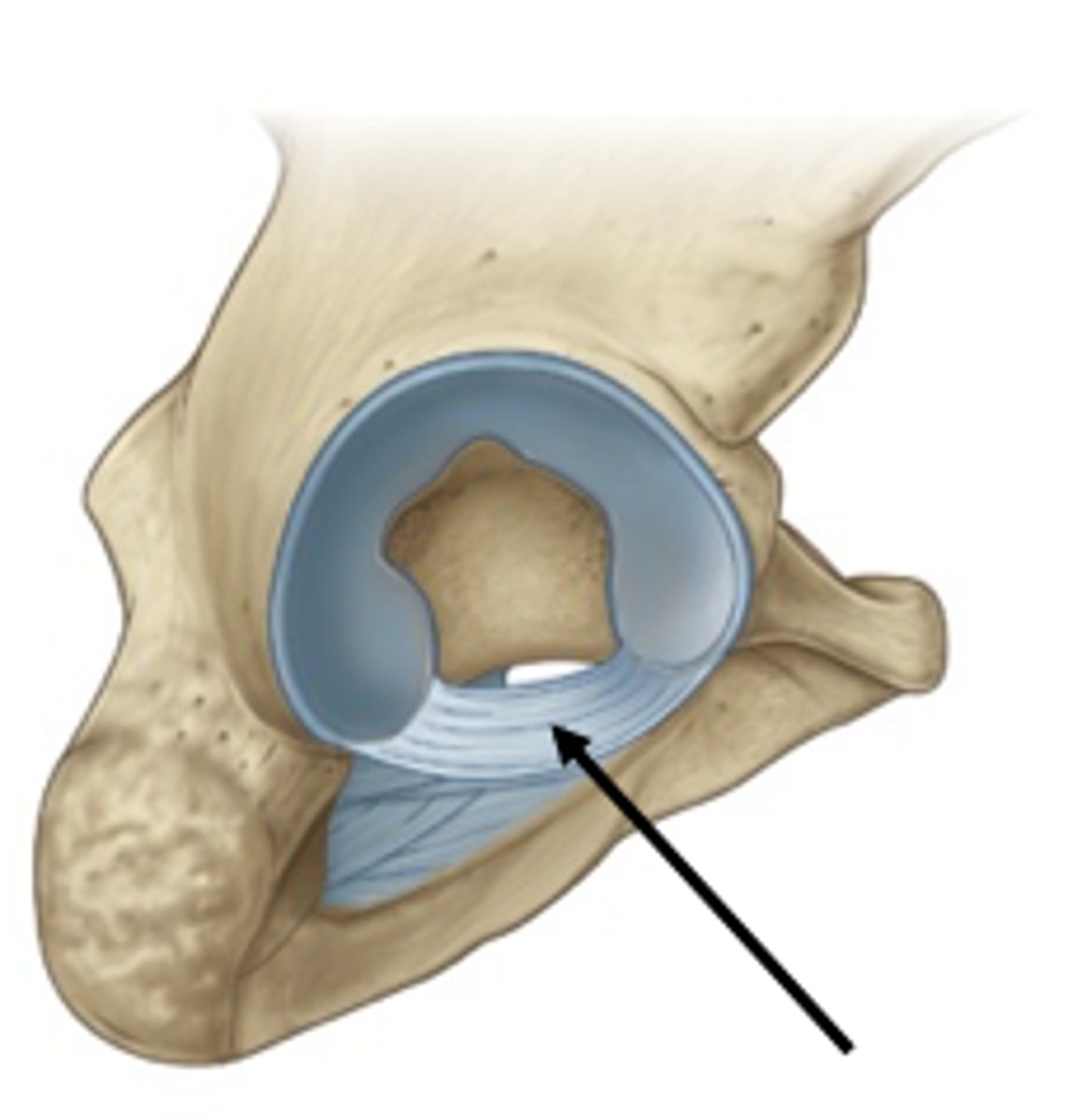
Coxal (hip) joint
Where the head of the femur inserts into the acetabulum of the hip bone; contain deep sockets and are very stable.
Acetabular labrum
Horseshoe-shaped ring of fibrocartilage that deepens socket, preventing dislocations of the hip.
iliofemoral ligament
Resits anterior displacement of hip and prevents hyperextension.
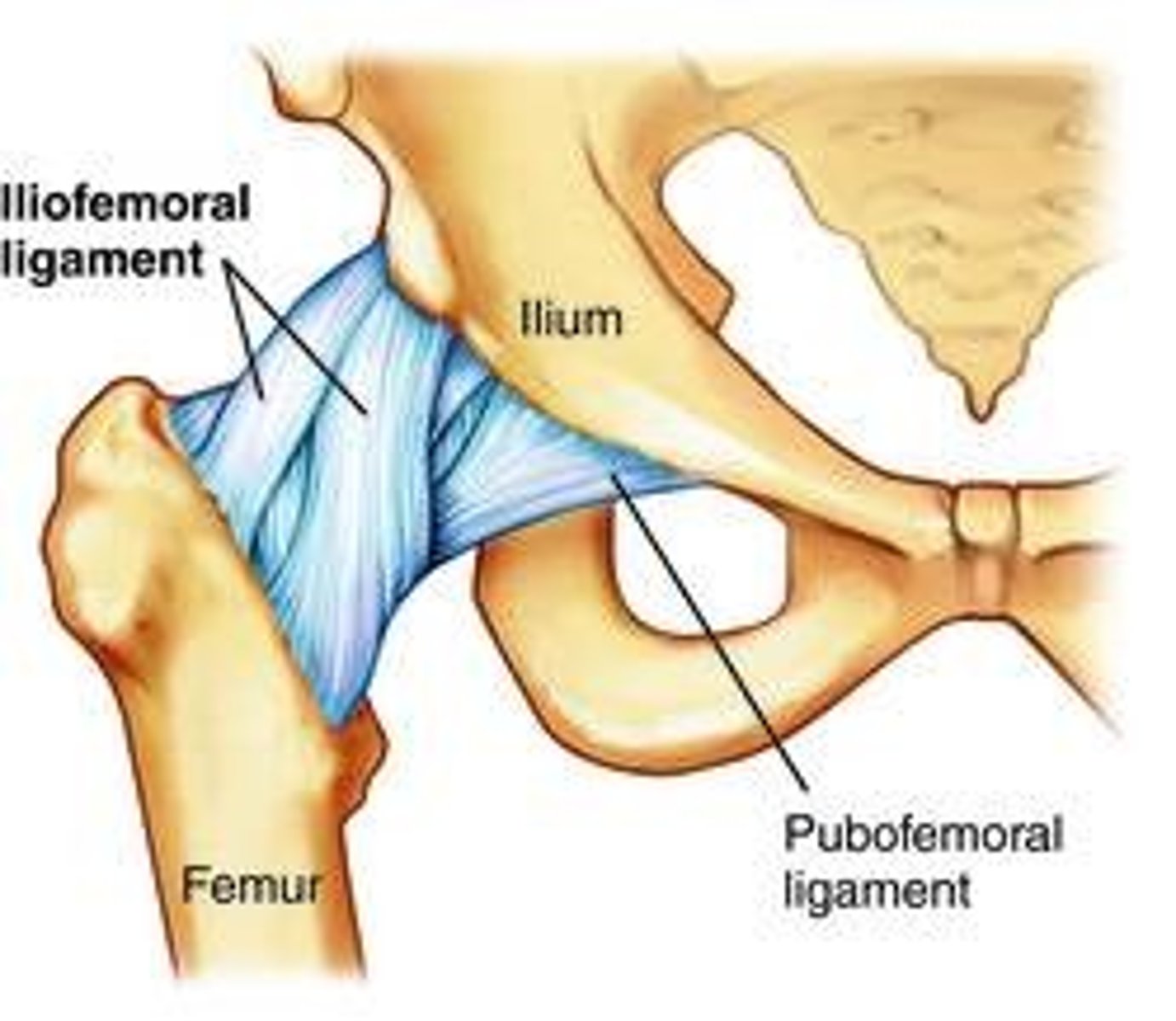
Pubofemoral ligament
Located anteromedially & inferiorly, limits excessive extension & abduction.
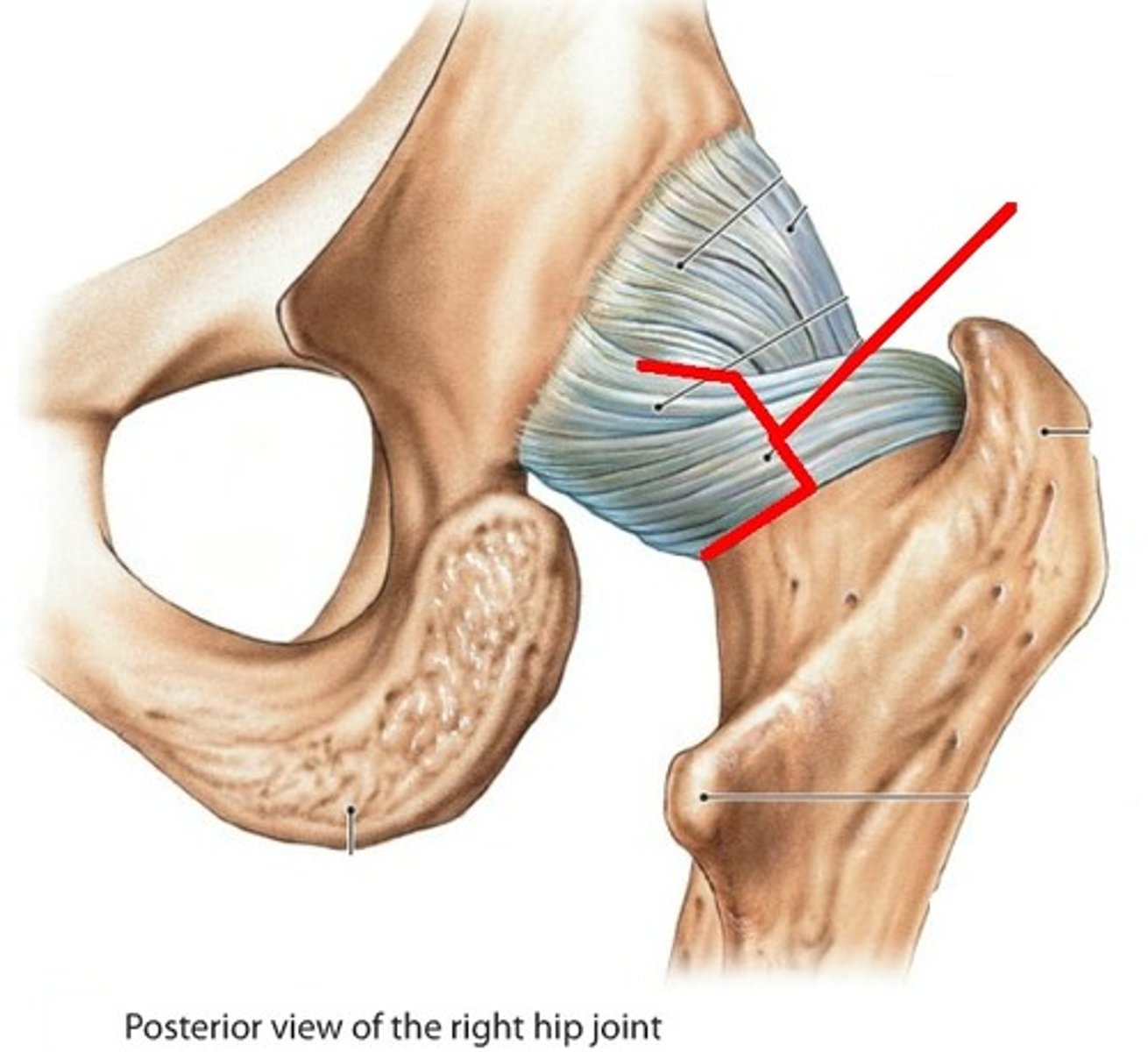
Ischiofemoral ligament
Resists posterior displacement of femoral head.
Fovea capitis
Pit in the head of a femur.
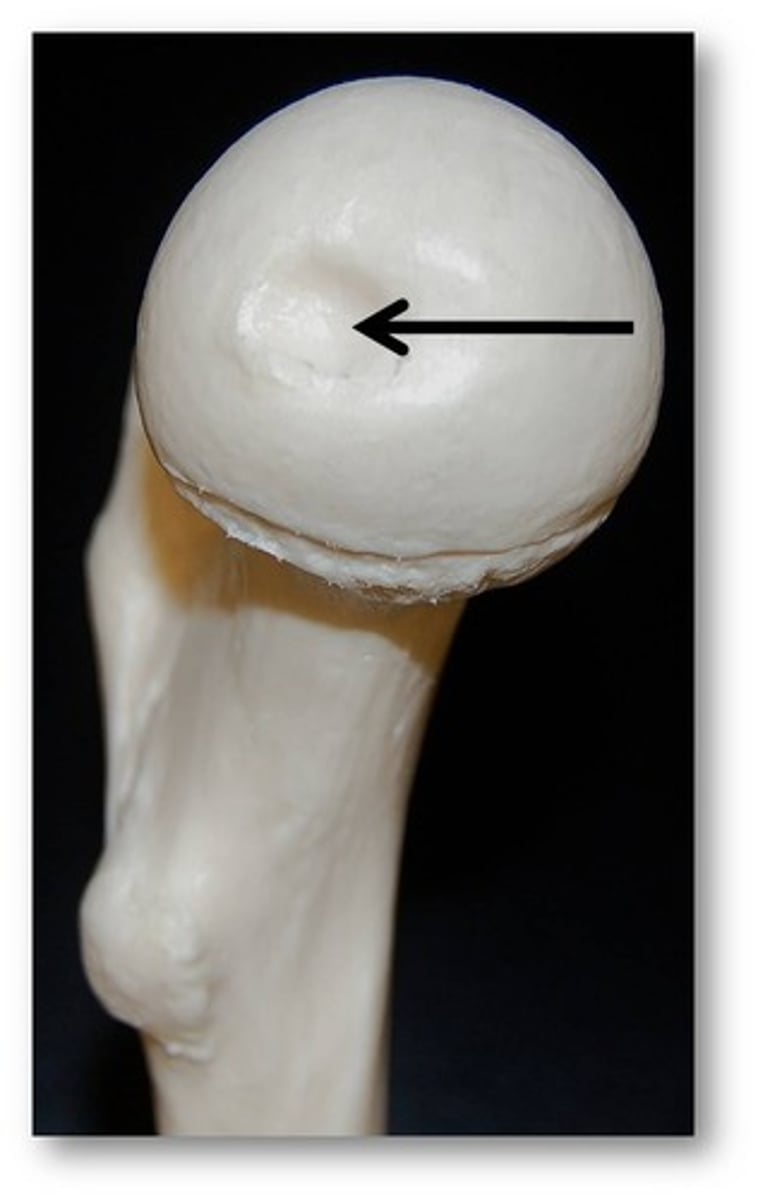
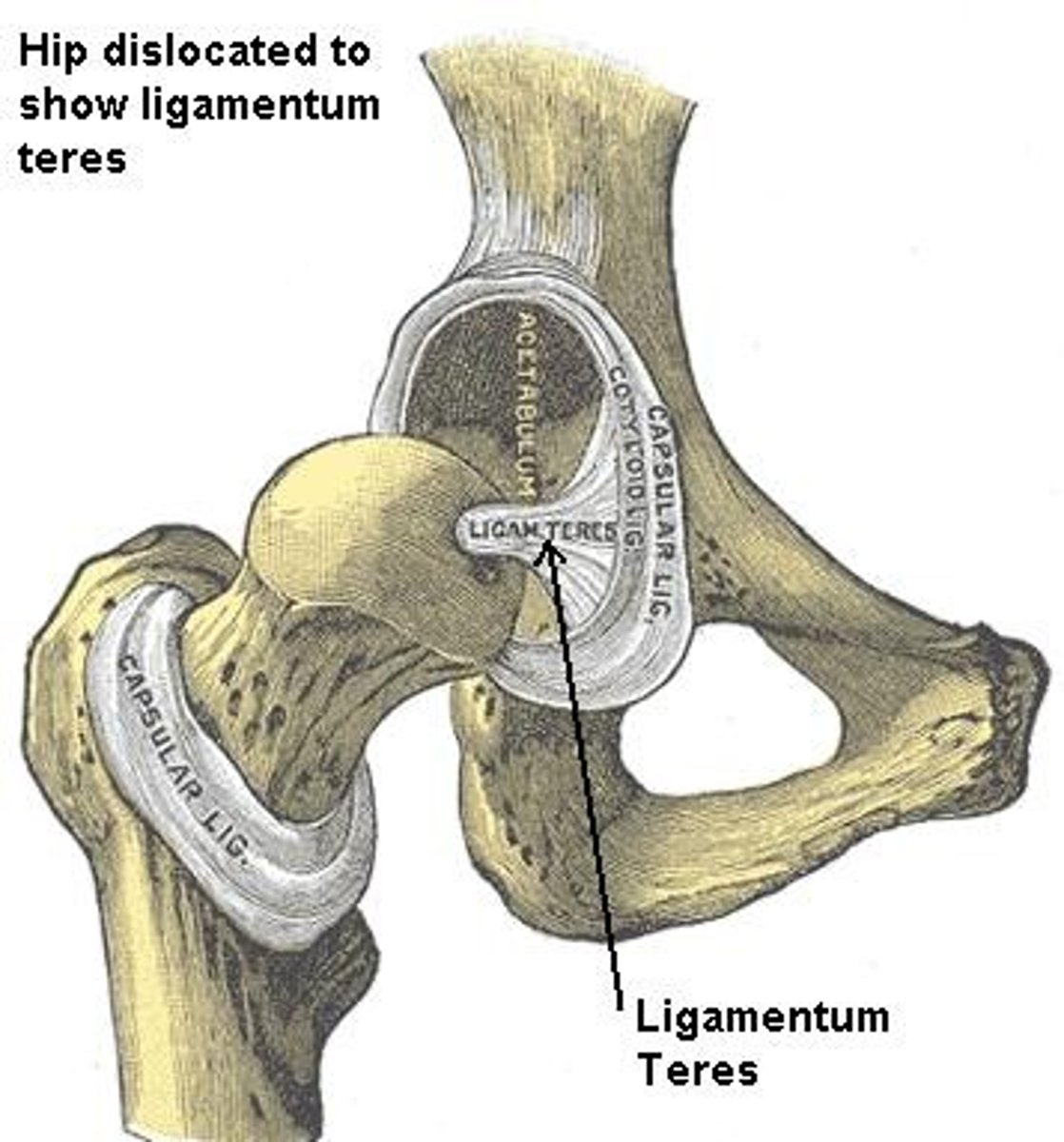
Ligamentum teres
Attaches to the lower margin of the acetabulum containing an artery that supplies blood to the head of the femur.
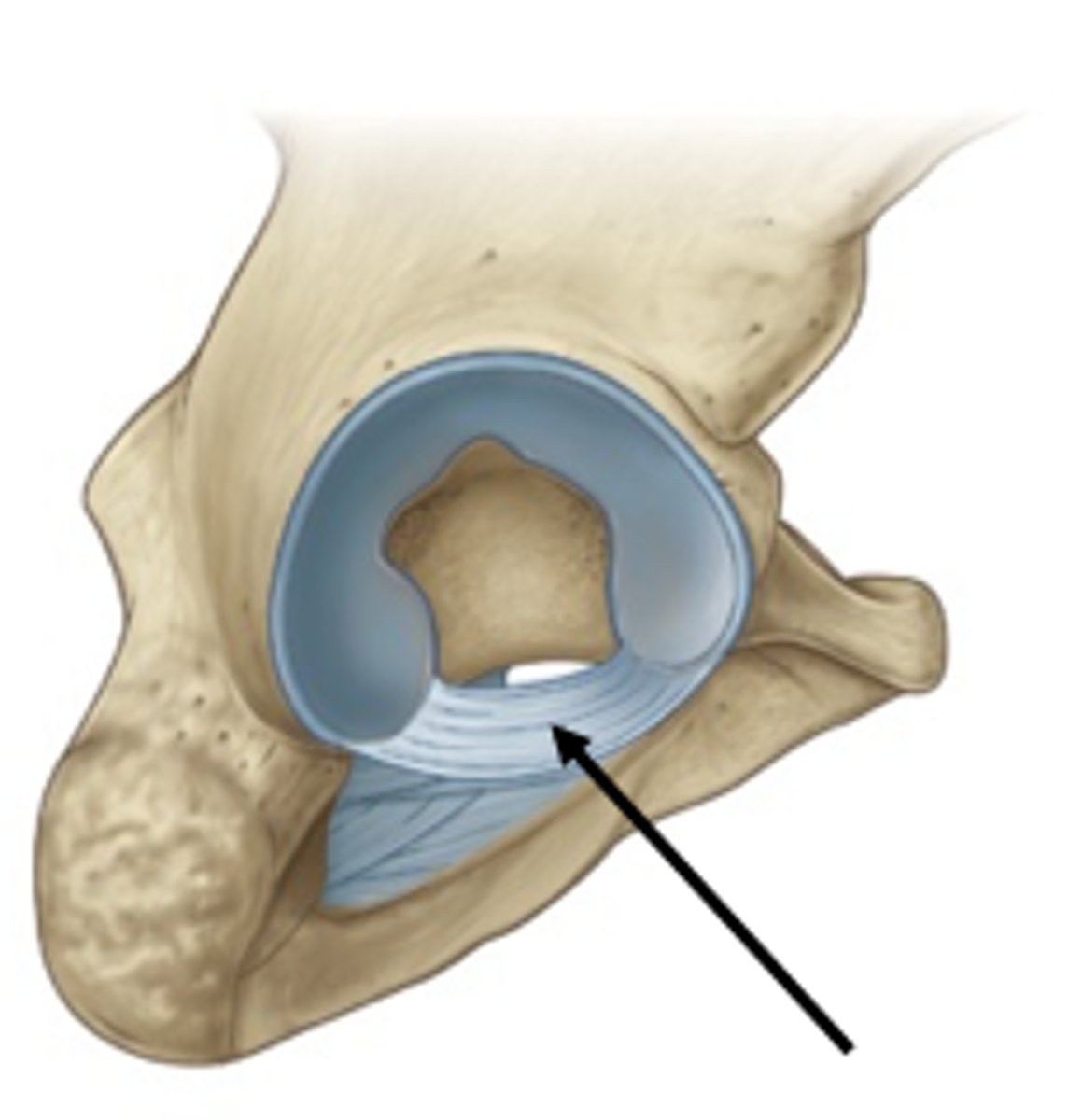
Transvere acetabular ligament
Bridges a gap in the inferior margin of the acetabular labrum.
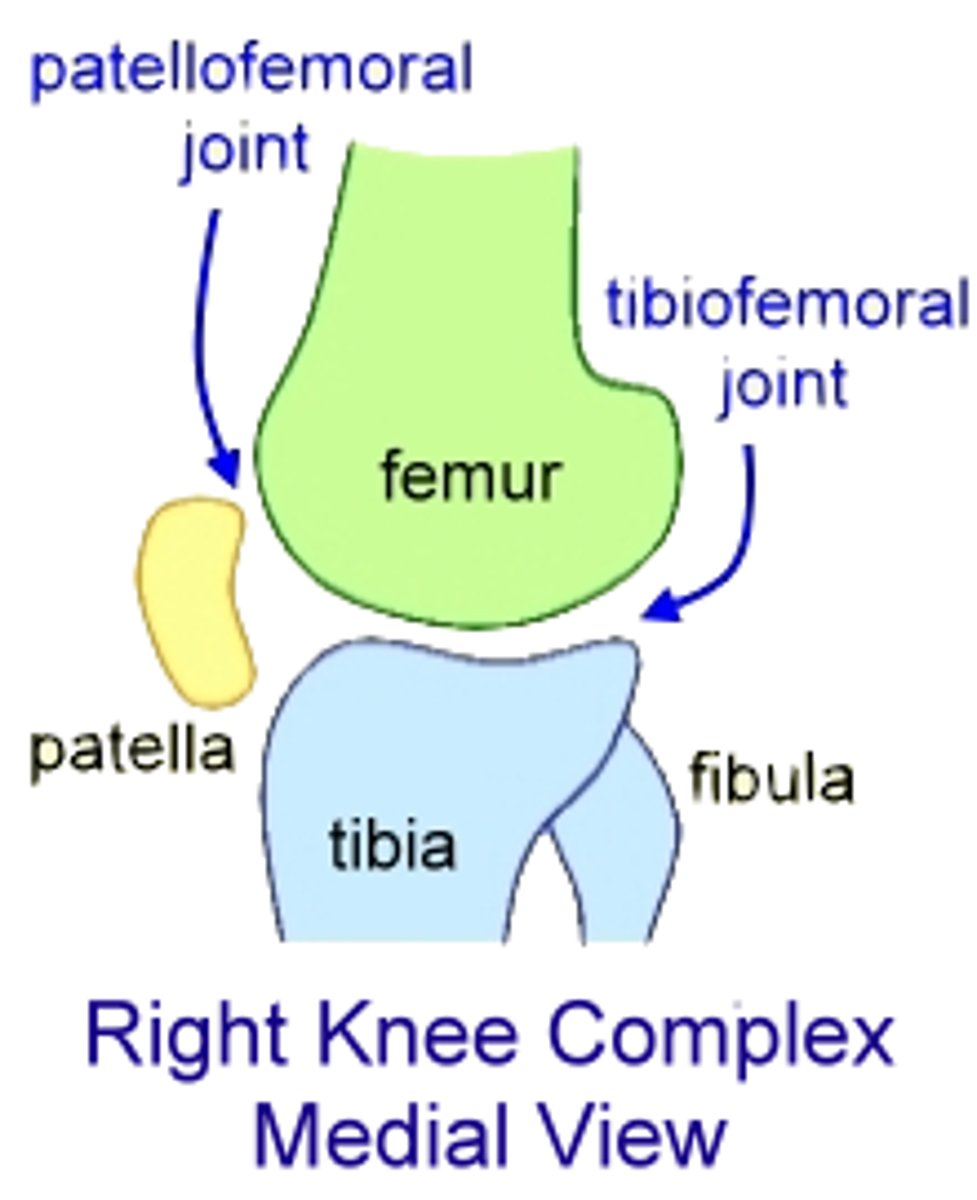
What is the Tibiofemoral joint?
The largest and most complex diarthrosis of the body.
What type of joint is the Tibiofemoral joint primarily?
A hinge joint.
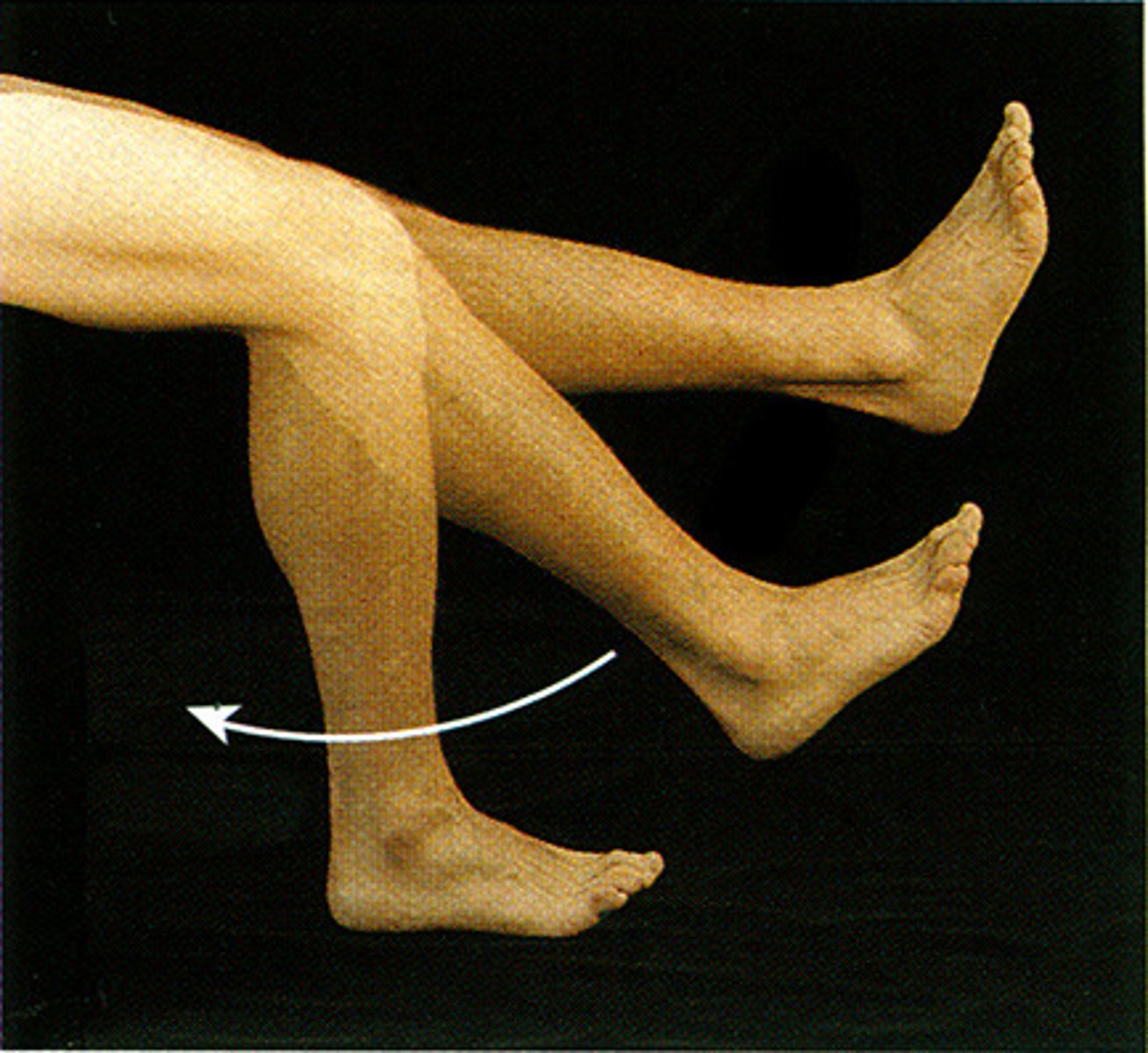
What movements is the Tibiofemoral joint capable of when the knee is flexed?
Slight rotation and lateral gliding.
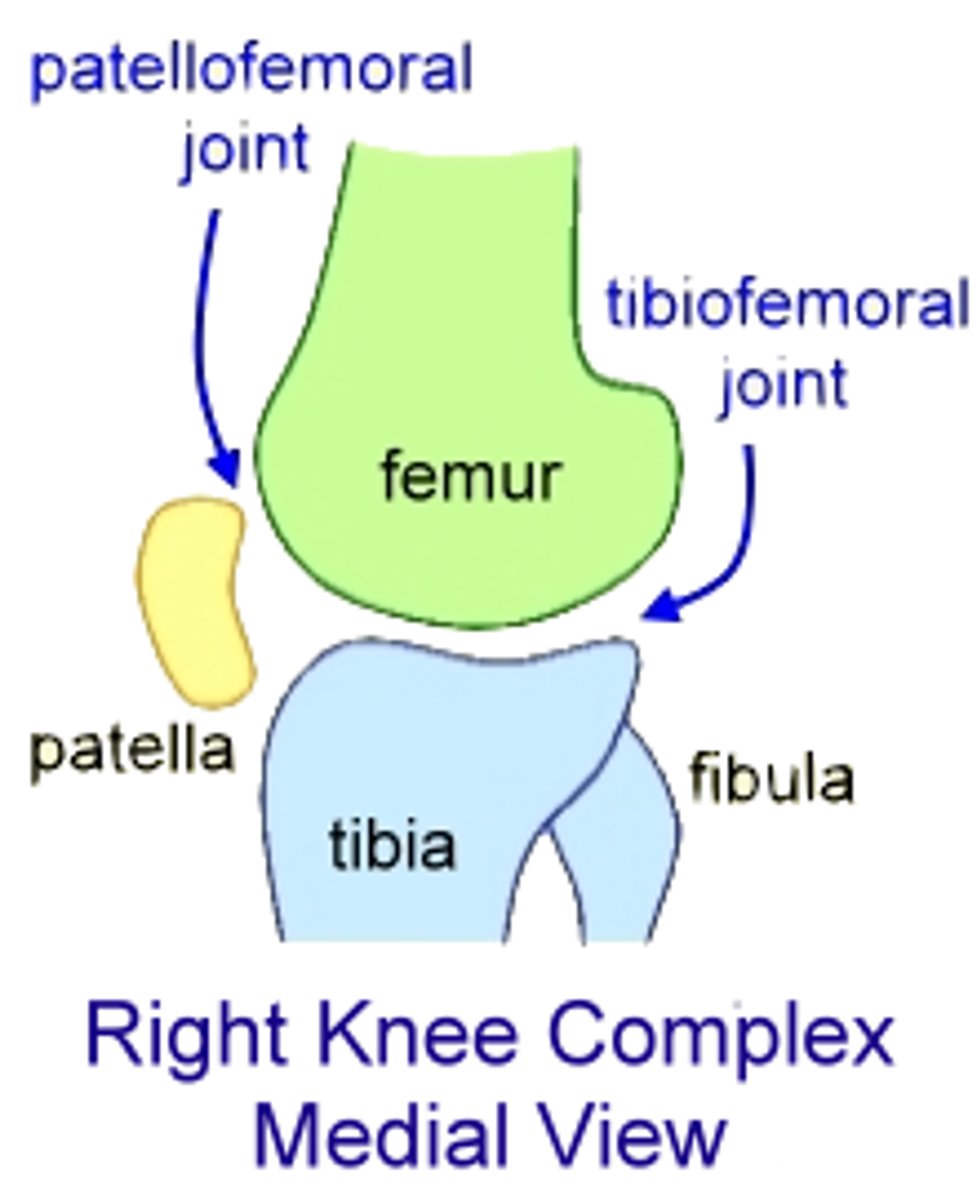
Patellofemoral joint
The point where the patella and its ligament articulate with the femur, forming a gliding joint.
Joint Capsule
Encloses only the lateral and posterior aspects of the knee joint, not the anterior.
Patellar Ligament
Covers the anterior aspect of the knee, along with the patella.
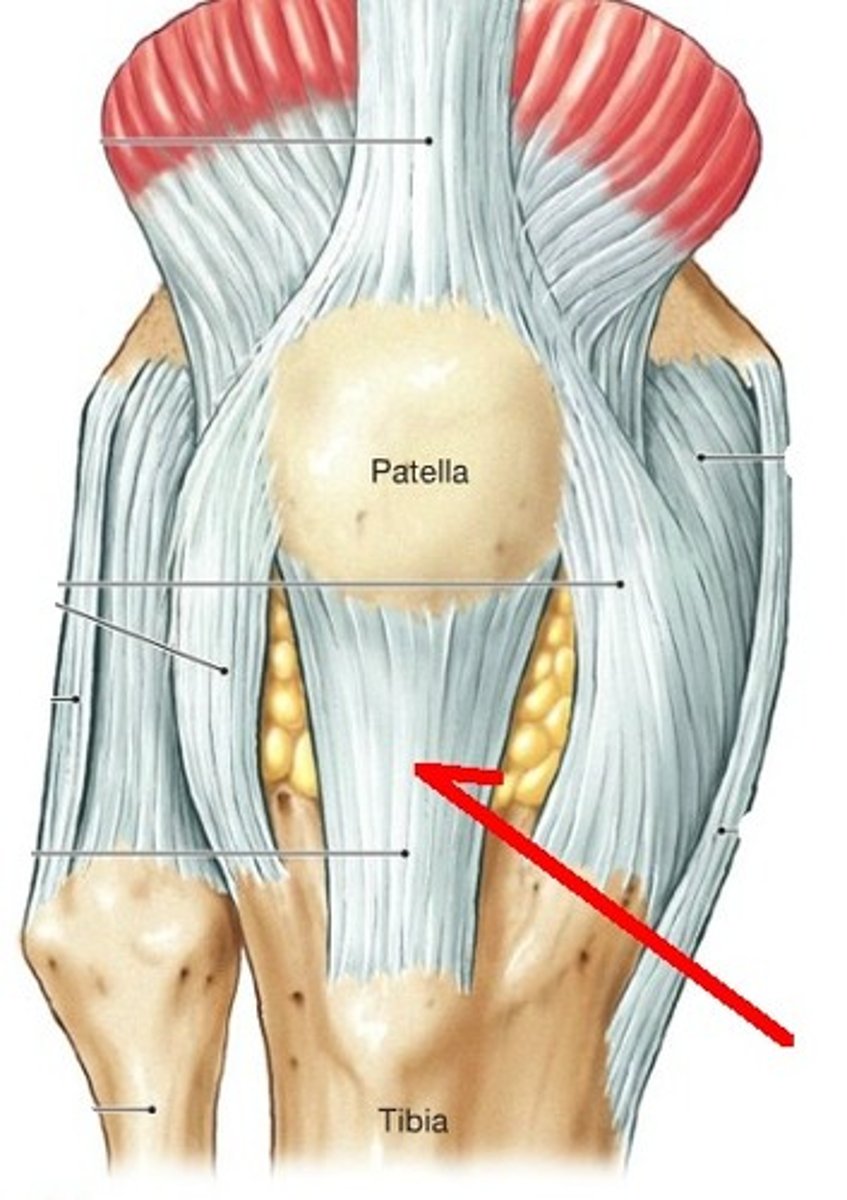
Lateral and Medial Patellar Retinacula
Extensions of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle that stabilize the knee.
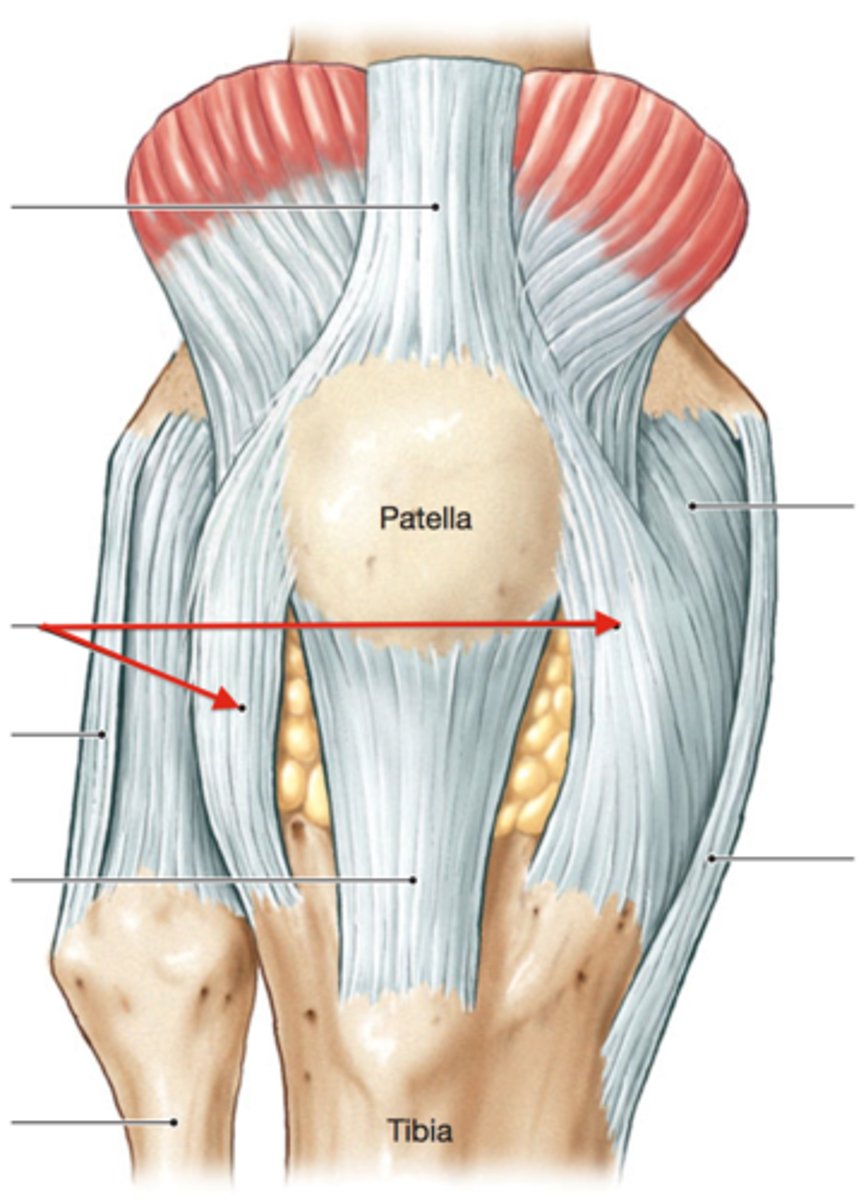
Quadriceps Femoris Muscle
The large anterior muscle of the thigh that stabilizes the knee.

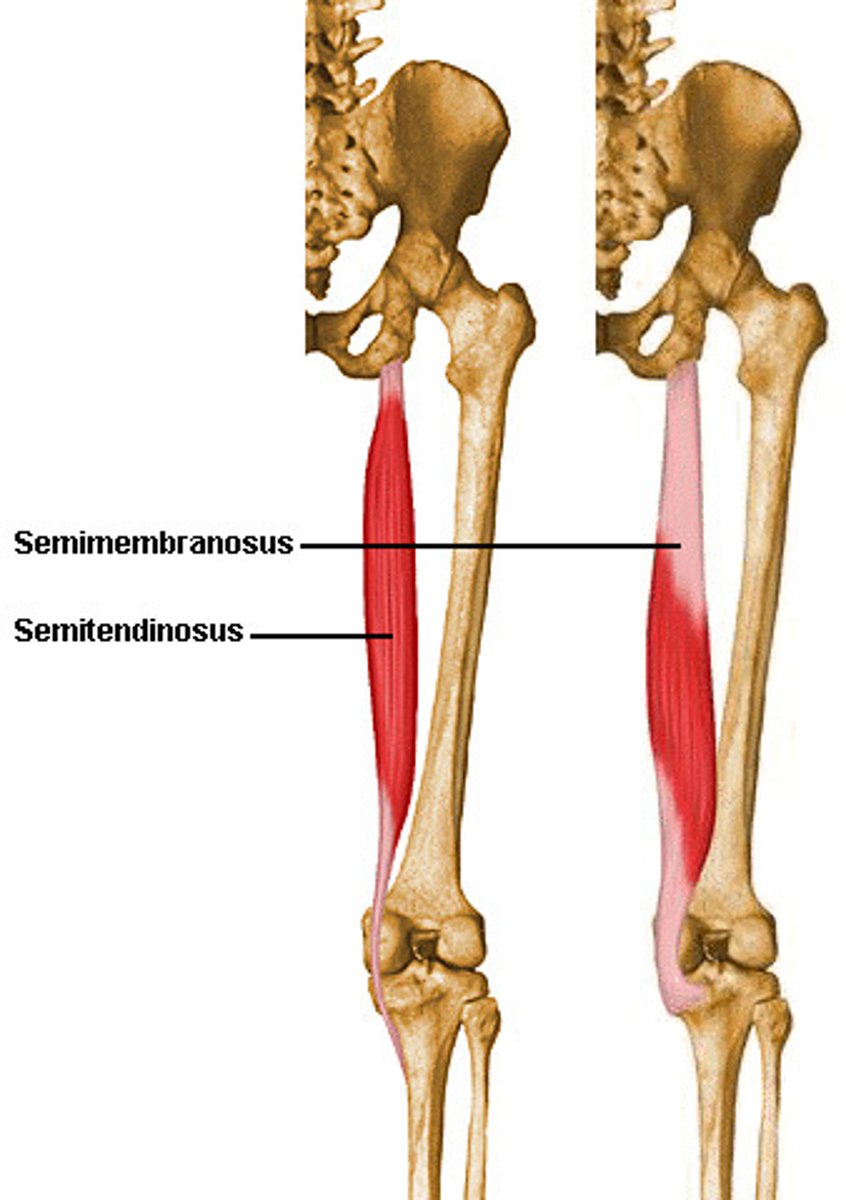
Semimembranosus Muscle
The muscle on the rear of the thigh that also helps stabilize the knee.
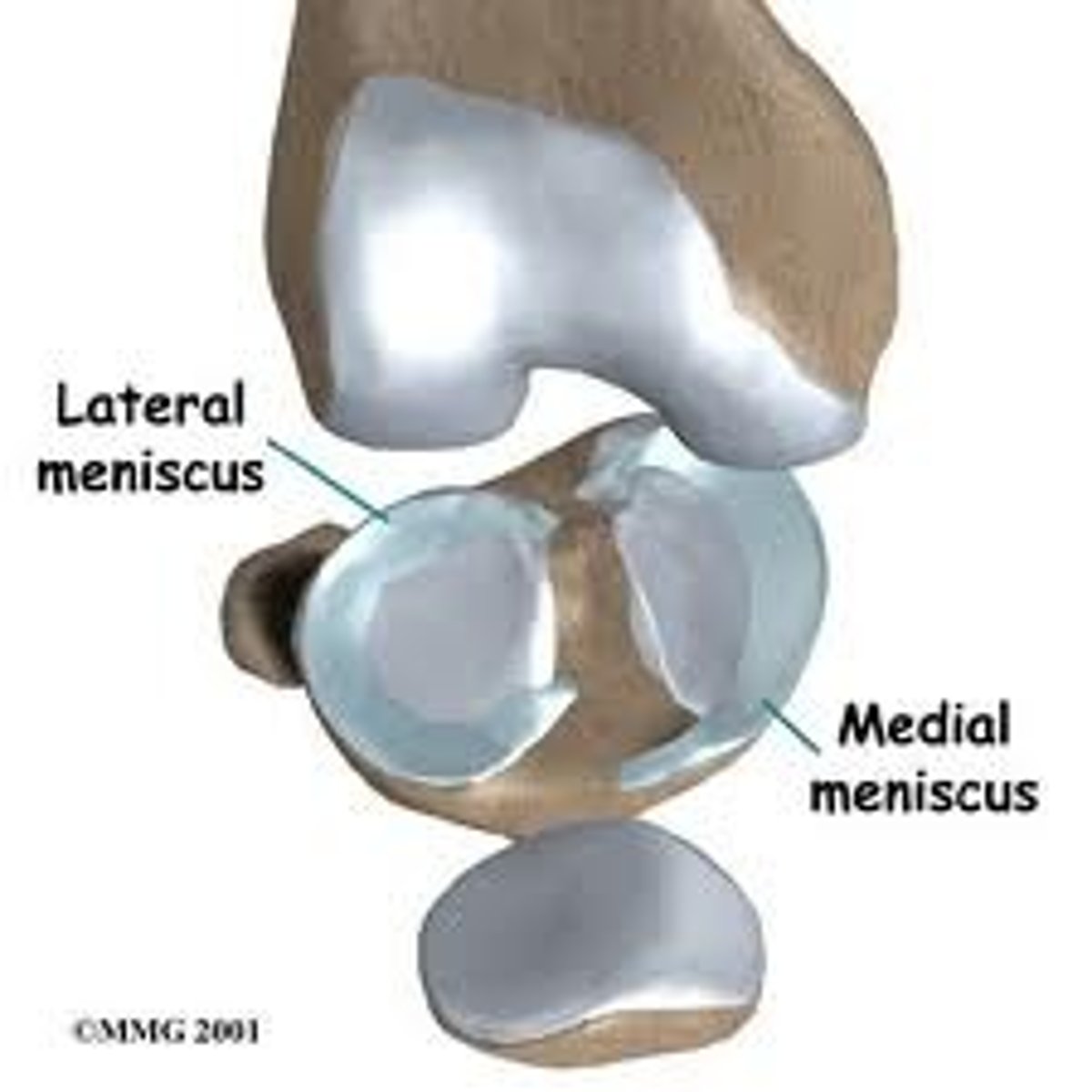
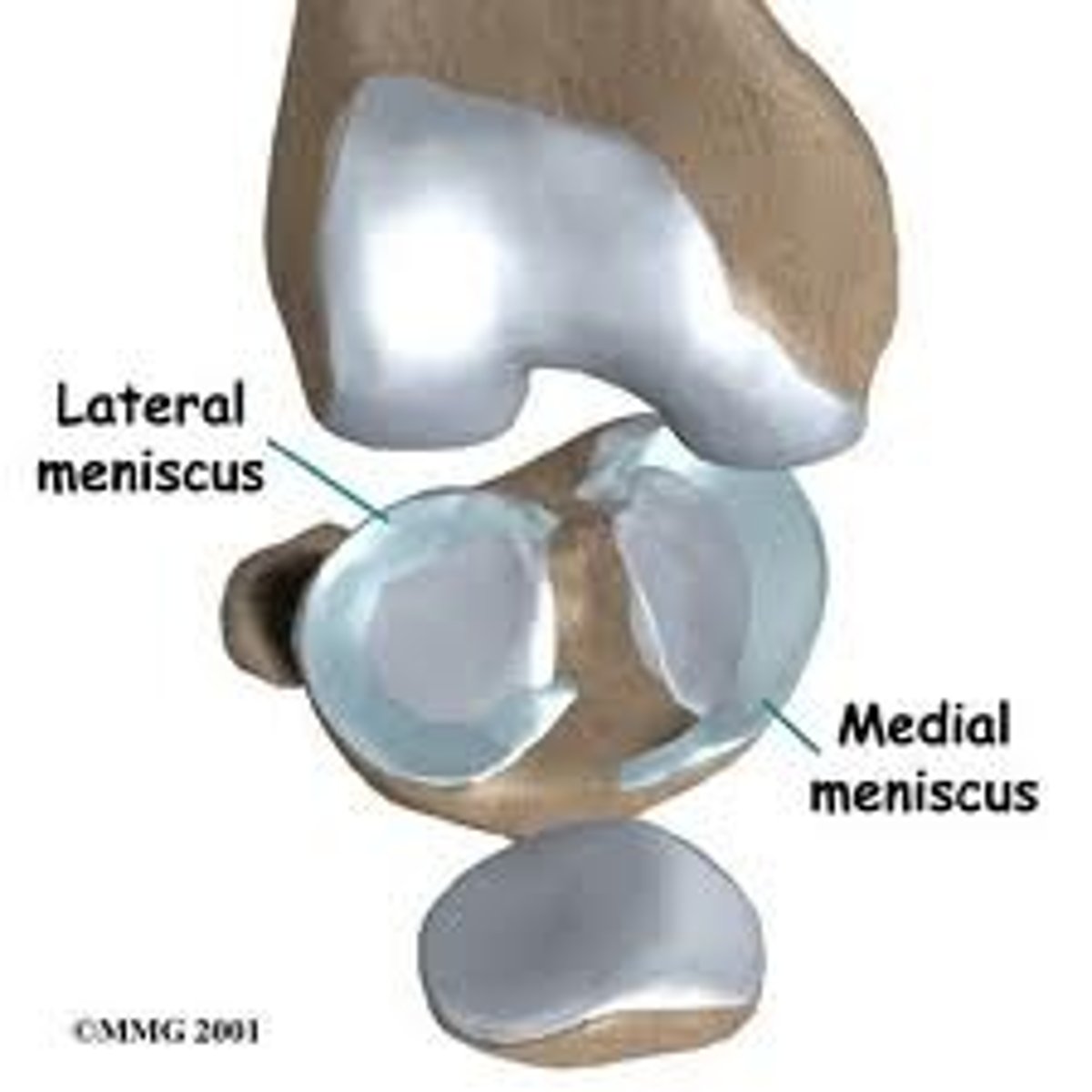
Lateral and Medial Menisci
C-shaped cartilages in the joint cavity that are joined by a transverse ligament.
Transverse Ligament
Joins the lateral and medial menisci.
Menisci
Absorb the shock of the body weight and prevent the femur from rocking side to side on the tibia.
Popliteal Region
The posterior region of the knee supported by extracapsular and intracapsular ligaments.
Extracapsular Ligaments
Ligaments external to the joint capsule, including the fibular (lateral) collateral ligament and the tibial (medial) collateral ligament.
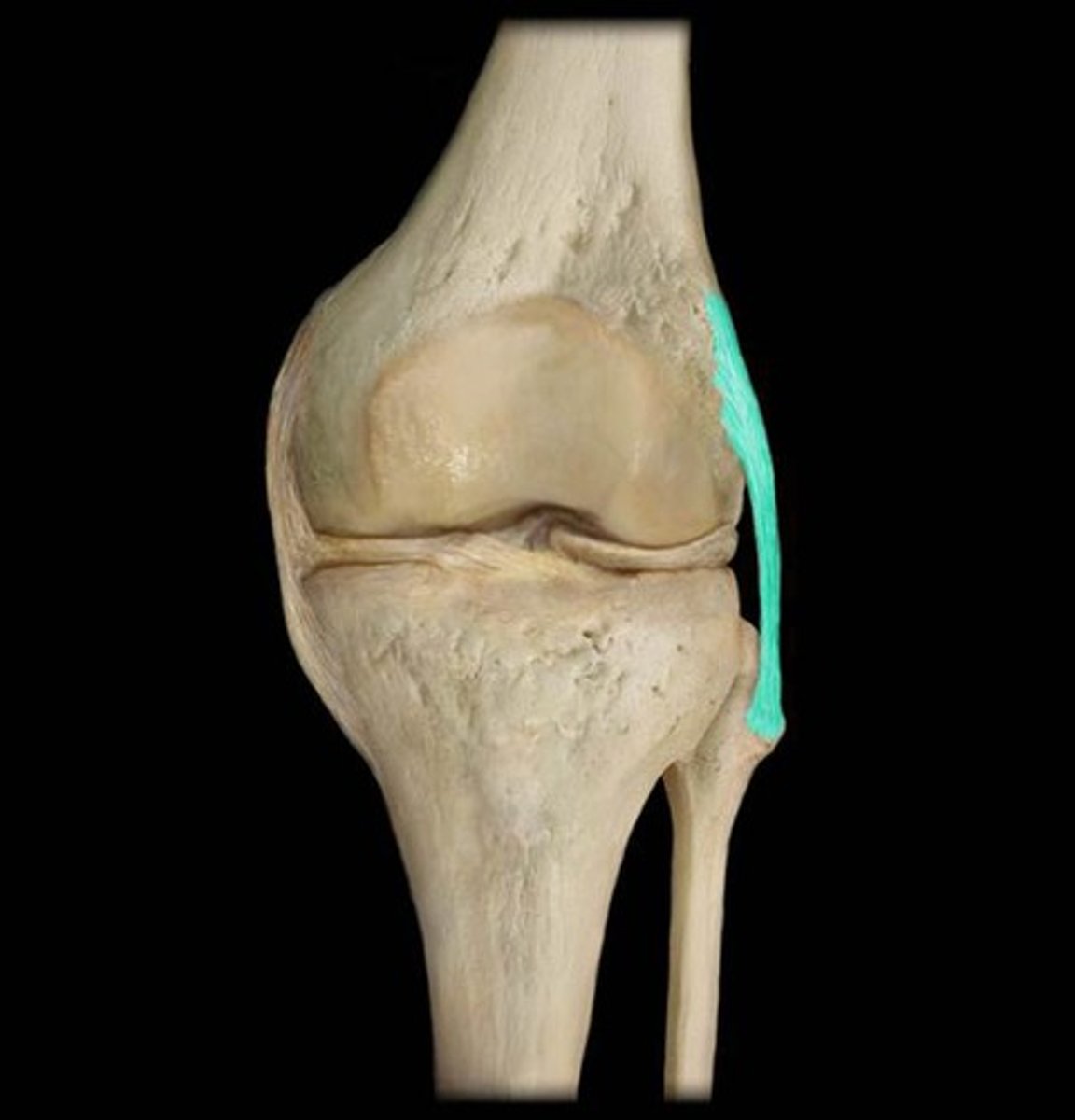
Fibular (Lateral) Collateral Ligament
An extracapsular ligament that prevents the knee from rotating when extended.
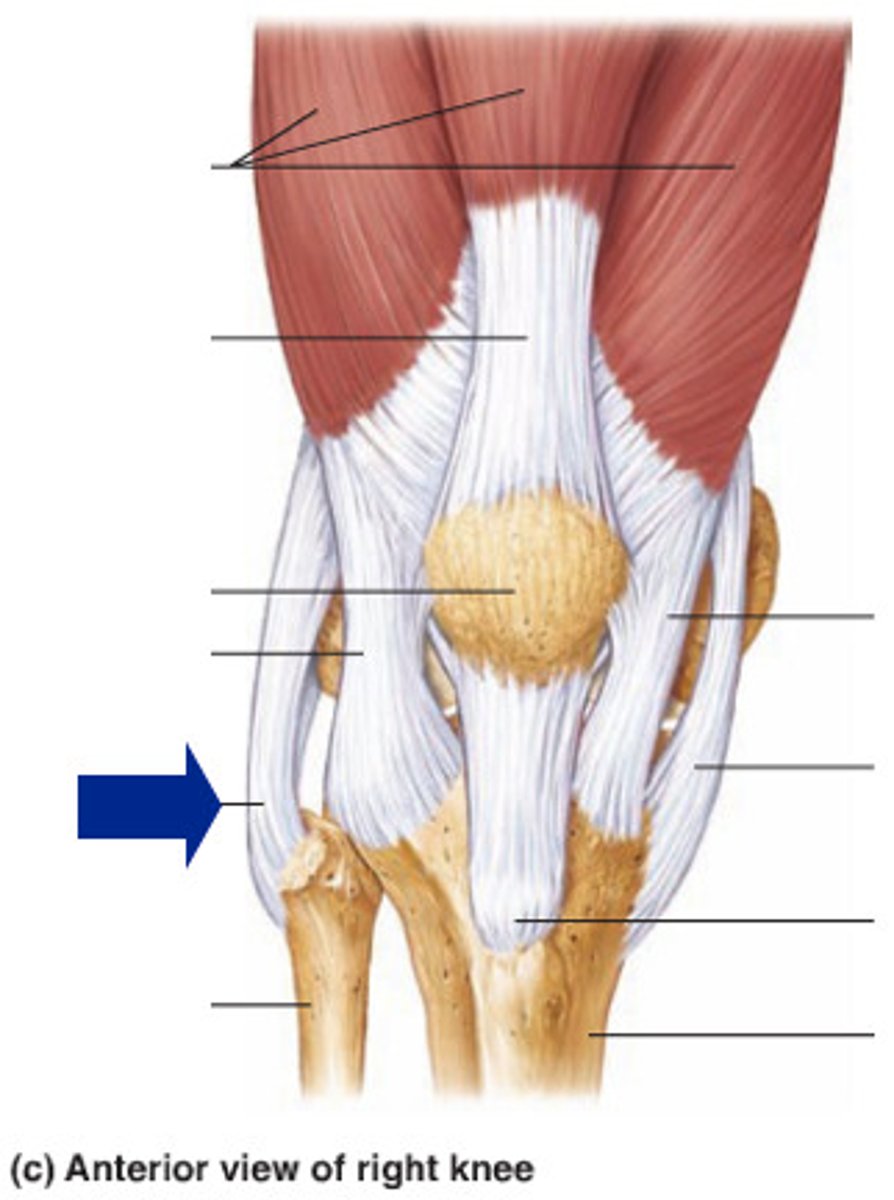
Tibial (Medial) Collateral Ligament
An extracapsular ligament that prevents the knee from rotating when extended.
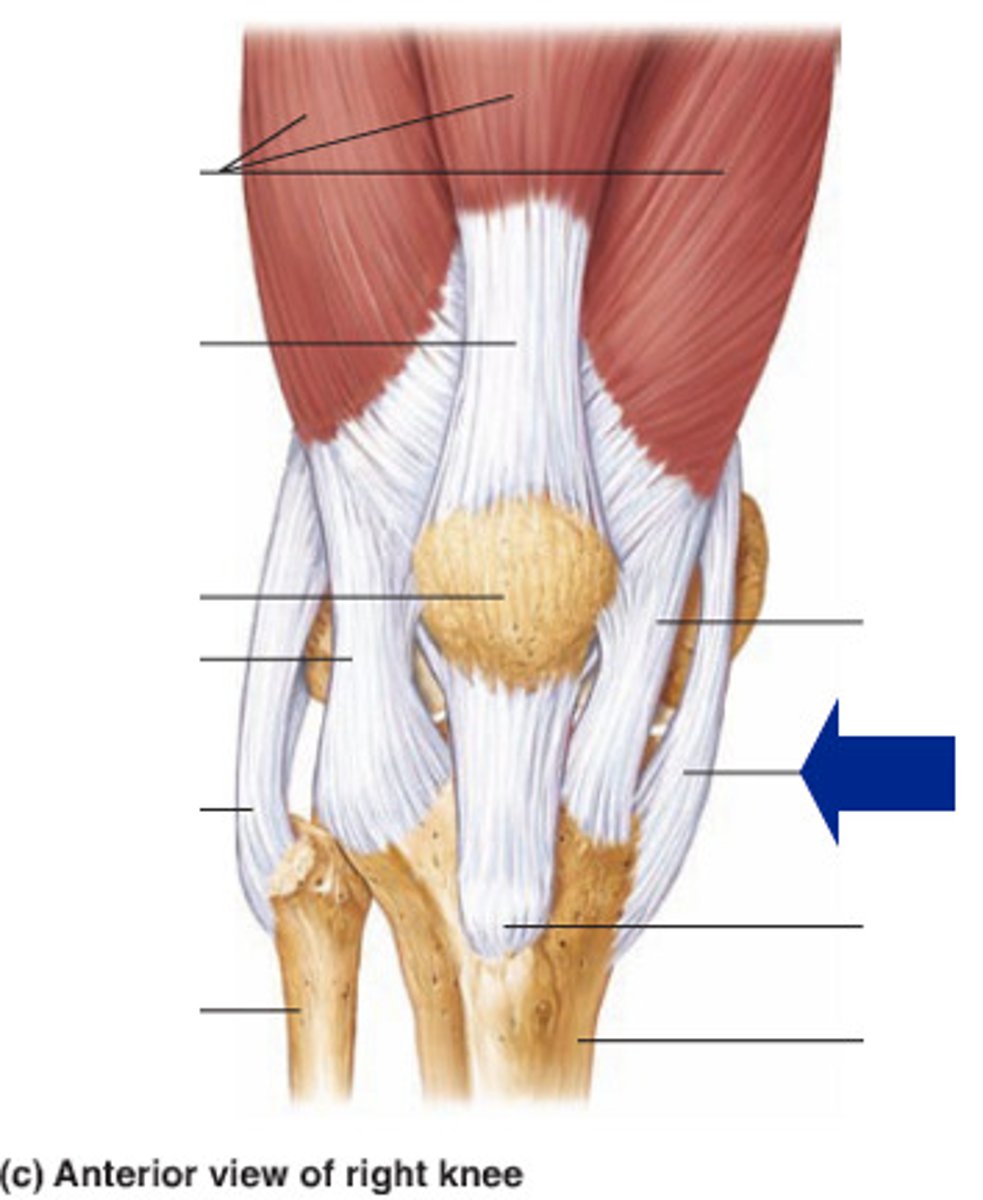
Intracapsular Ligaments
Lie deep within the joint and are excluded from the synovial cavity, including the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
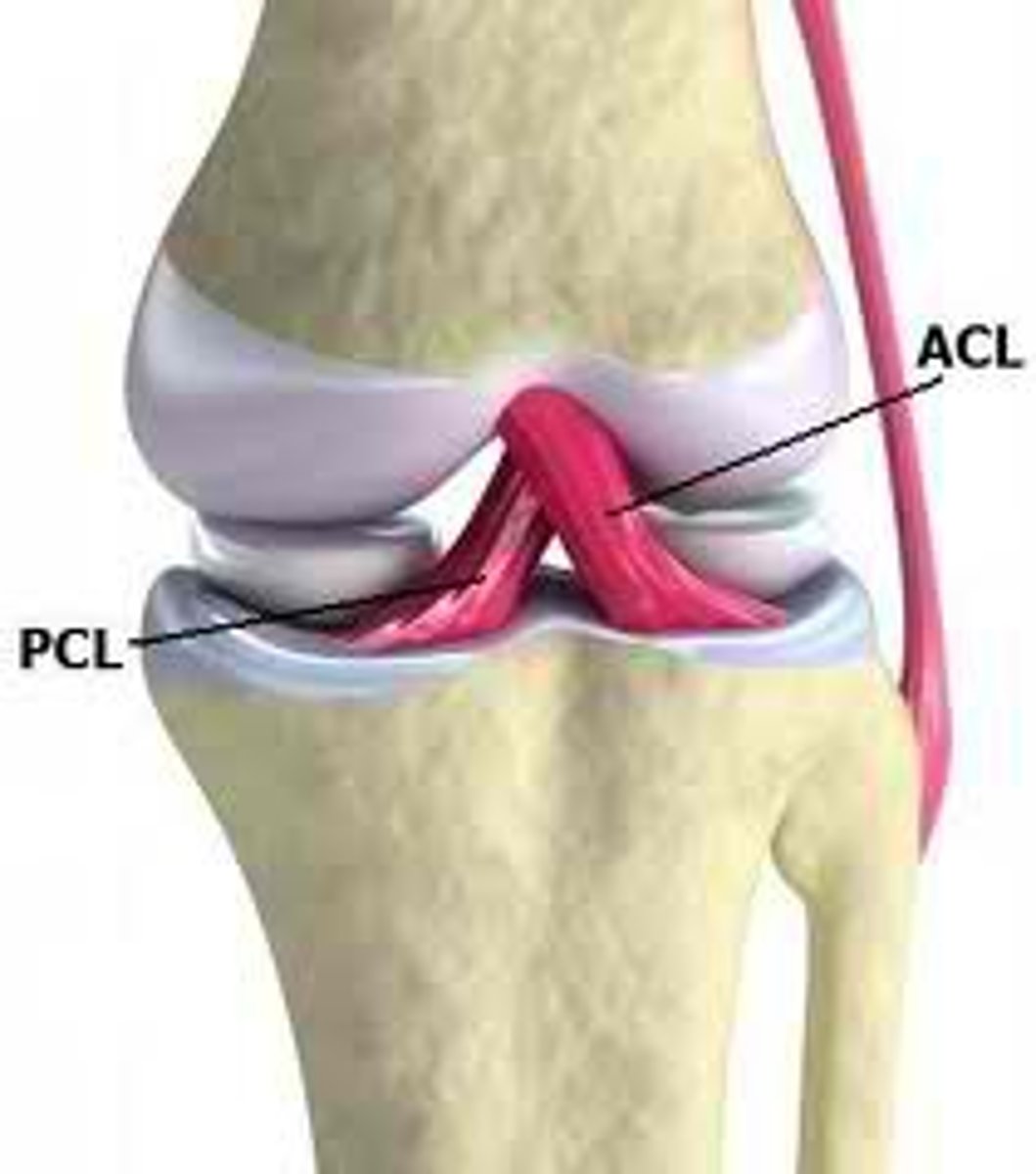
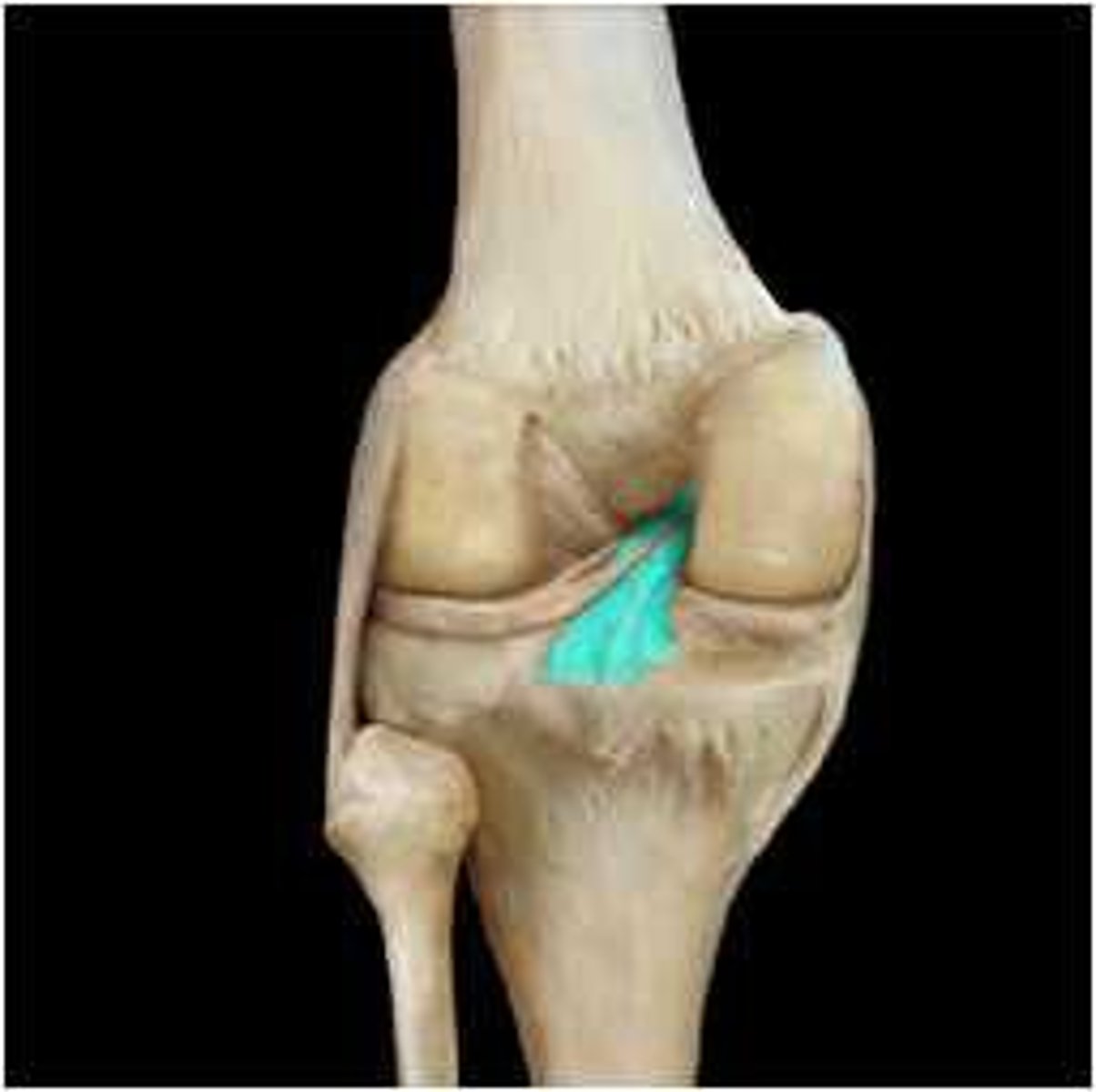
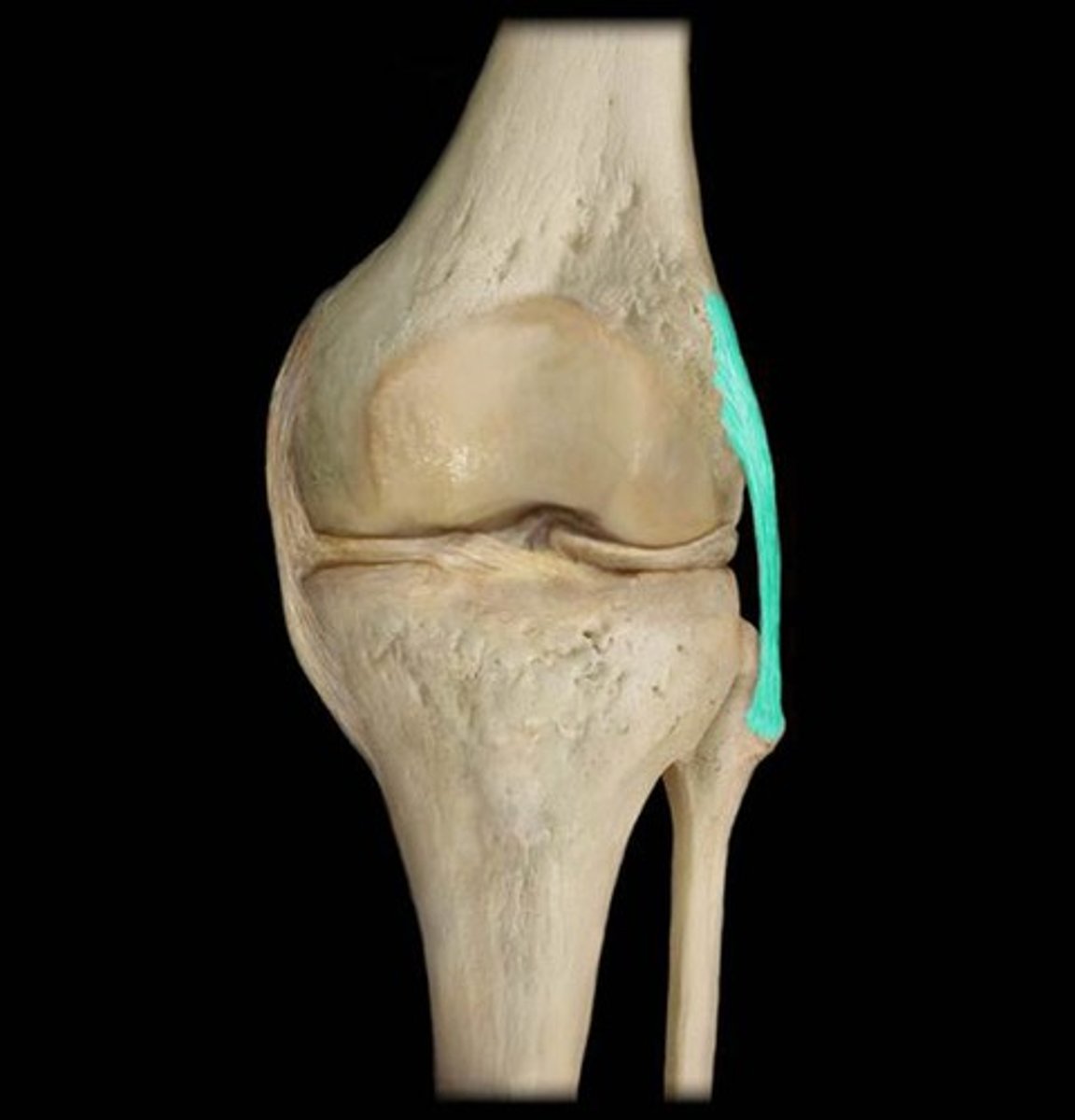
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
Prevents hyperextension of the knee and is one of the most common sites of knee injury.
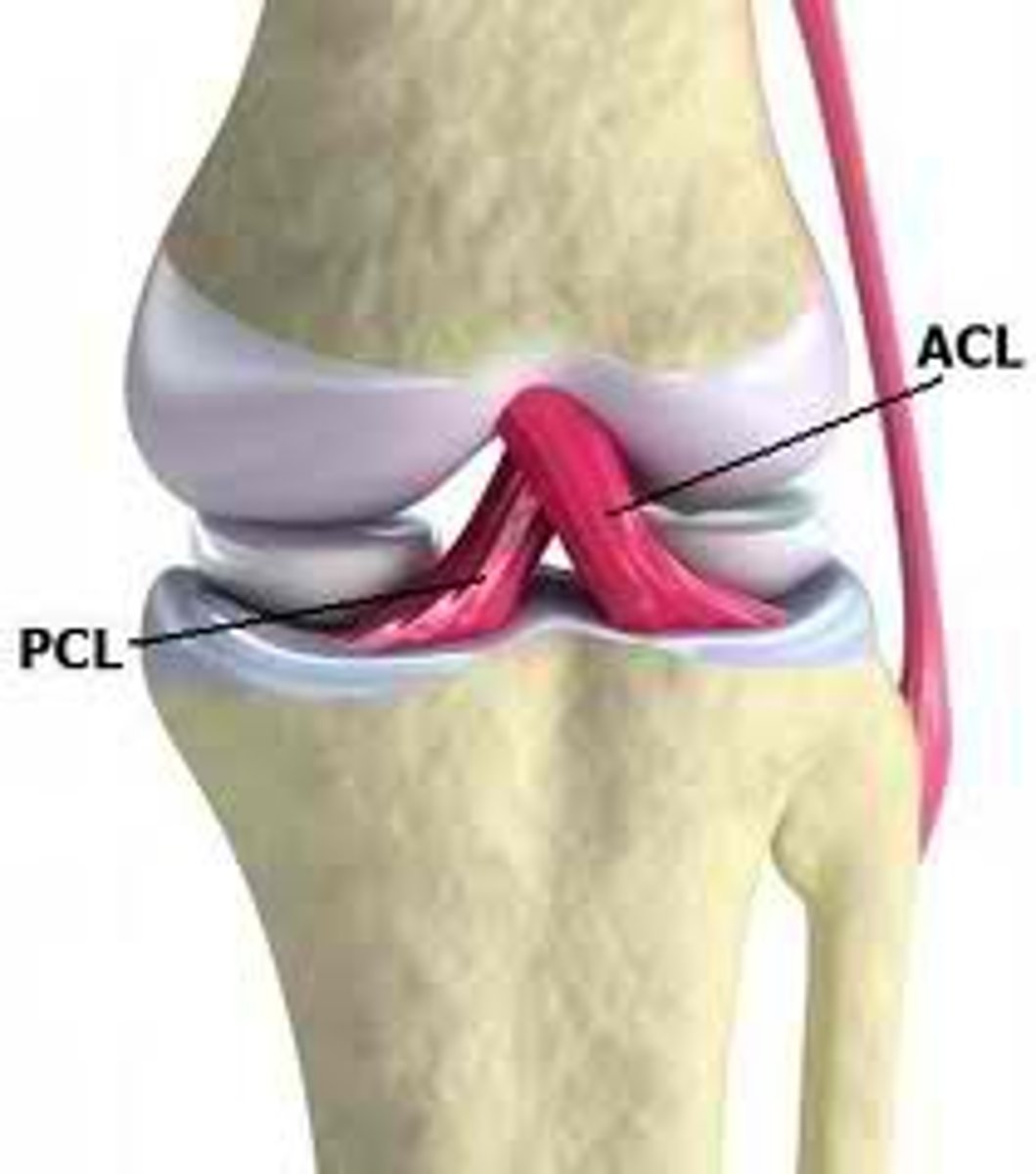
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
Prevents the femur from sliding off the front of the tibia and prevents the tibia from being displaced backward.
Superficial Infrapatellar Bursa
One of the four anterior bursae of the knee joint.
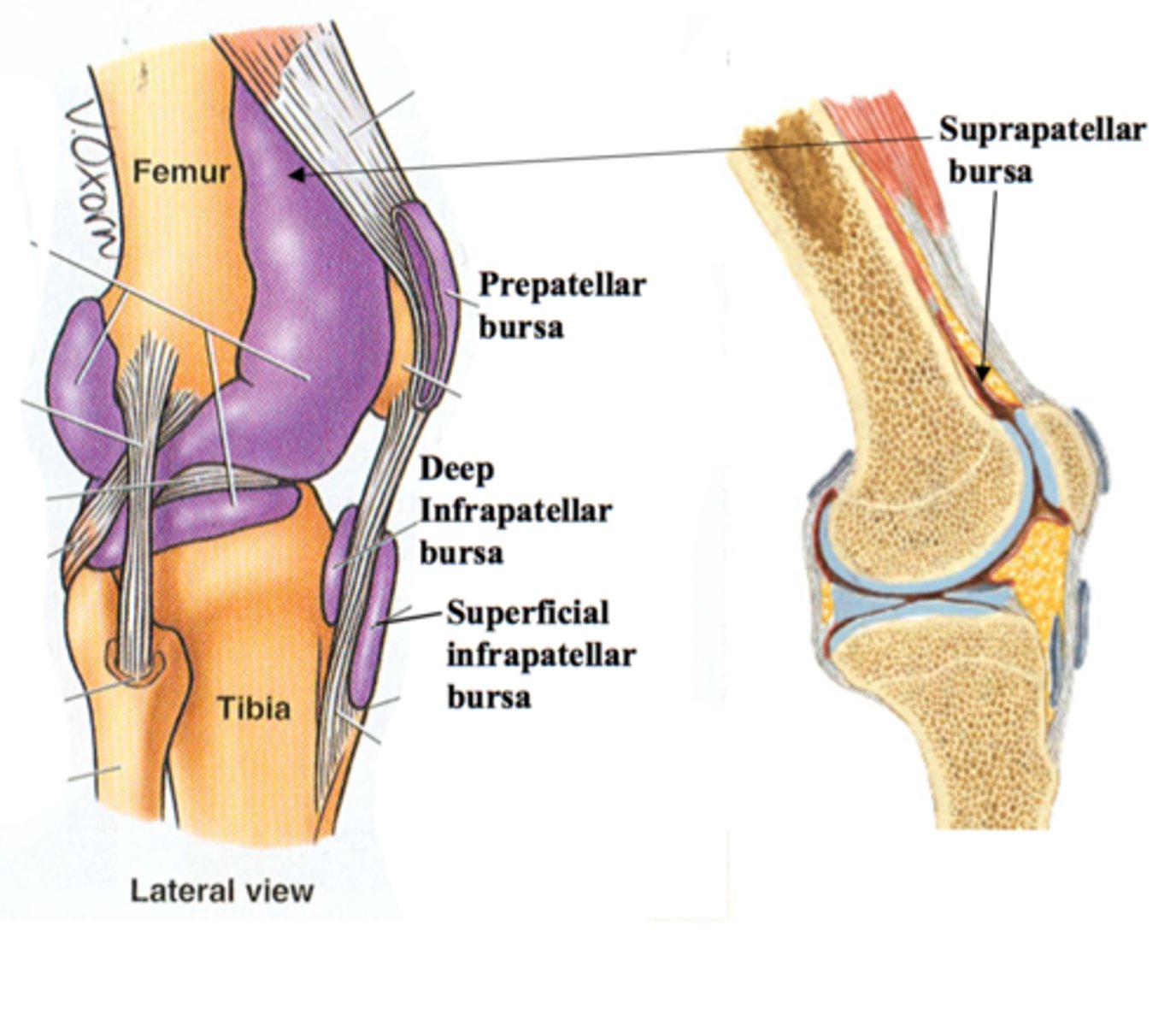
Suprapatellar Bursa
One of the four anterior bursae of the knee joint.
Prepatellar Bursa
One of the four anterior bursae of the knee joint.
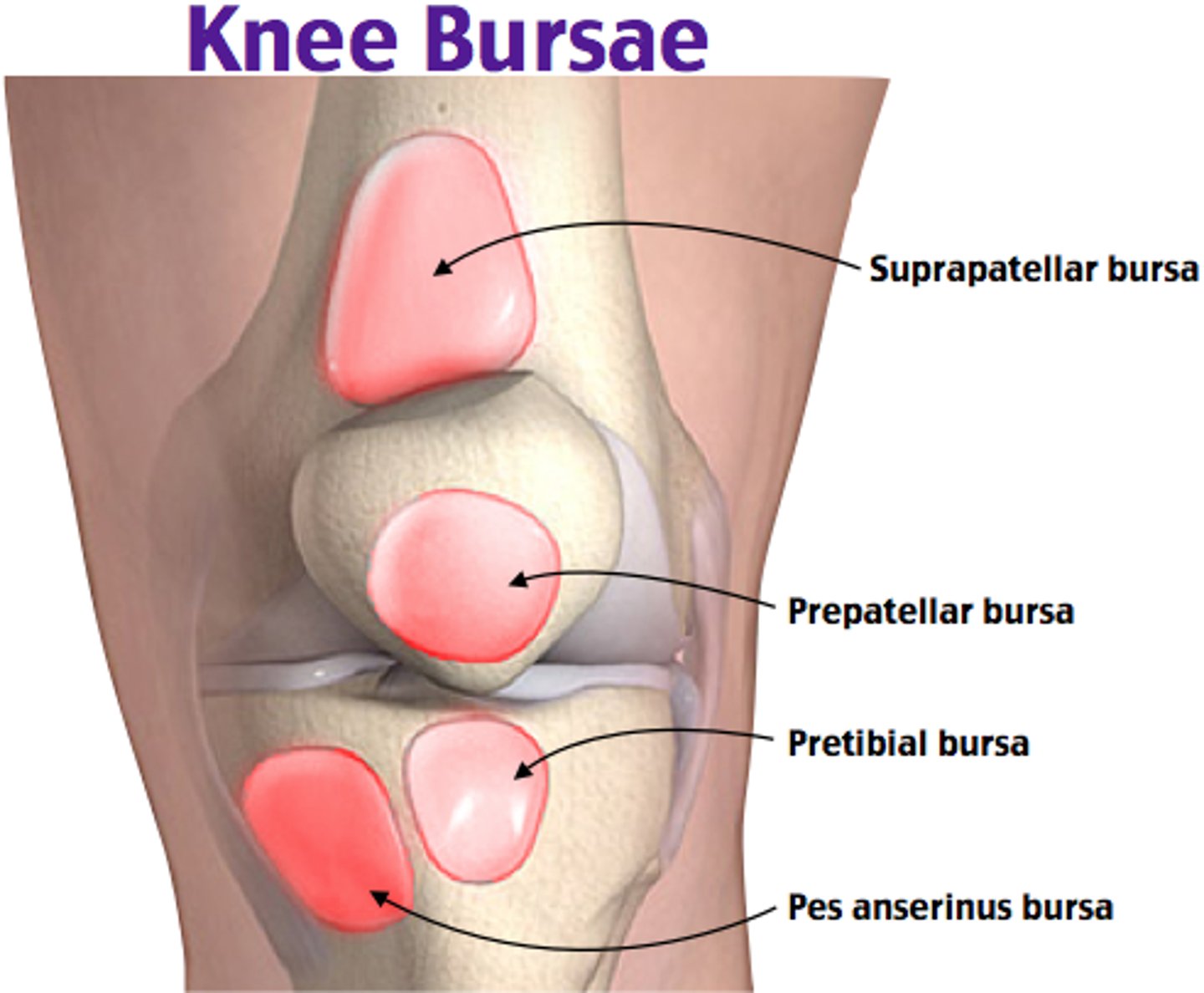
Deep Infrapatellar Bursa
One of the four anterior bursae of the knee joint.
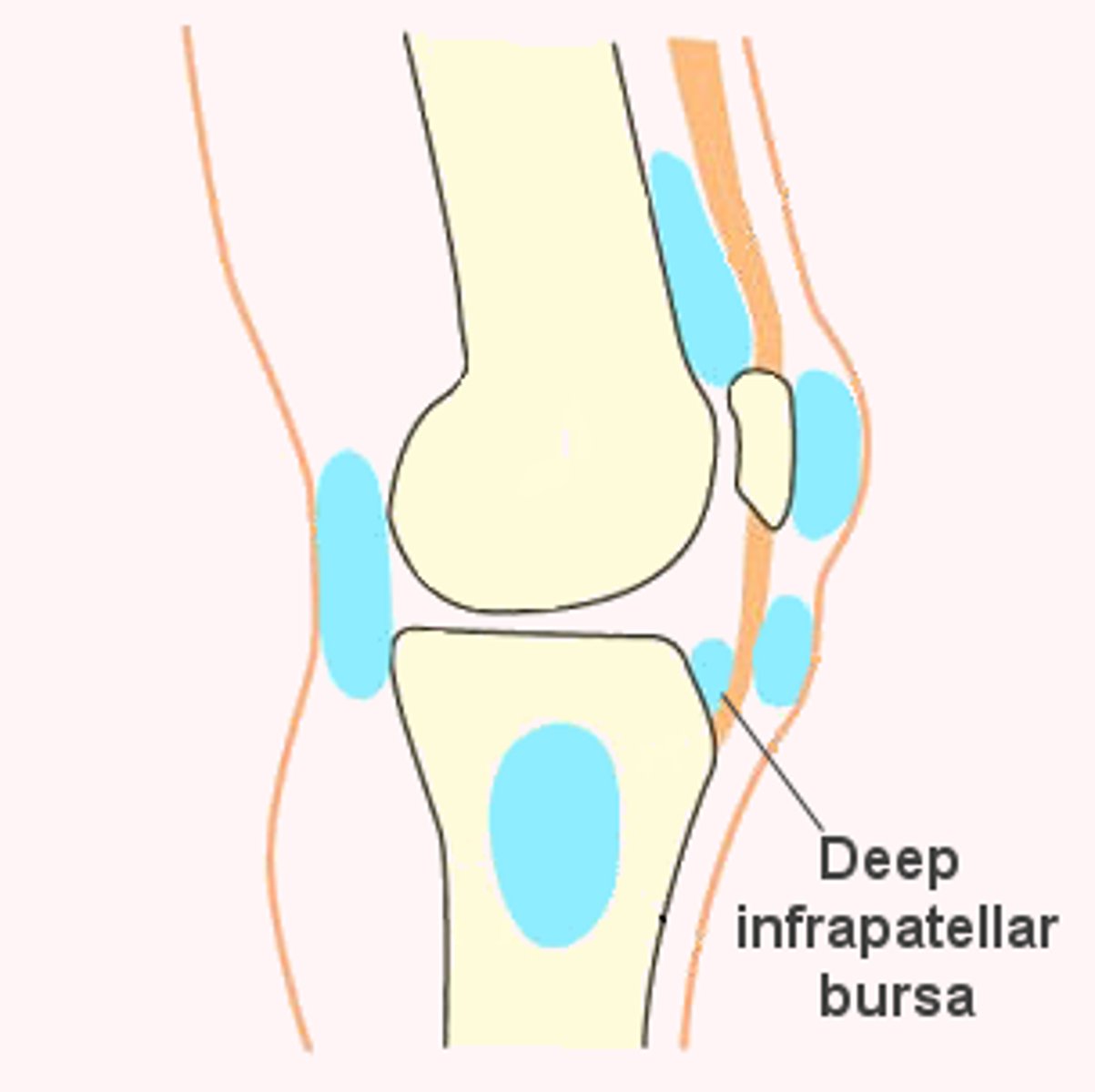
Popliteal Bursa
Located in the popliteal region of the knee joint.
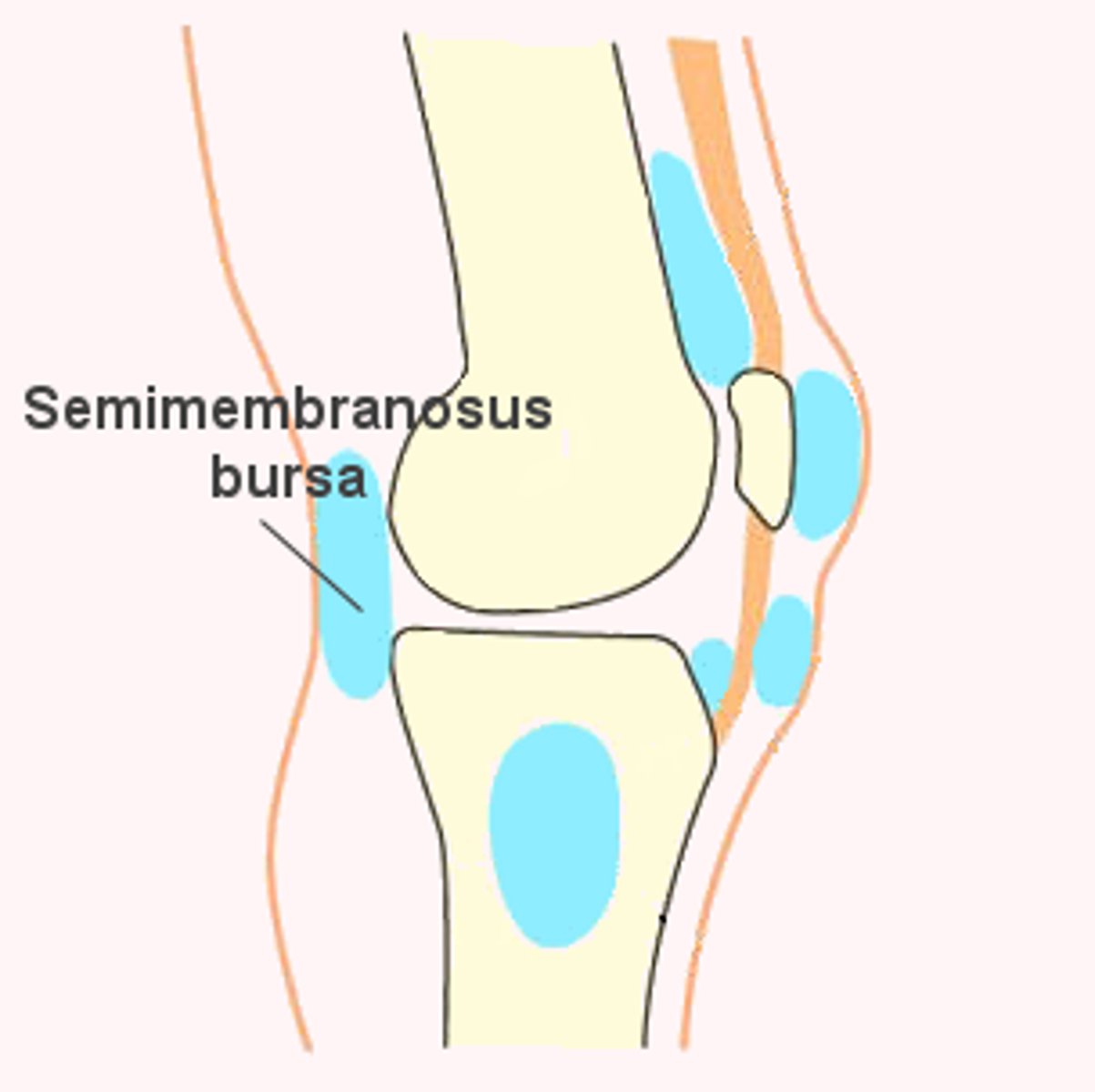
Semimembranosus Bursa
Located in the popliteal region of the knee joint.
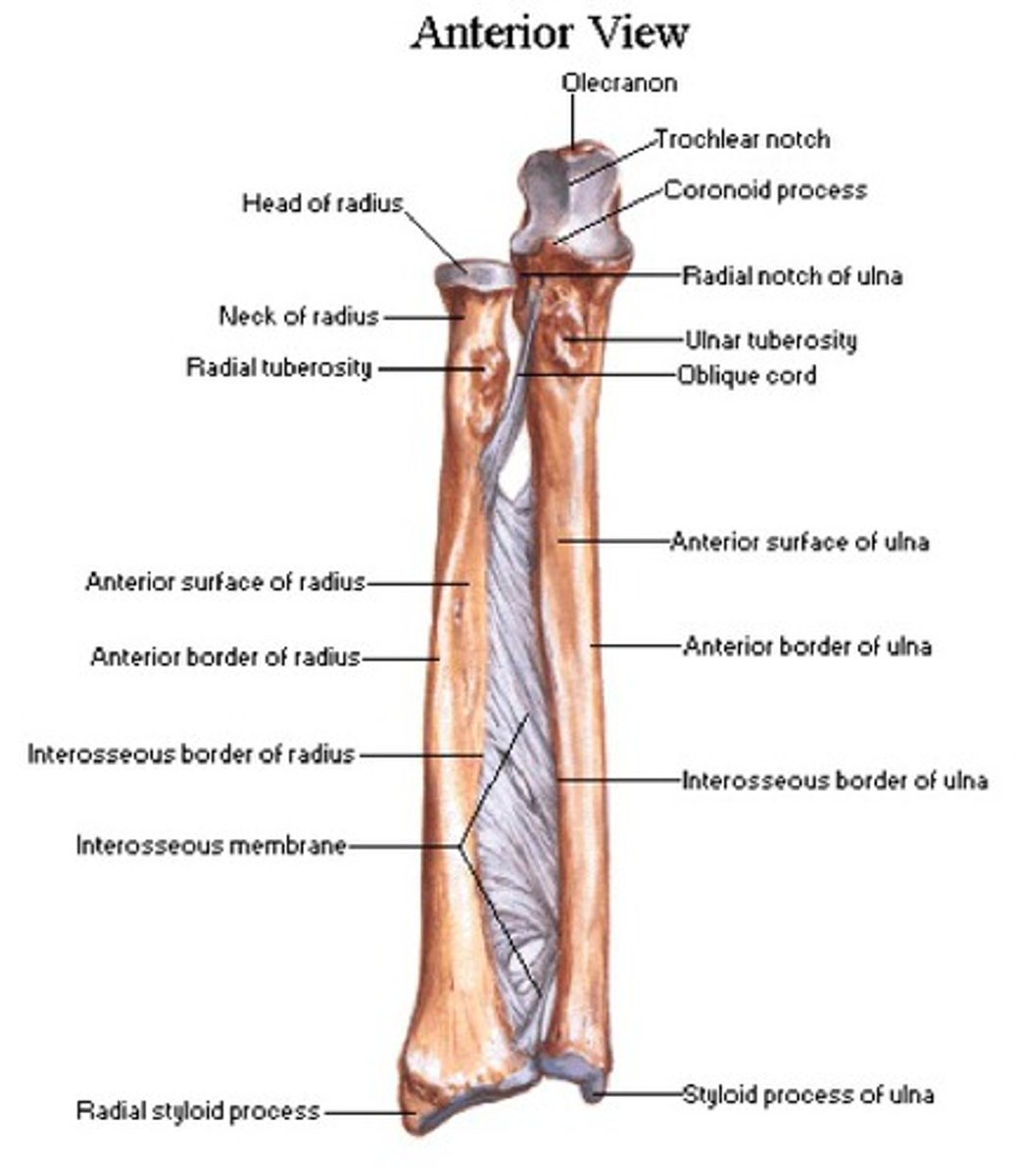
Important features of the radius
The radius has a head, neck, radial tuberosity, styloid process, articular facets, and ulnar notch.
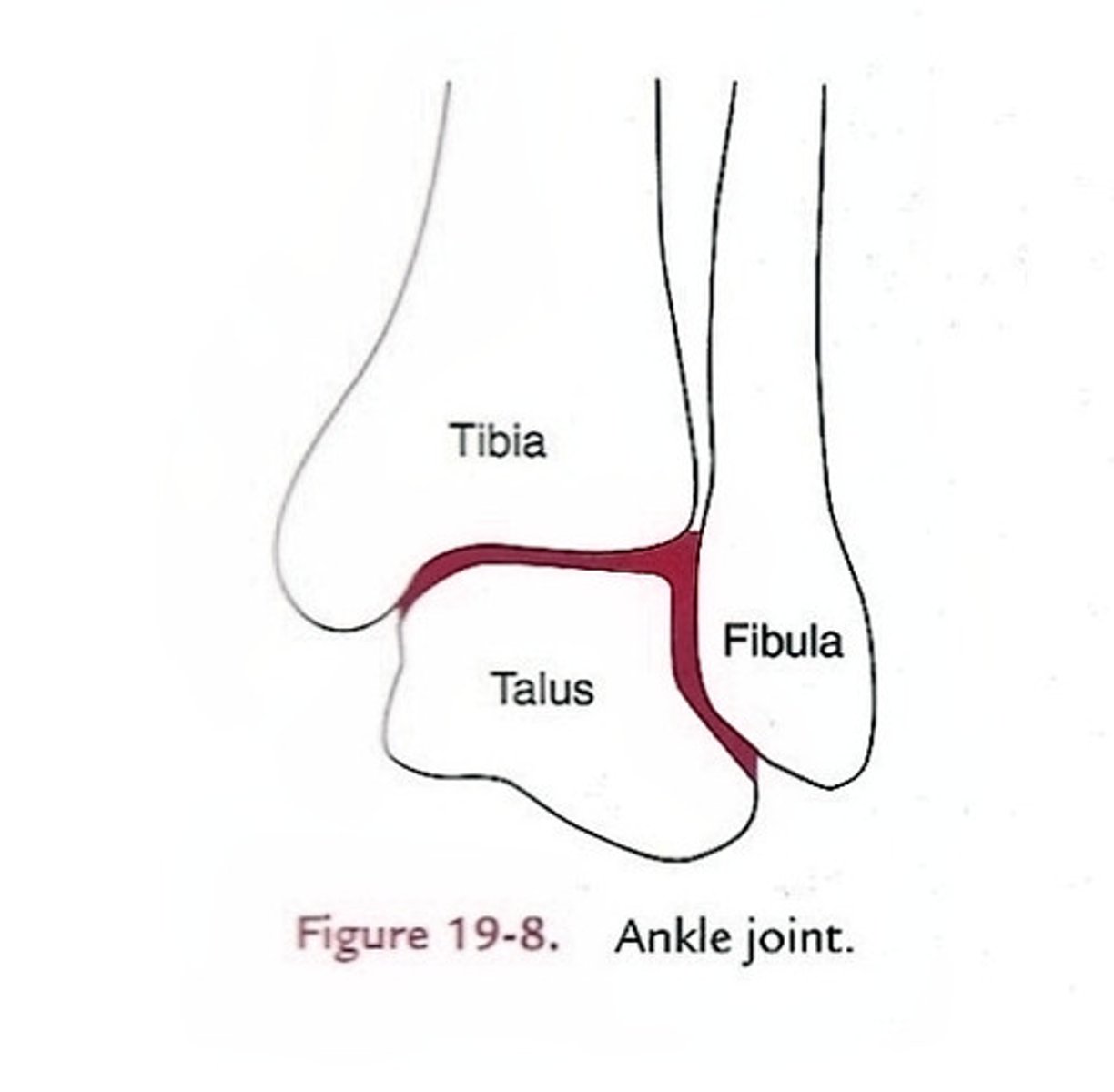
The talocrural joint
The ankle joint, including two articulations—a medial joint between the tibia and talus and a lateral joint between the fibula and talus, both enclosed in one joint capsule.
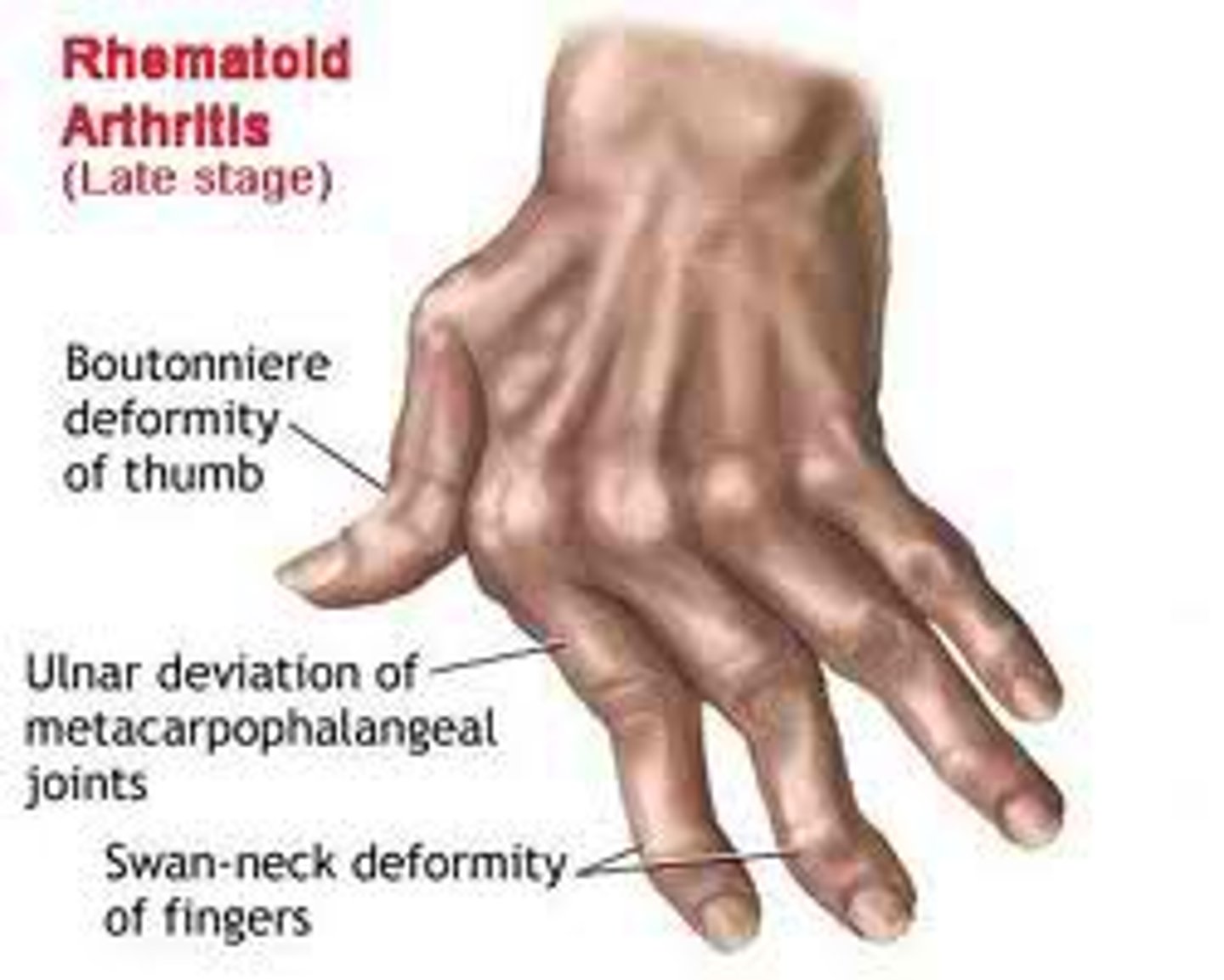
Arthritis
A broad term embracing more than 100 types of joint rheumatism.
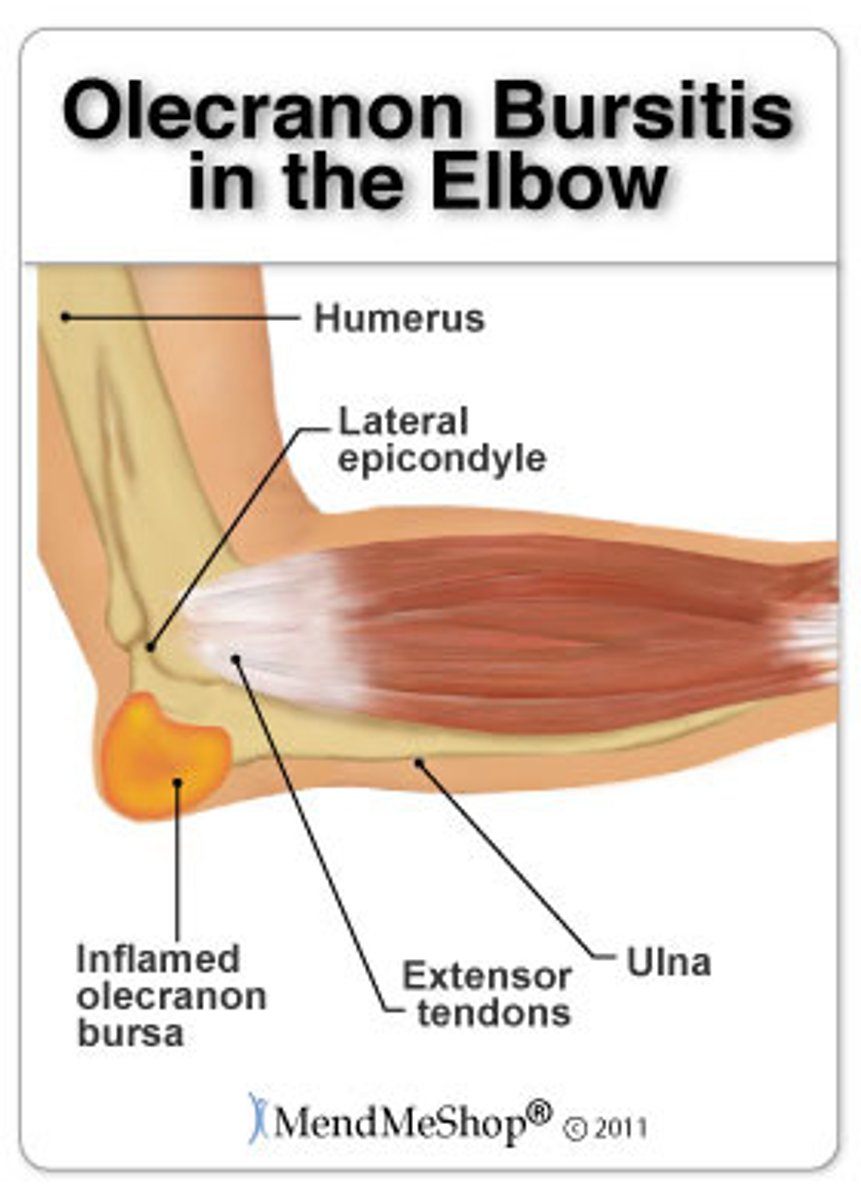
Bursitis
Inflammation of a bursa, usually due to overuse of a joint.
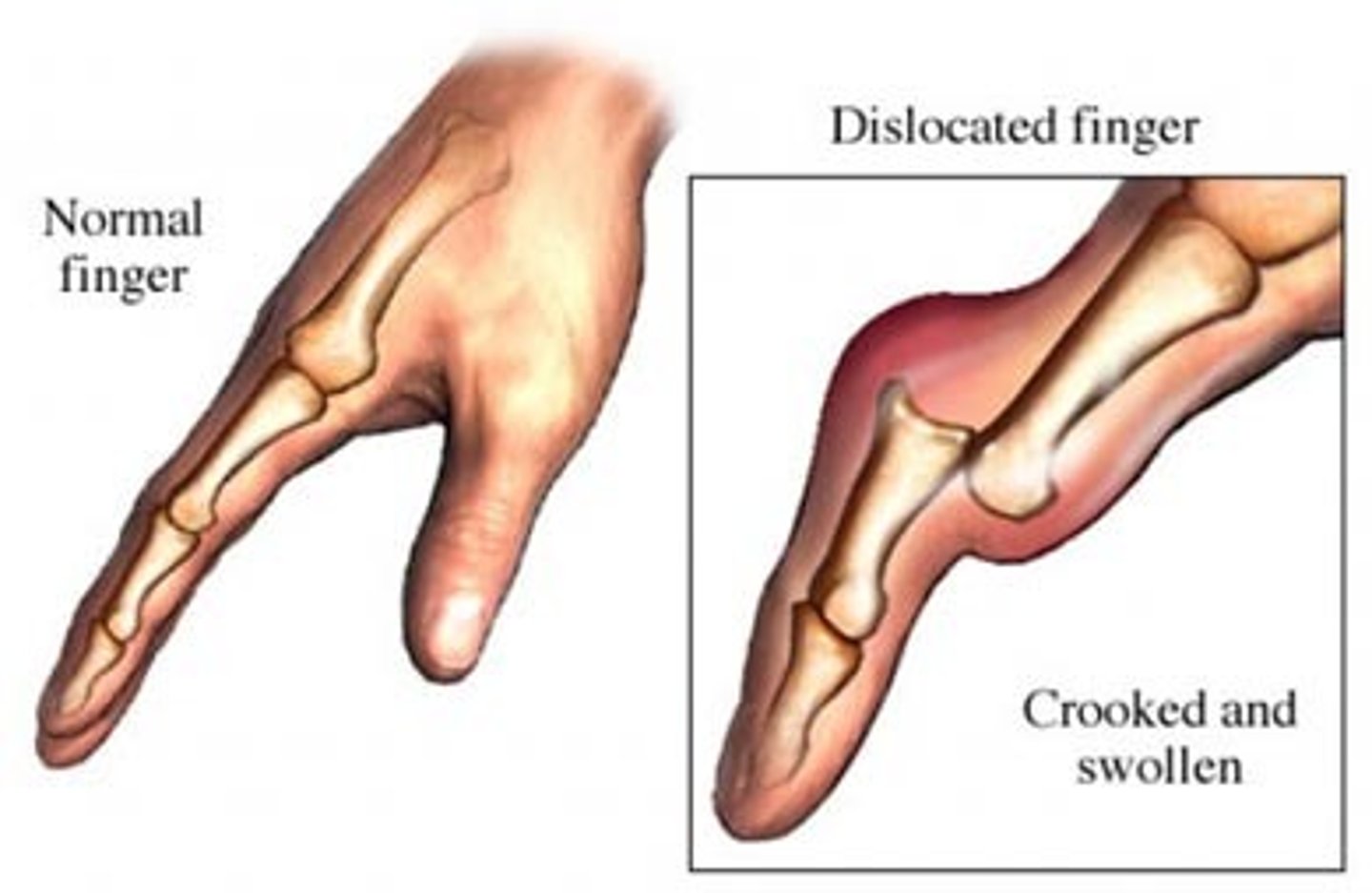
Dislocation
Displacement of a bone from its normal position at a joint, usually accompanied by a sprain of the adjoining connective tissues.
Gout
A hereditary disease, most common in men, where uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing pain and swelling.
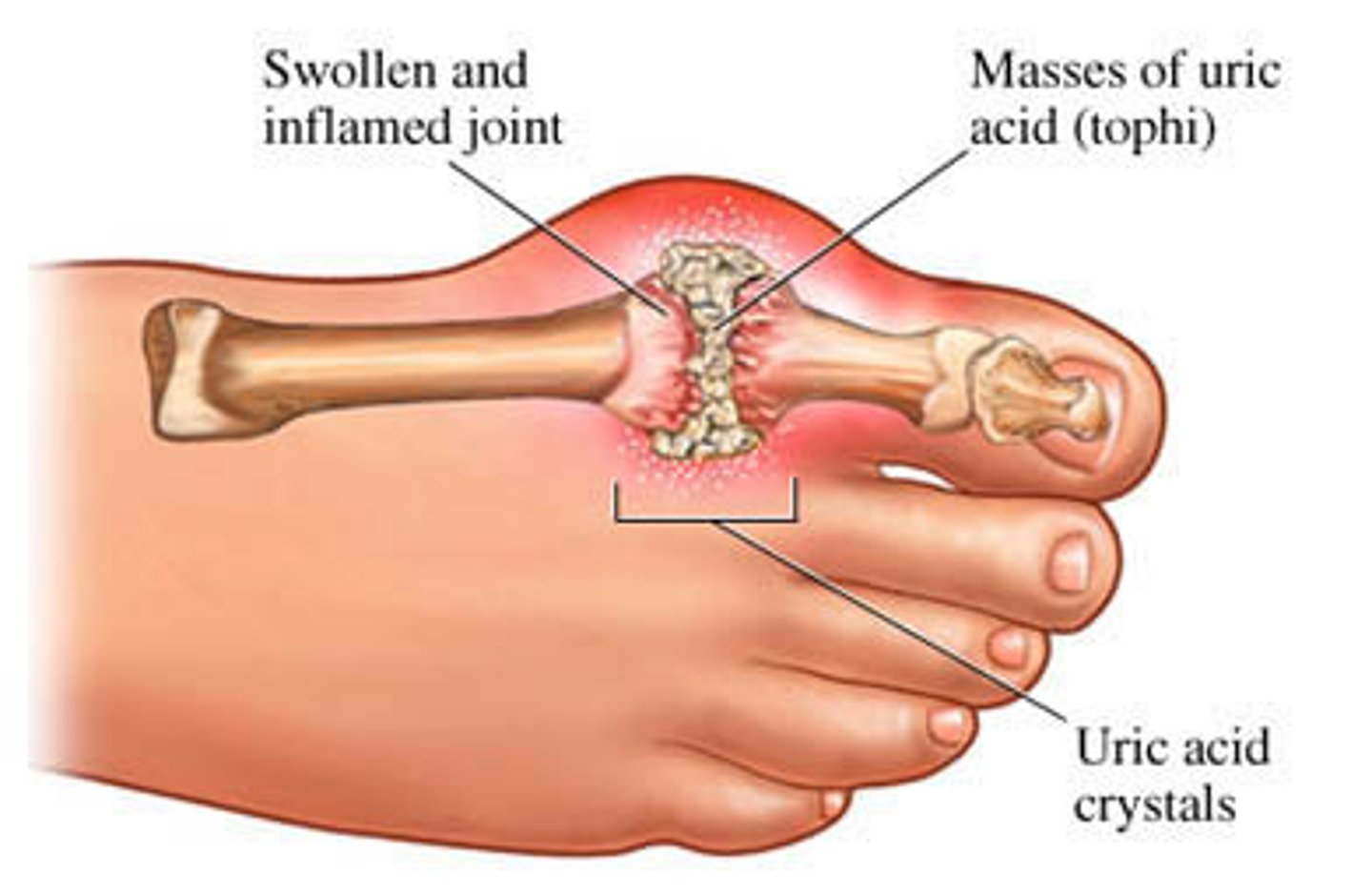
Rheumatism
A broad term for any pain in the supportive and locomotory organs of the body, including bones, ligaments, tendons, and muscles.

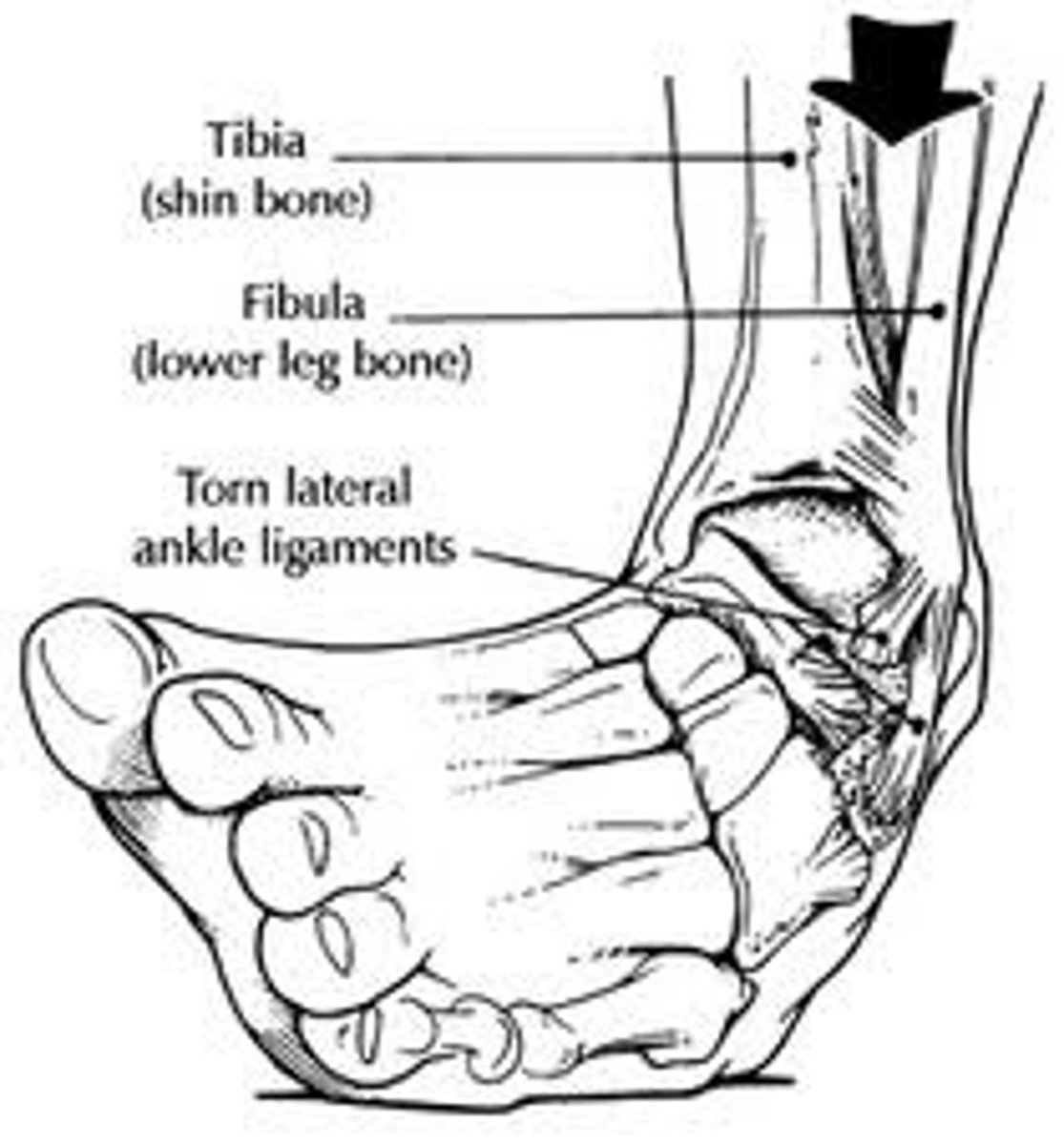
Sprain
A torn ligament or tendon, sometimes with damage to a meniscus or other cartilage.
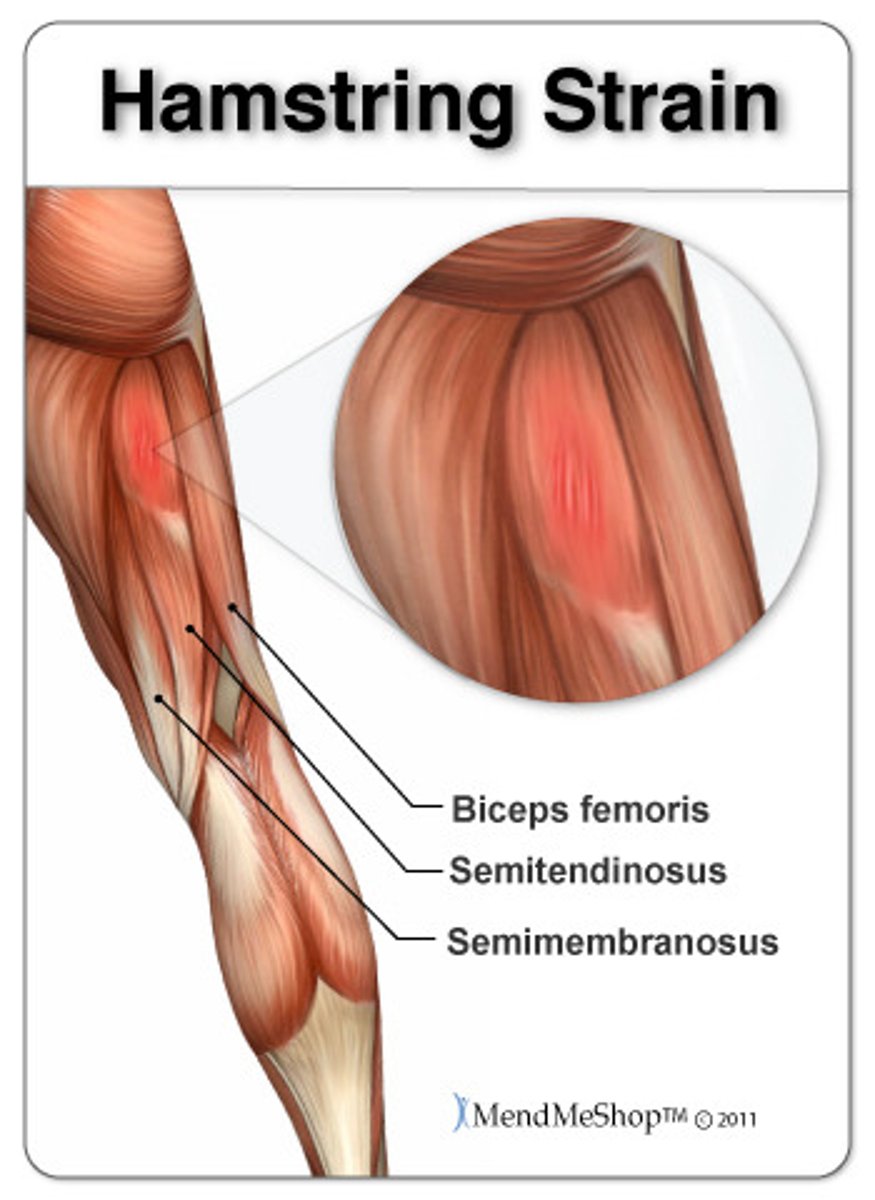
Strain
Painful overstretching of a tendon or muscle without serious tissue damage, often due to inadequate warm-up before exercise.
Synovitis
Inflammation of a joint capsule, often as a complication of a sprain.
Tendinitis
A form of bursitis in which a tendon sheath is inflamed.
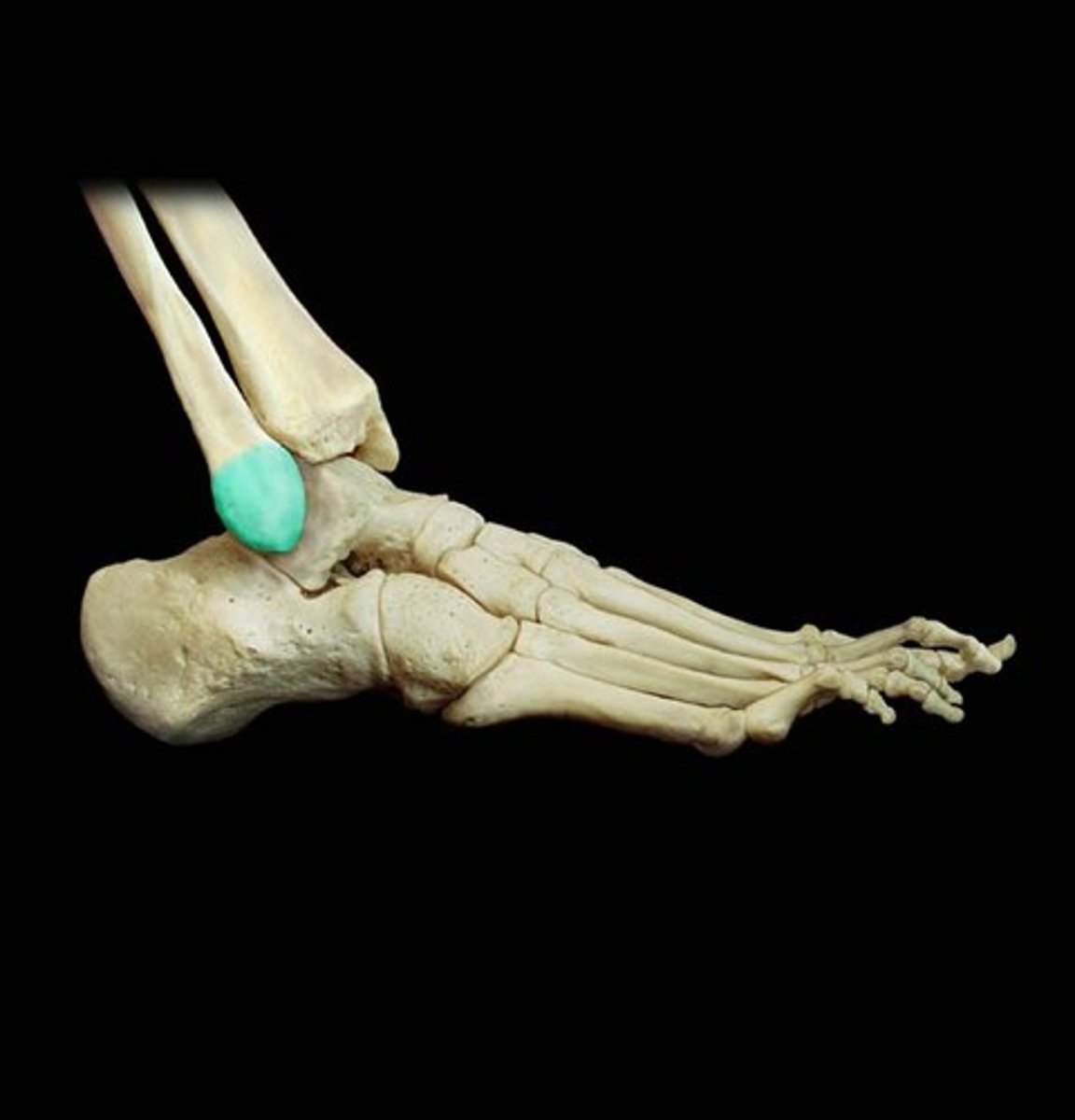
Malleoli
The malleoli of the tibia and fibula overhang the talus on each side like a cap and prevent most side-to-side motion.
Range of motion
The ankle has a more restricted range of motion than the wrist.
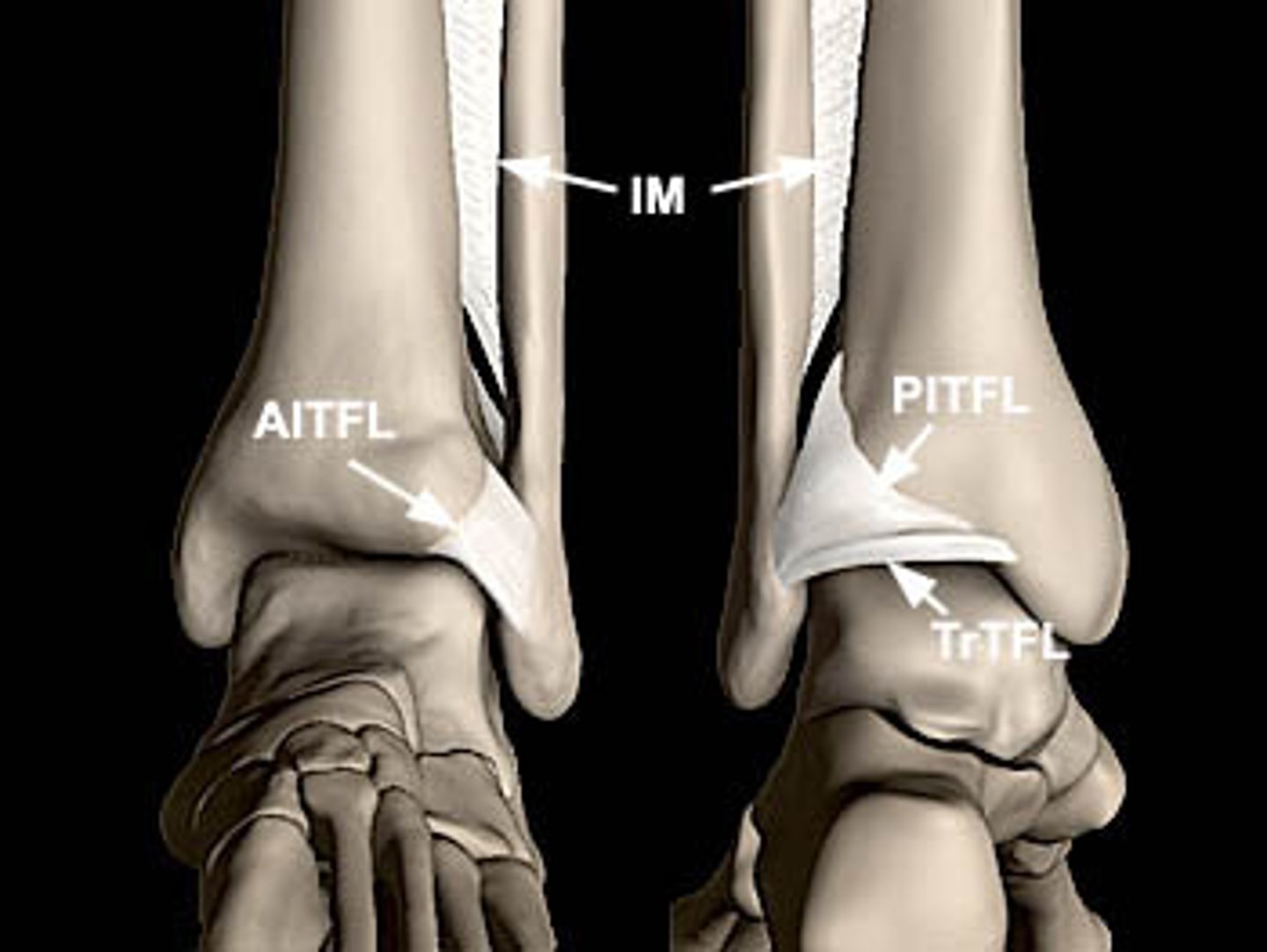
Anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments
Bind the tibia to the fibula.
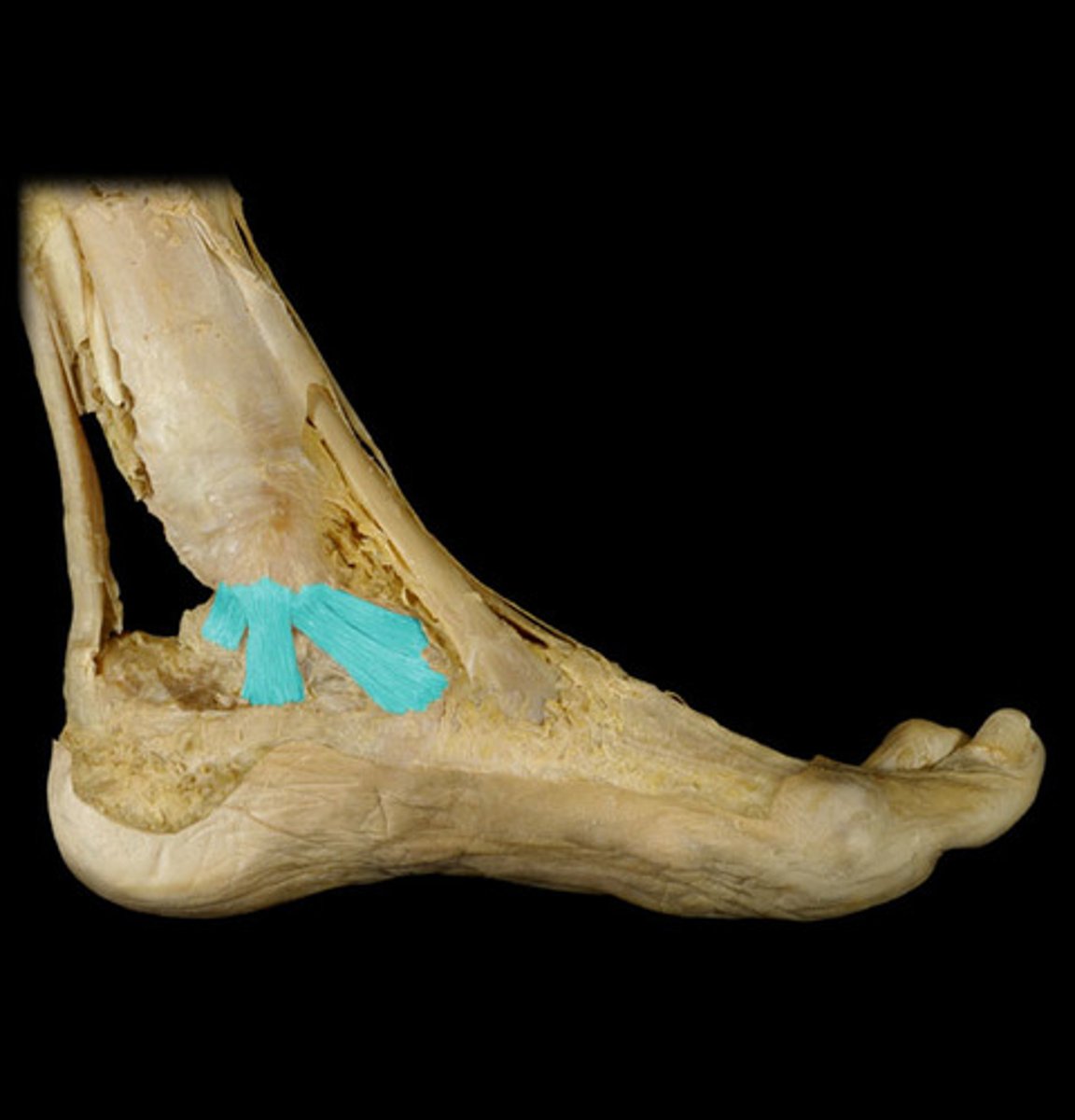
Medial (deltoid) ligament
Multipart ligament which binds the tibia to the foot on the medial side.
Lateral (collateral) ligament
Multipart ligament which binds the fibula to the foot on the lateral side.
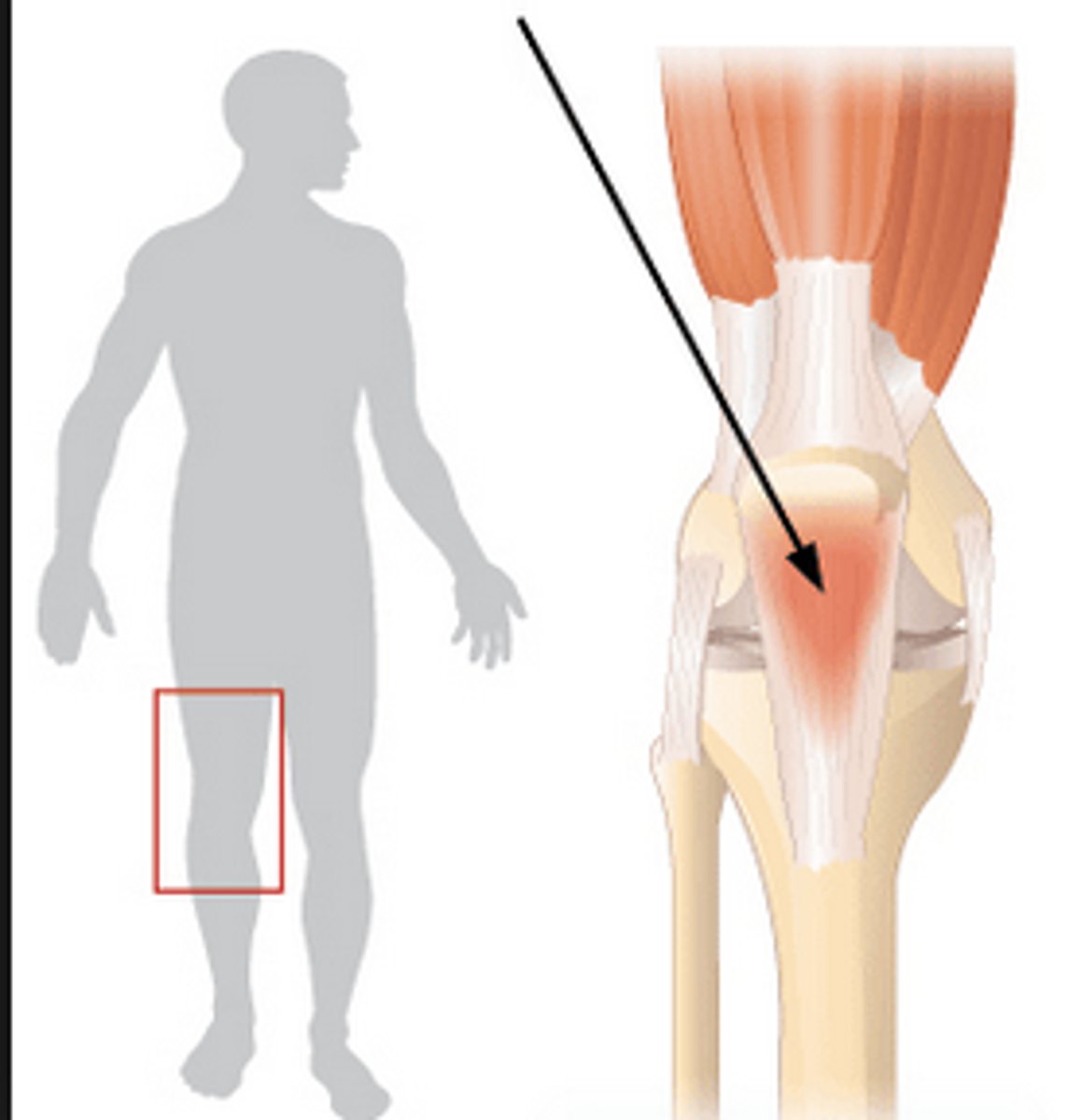
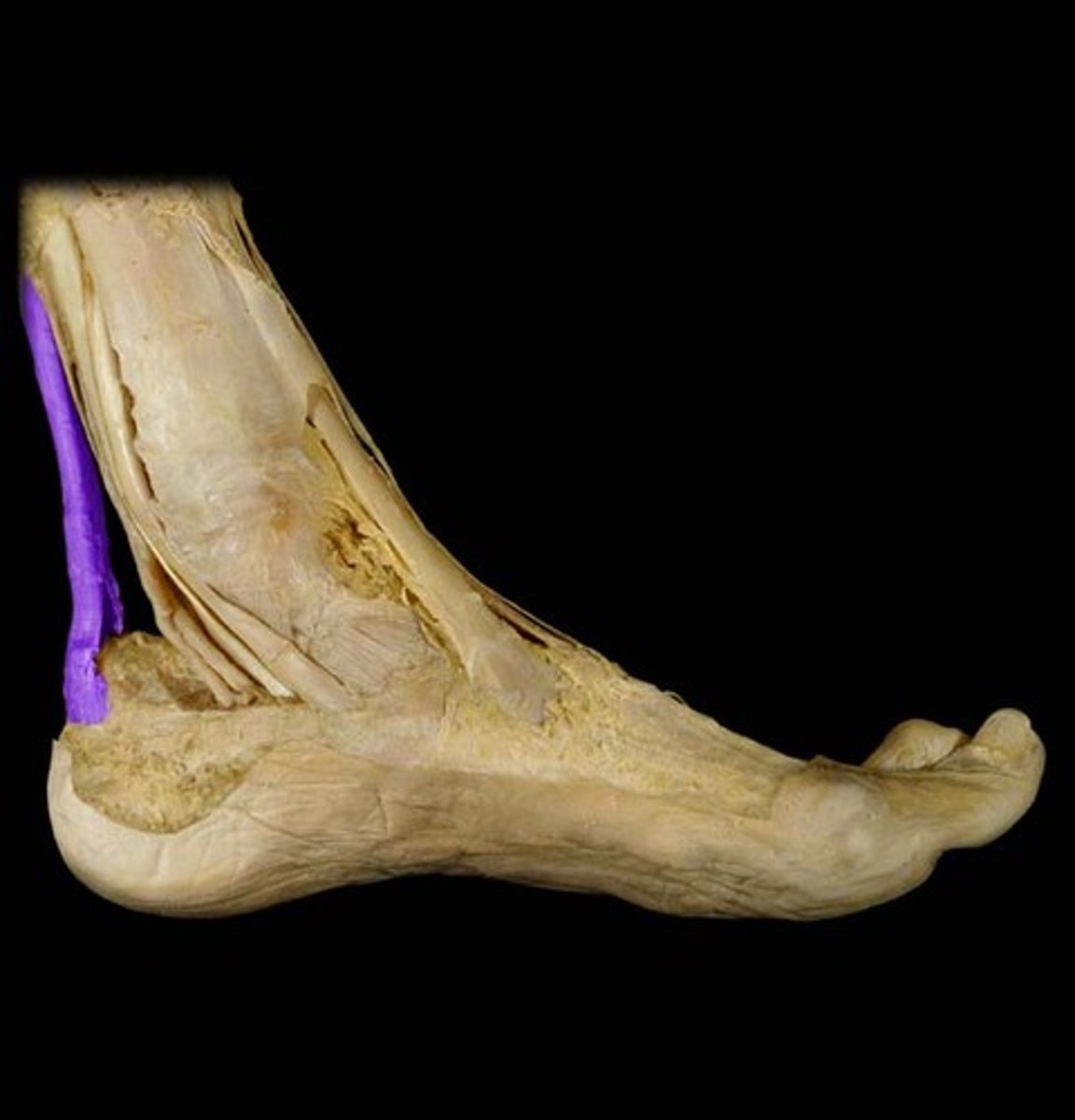
Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon
Extends from the calf muscles to the calcaneus, plantarflexes the foot and limits dorsiflexion.
Plantar flexion
Limited by extensor tendons on the anterior side of the ankle and by the anterior part of the joint capsule.