The respiratory system (Slides 1-23)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
1. Nasal cavities
2. Pharynx
3. Larynx
4. Trachea
5. Bronchi
6. Bronchioles
7. Terminal bronchioles
What is the respiratory portion of the respiratory system?
1. Respiratory bronchioles
2. Alveolar ducts
3. Alveoli
What is the entrance covered by skin from the nose of the nasal vestibule?
1. Sweat glands
2. Sebaceous glands
3. Coarse and moist vibrissae
What is the deeper in the vestibule of the nasal vestibule?
1. Respiratory epithelium (no keratin)
2. No sweat or sebaceous glands
3. Continues into the nasal cavity
What is the epithelial lining of the nasal cavity?
1. Respiratory epithelium
2. Roof of cavity and superior nasal conchae:
Specialized olfactory epithelium
What is the lamina propria (loose connective tissue) of the nasal cavity?
1. Loops of capillaries close to epithelium. Blood flows opposed to flow of inspired air
2. Seromucous glands
3. Plasma cells (IgA)
What is the respiratory epithelium?
1. Mucous lining of Most of nasal cavity and Organs of conducting portion.
2. Ciliated pseudostratified
columnar epithelium
3. Very thick basement membrane
4. Supported by lamina propria
What are the ciliated columnar cells of the respiratory epithelium?
Most numerous with 200-300 cilia on apical domain
What are the goblet cells of the respiratory epithelium?
Numerous. Predominate in some areas. Basal nuclei and apical granules with mucin
glycoproteins
What are the brush cells of the respiratory epithelium?
Much less numerous. Columnar. Few apical microvilli. Act as chemosensory
receptors
What are the small granule (Kulchitsky) cells of the respiratory epithelium?
Difficult to see. Numerous dense core granules. Part of the DNES. Do not reach
apical surface
What are the basal cells of the respiratory epithelium?
Stem and progenitor cells population. Active mitotic activity. Do not reach the apical
surface
In the Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium of the olfactory epithelium, what are the three major types of cells?
1. Olfactory neurons
2. Supporting cell
3. Basal cells
In the Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium of the olfactory epithelium, what is the lamina propria?
1. Loose CT
2. Nerve fibers
3. Olfactory glands (of Bowman)
4. Serous gland producing
flowing fluid that surrounds
the cilia of olfactory neurons
What are the olfactory neurons of the olfactory epithelium?
1. Bipolar neurons
2. Nuclei organized in an irregular, central row
3. Apical pole is the dendritic end
4. Knoblike swelling with a dozen basal bodies
5. Cilia extend from basal bodies into aqueous layer
6. Axons leave epithelium and enter the cribriform plate of ethmoid
bone
what are the supporting cells of the olfactory epithelium?
1. Columnar cells
2. Narrow base
3. Broad cylindrical apex with the nuclei
4. Bound to olfactory neurons by junctional complexes
5. Cell membrane with abundant ion channels
What are the Basal cells of the olfactory epithelium?
1. Small, spherical or cone-shaped
2. Near basal lamina
3. Stem cells
olfactory mucosa
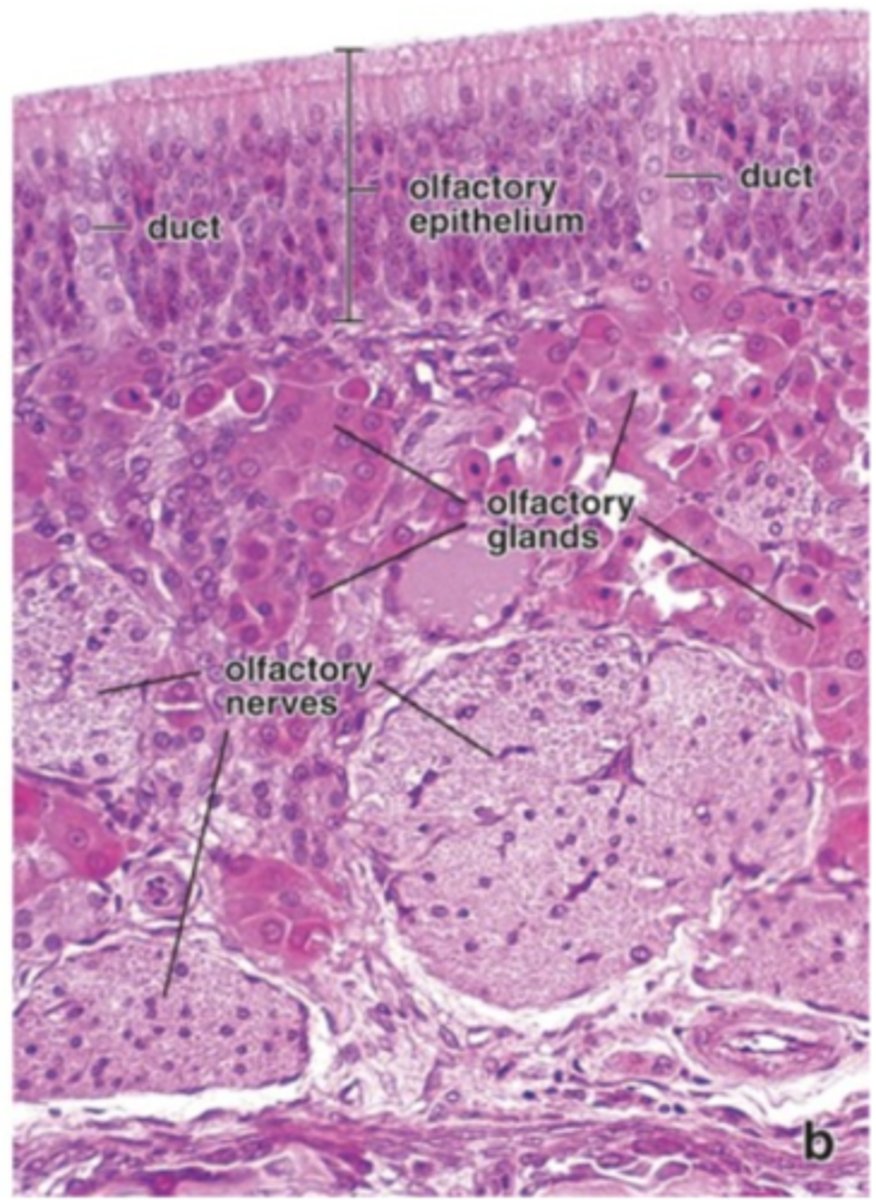
What are the paranasal sinuses?
1. Bilateral bone cavities
2. Open into nasal cavity
3. Lined by thin respiratory epithelium with few goblet cells
What is the lamina propria of the paranasal sinuses?
1. Few small glands
2. Continuous with periosteum
What is the nasopharynx of the pharynx?
1. Uppermost (first) portion
2. Communicates with nasal cavity
3. Respiratory epithelium
4. Mucosa contains the pharyngeal tonsil
5. Openings of the auditory tubes
What is the oropharynx and laryngopharynx of the pharynx?
Stratified squamous epithelium
What is the larynx?
Rigid walls reinforced by cartilages linked by ligaments (dense regular
connective tissue) and moved by skeletal muscle
What are the two kinds of cartilage does the larynx contain?
1. Hyaline cartilage
2. Elastic cartilage
Thyroid, Cricoid, and Inferior arytenoids are made up of what kinda of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
Epiglottis, cuneiform, corniculate, and superior arytenoids are made up of what kind of cartilage?
Elastic cartilage
What is the epiglottis?
Elastic cartilage covered by mucosa
What is the upper (lingual) surface of the epiglottis?
Stratified squamous epithelium
What is the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis?
Transition to ciliated pseudostratified epithelium
What is the lamina propria of the epiglottis?
1. Loose connective tissue
2. Mucous and serous glands
What are the vestibular folds?
1. Below the epiglottis and laryngeal vestibule
2. Partially covered by respiratory epithelium
3. Lamina propria with seromucous glands and some lymphoid nodules
What are vocal folds?
1. Below a ventricle found
beneath the vestibular folds
2. Covered with non-keratinized
stratified squamous epithelium
3. Dense regular CT (vocal
ligament) supports free end of
vocal fold
4. Large bundles of skeletal
muscle deep to mucosa
What does the trachea contain?
1. Mucosa
2. Submucosa
3. About a dozen of C-shaped hyaline cartilages
4. Adventitia (Dense CT)
What is the mucosa of the trachea?
1. Respiratory epithelium
2. Lamina propria of loose CT rich in
elastic fibers
3. Numerous seromucous glands
What is the submucosa of the trachea?
1. Loose CT (slightly denser than LP)
2. Blood vessels
3. Seromucous glands (continuous
with those of the LP)
4. Nerve tissue
What are the main cells of the tracheal epithelium?
1. Columnar ciliated epithelial cells
2. Goblet (mucous) cells
3. Basal cells
4. Brush cells and small (Kultchisky )
granular cells are less numerous
What are the ciliated cells of the tracheal epithelium?
1. Most abundant
2. Full thickness of epithelium
3. Cilia: short hair-like projections of the apical
surface
4. Function as mucociliary escalator
What are the mucous (goblet) cells of the tracheal epithelium?
1. Interspersed between ciliated cells
2. Full thickness of epithelium
3. Apical granules with mucin
4. Lack cilia
What are the brush cells of the tracheal epithelium?
1. Similar to those in the nasal epithelium
2. Basal cells and Kultchisky cells as in the nasal
respiratory epithelium
What is the lamina propria?
1. Loose connective tissue
2. Very cellular includes lymphocytes
3. Diffuse and nodular lymphoid tissue
(MALT or more specifically, BALT)
4. Collagen and elastic fibers
5. EF are more extensive between the LP
and submucosa
What are the cells of the lamina propria?
1. Fibroblasts
2. Plasma cells
3. Eosinophils
4. Mast cells
What is the submucosa?
1. Slightly denser, loose CT (compared
to LP)
2. In other organs it is dense CT
3. BALT (diffuse and nodular)
4. Large distributing blood and
lymphatic vessels
5. Serous and mixed glands (mucous
acini with serous demilunes) also
present
What kind of mucous does the submucosal glands secrete?
mostly mucous