Topic 3b - Properties of waves
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How is a sound wave generated
Particles move to cause pressure, which travels out in waves
How does a sound wave travel through air?
Particles bump into each other, transferring energy in waves
Infrasound
Sound below the range of human hearing (below 20Hz)
Ultrasound
Sound that is above the range of human hearing (above 20kHz)
What does energy not transfer? Why?
Mass, because particle oscillate, changing areas of pressure but ultimately staying in the same place
Why do sound waves require a medium to travel through, but light waves do not?
Sound waves rely on particles changing pressure, whereas lightwaves are not particles and do not require them
What can travelling waves all do
Reflection, refraction, diffraction, interfere
Reflection
Bounce back from a surface
Refraction (of waves)
Change speed and direction as they enter a medium which has a different density
Diffraction (of waves)
Spread out as they pass through a gap
Interfere (waves)
Two sources cancelling out, such as a trough and a peak cancelling out to make a flat area
Vibration
Periodic back and forth motion of particles
What are the two types of waves
Transverse and longitudinal
What direction are oscillations in a transverse wave compared to the direction of energy transfer?
Perpendicular
What direction are oscillations in a longitudinal wave compared to the direction of transfer?
Parallel
Example of a transverse wave
A person attaching a rope to a wall and swinging it up and down
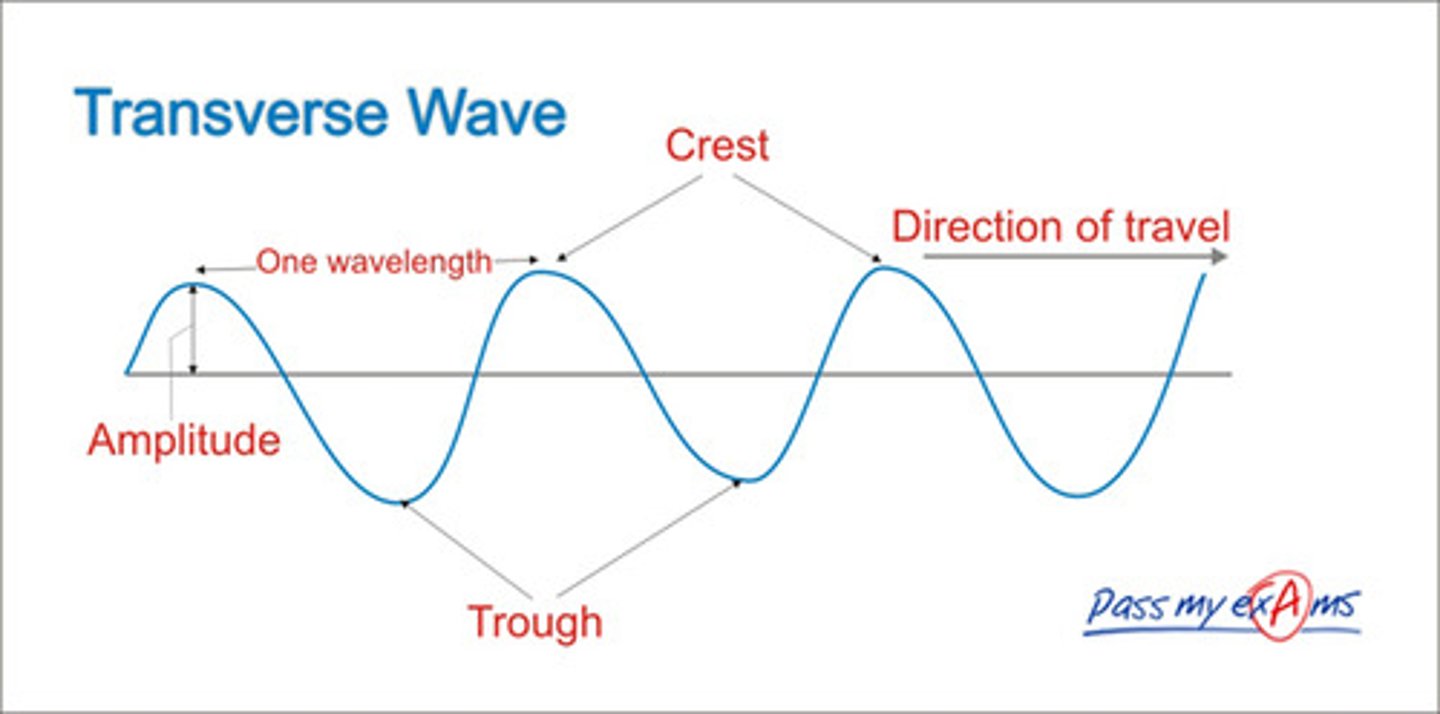
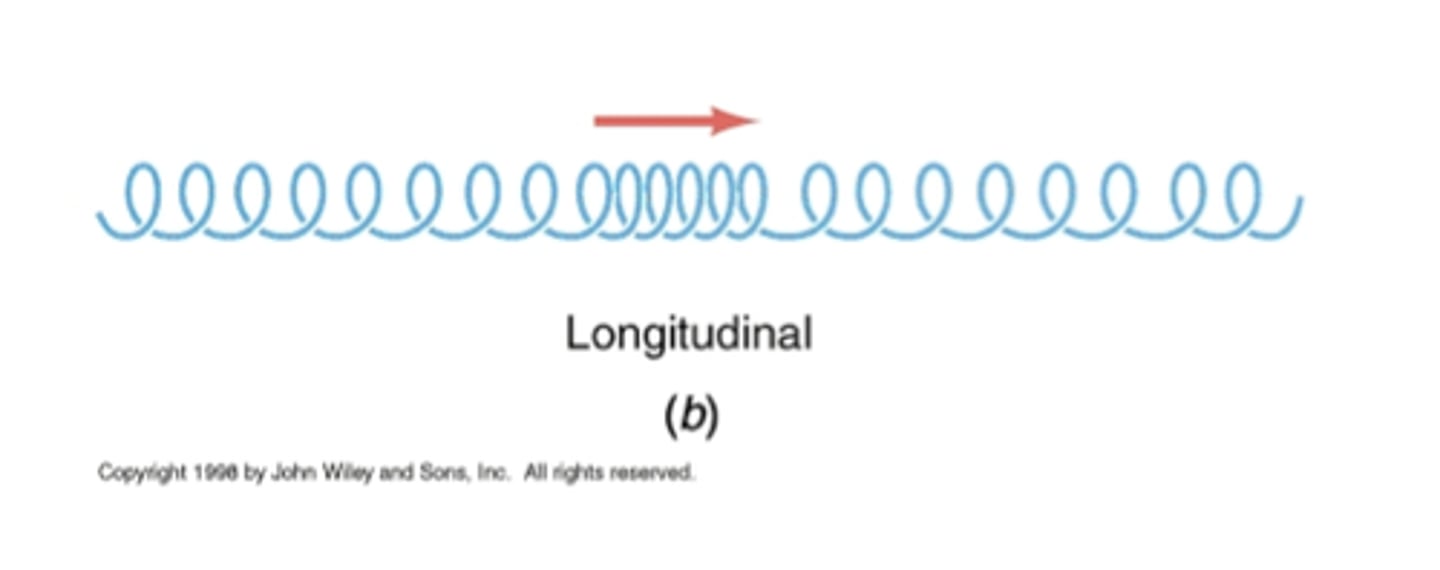
Example of a longitudunal wave
moving a slinky from side to side whilst the slinky is laying flat
Amplitude
Height of the ave
Wavelength
Length of the wave
Peak
Highest point in the wave
Trough
The lowest point in the wave
Equilibrium line
A line which represents the position of the particles when they are stationary
Frequency
How many waves pass a point in a second
Wavefront
The crest of the wave
Example of a wave being reflected (2)
Water hitting a wall, light bouncing off a mirror
Doppler effect
When an object is moving, the sound heard by an observer is different to that produced, as the moving object begins to catch up with its own sound waves
Example of the doppler effect
When the frequency of an ambulance siren seems to change as it moves towards and away from us
What is the doppler effect when an object moves closer?
As the source and the observer move together the space between the waves decreases, and so does the distance between wave fronts. this decreases the relative wavelength, increasing the frequency, making the sound become higher.
What is the doppler effect when things move apart?
The space between waves increases, and so does the distance between wavefronts, increasing the relative wavelength. therefore the frequency decreases, so a sound becommes lower.
What happens to colours due to the doppler effect when things move closer
Green light shifts to the blue end of the spectrum
What happens to colours due to the doppler effect when things move further apart
Green light shifts to the red end of the spectrum
Propagate
The direction in which the energy of a wave moves