breeding and selection
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is animal breeding?
The process of selective mating of animals with desirable traits to maintain or enhance these traits in future generations
What are the two types of breeding?
Artificial
Natural
What are the functions of breeding programmes?
To increase production, productivity, product quota amd cost efficiency
What does anthropocentric mean? What does this mean in terms of animal breeding?
Human focused
breeding for traits that benefit us
What is important to consider when breeding?
To maintain genetic diversity
Support conservation and breed use whilst considering animal welfare and sustainable systems
Animal sex can be determined in one of two ways, what are these?
Genotypic sex determination (chromosomal composition determines at point of fertilisation)
Environmental sex determination (environmental conditions during development determine sex)
XX/XY , most mammals what does the presence of Y initiate?
Male development (males = heterogametic)
ZZ/ZW, in birds, other reptiles, fish some mammals etc what does the presence of W initiate ?
Female development (females = heterogametic)
What are the types of environmental sex determination?
Temperature sex determination
Social sex determination (diff social situations)
Photoperiod (more daylight vs shorter days )
What is a trait?
Specific characteristic of an individual
Traits can be either: …
Quantitative or qualitative
What are qualitative traits?
Can be classified into categories and are controlled by a single or small number of genes, leading to distinct phenotypic variation (eg eye colour)
What are quantitative traits?
Cannot be categorised and are controlled by a large number of genes (polygenic) . These traits can be affected by the environment and their phenotypic presentation varies continuously (eg weight )
Qualitative traits are inherited in a simple Mendelian manner, what is Mendelian?
Inheritance patterns following laws of segregation and independent assortment, gene inherited from parent segregate into gametes at equal frequency
Eg Aa x Aa = AA, aa, Aa, Aa
Quantitative traits are best explained by fishers’ infinitesimal model, what does this mean?
Variation in quantitative traits influenced by an infinitely large number of genes, each making an infinitely small (infitesimal) contribution to the phenotype
Phenotype is also influenced by the environment

Some traits will be dominant, others will be ….?
Recessive
What are epistatic interactions?
Actions of one gene on another, one gene can mask another
(Eg albinism where recessive phenotype masks expression of pigment genes)
Inherited disorders are usually associated with a mutation in what?
In locus coding for a protein for development or metabolism , usually recessive
Follows mendels law
What are polygenic traits?
Measured on a continuous scale and can be affected by the environment eg growth rates
Polygenic traits are complex traits involving what?
Many metabolic pathways, lots of enzymes, receptors, transporters, proteins and lots of loci
Polygenic traits can be affected by the environment give an example
Height , weight etc
Consider two twins with identical genetics raised in different environments ending up different
Environmental conditions can cause the same genotype to…?
Produce different phenotypes, different outward expression
Is disease resistance considered a quantitative or qualitative trait?
Quantitative - resistance phenotype is a continuous distribution, some more resistant and some less resistant to disease
What are QTLs?
Quantitative trait loci, the genomic locations that influence phenotypic variation of a trait
Statistical markers can be used when breeding
Many of the traits which are suggested to affect the quality of meat and considered to be what kind of traits ?
Quantitative traits
What can we use QTLs for breeding relating to quality of meat?
Marbling, tenderness, fat content, colour etc
QTL which have a heritable link are desired, some meat traits are more heritable than others , what can be said about fat colour, meat colour, meat texture and marblings heritability?
Fat colour. (0.01)
Meat colour (0.16)
Meat texture (0.31)
Marbling (0.49)
What is phenotypic plasticity?
How phenotype can change beyond what we’d naturally expect to see
Some traits can have the same genotype but have a different phenotype depending on the environment, the phenotype is responding to the environment rather than the genotype, what is this called?
Phenotypic plasticity
What makes up a phenotype ?
Phenotype = additive value of genes (breeding value ) + non additive genetic effects at each locus + environmental effects
What can be said about our level of control over phenotype ?
even though they are controlled by a large number we can have some influence and some control, although some outcomes are not always guaranteed because they are complex
Clues in breeding when predicting progeny phenotype can come from what?
Own performance
Measures of performance
Performances of relatives
Performance in related traits
Genomic information
What is BLUP and what is its use?
Best linear unbiased prediction
Method of estimating random effects
Combining information to estimate genetic value and adjusting for environmental factors
Are all qualitative traits heritable ?
No
Why can quantitative traits never be 100% heritable?
Due to environmental influence
Heritability can be measured in percentage or a decimal, 0 meaning and 1 meaning what?
0 = will not be passed on
1 = guarantee to pass on
What is pleiotrophy?
One gene has influence over more than one trait,
Can be isolated as one gene
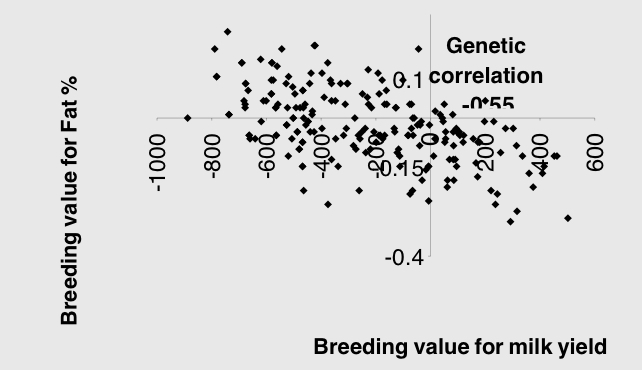
What can be said about traits affecting other traits in relation to this diagram?
No guarantee that we want both traits to increase/decrease/one to increase and one to decrease
There is a negative correlation between milk yield and fat percentage, selecting for milk yield could decline fat percentage, which is more valued?

Lower heritability leads to more variation, why?
Due to environmental impacts
Harder to predict outcomes across generations
Whilst improvements can be made across a species, what are we making changes within?
Within a population, across breeds/establishments, not the whole species
Selective breeding looks to mate animals with desirable traits to either maintain these or enhance these in future generations, what is the challenge in this ?
Challenge with consumer/market demands evolving, possibility adding more pressure to those in less vertically integrated farming/animal systems
In the environment animals will select their own mating partner, in captivity we make the selection for them, what are the 3 breeding options?
cross breeding
Within breed/ line selection
Inbreeding
What are pros and cons of inbeeeding?
Can increase desirable traits but can also reduce gene pool, build in recessive genes
What is crossbreeding?
Looks to mating together animals from different breeds to exploit their complementary traits as well as exploit heterosis
Creating more adaptable individuals
What is hybrid vigour?
Increase in characteristics of a hybrid organism over its parents
Creating off spring that is better than its parents
what are the negative effects of crossbreeding?
Positive outcomes not guaranteed
Can make small populations if we mix breeds
Environmental challenges pit pressure on animals but can increase variation in genetics
Heterosis is greatest for traits associated with what?
Survival, fitness and reproduction
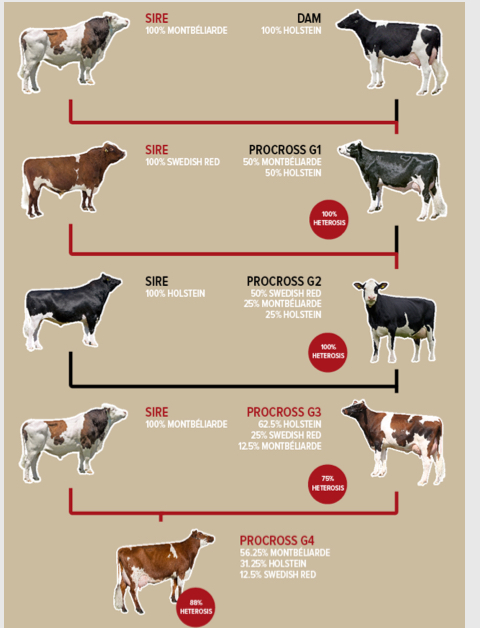
What is systematic cross breeding?
Looks beyond the first generation at a structured multi generational process to achieve specific genetic goals (long term planned strategies)
Procross g4 is goal
What are composite breeds?
New breeds produced through the process of systematic cross breeding (maintained over many generations until a distinct uniform population exists )
What is within breed/line selection?
Involves breeding distantly related individuals (inbreeding is more closely related )
Looking to concentrate desirable traits from common ancestors without the same level of risks with inbreeding
Why is it important to record performance accurately and objectively with within breed/line selection?
If undesirable animals end up in breeding population, goal is harder to achieve
With within breed/line selection what does the breeding goal look like ?
What we want to improve (likely to look to improve outputs)
Why do we need to compare to animals in the same environment with within breed/line selection?
Different environment will have a different impact on performance
What is the EBV?
Estimated breeding value - numerical value to how good the animal is that has been bred
Positive number = above average , negative number = below average
the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) is the statistical method used to calculate the result of breeding 2 individuals together, calculates the EBV
What can EBV help with?
Help farmers to select which animals to breed with others or which animals to buy in/ purchase semen for
Variation in their availability and depth
What does 0, positive and negative mean in terms of EBV
positive number = above average
0 = breed average
negative = below average
Why do we want to select animals with highest EBV to be parents of next generation?
Generation on generation improvement (cumulative , permanent and cost effective - mostly)
What selecting animals with highest EBV to be parents of next generation be influenced by?
Heritability , selection pressures, accuracy of selection, generational intervals, genetic correlation with other traits
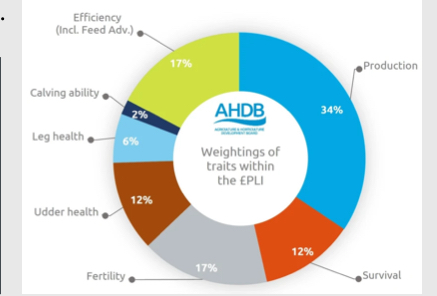
What is a selection index?
Composite score based on the breeding values of all the traits that someone may want to change to move towards a specific goal