AP Chemistry Formulas and Common Ideas
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
How much does 1 mole equal to particles?
6.022×10²³ particles
Formula for Moles
Grams/MM
Formula for changing gas laws
PV=NRT R=0.08206
Molarity Formula
M=mol/Liters
STP always occupies how many Liters?
22.4 Liters
How do you find Empirical Formula?
If given percent of element convert to grams and divide by MM. The smallest number of each is to be divided by all. That will give you the Empirical Formula.
How do you find the Molecular formula?
Once you’ve found the empirical formula, multiply by the molar mass of the compound divided by the molar mass of the empirical formula.
Coulombs law
describes the force between two charged objects, indicating that the force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Photoelectron spectrum (PES)
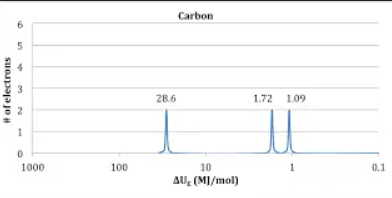
Atomic Radius trend
Decreases across a period and increases down a group due to increasing nuclear charge and electron shielding.
Ionization Energy trend
Increases across a period and decreases down a group. This trend occurs because higher nuclear charge attracts electrons more strongly, while additional electron shells increase shielding and distance from the nucleus.
Electronegativity trend
Increases across a period and decreases down a group. F has the highest electronegativity
Ionic bonds
Strong and hold ions tightly in a lattice. High melting and boiling points. Metal and Non-metal.
Lattice energy
Bond energy required to break ions out
Difference between Interstitial alloy and substitutional alloy
Interstitial alloy are metal atoms with two vastly different radii combine, while substitutional alloys have similar radii and replace each other in the lattice.
Metallic Bonding
“sea of electrons” Good conductors of electricity and heat.
Molecular covalent bonding
A type of chemical bonding where atoms share pairs of electrons to achieve stability. These compounds generally have low melting points and do not conduct electricity. (Non-metals)
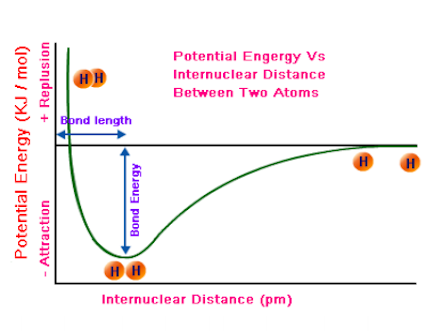
Internuclear distance
Elements with more bonds will be closer to the left and down more (double or triple bonds), while single bonds will be further to the right and up to the axis more.
Network Covalent
Diamonds, high boiling/melting point (SiO2)
Formal Charge
(# of valence electrons in free, neutral atom)-(# of valence electrons allocated {# of lone pair electrons+1/2# of shared electrons} to bonded atom) -see what group the element is and subtract by number of valence electrons. when there is more zeros in the balanced Lewis dot that is the better Lewis dot
Linear
180 degree bond angle; straight shape. Hybridization: sp
Trigonal Planar
120 degree bond angles; flat shape. Hybridization: sp2
Bent or Angular
Bond angles less than 120 degrees; V-shaped molecule. Hybridization: sp2 or sp3.
Tetrahedral
109.5 degree bond angles; three-dimensional shape. Hybridization: sp3.
Trigonal Pyramid
107 degree bond angles; pyramid shape with one lone pair of electrons. Hybridization: sp3.
Bent or Angular
2 lone pairs of electrons create a V-shape, affecting bond angles.
Trigonal Bipyramidal
90 degrees, sp3d
Seesaw
molecular shape with five regions of electron density, one equatorial lone pair, resulting in 90 and 120 degree bond angles.
T-shape
molecular shape with three bonding pairs and two lone pairs of electrons, creating 90-degree bond angles.
IMFs
LDF, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding
Dissolving
“LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE”
Distillation
A separation technique that takes advantage of differences in boiling points of substances in a mixture.
The Kinetic Energy of a single gas molecule
KE=1/2mv²
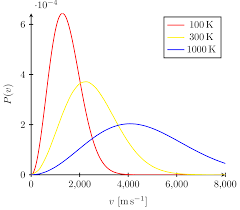
Maxwell-Boltzmann Diagrams
Graphical representations of molecular speed distributions in gases, illustrating the relationship between temperature and the kinetic energy of gas molecules.
Combined Gas Law
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
Dalton’s law
Ptotal=Pa+Pb+Pc…
Partial Pressure
Pa=Ptotal(Xa) Xa=moles of gas A/total moles of gas
Molar Mass equation
MM=drt/p
Energy and Electromagnetic radiation
deltaE=hv=h times c/wavelength Planacks constant=h=6.626×10^-34
Beers Law
A=Ebc E=molar absortivity b=path length in cm, c=concentration in mol/L
What two characteristics must an effective collision have?
(1) Sufficient kinetic energy (2) Correct orientation
Strong Acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HCIO3, HCIO4, HNO3, H2SO4
Which of the IMFs is generally the weakest?
LDF
What type of alloy is made when the radii of the atoms are similar in size?
Substitutional
How will the percent ionization of a weak acid change if water is added to it?
Increase
According to Coulomb’s Law, which TWo properties of an electron determine the strength of attraction to the nucleus?
Effective nuclear charge and Distance between electrons and nucleus
If Q increase, the voltage (Ecell) of the battery ? relative to E?
Decreases
Distillation separates mixtures based on
Boiling points
If a reaction increases the number of moles of gas, the sign for delta S would be
Positive
Which of the following does NOT speed up a chemical reaction?
Increase the concentration of a product
Temperature is the (blank) of particles?
Average kinetic energy
Percent ionization
The degree to which an acid or a base dissociates in solution, expressed as a percentage of the total concentration.
Adding conjugate base to a weak acid solution (blank) the percent ionization of the acid?
Decreases
What is the approximate bond angle of H2O?
109.5 degrees
Which TWO properties would cause high lattice energy in an ionic solid?
Small ionic radii and high ion charges
If a reaction is exothermic, the average bonds in the products formed are (blank) than the average bonds in the reactants?
Stronger
If a reaction is endothermic, the average bonds formed in the products are (blank) than the average bonds broken in the reactants?
Weaker
MaVa=MbVb at which point in a monoprotic acid/base titration?
The equivalence point
When forming an ionic bond…
Electrons transfer from a metal to a nonmetal
T or F: As acid concentration increases, percent ionization also increases
False
At constant volume, decreasing the temperature of a gas will cause the pressure to…
Decrease
An endothermic reaction feels ? and has a ? delta H
Cold;positive
If delta G is negative, then K is
Greater than 1
T or F: Spontaneous reactions are always fast
False
What are TWO components of a buffer?
Conjugate (base or acid) and Weak (acid or base)