Wave and Energy
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
mechanical and electromagnetic waves
Waves are classified as ____ [2].They either move in circular or straight motion.
Transverse wave
Longitudinal wave
Types of Waves [2]
Transverse wave
[Types of Waves] Movement of the particles of the medium are perpendicular to the direction of the wave motion
Longitudinal wave
[Types of Waves] Movement is parallel to the direction of the wave
Wavelength
____ - refer to the Distance between two corresponding points on a wave train.
Wave Frequency
____ - is Expressed in hertz which corresponds to the number of times the wave source completes a vibration in one second.
Wave Frequency
____ - corresponds to the number of times the wave source completes a vibration in one second
Period
____- refer to the time it take the wave source to make one complete vibration
Period
____ - is the reciprocal of frequency
Amplitude
____ - is the highest or lowest displacement from a wave’s equilibrium position
Increase in amplitude
[Increase/ Decrease] ____ in amplitude causes a transfer of more energy
Speed
____ - is directly proportional to frequency and wavelength
Speed is directly proportional to frequency
Speed ___ [directly /inversely proportional] to frequency ?
Speed is directly proportional to wavelength
Speed ___ [directly /inversely proportional] to wavelength?
Doppler Effect
_____ - occur when the speed of the wave is greater than the speed of the source.
Sound
Sound vs. Light
Sound Waves
Light
Sound vs. Light
Light Waves
Sound
Sound vs. Light
Longitudinal
Light
Sound vs. Light
Transverse
Sound
Sound vs. Light
Mechanical
Light
Sound vs. Light
Electromagnetic
Sound
Sound vs. Light
Propagated (spread) through a medium
Light
Sound vs. Light
Can be propagated (spread) without a medium (vacuum)
Sound
Sound vs. Light
Gas (slowest)
Light
Sound vs. Light
____ - In Gas (fastest)
Sound and Light
Sound vs. Light
Liquid
Light
Sound vs. Light
Solid(slowest)
Sound
Sound vs. Light
Solid (fastest)
Intensity
Pitch
Characteristics of Sound Waves [2]
Intensity
[Characteristics of Sound Waves]
loudness (amplitude/strength)
Pitch
[Characteristics of Sound Waves]
Highness or lowness of sound (frequency)
White light
_____ is not a color rather it is the presence of all frequencies of visible ligh
Black
____ is the absence of the visible light spectrum
White
Black
____ - is capable of reflecting all visible light spectrum and ___ is capable of absorbing all visible light spectrum and converted it to heat energy.
another color will be produced
When the colors of light with varying degrees of intensity are mixed/added, _____will be produced.
Red (R)
Blue (B)
Green (G)
Primary Colors of Light [3]
Yellow (Y) = R + G
Cyan (C) = B + G
Magenta (M) = B + R
Secondary Colors of Light
Yellow (Y)
Red + Green = ___ ?
Cyan (C)
Blue + Green = ___ ?
Magenta (M)
Blue + Red = ___ ?
White
Red + Blue+ Green = _____ ?
White light
_____ light can also be formed when the three primary colors with same intensity are added.
Red + Cyan
Green + Magenta
Blue + Yellow
Complementary Colors of Light [3]
White
Red + Cyan =____?
White
Green + Magenta____ ?
White
Blue + Yellow ____ ?
light which reflects off or transmits through the object.
The color of objects is not in the object but rather in the____ the object.
color subtraction
"In ____, the final color of an object is found by starting with one color (or a mix of colors) and seeing which colors are taken away from the original."
The object absorbs Blue under White light (which contains R+G+B).
Result: Yellow (Y) appears because blue is canceled (turned to heat), leaving red + green.
Explain: White Light (W) Minus Blue (B):
W−B =(R+G+B)−B
=R+G=Y
The object tries to absorb Blue under Red light (which has no blue to subtract).
Result: Red (R) appears because no blue is present to cancel.
Explain: Red Light (R) Minus Blue (B):
R−B=R
The object absorbs Blue under Magenta light (which is R+B).
Result: Red (R) appears because blue is canceled (turned to heat), leaving red.
Explain: Magenta Light (M) Minus Blue (B)
M−B= (R+B)−B =R
Law of Reflection
_____ - states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.”
normal line
Law of Reflection
The ____ is always drawn perpendicular with the reflecting surface
normal line
Law of Reflection
Angle of incidence and reflection is measured from the _____
multiple images will be formed
When light hits reflecting surfaces several times, ____ will be formed
number of images formed increases
If the angle between two reflecting surfaces such as mirror decreases, the number of images formed ____ [increases/decreases]
bends(refract)
Light____ when it travels obliquely from one transparent medium to another
toward or away from the normal
Light is bent ____ as it changes its speed when traveling through different optical media.
index of refraction (optical density)
A measure of how fast or slow light travels from one medium to another is called the _____ ?
optical density
index of refraction is aka ____ ?
Index of refraction
_____ -is a dimensionless quantity, and its value is always greater or equal to 1 since light travels fastest in a vacuum than any other media.
vacuum
Light travels fastest in a_____ than any other media.
light bends away
When the first medium has greater index of refraction than the second medium,light ____[bends away/bends toward] from the normal.
light bend toward
If medium 2 is denser than medium 1, light ____[bends away/bends toward] the normal
Snell’s law
____ -is the basic law of refraction that shows the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction
refracted ray travels slower than the than the incident ray (entering a denser medium)
When Angle of incidence(θi)>Angle of refraction (θR) : The refracted ray travels____ [faster/slower] than the incident ray (entering a denser medium)
The refracted ray travels faster than the incident ray (entering a less dense medium
When Angle of incidence(θi)<Angle of refraction (θR) : The refracted ray travels_____[faster/slower] than the incident ray (entering a less dense medium
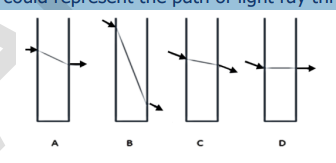
C
When light passes from air into glass, it slows down and bends toward the normal. When it exits from glass back into air, it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
Which of the diagrams shown below could represent the path of light ray through a glass block in the air?
Interference
____ -of wave is the meeting or superimposing (combine) of one wave on another wave.
Interference
_____ occurs when two or more light waves meet and combine (superimpose).
Constructive Interference
Destructive Interference
Types of Interference [2]
Constructive Interference
[Types of Interference ]
When: Waves arrive in phase (crest aligns with crest, trough aligns with trough
Constructive Interference
[Types of Interference ]
Result: Waves reinforce each other, creating a supercrest (brighter light) or supertrough.
Destructive Interference
[Types of Interference ]
Waves arrive opposite phase (crest meets trough with the same amplitude).
Destructive Interference
[Types of Interference ]
Result: Waves cancel each other, leading to no light (darkness).
reversed
Reflection in Plane Mirrors
The image is____ [reversed/the same] in a plane mirror.
virtual image is of the same size as the object in front of the mirror.
Reflection in Plane Mirrors
The virtual image is
_____ - [Same/greater] size as the object in front of the mirror
virtual or real image
The image may be _____or ____ depending on the type of curved mirror used (concave or convex) and object’s position.
Concave Mirror
Convex Mirror
Type of Curved Mirror [2]
Concave Mirror
[Type of Curved Mirror] Can produce real or virtual images, depending on the object's position.
Convex Mirror
[Type of Curved Mirror] Always forms a virtual, diminished image (smaller image)
Concave Mirror
[Type of Curved Mirror] moving the object changes the image (real/virtual, enlarged/reduced).
Diverging Mirror
Diverging Lens
[Classify What Lens and Mirrors]
Image Type: Virtual
Orientation: Upright
Size: Reduced
Converging Mirror
Converging Lens
[Classify What Lens and Mirrors]
Orientation: Upright
Size: Enlarged (when object is close to mirror)
Real Images (depending on object distance):
Real, Inverted, Enlarged
Real, Inverted, Same size
Real, Inverted, Reduced
Convex Mirror
Diverging Mirror is aka ___ ?
Concave Lens
Diverging Lens is aka ___ ?
Concave Mirror
Converging Mirror ____ ?
Convex Lens
Converging Lens is aka ___ ?
focal point (F)
When object is placed at an infinite distance, image is at _____
infinity
When object is at focal point (F), the image is at ______ . It will be perceived as a point in space.
Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
[Classify What Eye Defect] ____ - is the inability to see nearby objects clearly.
Nearsightedness (Myopia)
[Classify What Eye Defect] ____ - is the inability to see far objects clearly
[Classify What Eye Defect] Cause: Image forms behind the retina
Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
[Classify What Eye Defect]
Correction:
Lens Type: Converging lens (convex)
How It Works:
Increases refraction of incoming light rays
Bends rays more toward the principal axis
Shifts focus forward onto the retina
Nearsightedness (Myopia)
[Classify What Eye Defect]
Cause: Image forms in front of the retina
Nearsightedness (Myopia)
[Classify What Eye Defect]
Lens Type: Diverging lens (concave)
How It Works:
Spreads out incoming light rays
Bends rays more toward the principal axis
Shifts focus backward onto the retina
Myopia
Nearsightedness is aka __ ?
Hyperopia
Farsightedness is aka __ ?
Mirror or Lens Equation
It is an equation relating object distance and image distance with focal length.
Object Distance (𝑑ₒ)
In a spherical mirror or lens:
____ - is the distance from the object to the pole (center) of the mirror/lens.