math-125 final
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
integration by parts
∫u dv = uv - ∫v du
LIATE to assign u: Logarithmic functions, Inverse trig functions, Algebraic functions, Trig functions, Exponential functions
sin(θ) = x
√(a2-x2)
tan(θ) = x
√(a2+x2)
sec(θ) = x
√(x2-a2)
partial fraction decomposition
a way to simplify any rational function by splitting the denominator into several lower-degree denominators and solving for the numerators
steps: 1) factor denominator; 2) set up A, B, and C; 3) pick values of x to find A, B, and C; 4) integrate each fraction
improper
an integral is ____ if…
1) it has an unbounded region of interpretation
2) it has an integrand that is unbounded somewhere within the region of integration (lower bound, upper bound, or unbounded within the region
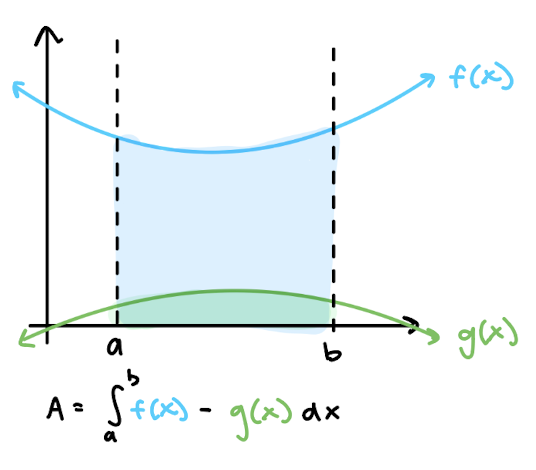
area between curves
top function - bottom function
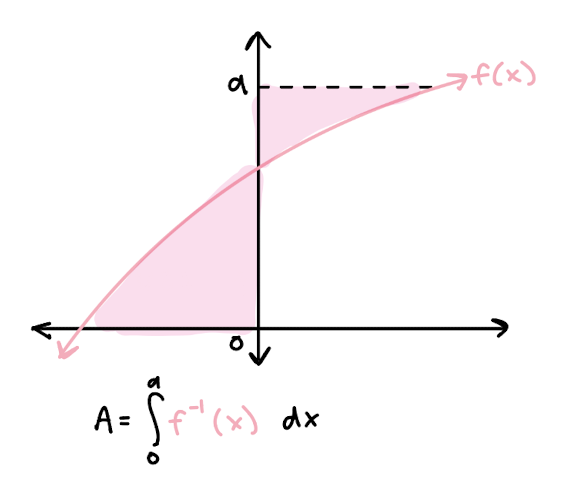
area between function and y-axis
put into terms of y and integrate
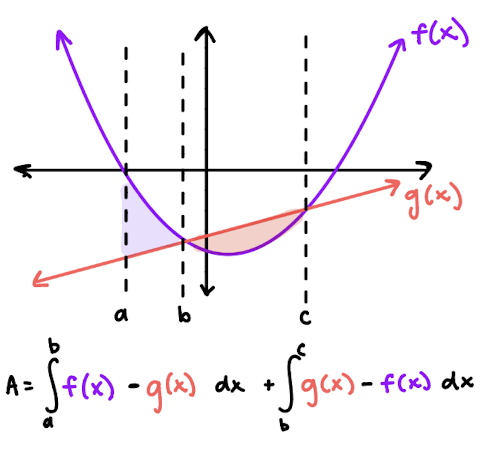
area between curves that intersect
set up two integrals — one before intersection point, one after intersection point
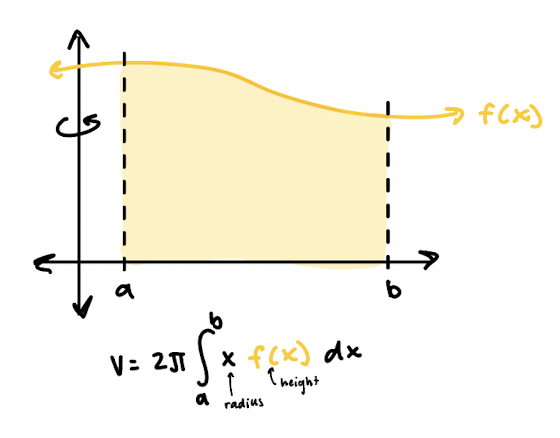
disk method
if f is continuous over a region [a, b] and the solid is obtained by rotating the function about the x-axis, the volume of the solid is…
![<p>if f is continuous over a region [a, b] and the solid is obtained by rotating the function about the x-axis, the volume of the solid is…</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/720496e1-4fa4-448d-b3b2-7bc7fbedb8c9.png)
washer method
the area of cross section = Aouter - Ainner; use when “slices” are perpendicular to axis of rotation

shell method
rotation around the y-axis; use when “slices” are parallel to axis of rotation
arc length
using pythagorean theorem to find small segment lengths of a function

surface of revolution
if f(x) is a continuous, differentiable function and we rotate it around the x-axis, we create a surface of revolution
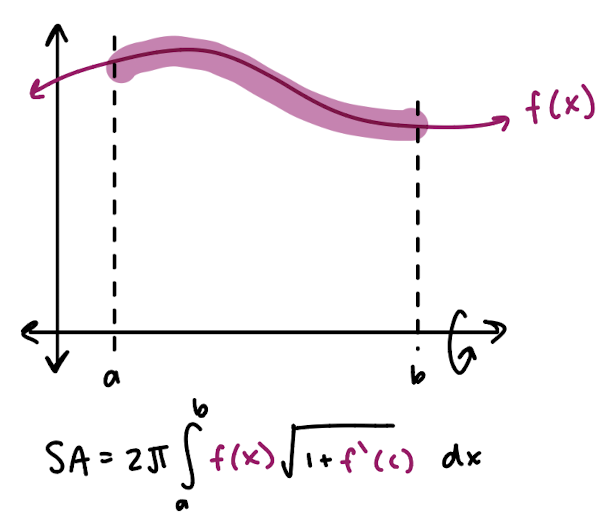
midpoint rule
approximate area by summing rectangles of height f(cj) and base Δx, where cj = middpoint between xj-1 and xjf
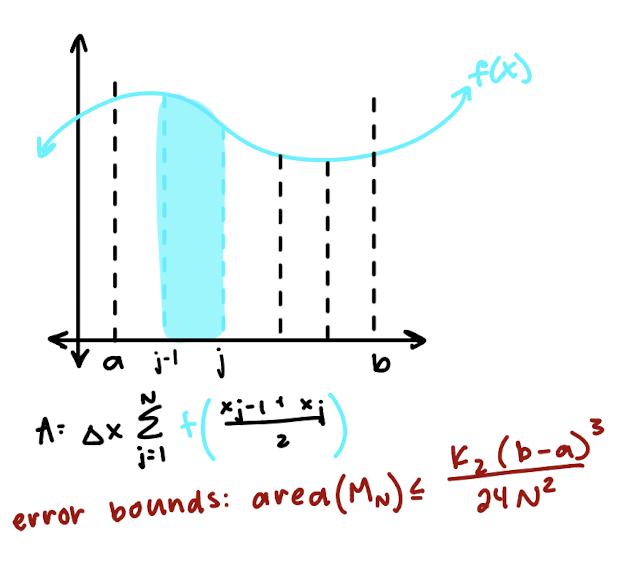
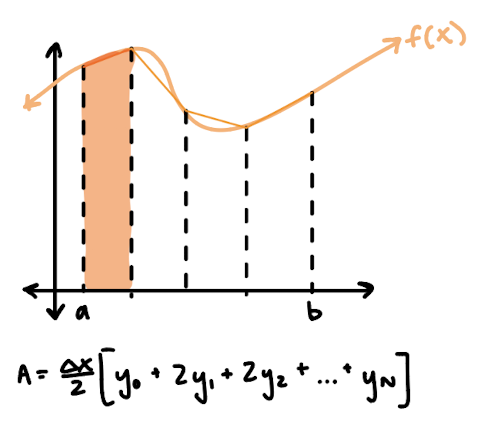
trapezoidal rule
approximate area by summing trapezoids
simpson’s rule
fit a parabola to each pair of 2 consecutive intervals and compute area underneath
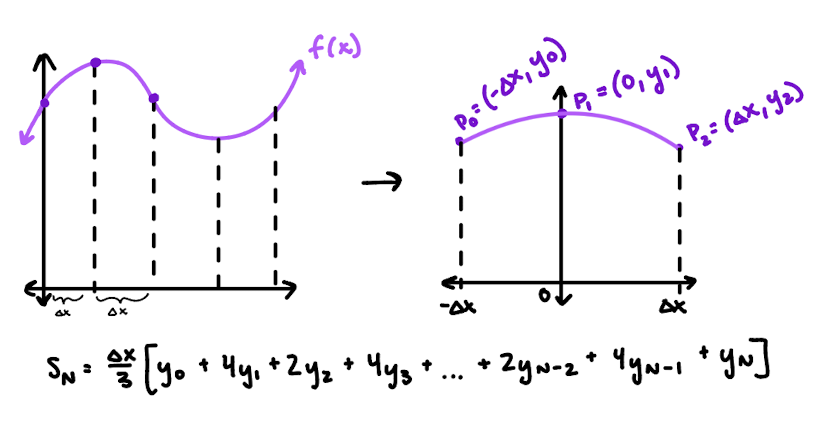
sequence
{an}
an ordered collection of numbers defined by some function f on a set of sequential integers
recursive sequences
sequence where the next term is based on previous terms
Fibonaces Sequence: F0 = 0, F1 = 1, Fn = Fn-2 + Fn-1
bounded sequence from above
if there is some number M such that an </= M, M is called “upper bound”
bounded sequence from below
if there is some number m such that an >/= m, m is “lower bound”
monotonic sequence
if {an} is increasing for all n (ex: an < an+1)
if (an} is decreasing for all n (ex: an > an+1)
monotonic sequences converges
if {an} is monotonic increasing and an < M, then {an} converges
if {an} is monotonic decreasing and an >/= m, then {an} converges
convergence of infinite series
an infinite series converges to the sum S if the sequence produced by its partial sums {SN} converges to S
geometric series
an = crn
c1r does not equal 0
partial sums = [c(1-rN-1)] / [1-r]
nth term divergence test
if limit of an as n approaches infinity doesn’t equal 0, then sum of an from n = 1 to infinity diverges
positive series
sum of an where an > 0
if the partial sums SN are bounded above, then an converges
if the partial sums SN are not bounded above, then an diverges
integral test
an = f(n) - positive, decreasing, continuous function of x when x>/= 1
if integral of 1→infinity f(x)dx converges, so does series
if integral of 1→infinity f(x)dx diverges, so does series
p-series convergence
if p > 1 in sum of 1/np , the series converges
direct comparison test
assume there exists M > 0 such that 0 </= an </= bn for all values of n greater than or equal to M
if bn converges, an also converges
if bn diverges, an also diverges
limit comparison test
let an and bn be 2 positive sequences such that lim of n→infinity of an / bn = L
if L > 0, then an converges if and only if bn converges
if L = infinity, if an converges, bn converges
if L = 0, if bn converges, an converges
alternating series
terms alternate from positive to negative
(-1)n-1 an or (-1)n
always converges
converges conditionally if an = 1/n (harmonic)
absolute convergence
if |an| converges
implies an converges
conditional convergence
if an converges but not |an|
ratio test
assume that the following limit exists
P = lim n→infinity | (an+1) / an |
if P<1 an converges absolutely
if P>1, an diverges
if P=1, the test is inconclusive
root test
assume the following limit exists: L = lim n→infinity n√|an|
if L<1, converges absolutely
if L>1, diverges
if L=1, inconclusive
power series
sum of n=0 to infinity of an(x-c)n
converges if |x-c|<R
diverges if |x-c|>R
taylor polynomials
approximations of functions as polynomials that “agree” with the function at a point and that point’s first n derivative (rate of change/slope)
TN (x) = f(c) + [f’(c)/1!](x-c) + [f’’(c)/2!](x-c)2+…+[fN(c)/N!](x-c)N
maclourin series
a Taylor series that is centered at 0