mastering biology chapter 13
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:58 PM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
natural selection
* individuals with certain inherited traits are more likely to survive & reproduce than individuals without those traits
* nature chooses who survives & reproduces
* nature chooses who survives & reproduces
2
New cards
stabilizing selection
natural selection that favors intermediate phenotypes
3
New cards
directional selection
* natural selection that favors 1 extreme phenotype
* seen in environments that change over time
* can be caused by changes in weather, climate, or food availability
* seen in environments that change over time
* can be caused by changes in weather, climate, or food availability
4
New cards
disruptive selection
* natural selection that favors both extreme phenotypes
* shows phenotypes of both
* most rare
* shows phenotypes of both
* most rare
5
New cards
sexual selection
natural selection in which individuals with certain inherited traits are more likely to obtain mates than others
6
New cards
intrasexual selection
natural selection in which individuals of the same sex compete with one another for mates
7
New cards
intersexual selection
individuals of 1 sex are choosy in selection of their mates
8
New cards
balancing selection
natural selection that maintains stable frequencies of 2 or more phenotypic forms in a pop.
9
New cards
artificial selection
* selective breeding of organisms to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in offspring
* humans choose who survives & reproduces
* humans choose who survives & reproduces
10
New cards
inbreeding
* maintains desired traits in offspring by mating closely related individuals
* pros: can get improved organisms & no special tools/lab equipment are needed
* cons: undesireable traits from both parents may appear & disease can accumulate in population
* pros: can get improved organisms & no special tools/lab equipment are needed
* cons: undesireable traits from both parents may appear & disease can accumulate in population
11
New cards
hybridization
* 2 organisms of different but closely related species are mated with the hope of getting the best qualities of each parent in the offspring
* hybrids are almost always sterile
* does not work in unrelated genes
* hybrids are almost always sterile
* does not work in unrelated genes
12
New cards
genetic engineering
takes DNA from 1 organism & inserts it into another organism's DNA sequence to ensure the organism will have that specific trait
13
New cards
speciation
formation of a new species
14
New cards
allopatric speciation
pop. of same species become isolated due to geographical changes
15
New cards
sympatric speciation
pop. of same species evolve differently until they can no longer interbreed, taking place w/o geographic isolation
16
New cards
evolution
* idea that living species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from present-day ones
* genetic changes in a pop. from generation to generation
* genetic changes in a pop. from generation to generation
17
New cards
convergent evolution
* species from diff. evolutionary branches coming to resemble one another
* can result from living in similar environments or natural selection favoring similar adaptations
* can result from living in similar environments or natural selection favoring similar adaptations
18
New cards
divergent evolution
organisms with a common ancestor becoming different as time goes
19
New cards
common descent
theory that all modern organisms descended from a single ancestral species i.e. tree of life
20
New cards
evolutionary tree
branching diagram that reflects a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships among groups of organisms
21
New cards
adaptation
inherited character that enhances an organism’s ability to survive & reproduce in a certain environment
22
New cards
DNA sequences
* aligned sequences used to figure out which organisms are most closely related to one another
* shows that all species have a common ancestor i.e. DNA shared by humans, bacteria, & dinosaurs
* shows that all species have a common ancestor i.e. DNA shared by humans, bacteria, & dinosaurs
23
New cards
mutation
change in the genetic information of a cell
24
New cards
fossil
* preserved remnant/impression of an organism that lived in the past
* shows a progression of evolution i.e. giant sloth fossils share similarity with current sloths
* ex: trace, amber, cast, mold
* shows a progression of evolution i.e. giant sloth fossils share similarity with current sloths
* ex: trace, amber, cast, mold

25
New cards
fossil record
highly ordered sequence in which fossils are found in layers of sedimentary rock
26
New cards
homology
similarity in characters resulting from shared ancestry
27
New cards
homologous structures
similar structures in different species due to common ancestry i.e. limbs of humans, whales, & bats
28
New cards
vestigial structures
* Feature of an organism that is a historical remnant of an important structure in the organism’s ancestors i.e. human appendix, snake pelvic bone
* Provides evidence of ancestry & traces the evolutionary origin of species
* Provides evidence of ancestry & traces the evolutionary origin of species
29
New cards
embryo
* unborn organism in the process of development
* can share similarity with other embryos & show structures that are not visible when the organism is fully formed i.e. gill arches
* can share similarity with other embryos & show structures that are not visible when the organism is fully formed i.e. gill arches
30
New cards
gene flow
transfer of alleles from 1 pop. to another as a result of the movement of individuals or their gametes
31
New cards
gene pool
all copies of every type of allele at every locus in all members of a population
32
New cards
relative fitness
contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals in the population
33
New cards
microevolution
change in a population’s gene pool over generations
34
New cards
genetic drift
* change in the gene pool of a population due to chance
* effects are most pronounced in small pop.
* effects are most pronounced in small pop.
35
New cards
bottleneck effect
* genetic drift resulting from a drastic reduction in pop. size
* surviving pop. is no longer genetically representative of the original pop.
* surviving pop. is no longer genetically representative of the original pop.
36
New cards
founder effect
* genetic drift that occurs when individuals become isolated from a larger pop.
* new gene pool is not reflective of that of the original pop.
* new gene pool is not reflective of that of the original pop.
37
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
* state in which frequencies of alleles & genotypes in a population remain constant from generation to generation
* happens only in very large populations with no gene flow between pop., no mutations, random mating, & no natural selection
* pˆ2 + 2pq + qˆ2 = 1
* p + q = 1
* happens only in very large populations with no gene flow between pop., no mutations, random mating, & no natural selection
* pˆ2 + 2pq + qˆ2 = 1
* p + q = 1
38
New cards
taxonomic system
* kingdom
* phylum
* class
* order
* family
* genus
* species
* phylum
* class
* order
* family
* genus
* species
39
New cards
phylogeny
study of how living & extinct organisms are related to one another
40
New cards
phylogenetic systematics
groups species into larger categories based on evolutionary relationships
41
New cards
cladogram (phylogenetic tree)
diagram used to show evolutionary relations among organisms
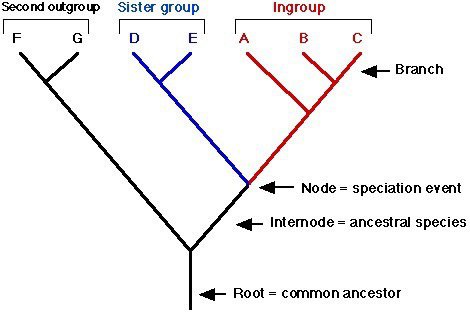
42
New cards
clade
group of living & extinct species that includes a single common ancestor
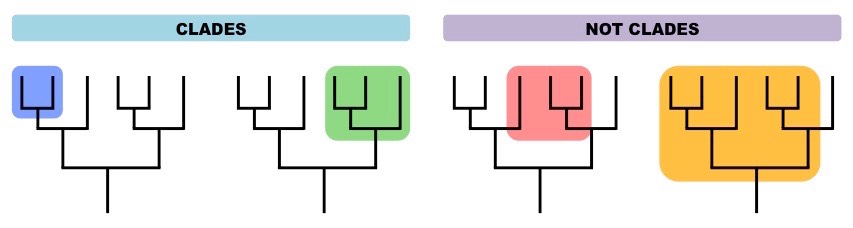
43
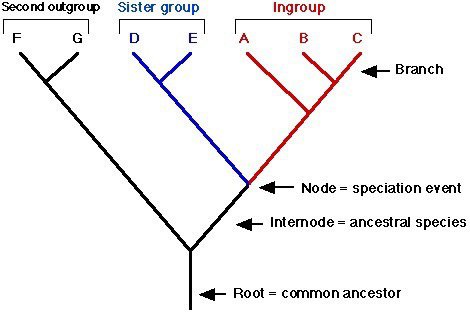
New cards
node
last point at which new lineages share a common ancestor
44
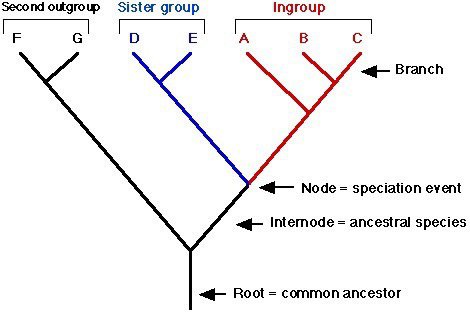
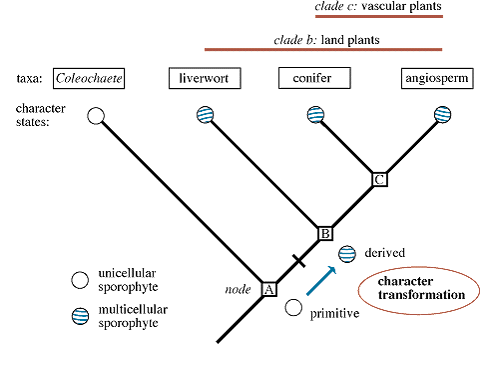
New cards
root
common ancestor shared by all organisms in a cladogram
45
New cards
derived character
* trait that arose in the most recent common ancestor of a lineage
* is passed on to its descendants
* is passed on to its descendants
46
New cards
symbiosis
* close, continuous association between organisms of different species
* at least 1 of the species benefits
* at least 1 of the species benefits
47
New cards
mutualism
both members benefit
48
New cards
commensalism
1 member benefits & the other is neither harmed/benefited
49
New cards
parasitism
1 member benefits & the other is harmed
50
New cards
ecological succession
* natural, gradual changes in the types of species in an area
* can be primary/secondary
* can be primary/secondary
51
New cards
primary succession
* begins without soil
* starts with the arrival of living species (pioneer species)
* simple plants die, adding nutrients to the soil
* other organisms begin to move in
* starts with the arrival of living species (pioneer species)
* simple plants die, adding nutrients to the soil
* other organisms begin to move in
52
New cards
secondary succession
* begins in a place that already has soil & is once the home of organisms
* occurs faster
* area colonized by organisms is disturbed before being recolonizing after the disurbance
* occurs faster
* area colonized by organisms is disturbed before being recolonizing after the disurbance
53
New cards
pioneer species
species that are the first to colonize barren environments i.e. bacteria, lichen, moss, fungi
54
New cards
climax community
relatively stable group of plants & animals that is the end result of succession
55
New cards
population growth
* increase in the # of individuals in a pop.
* growth = births - deaths
* growth = births - deaths
56
New cards
k-selected species
* large species that inhabit stable environments
* few offspring at each birth
* offered extended parental care
* offspring have better chance of survival, many surviving into old age
* few offspring at each birth
* offered extended parental care
* offspring have better chance of survival, many surviving into old age
57
New cards
r-selected species
* inhabit disturbed environments
* many offspring at each birth
* offered little to no parental care
* offspring have a lower chance of survival
* many offspring at each birth
* offered little to no parental care
* offspring have a lower chance of survival
58
New cards
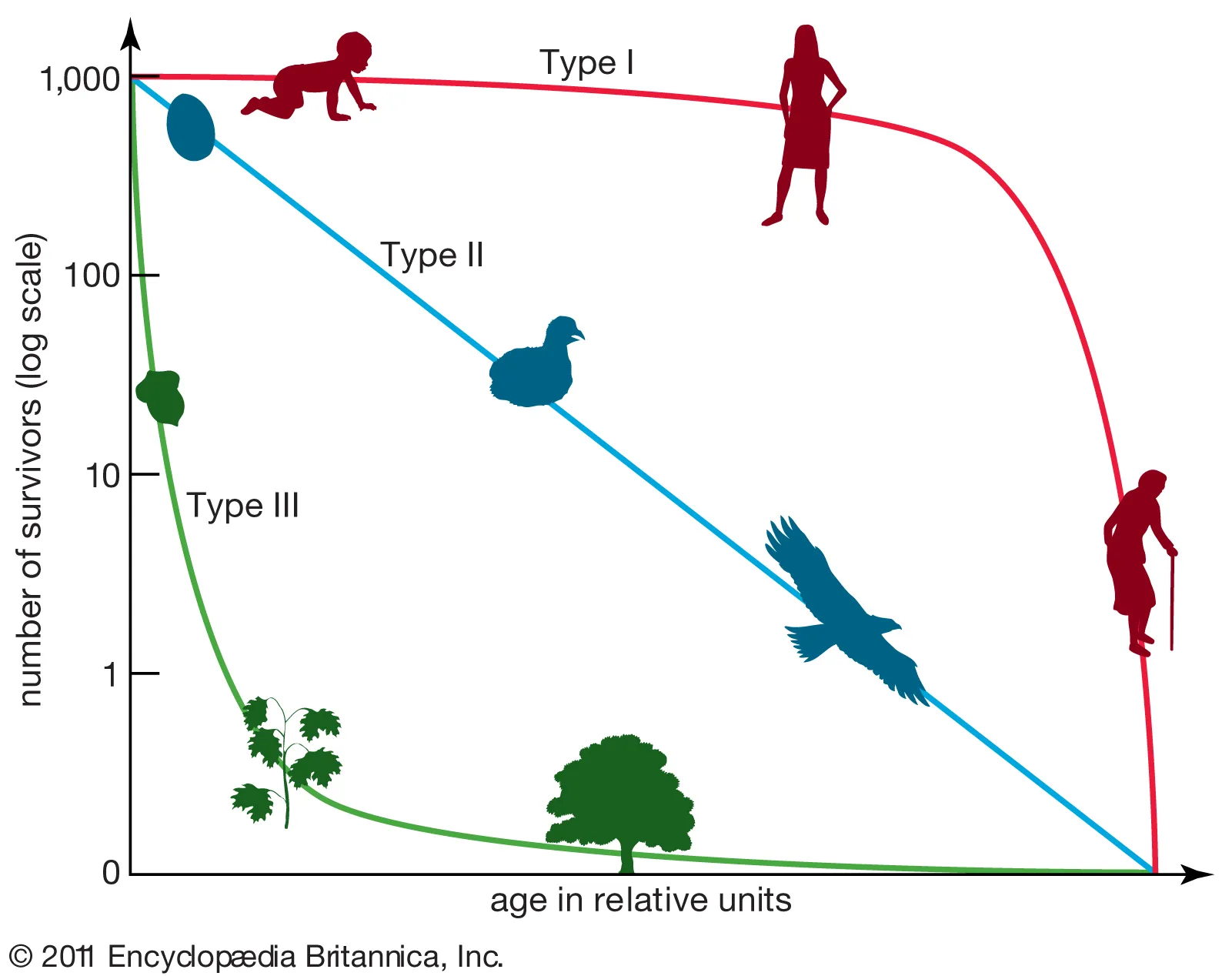
j-shaped curve
exponential growth
59
New cards
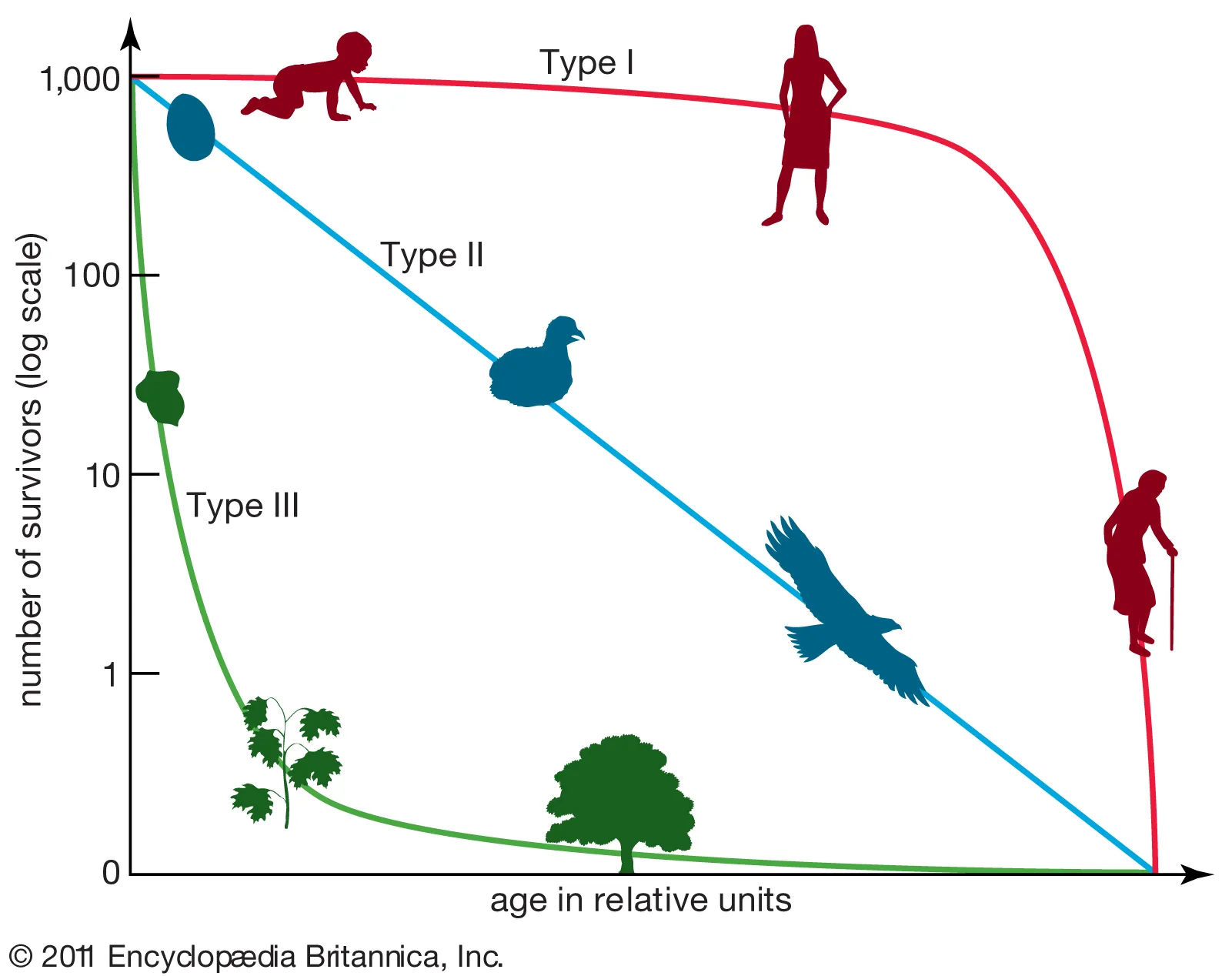
type II survivorship curve
organisms mostly die equally at each interval
60
New cards
logistic growth
* growth that decreases as resources become scarce
* levels off when carrying capacity reaches the limit
* levels off when carrying capacity reaches the limit
61
New cards
carrying capacity
number of organisms an ecosystem can support
62
New cards
limiting factors
constrains the size of a pop.
63
New cards
density dependent limiting factor
biotic factors i.e. predation, parasites, disease, competition
64
New cards
density independent limiting factor
* abiotic factors i.e. drought, changes in weather, natural disasters
* can occur in both small & large pop. (not dependent on pop. size)
* can occur in both small & large pop. (not dependent on pop. size)
65
New cards
positive feedback
drives change by moving a system in 1 direction i.e. melting of polar ice caps
66
New cards
negative feedback
keeps a system in balance i.e. predator prey relationships