Intro to earth science definitions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
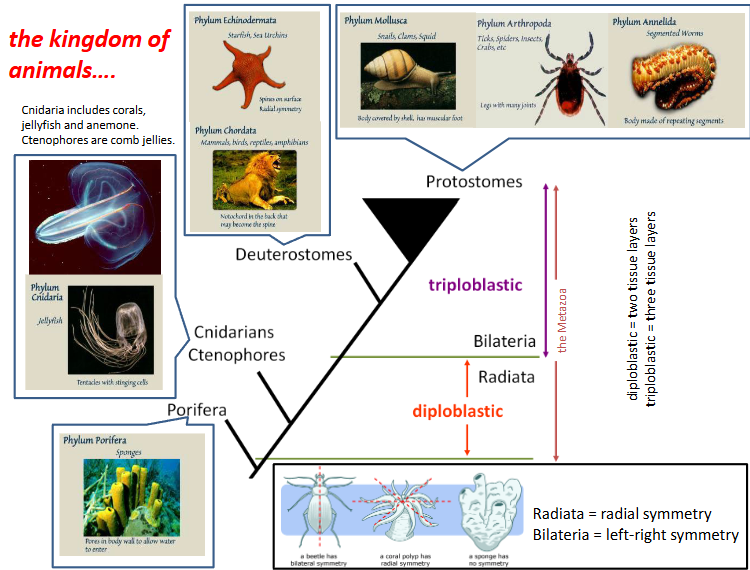
Protosomes
Mouth develops from the blastopire during embryonic development
e.g. molluscs, arhtropods, annelids
Deutrosomes
Anus develops first
e.g echinoderms, chordates
The three domains in the tree of life are..
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
The origin of life from non-living matter is..
Abiogenesis
One model for the evolution of eularyotes from prokaryotes is..
The endosymbiotic theory of cell evolution
The boundary between the Hadean and Archaea is at…
4.0Ga
Different stable isotopes of an element are defined on the basis of..
Variation in the no. of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom
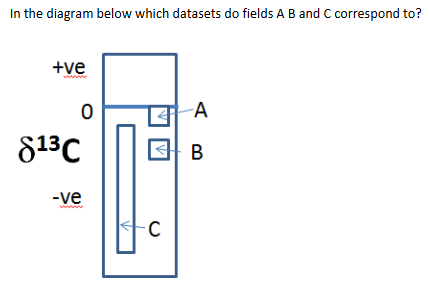
(a) A = marine bicarbonate B = atmospheric Co2 C = living autotrophic organisms
This is due to the fact that living organisms (photosynthesis - plant, algae..rewuires less energy for them) have a more negative (12C) value than marine bicarbonate, formed from inorganic precipitation of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) or from organisms with carbonate shells.(13C)
What is a polymorph of calcium carbonate?
Aragonite
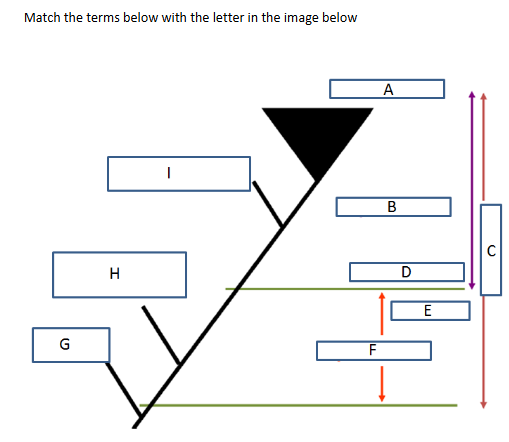
What is the kingdom of animals in order?
Vendobionta
Refers to an extinct group of Ediacaran organisms with soft, quilted bodies
Pneu structure
internal structure of an organism with a fluid-filled, inflatable body, like a mattress
Tekites
natural glass objects formed by intense heat and pressure of meteorite impacts
very low water content indicates that it was formed under conditions where water was rapidly driven off, hence HIGH Temperature and HIGH Pressure
Shocked quartz
A form of quartz that has been deformed by intesnet pressure like the bolide (meteorite) impact.
Wide geographic distribution, making it the strongest and most global evidence of a large impact event.
Suveite
Type of impact breccia only found near the impact site, luke Chicxulub
Ejecta blanket
Refers to materal ejected around the impact site, not found globally.
Lazarus taxa
Species or groups that diseappear from the fossil record for one or more periods. Presumed to be decreased population size or poor preseration conditions, later reappearing again.
Reapperance of an exticnt group is known as
Lazarus taxa
What is the boradest effect from the K-T boundary between fern spike or tsunami deposit
Fern spike
Elatina formation, South Australia
Late proerozoic (~634Ma), glacial deposit
Laminated siltstone
Tidal depsoits (e.g. low altitude)
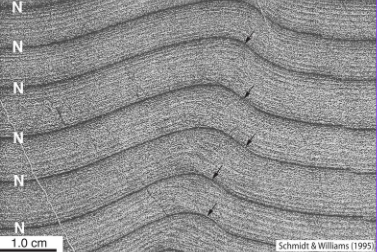
Contributing factor of a cooler planet back then…
Highe albedo → Low albedo. There was more land mass before, and land surfaces had High albedo that reflected 90% of solar radiation back into space, whereas open ocean would absorb at least 94% of sun.
The rise of atmospheric oxygen, reducing methane (potent greenhouse gas) therefore contributing to a cooler earth.
What is geological record of a snowball earth event?
varies in detail
same general stratigraphy
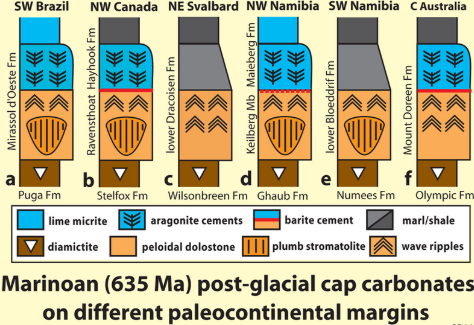
Stromalites
a calcareous mound built up of layers of lime-secreting cyanobacteria and trapped sediment, found in Precambrian rocks as the earliest known fossils, and still being formed in lagoons in Australasia.
Cyanobacteria
a division of microorganisms that are related to the bacteria but are capable of photosynthesis. They are prokaryotic and represent the earliest known form of life on the earth.
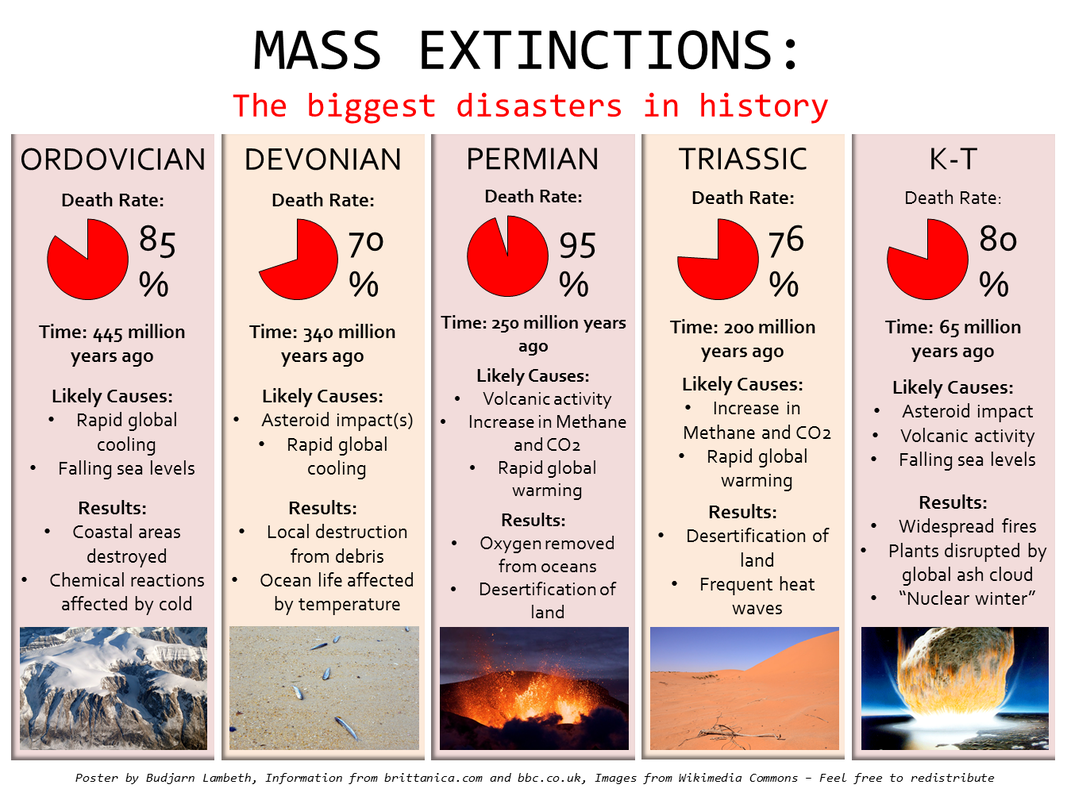
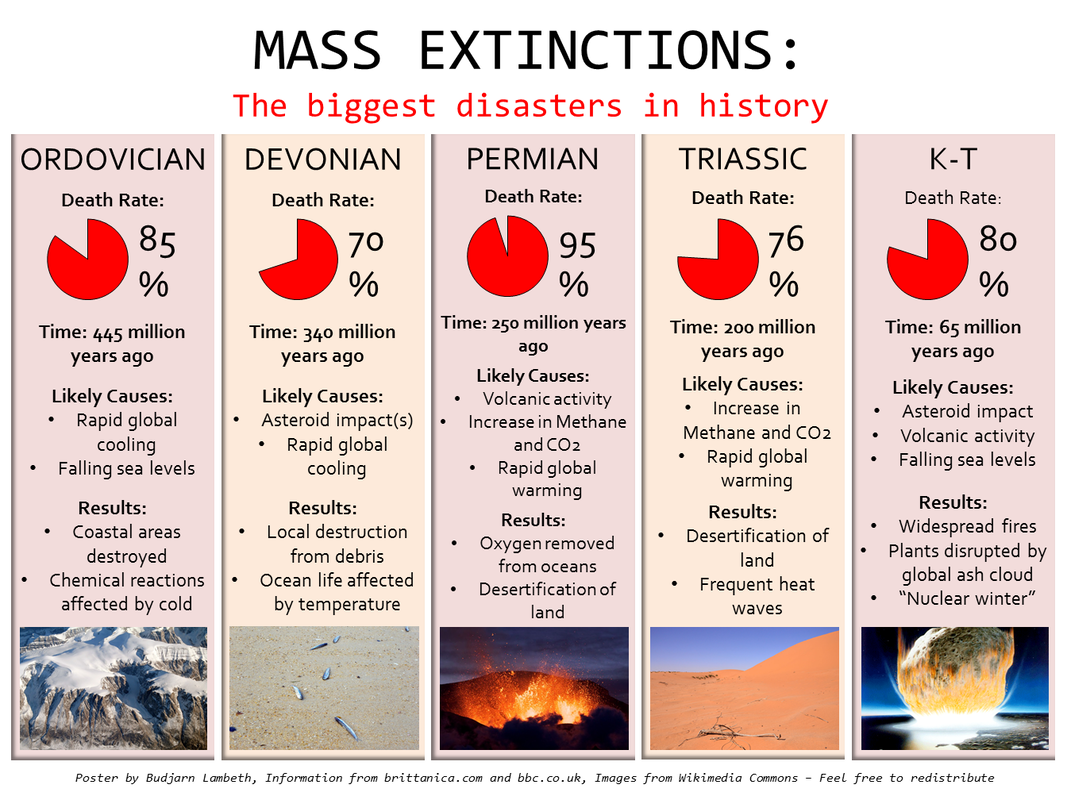
Ordovician: 440 mya -> small marine organisms died out Devonian: 365 mya -> tropical marine species extinct Permian: 250 mya -> Largest mass extinction event, many vertebrates Triassic: 210 mya -> more vertebrates which lead to dinosaurs to flourish K-T: 66/65 mya -> dinosaurs were K.O'd and mammals emerged
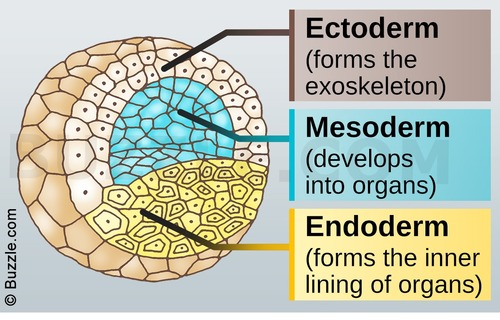
The three germ layer
Ectoderm = Forms exoskeleton
Mesoderm = Develops into organs
Endoderm = Forms the inner lining of organs
Difference between diploblastic vs triploblastic
Diploblastic | Triploblastic |
Animals are radially symmetric | Animals are bilaterally symmetric |
No mesoderm | Mesoderm |
No body caivity | Body cavitiy in coelom |
Endoderm forms true tissues and the gut | Endoderm forms lungs, stomach, colon, liver, urinary bladder etc. |
Ectoderm forms epidermis, nervous tissue and nephridia | Ectoderm forms epidermis, hair, eye lens, brain, spinal cord.. |
No organs | Organs |
Not complex | Complex |
EXAMPLES: Jellyfish, comb jellies, corals and sea anemones | EXAMPLES: Molluscs, worms, arthropods, echinodermeta and vertebrates |
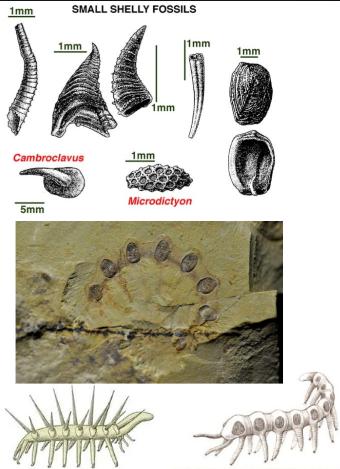
Small shelly fossils
Biomineralised tissue
Uncertain affinites and function
Microdictvon and Cambroclavus as shields and spines on soft-bodied lobopods (from extinct phylum lobopodia)
Defence mechanism = implies there was predation
Burgess Shale, Middle Cambrian = Canada
deeper water setting
series of fossiliferous levels
buried in situ below depositing event beds (e.g. avalance)
incorpodated into depositing
valuable source of data on biodiversity

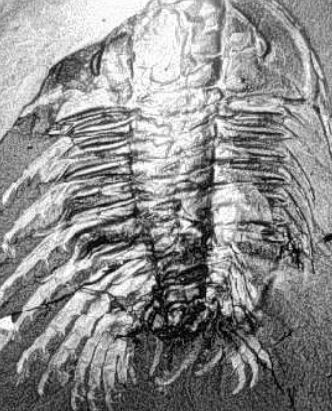
Olenoides
Spines on limbs used for capturing and shredding prey
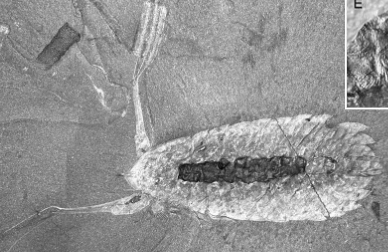
Leanchoilia
mid-gut glands replaced in calcium phosphate
digestive function
implies macrophagy (feeding of foods large relative to size of organism) and predation/scavenging
Anomalocaris
‘pineapple’ shaped jaw with ‘blades’,
Great Oxidation Event (GOE) SUMMARY
~2.4-2.1ga during the Paleoproterozoic era
Caused by cyanobacteria producing O via photosynthesis. Began to accumate in the atmosphere and oceans.
Before GOE: Earth’s atmosphere had little to no O; methane, ammonia and other gases were dominante.
Formation of branded iron formations (BIFs) as oxygen reacted with dissolved iron in oceans.
Mass extinction of many anaerobic (oxygen-intolerant) organisms
May have been a trigger for ‘‘Snowball Earth’’ glaciations due to methane reduction (potent greenhouse gas)
Aerobic life and complex multicellular organisms emerged
How stromatolies grow
Microorganisms live on the surface of the stromatolite
Sediments deposited on the microorganisms
React by growing upward trhough the sediment, forming a new layer
Modern stromatolies are still growin in Shark bay, Australia