biology - year 9
1/33
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
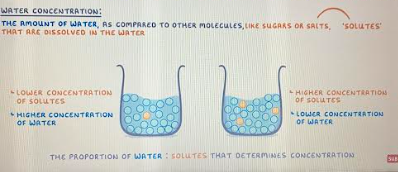
what determines water concentration
the concentration of water: solutes
how is active transport different to diffusion
diffusion is high to low concentration (not low to high) and doesn’t require energy
what can impact the rate of diffusion
temperature/concentration gradient
what is osmosis
osmosis is the net movement of water particles across a partially permeable membrane, from a higher water concentration to a lower water concentration.
passive transport

give an example of osmosis
glucose/ water going into animal cells
how are nutrients absorbed in the gut
nutrients go into the villi that line your gut (the villi have a very large surface area + good blood supply)
this is active transport so requires energy
describe the gas exchange in the lungs during inspiration
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas is exchanged during breathing. Within the human lungs the alveoli provide an efficient exchange surface adapted for gas exchange. This involves the ‘swapping’ of gasses. For example: Absorbing oxygen, which is needed for respiration, into the blood from the air.
(absorbing oxygen into blood through alveoli in lungs)
gas exchange in lungs during exhalation
CO2 that was absorbed in the blood swaps with the oxygen (exchange) through the alveoli and is exhaled through the mouth/nose
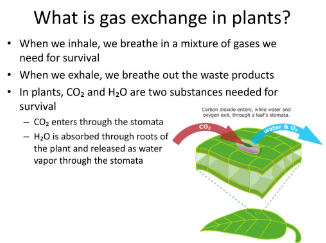
explain how gas exchange takes place in plants
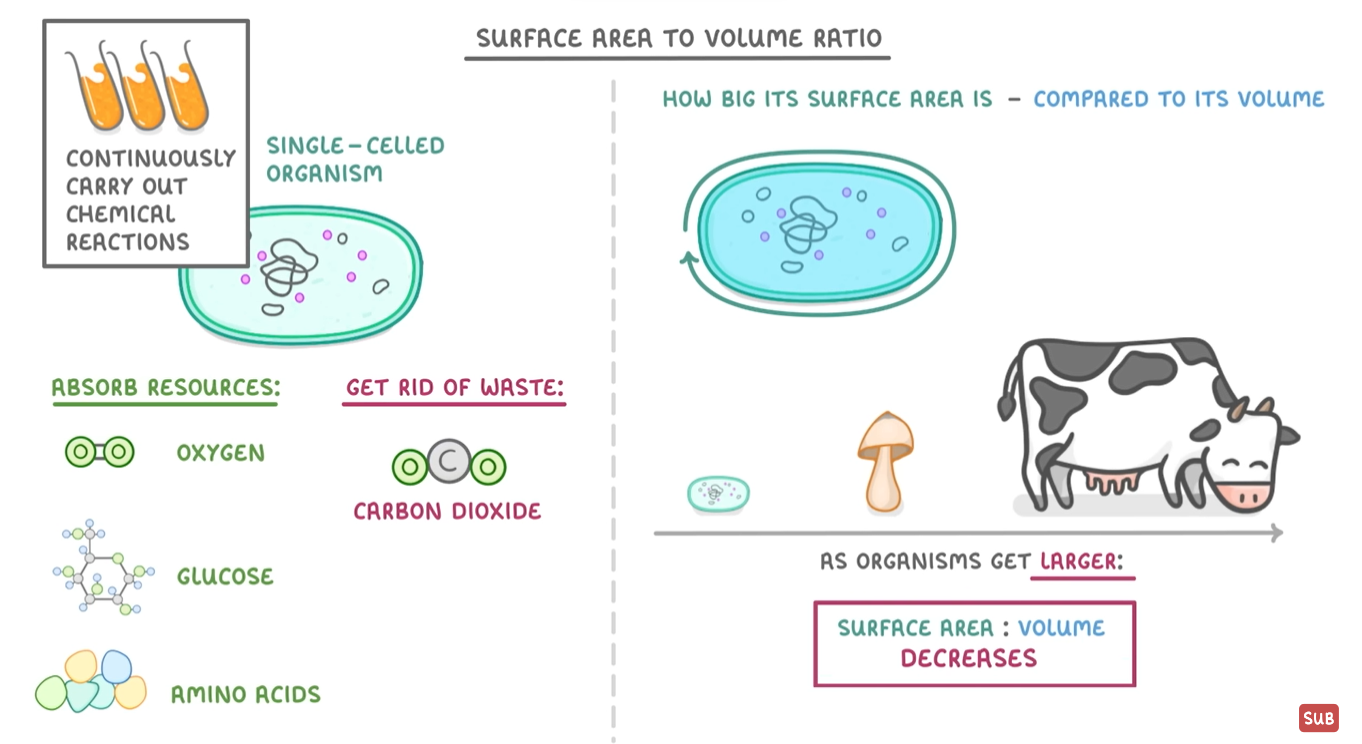
what is surface area: volume ratio?
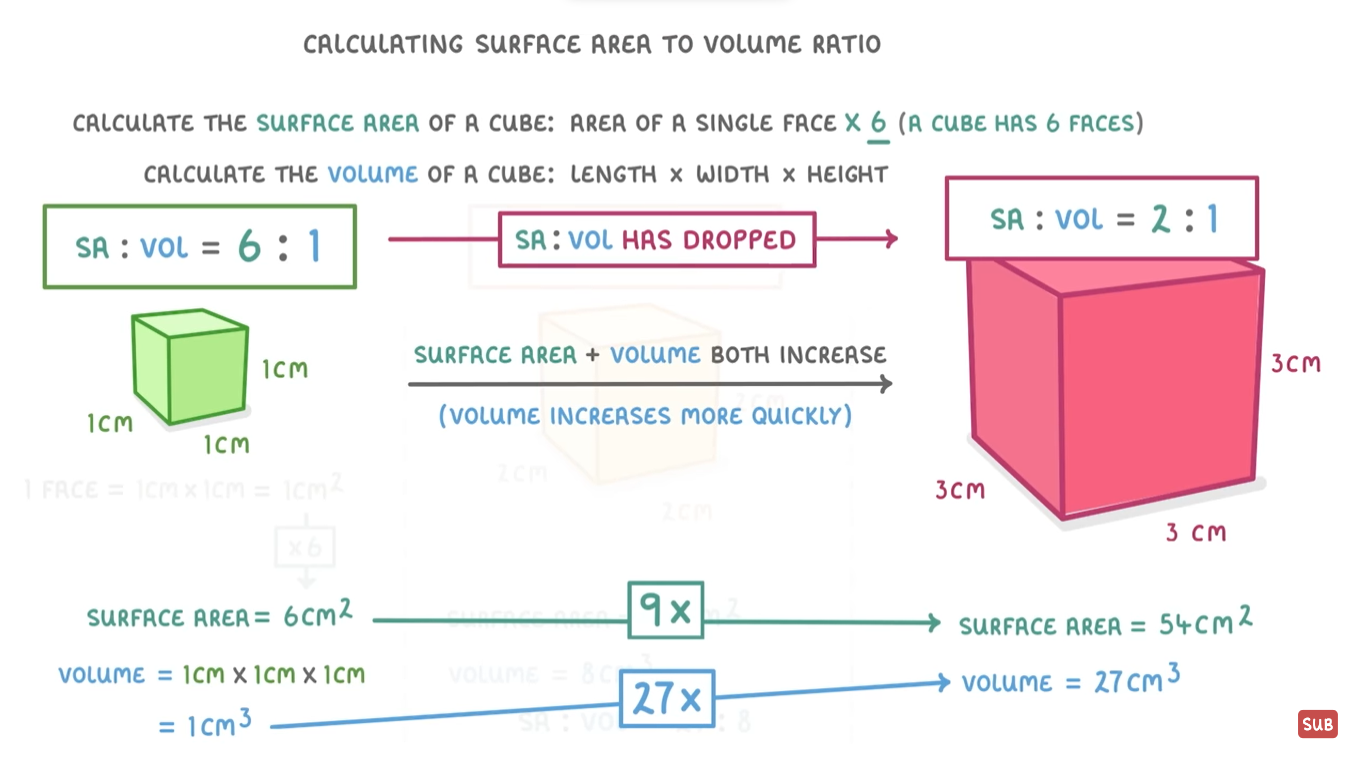
how to we work out surface area: volume ratio
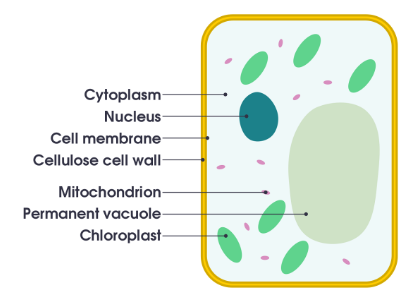
what do plant cells have that animal cells dont
vacuole
chloroplast
cell wall
describe active transport
the movement of cells from a low to high concentration, meaning that it requires energy
define ‘diffusion’
the spreading out of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
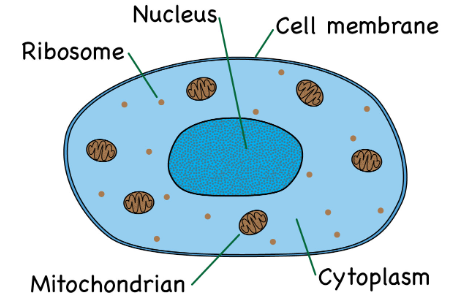
what is the function of a nucleus
the nucleus contains genetic material that controls the cell
what is the function of the mitochondria
contains most of the reactions for aerobic respiration
what is the function of a Ribosome
where proteins are made
what is the function of chloroplasts
absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis
what is the function of a cell wall
protects the cell and keeps it in uniform shape
what does an animal cell look like
what does a plant cell look like
what is the difference between a prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell?
prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells
bacterial cells are prokaryotic
animal + plant cells are eukaryotic
Photosynthesis
__________ is the process by which green plants and some other organisms convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of _______ molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, through a semipermeable membrane, in order to equalize the concentration on both sides.
specialised cells
Specialized cells are cells that have specific ___________ and functions in the body. They are uniquely adapted to carry out particular tasks, such as transmitting electrical signals (neurons), carrying oxygen (red blood cells), or fighting infections (white blood cells). These cells possess distinct structures and characteristics that enable them to perform their designated roles efficiently.
What is the main function of xylem in plants?
The main function of xylem is to transport water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
what are xylem and phloem?
in plants
transport substances (food +water)
go together to from tubes
What is the primary function of phloem in plants?
The primary function of phloem is to transport organic nutrients, such as sugars and amino acids, from the leaves to other parts of the plant, including the roots, stems, and fruits.
is diffusion passive or active transport
passive
What are specialised cells?
Specialised cells are cells that have unique structures and functions to perform specific tasks in the body. They are adapted to carry out specific functions efficiently, such as nerve cells transmitting electrical signals, red blood cells carrying oxygen, and muscle cells contracting for movement.
how nutrients is absorbed into the gut
Process of Nutrient Absorption
Nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine.
Villi and microvilli increase surface area for absorption.
Nutrients pass through cell membranes via active or passive transport.
Water-soluble nutrients enter blood capillaries.
Fat-soluble nutrients enter lymphatic vessels.
Absorbed nutrients are transported to cells for energy and growth.
diffusion
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down a concentration __________.
gas exchange
Gas exchange is the process by which _______ is exchanged between an organism and its environment. It occurs in the respiratory system, where oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is released. This exchange happens through diffusion, where gases move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
How does gas exchange occur in plants?
Gas exchange in plants occurs through tiny openings called stomata, primarily found on the surface of leaves. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) through the stomata and release oxygen (O2) as a byproduct. This exchange of gases is facilitated by diffusion, where CO2 moves from an area of higher concentration outside the leaf to an area of lower concentration inside the leaf, while O2 moves in the opposite direction. The stomata also help regulate water loss by opening and closing to prevent excessive transpiration.