Thigh - Lower Limb Hip to Knee
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the outer later of deep fascia in the lower limb?
fascia lata
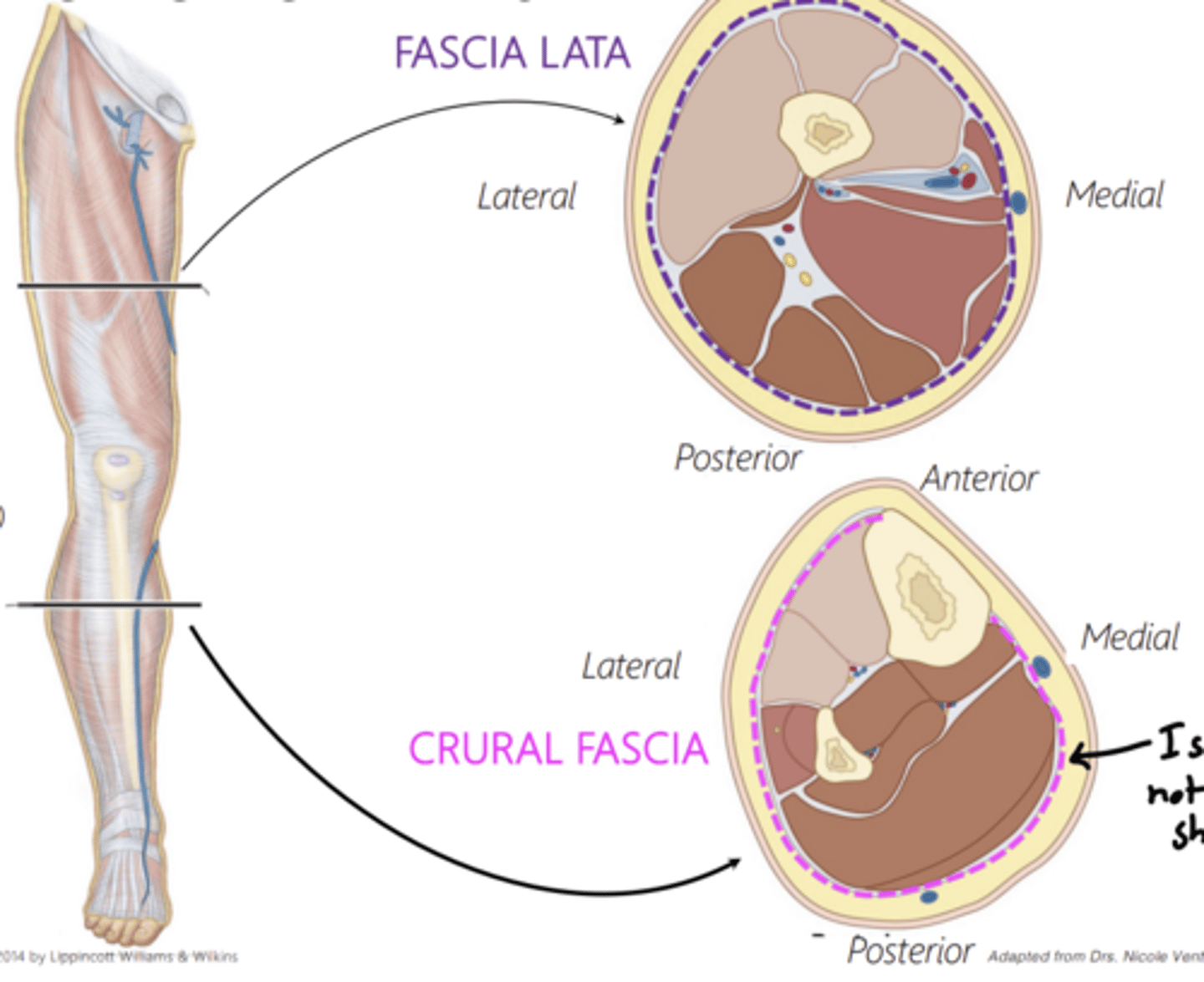
Fascia Lata forms what?
a thick "stocking"-like memrbane
What is the superior line of attachment for the Fascia Lata?
starts at inguinal ligament and iliac crest, wraps around the hip bone
How does the Fascia Lata continue inferiorly?
continuous with deep fascia of the leg
What is the Fascia Lata laterally thickened into?
iliotibial tract (longitudinal band)

The Fascia Lata splits in the gluteal region to enclose WHAT anteriorly?
fascia lata muscle
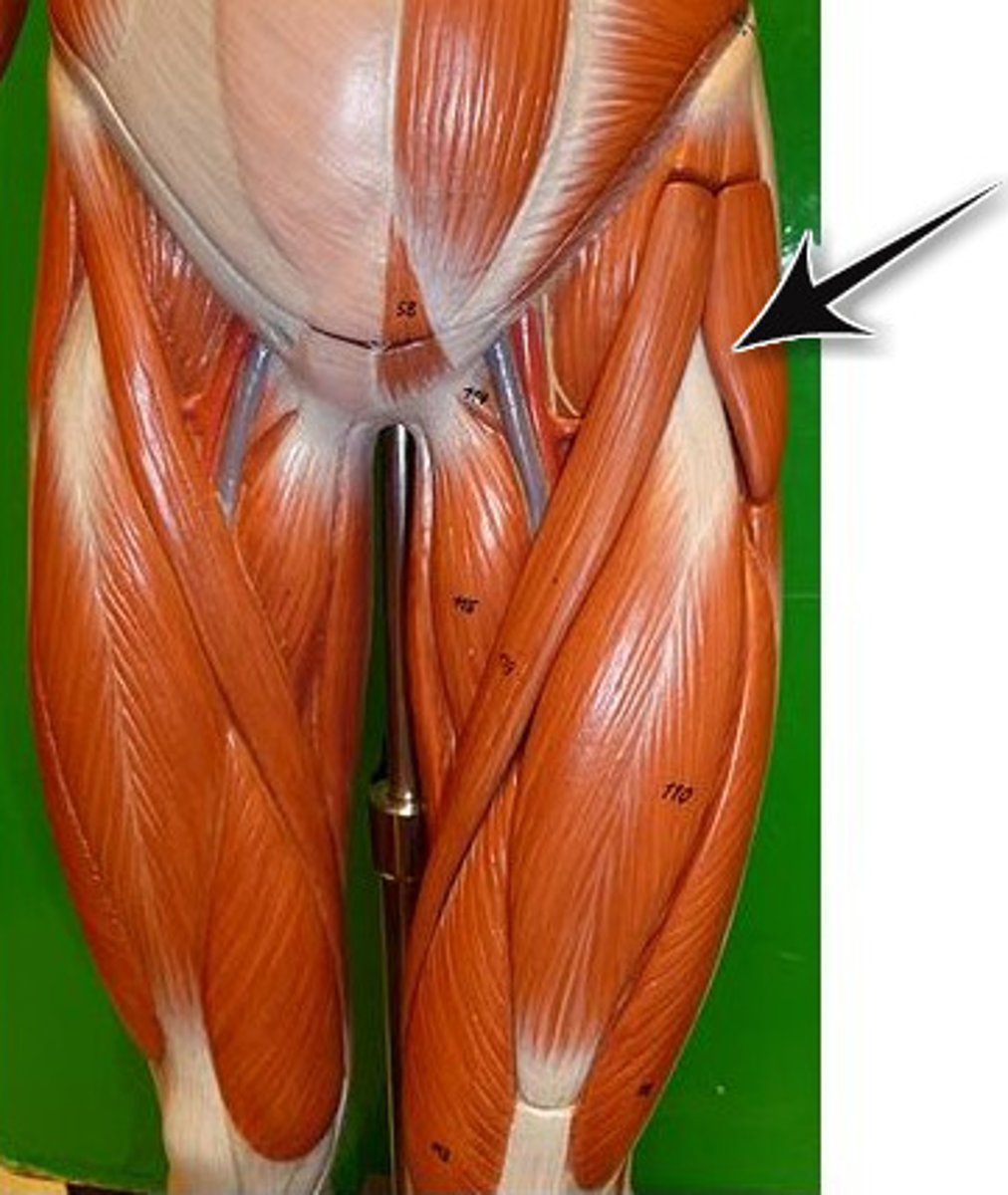
The Fascia Lata splits in the gluteal region to enclose WHAT posteriorly?
gluteus maximus
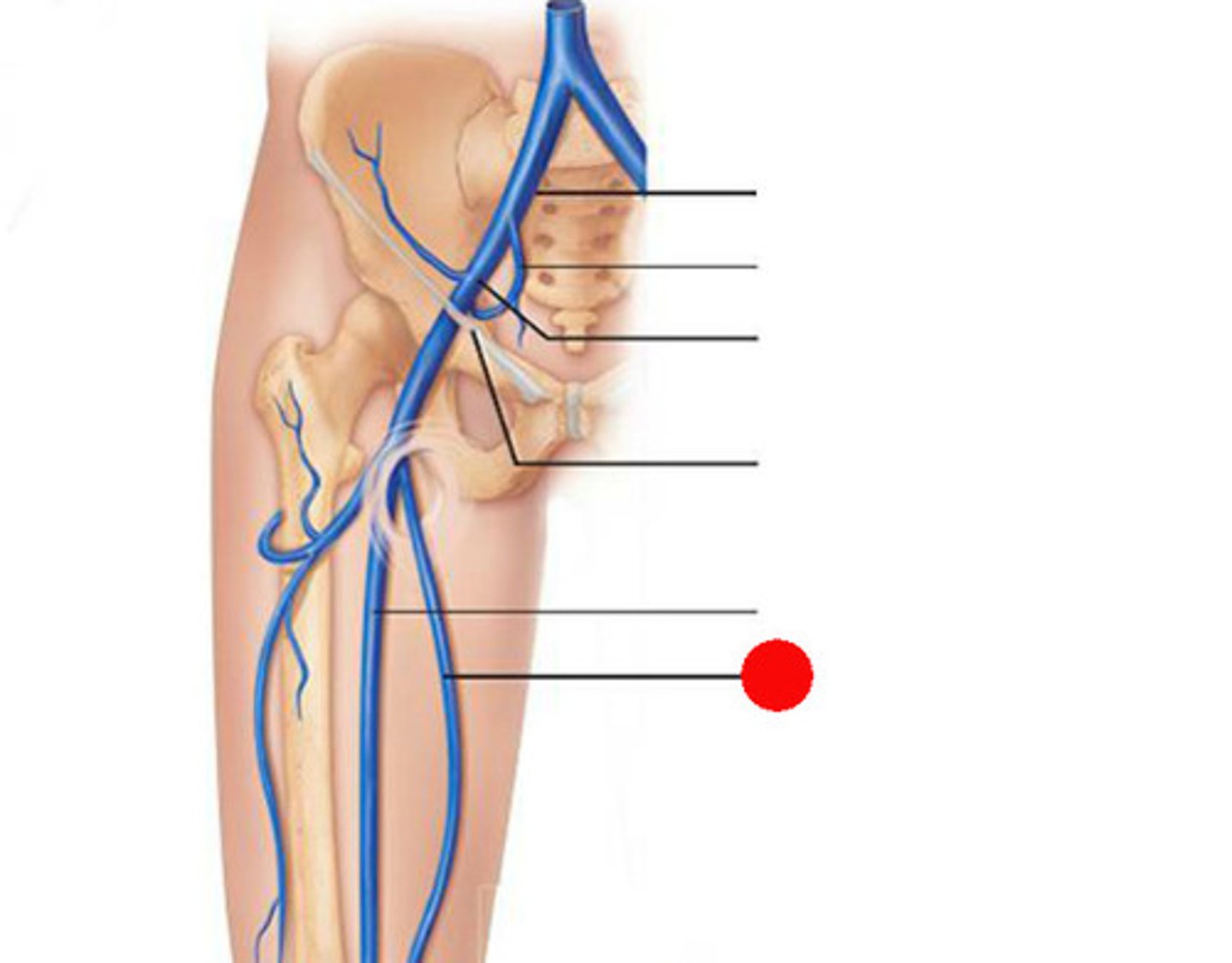
Saphenous Opening
opening in the anterior aspect of the thigh just inferior to the medial end of the inguinal ligament
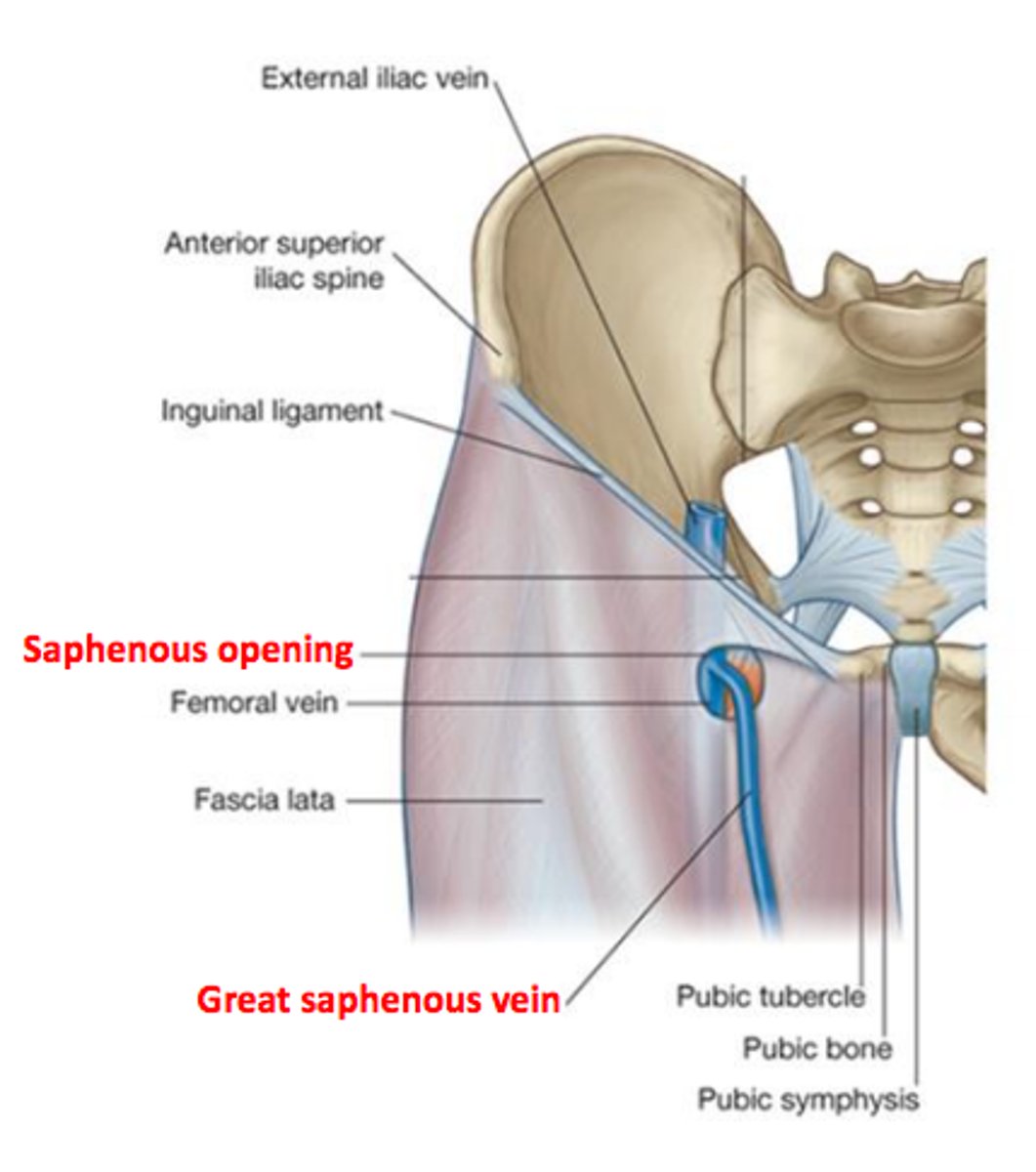
What does the Saphenous Opening allow?
for the saphenous vein to pass from superficial fascia through deep fascia
The passage of the saphenous vein from superficial to deep fascia allows for the connection with what?
the femoral vein
Femoral Triangle
wedge-shaped depression formed by muscles int he upper thigh
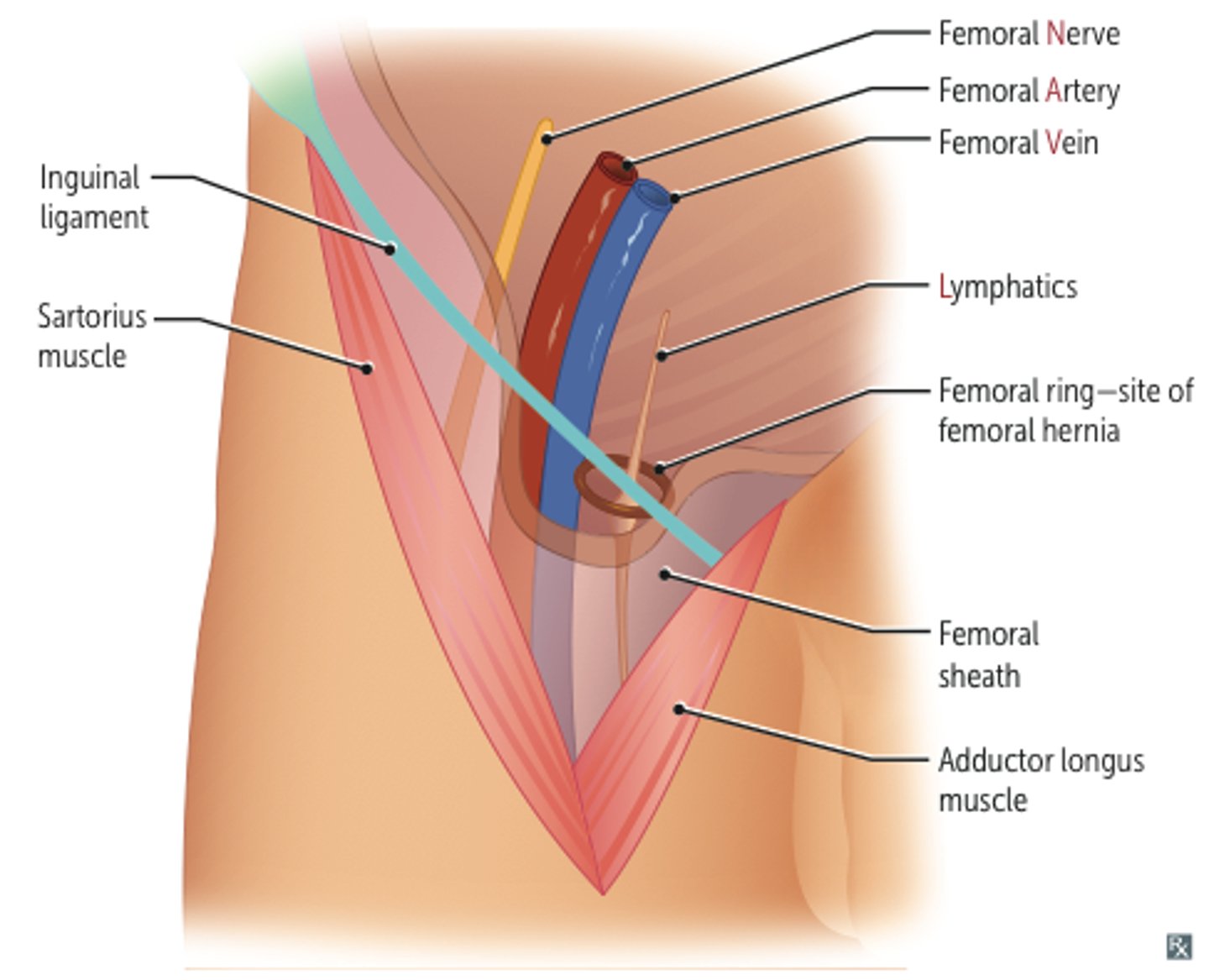
What are the 3 boundaries of the femoral triangle?
1. base
2. medial border
3. lateral border
Base boundary of the Femoral Triangle:
inguinal ligament

Medial boundary of the Femoral Triangle:
adductor longus
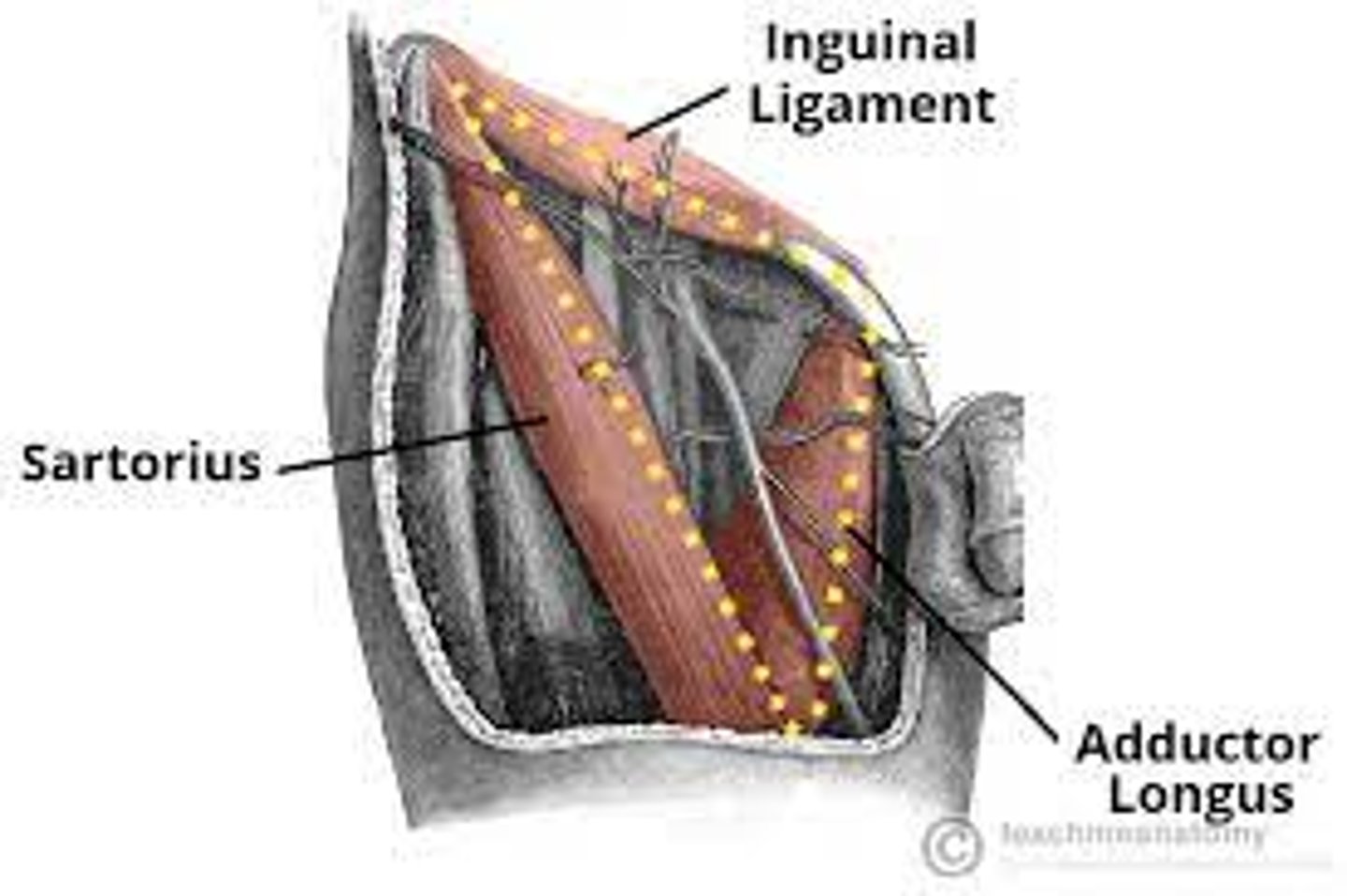
Lateral boundary of the Femoral Triangle:
sartorius muscle
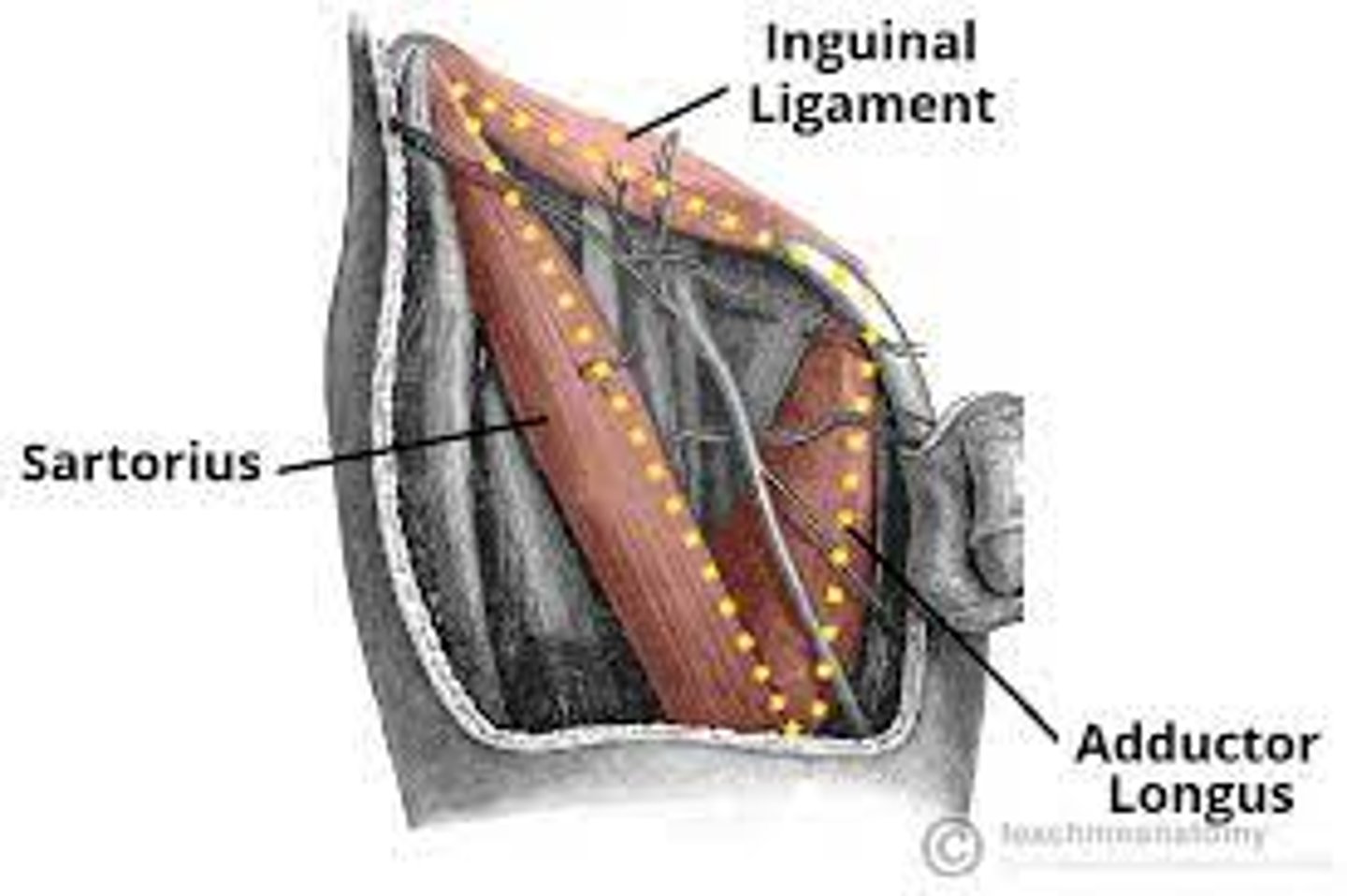
What are the Contents of the Femoral Triangle?
- femoral nerve
- femoral artery
- femoral vein
- empty space (femoral canal)
- deep lymph nodes
*NAVEL
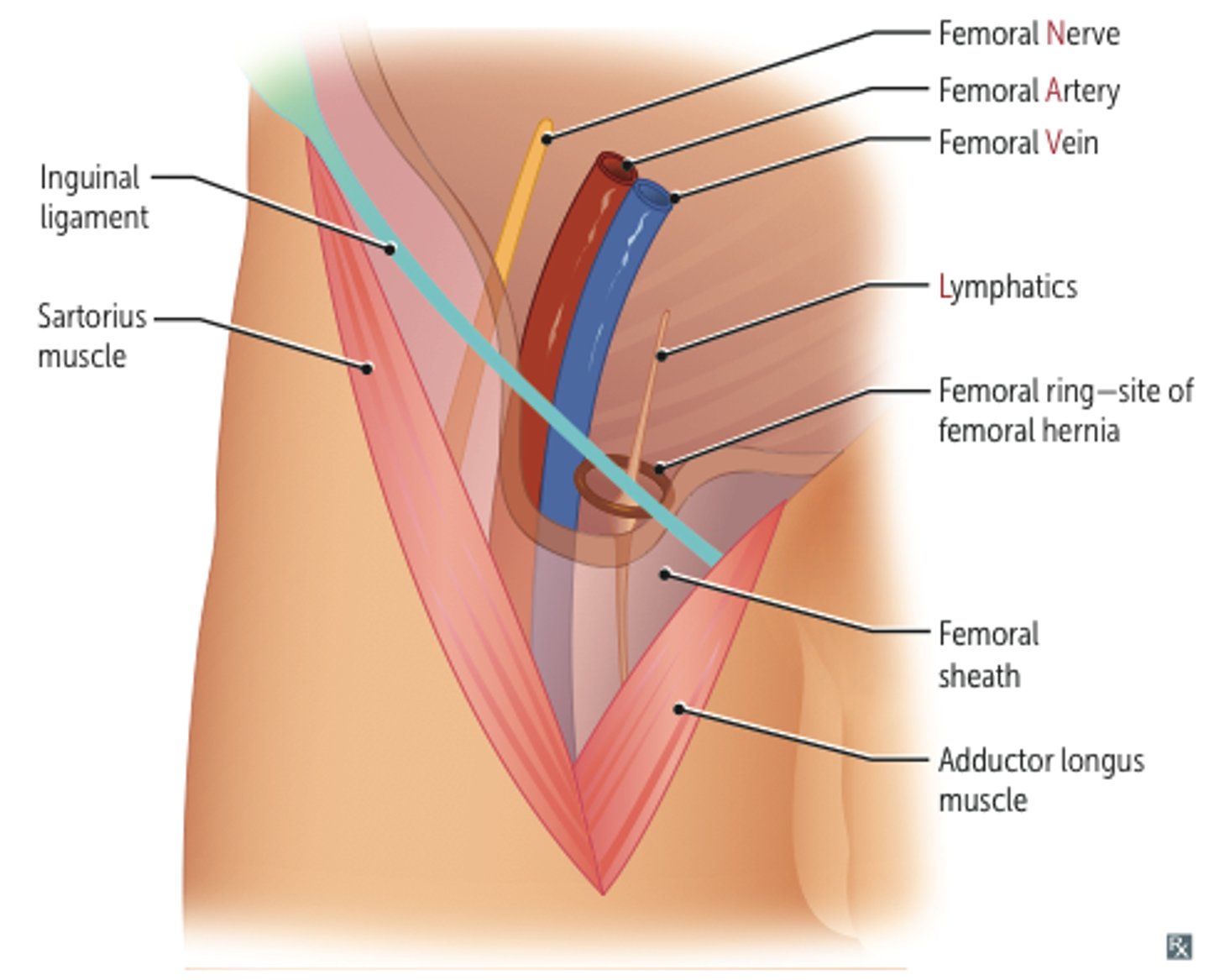
Femoral Sheath
funnel-shaped sleeve of fascia that surrounds the femoral artery, vein, and associated lymphatics within the femoral triangle

Each structure within the femoral sheath is individually contained within what?
its own fascial compartment
Most Medial of Femoral Sheath:
femoral canal which contains lymphatics and empty space
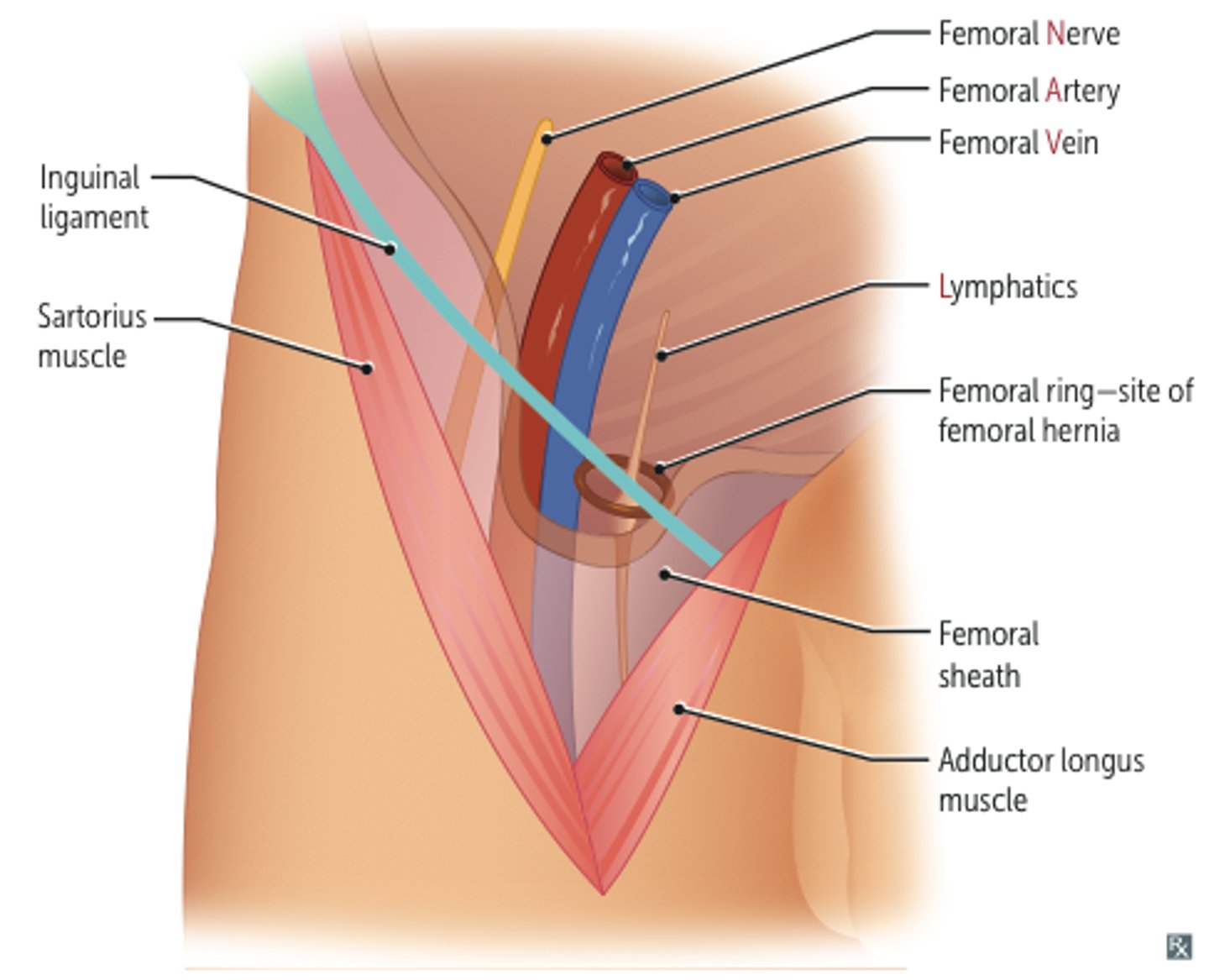
Superior border of Femoral canal:
femoral ring

What is clinically relevant for the femoral sheath?
femoral hernia
How many compartments are there for the thigh?
3
What forms these 3 muscle compartments of the thigh?
intermuscular septa
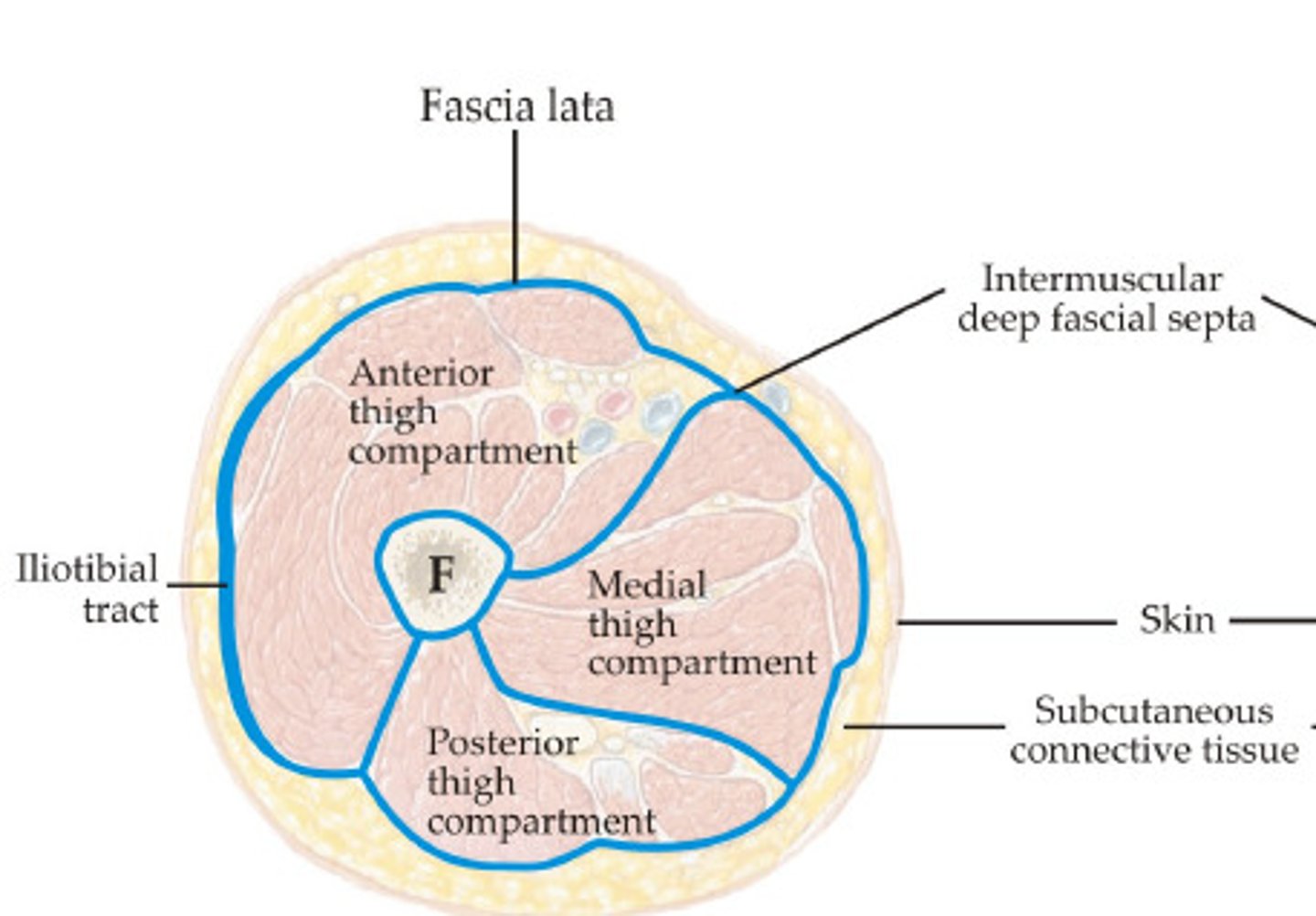
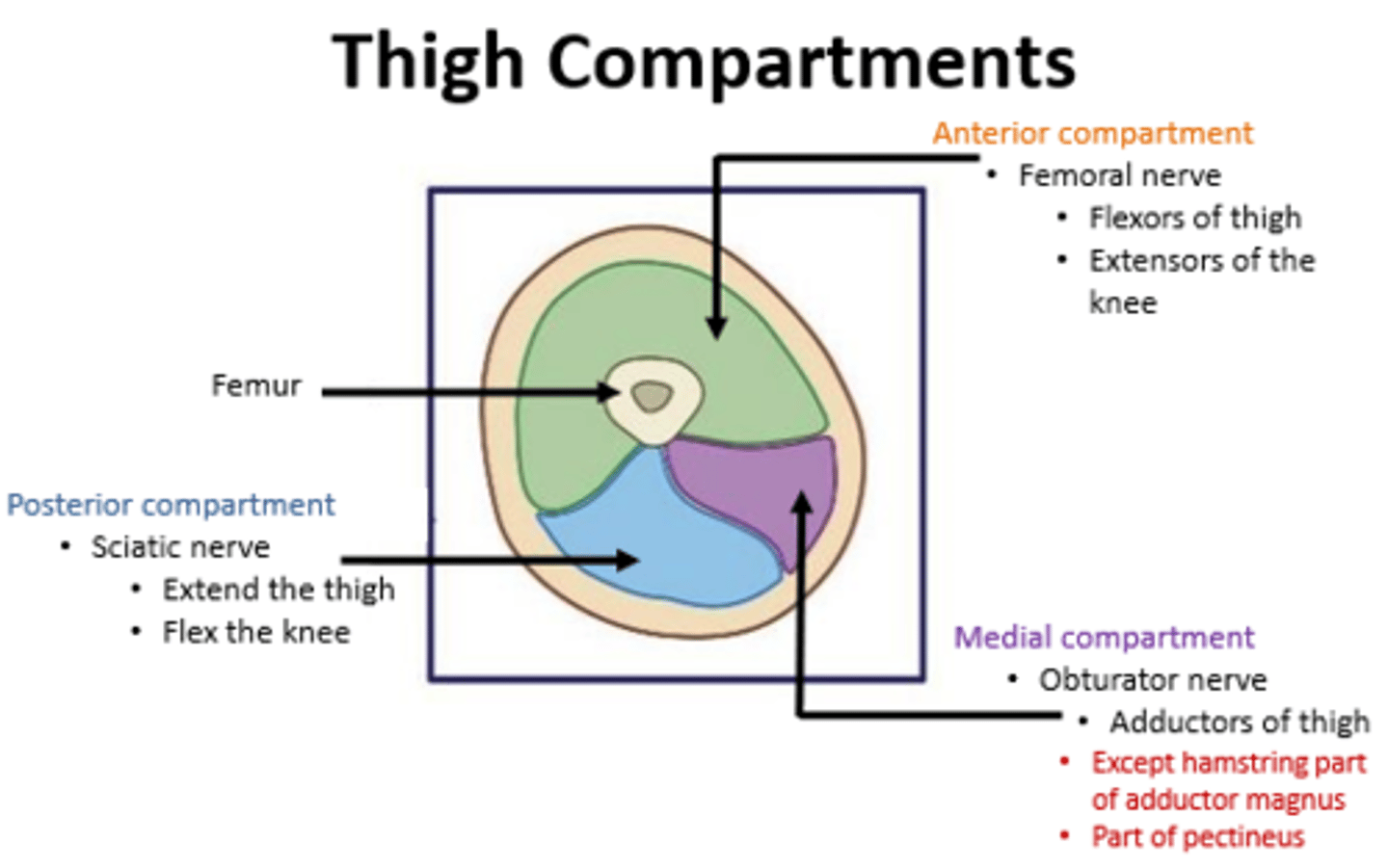
What are the 3 compartments of the thigh?
1. anterior compartment
2. medial compartment
3. posterior compartment
Fascia Lata completely invests what?
the thigh
Anterior compartment of the thigh is innervated by?
femoral nerve
Posterior compartment of the thigh is innervated by?
sciatic nerve
Medial compartment of the thigh is innervated by?
obturator nerve
Anterior compartment include what?
sartorius and 4 "quads" (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius)
Posterior compartment includes what?
hamstrings
Medial compartment includes what?
- gracilis
- pectineus
- adductor longus
- adductor brevis
- adductor magnus
- obturator externus
Anterior compartment of the thigh function
muscles that extend the knee
Posterior compartment of the thigh function
muscles that extend the thigh at the hip joint and flex the leg at the knee joint
Medial compartment of the thigh function
muscles that adduct thigh at the hip joint
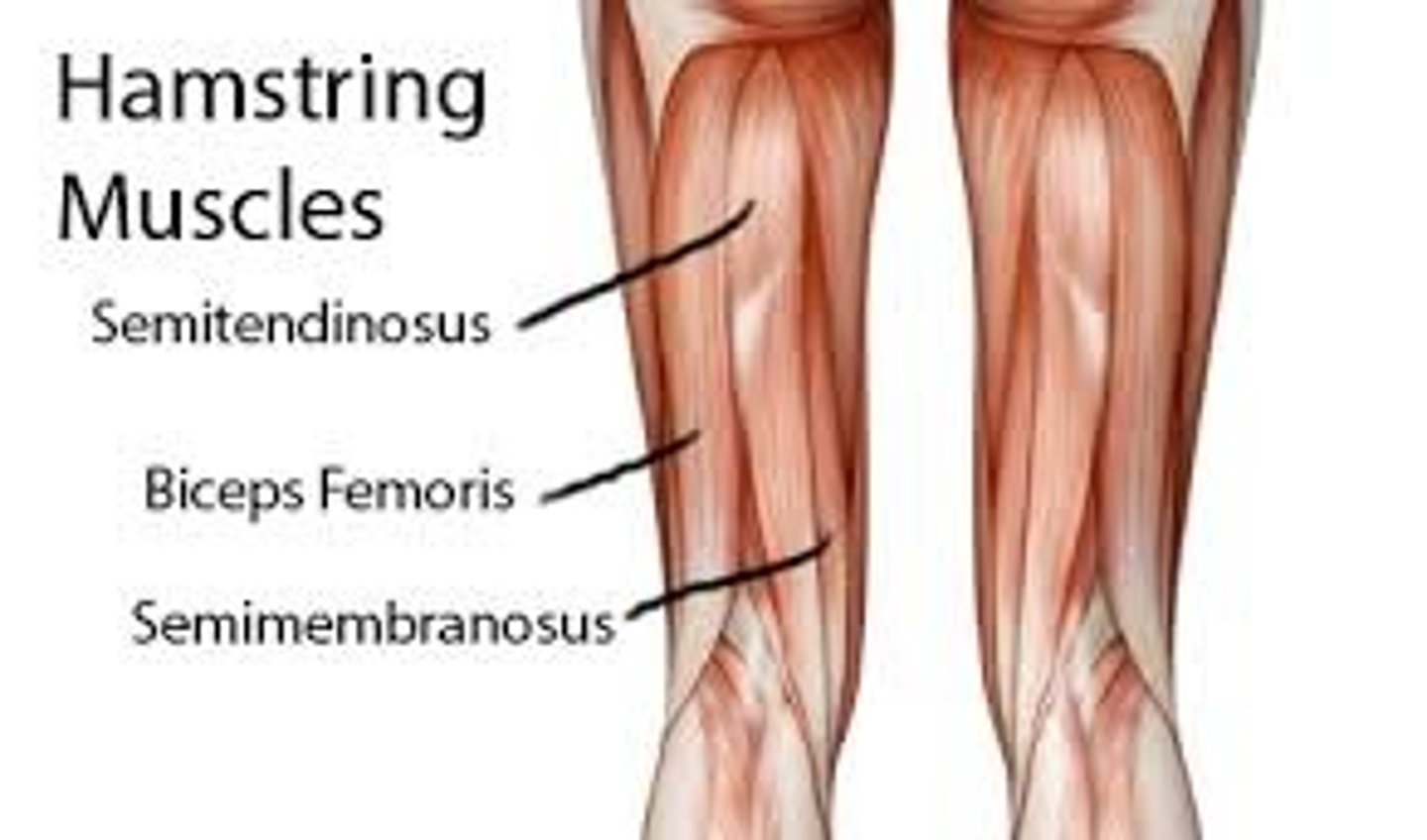
Posterior Compartment Muscles - 3 Hamstring muscles
1. biceps femoris
2. semitendinosus
3. semimembranosus
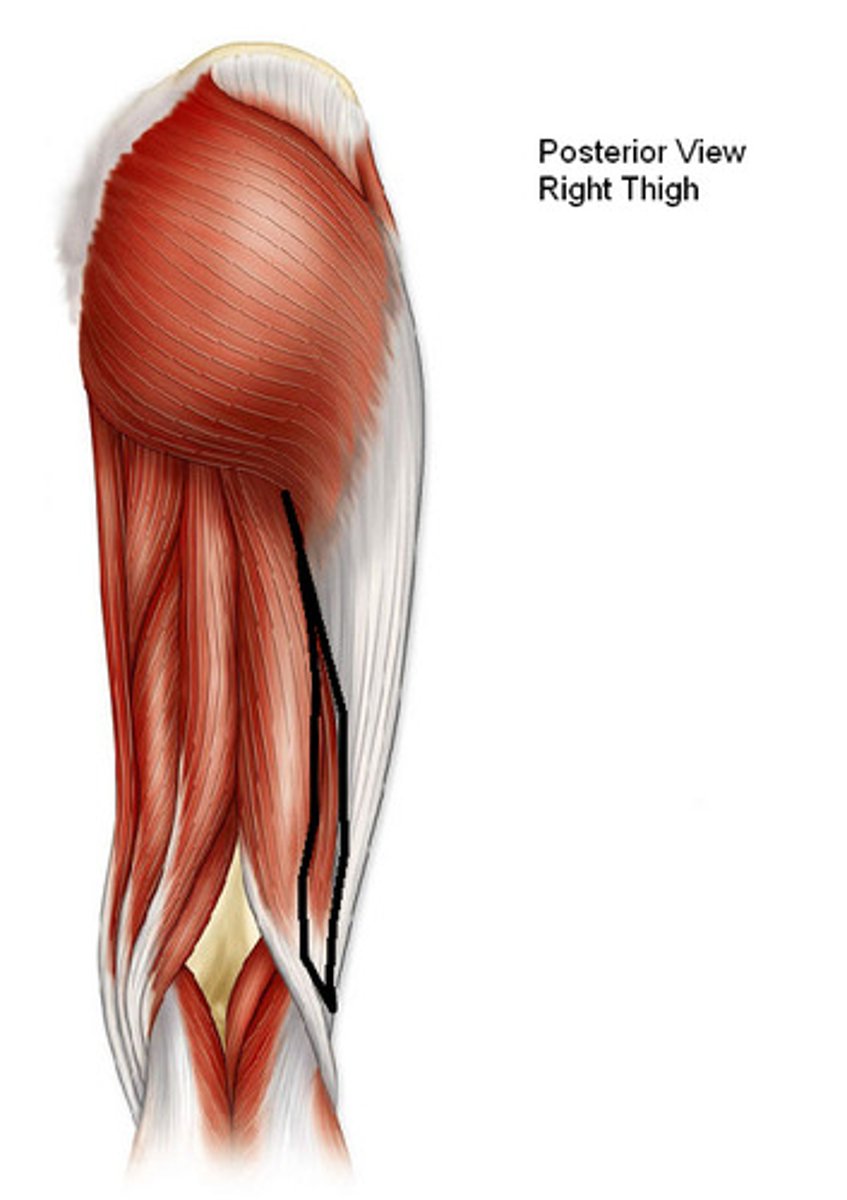
All except what muscle of the posterior compartment cross both the hip and knee joints?
short head the biceps femoris
Biceps Femoris - Long head (posterior compartment): Origin
ischial tuberosity
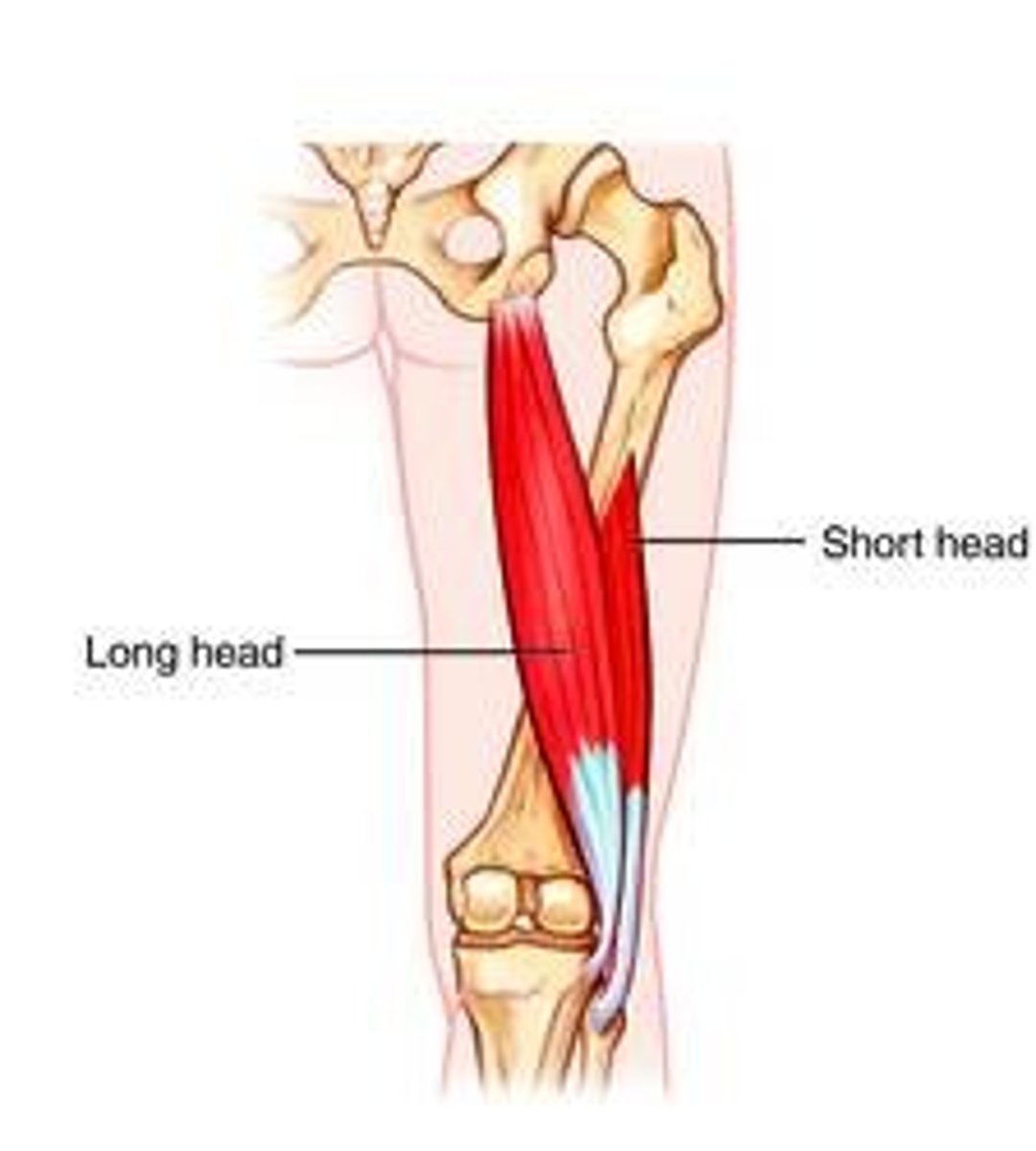
Biceps Femoris - Long head (posterior compartment): Insertion
1. fibula
2. fibular collateral ligament
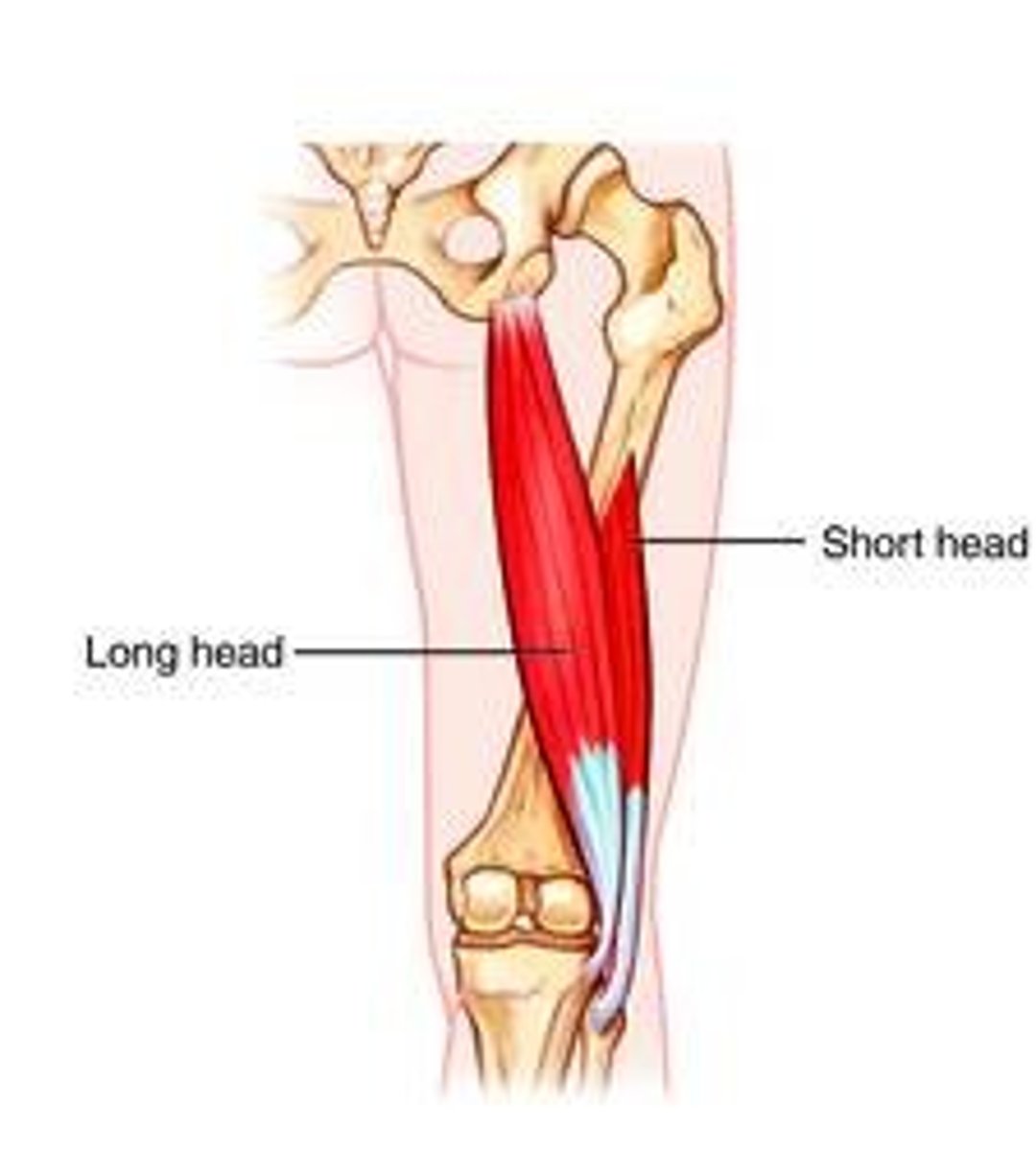
Biceps Femoris - Long head (posterior compartment): Action
flexes leg at knee joint, extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint and laterally rotates leg at knee joint
Biceps Femoris - Short head (posterior compartment): Origin
ischial tuberosity
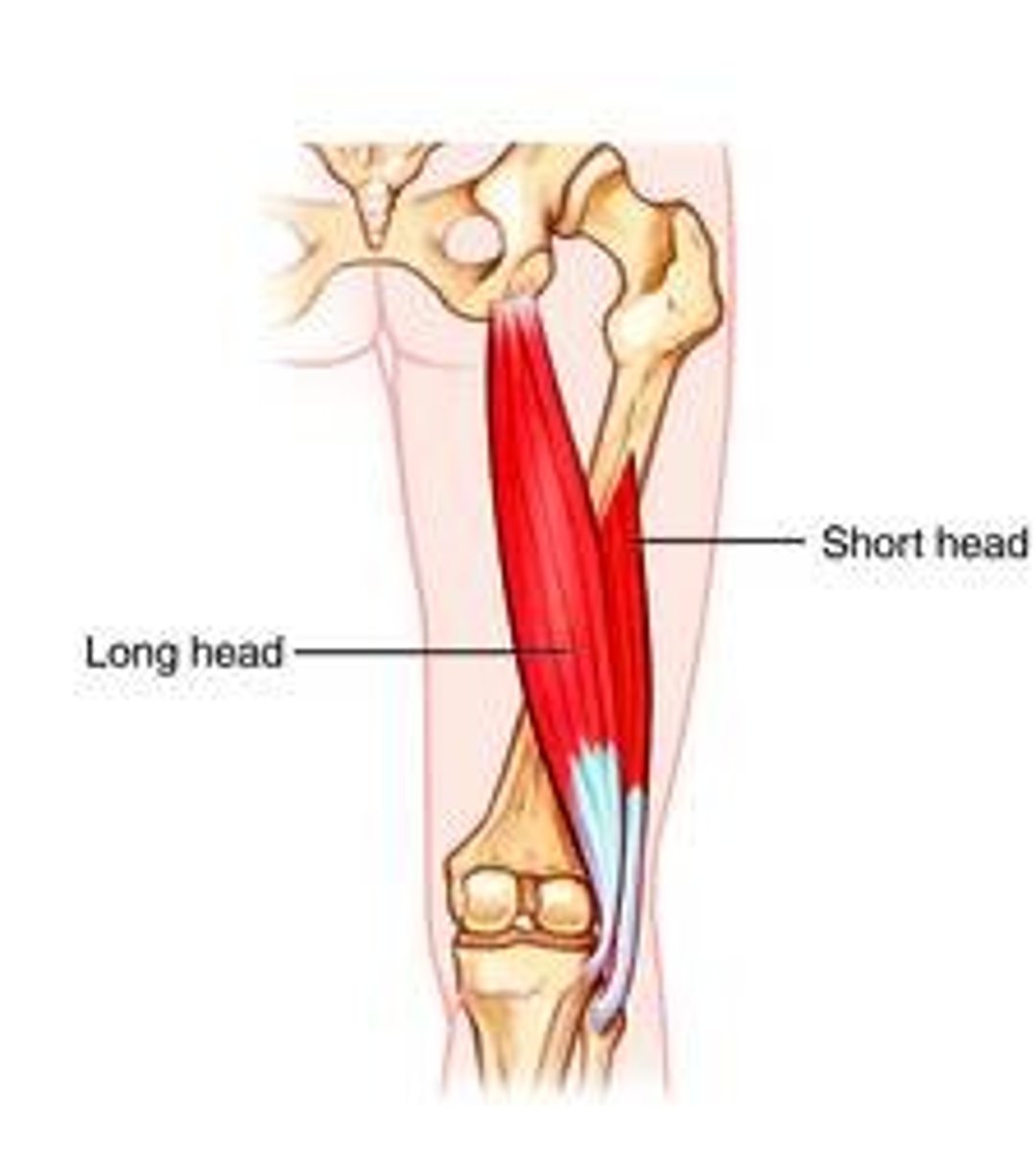
Biceps Femoris - Short head (posterior compartment): Insertion
1. fibula
2. fibular collateral ligament
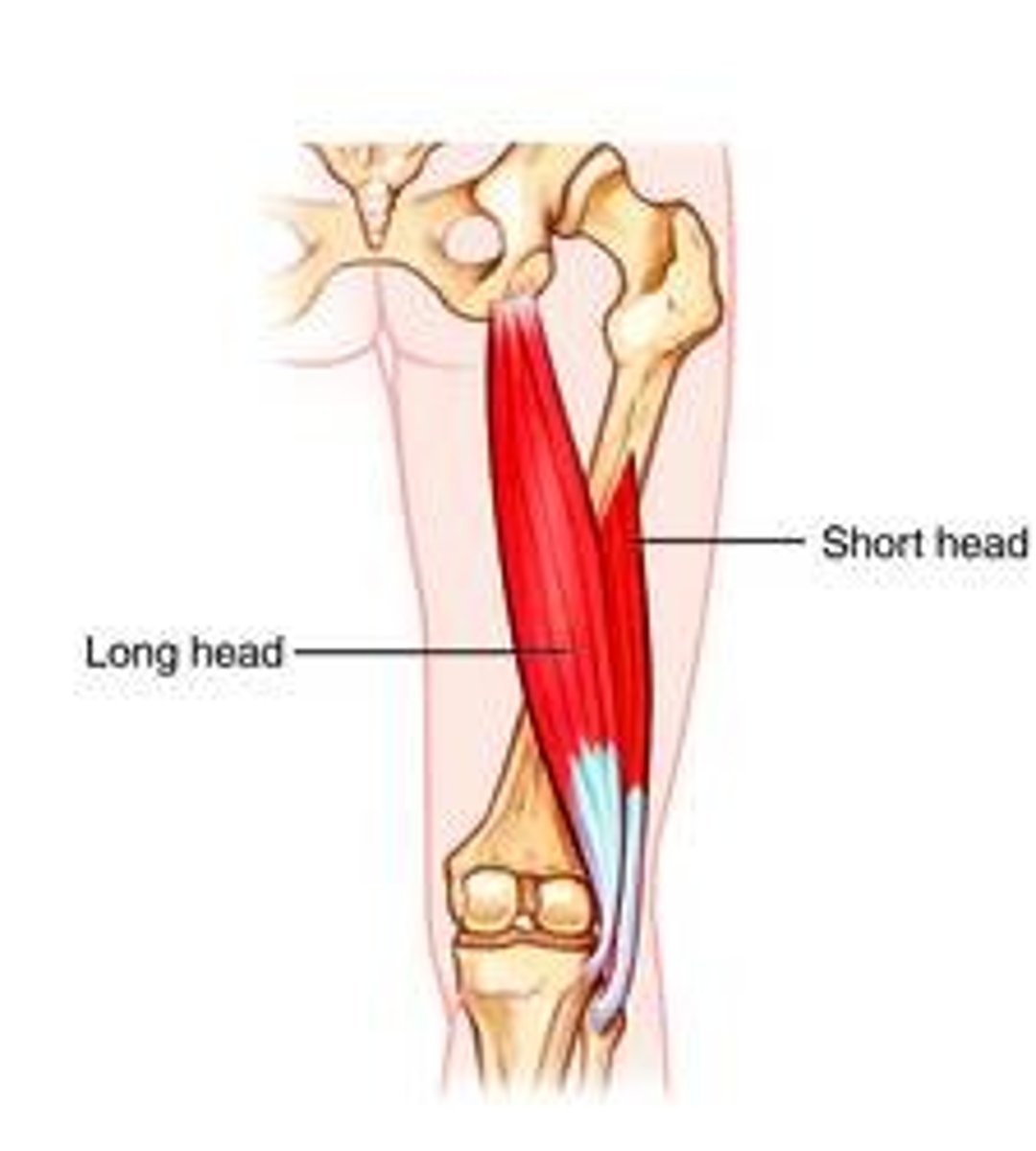
Biceps Femoris - Short head (posterior compartment): Action
flexes leg at knee joint, extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint and laterally rotates leg at knee joint
Semitendinosus (posterior compartment): Origin
ischial tuberosity
Semitendinosus (posterior compartment): Insertion
proximal tibia
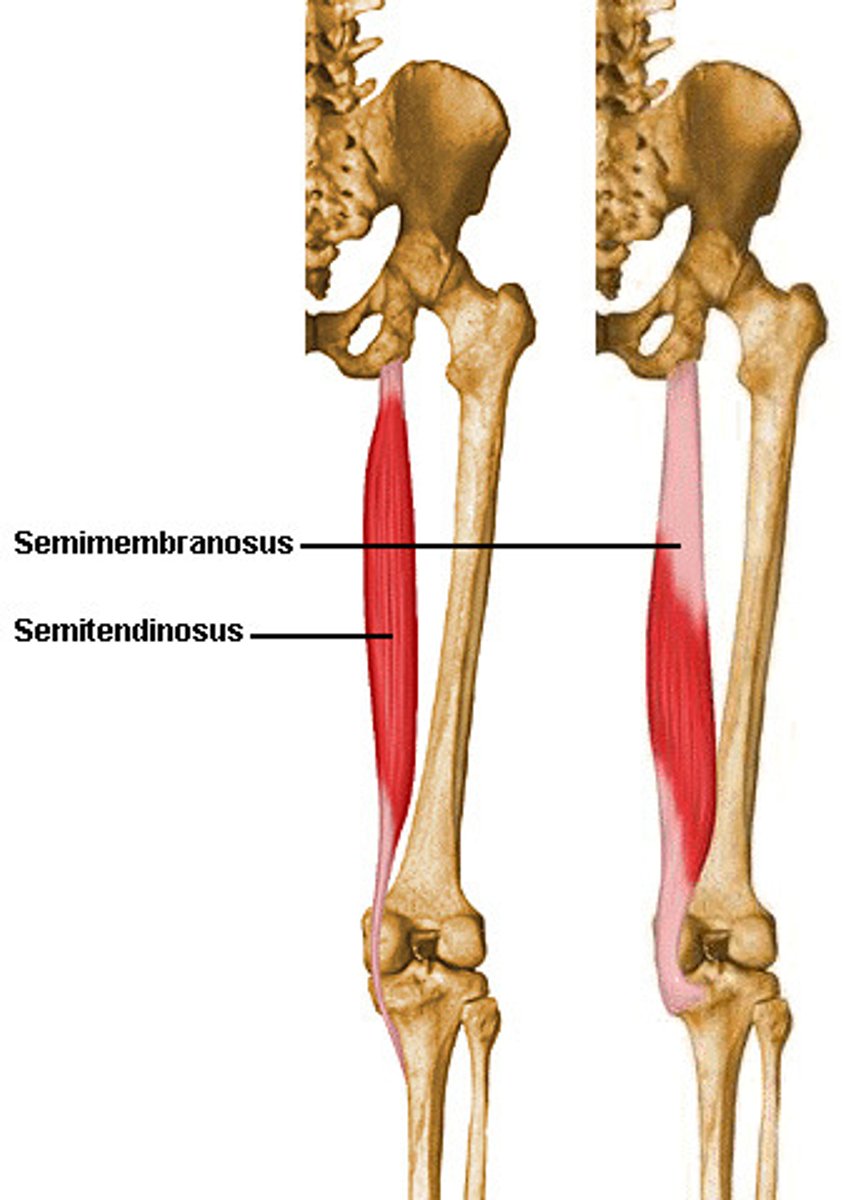
Semitendinosus (posterior compartment): Action
flexes leg at knee joint and extends thigh at hip joint, medially rotates thigh at hip joint and leg at knee joint
Semimembranosus (posterior compartment): Origin
ischial tuberosity
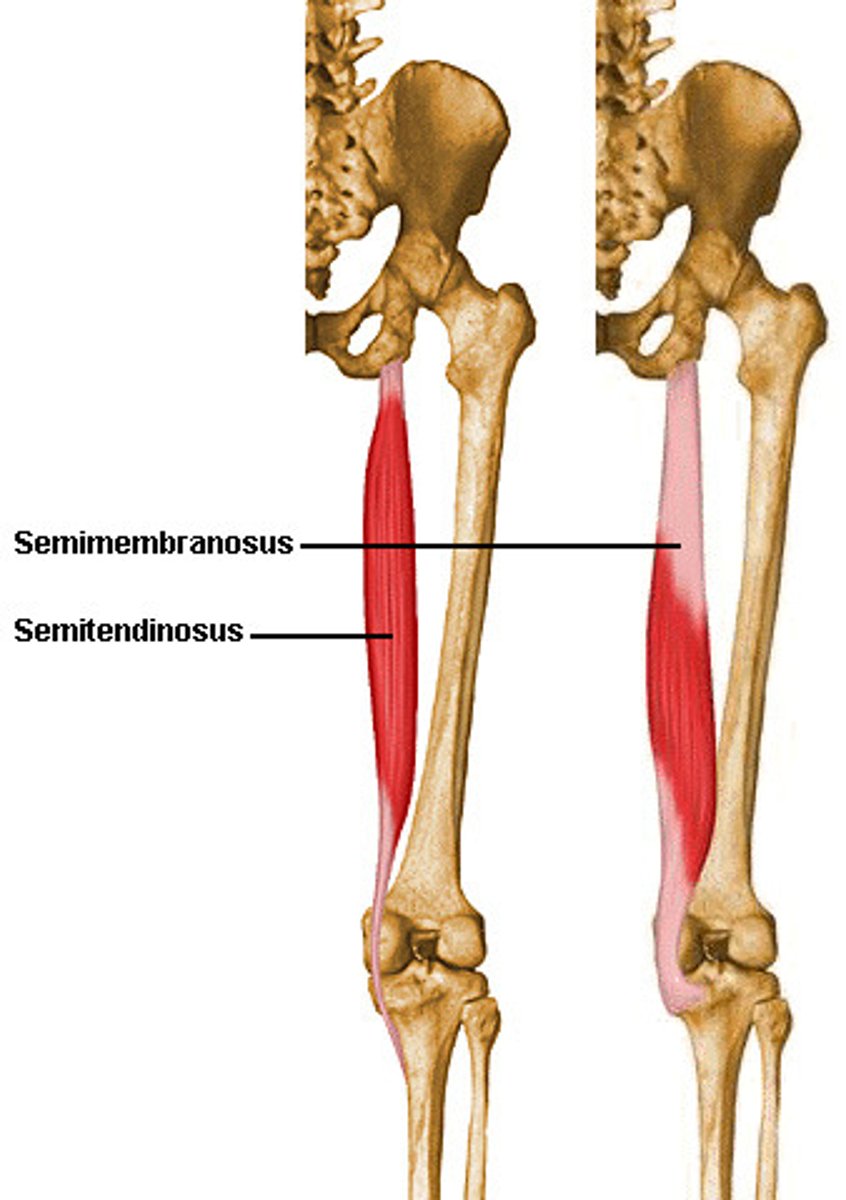
Semimembranosus (posterior compartment): Insertion
tibial condyle
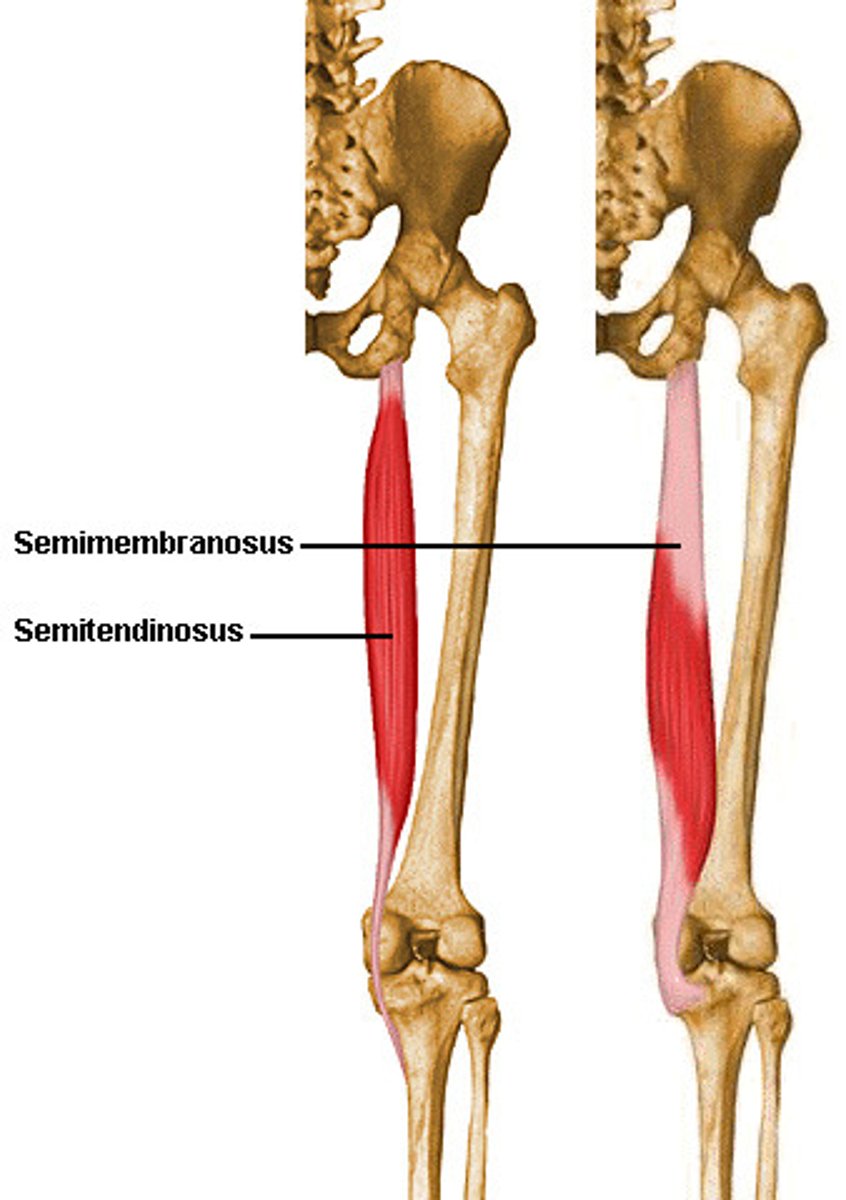
Semimembranosus (posterior compartment): Action
flexes leg at knee joint and extends thigh at hip joint, medially rotates thigh at hip joint and leg at knee joint
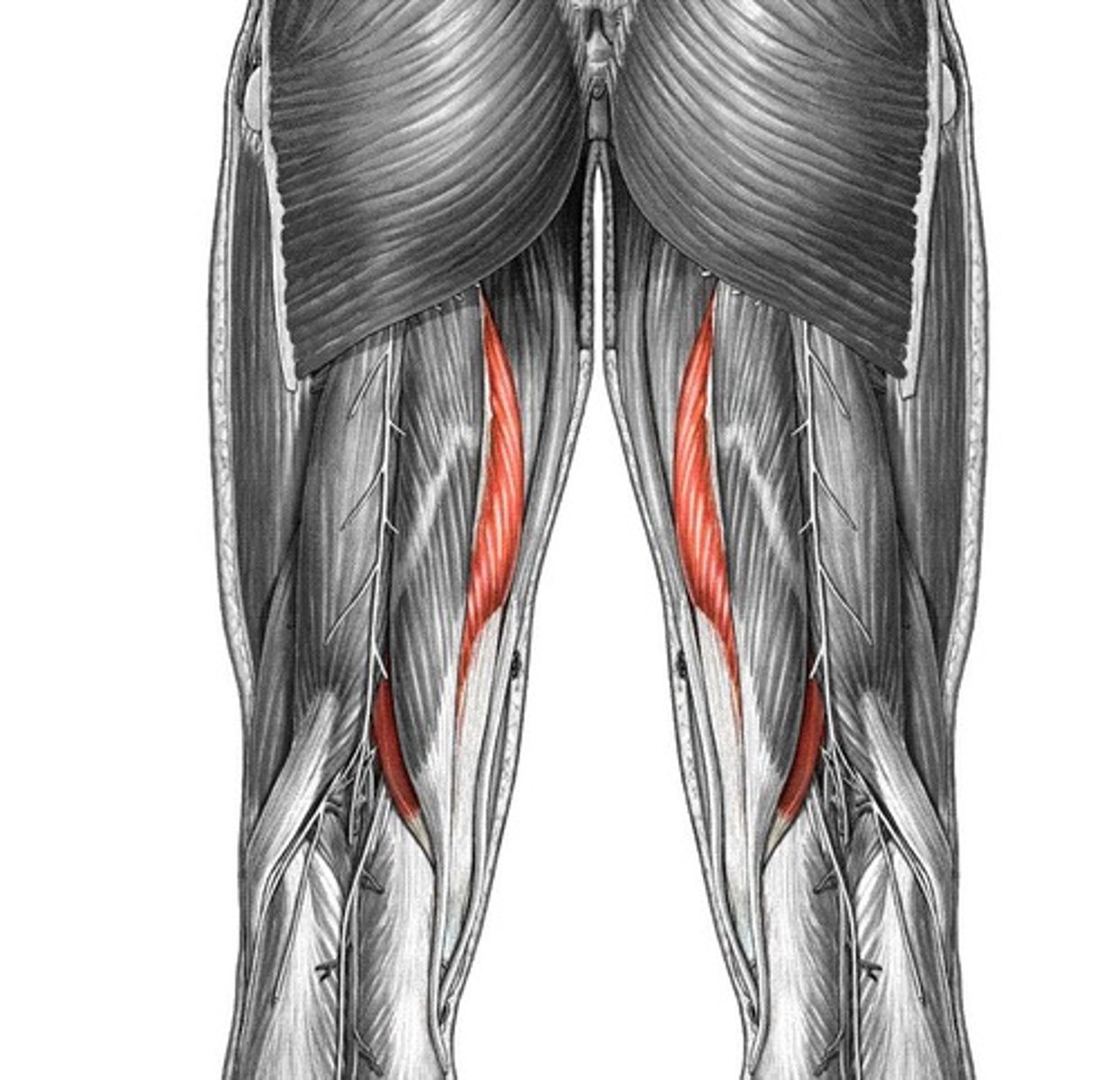
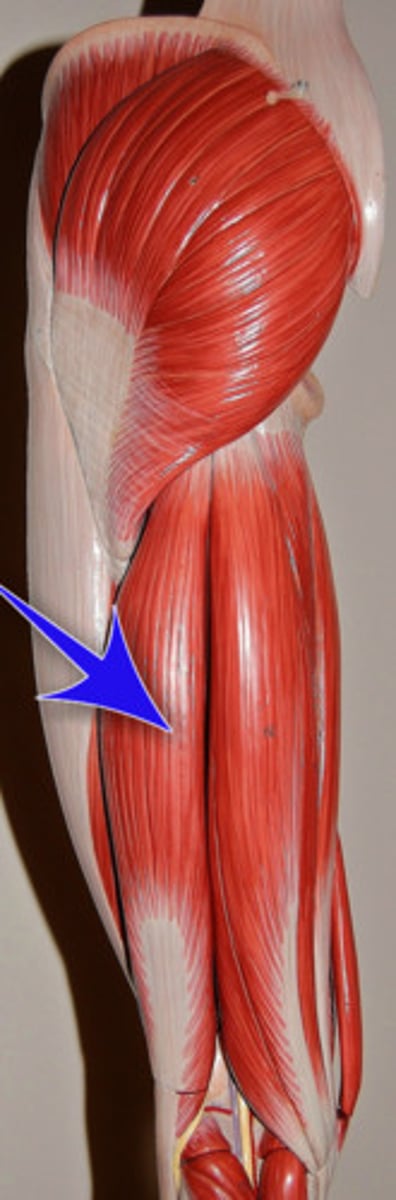
What is the most lateral posterior compartment muscle?
biceps femoris
What is the medial to biceps femoris in the posterior compartment muscle group?
semitendinosus
What is deep to the semitendinosus muscle in the posterior compartment muscle group?
semimembranosus
Hamstring injury is common in sports that requires what?
high degree of power and speed
What does the Hamstring injury range from?
mild strain to complete tear
Avulsion injury (hamstring injury)
avulsion of the ischial tuberosity with proximal hamstring origin attachment
What is the weakest element of the proximal hamstring unit in adolescents?
ischial apophysis