Radiology Exam 1
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
x-ray source
component that produces x-rays for imaging.
incisive canal
what is 3
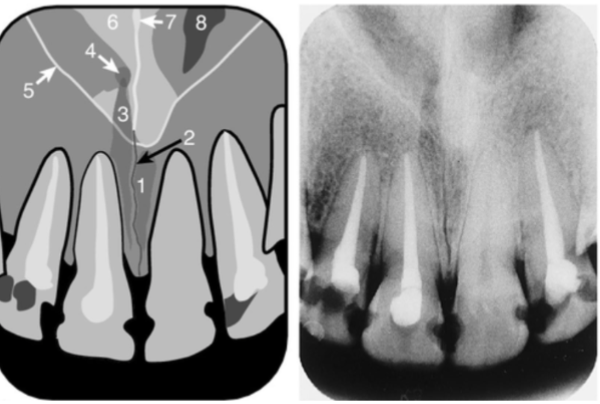
superior foramen of incisive canal
what is 4
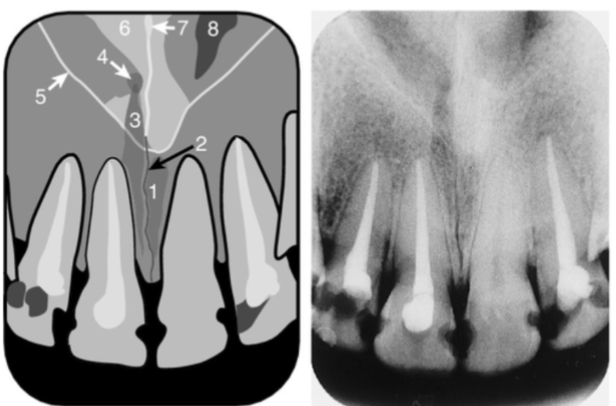
inferior meatus
what is 1
nose
what is 1
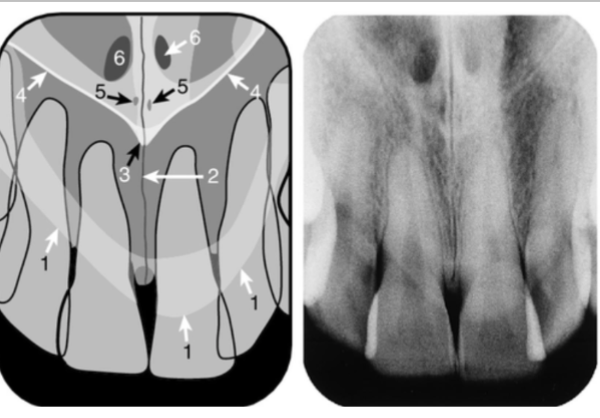
image receptor
component that receives/detects X rays
Image display
Device used to visualize and interpret radiographic images.
attenuation
reduction in x-ray beam intensity as it travels through anatomy, thicker and denser= more attenuation
radiolucent
less attenuating, describes materials that allow X-rays to pass through with little resistance
radiopaque
more attenuating, describes materials that do not allow X-rays to pass through easily, appearing white on radiographic images.
optical density
degree of darkening or opacity of an exposed film
contrast
range of densities between the darkest and lightest areas on a radiographic image, affecting visibility of structures
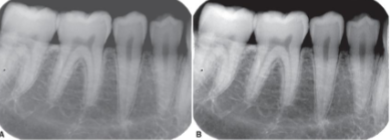
right
which picture is high contrast
location of x-ray sensor
what is the difference between intraoral and extraoral dental radiography
sharpness
measures how well boundary between two differing radiodensity areas is defined
spatial resolution
measures how well an image reveals small objects that are close together
magnification
increase in size of object on image compared to actual size of object
size distortion
difference between object size on image and actual object size
shape distortion
difference in appearance of an object shape on image compared to actual object shape
long source-receptor distance
source receptor distance that reduces magnification and improves image detail.
small
a object- receptor distance that decreases magnification and increases image detail.
receptor parallel to long axis of object
receptor position that minimizes distortion and optimizes image quality
central beam perpendicular to object and receptor
alignment of x-ray beam that ensures minimal distortion and optimal image quality
small
size of focal spot that DECREASES distortion and magnification
focal spot
area on the target of x-ray tube where x-rays are produced
penumbra/geometric unsharpness
the partial shadow or distortion at the edges of an x-ray image caused by the size of the focal spot
foreshortening
image shorter than true object
object not parallel to receptor, central ray not perpendicular to OBJECT
what can cause foreshortening
elongation
image longer than true object
object not parallel to receptor, central ray not perpendicular to RECEPTOR
what can cause elongation
periapical
show entire length of tooth and surrounding periapical bone
bitewing
show only crowns and adjacent alveolar crests
occlusal
show area of teeth and bone larger than periapical images
full mouth series (FMX)
a comprehensive set of dental radiographs that captures the complete view of all teeth and surrounding structures, typically including periapical and bitewing images.
position indicating device
attached to tube head to direct x-ray beam
receptor
detects/records x-rays
paralleling (preferred) and bisecting angle
techniques for periapical x-ray
paralleling technique
A radiographic technique in which the receptor is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth, MORE ACCURATE
bisecting technique
distortion more likely than with paralleling, positioned parallel to imaginary bisecting angle between tooth and receptor
vertical angulation
angle between x-ray beam and line parallel to floor/occlusal plane, significant influence of DIMENSIONAL ACCURACY
positive angulation
angulation where cone points DOWNWARD
negative angulation
angulation where cone points UPWARD
elongation
what does a vertical angle that is too SMALL cause (under-angulation)
foreshortening
what does a vertical angle that is too LARGE cause (over-angulation)
FDA approved
what is a requirement of x-ray devices to ensure that the devices meet safety and effectiveness standards
horizontal and perpendicular to operator
positioning of handheld device to ensure operator safety
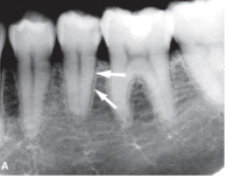
lamina dura
what is indicated by the arrows
eggshell effect
x-rays are more attenuated at the curves of a bony structure than those traveling at right angles to surface
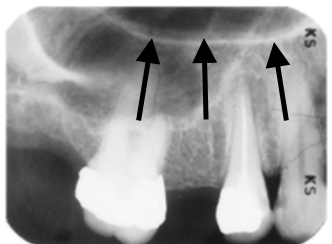
alveolar crest
what is indicated by the arrows
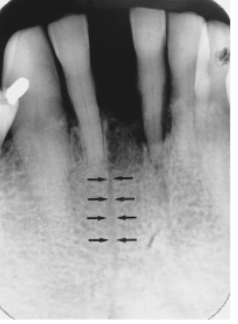
PDL space
what is the DARK LINE indicated by the arrows
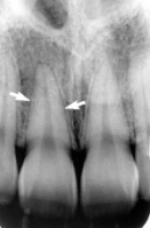
root shape
what leads to appearance of double PDL space as shown in the image
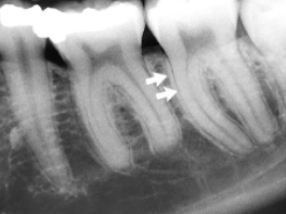
anatomic superimposition
why aren’t buccal and lingual cortices distinguishable on BWs and PAs?
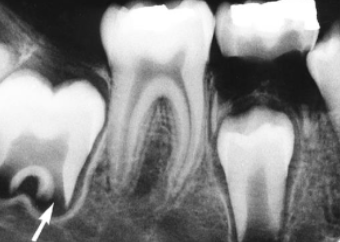
dental papilla
what is indicated by the arrow: structure that forms dentin and pulp
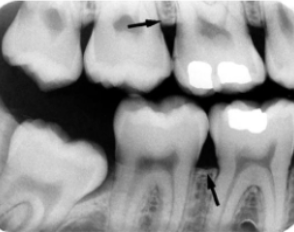
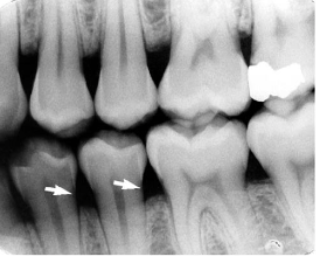
cervical burnout
what is indicated by the arrows: a radiolucent area seen at the cervical portion of teeth due to optical illusion, often mistaken for decay
anterior nasal spine
identify the structure
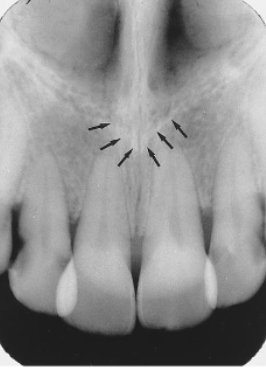
median palatal structure
identify the sucture
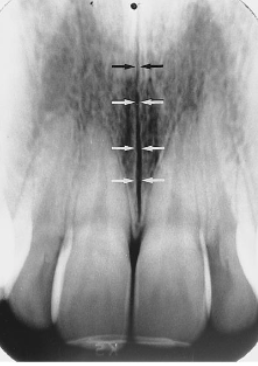
incisive foramen
identify the structure
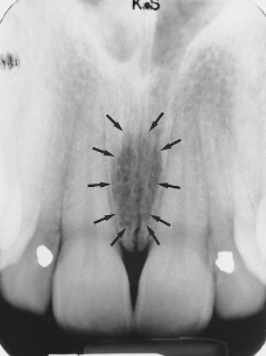
superior incisive foramina
identify the structures

nasal septum
identify the structure
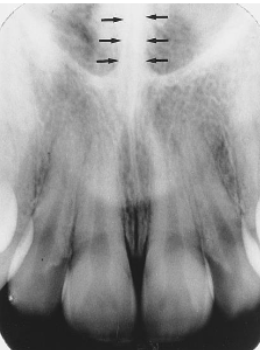
inferior nasal conchae
identify the structure
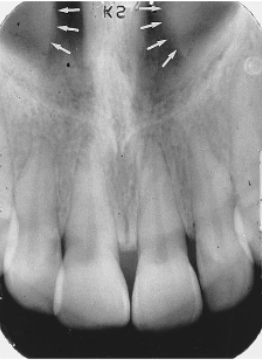
nasal cavity floor
identify the structure
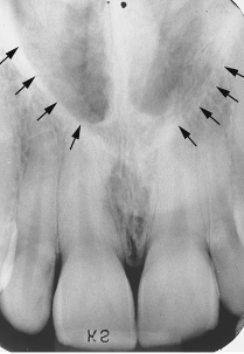
inverted Y (junction)
identify the structure
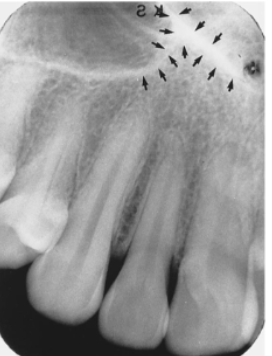
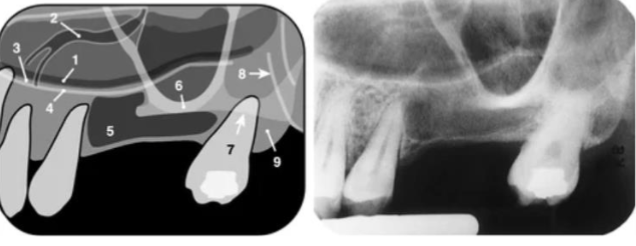
lateral (incisive) fossa
what is indicated by the arrows
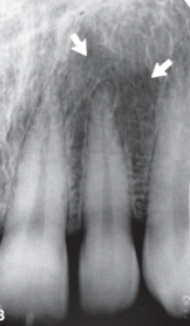
pneumatized sinus floor
what is indicated by the arrows
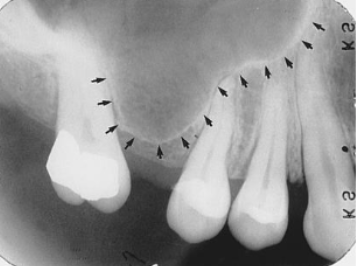
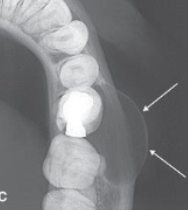
tuberosity
what is indicated by the arrows
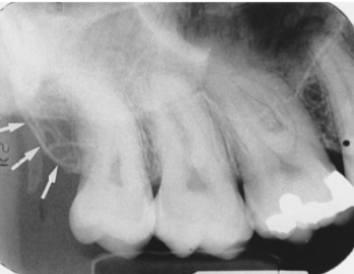
antral alveolar canal
what is indicated by the arrows
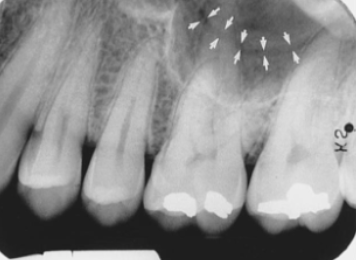
septation
what is indicated by the arrow
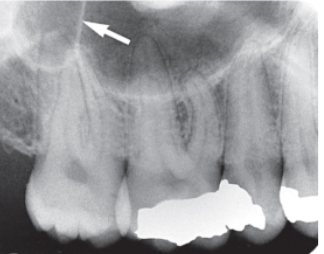
hamulus
what structure is indicated by the arrow
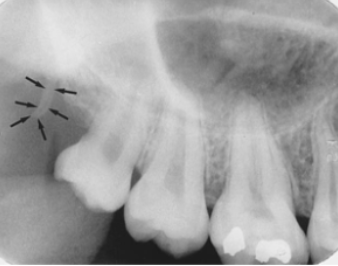
zygomatic process
what structure is indicated by the arrow
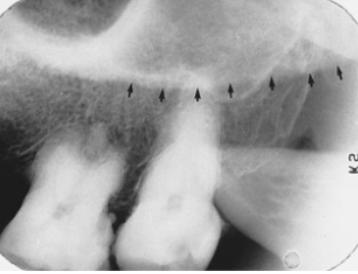
coronoid process
what is indicated by the arrows
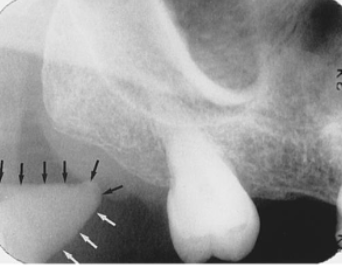
lateral pterygoid plate
what is indicated by the arrows
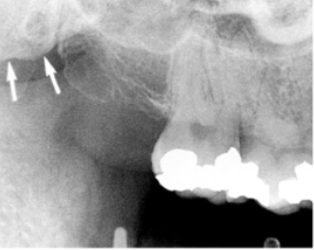
nasolabial fold
what is indicated by the arrows
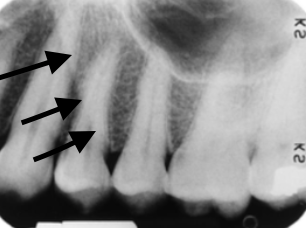
floor of maxillary sinus
what is indicated by the arrows
hard palate/floor of nose
what is indicated by the arrows
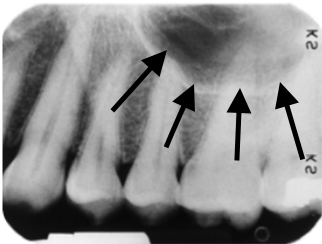
nutrient canal
what is indicated by the arrows
mental/sublingual fossa
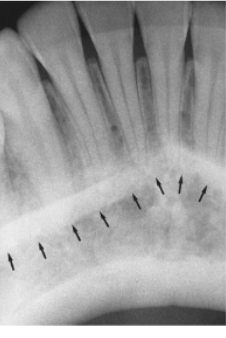
what is indicated by the arrows
mental ridge
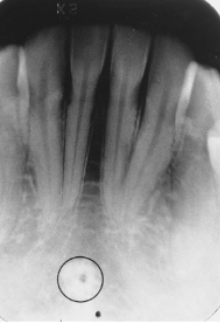
what is indicated by the arrows
lingual foramen
what is indicated by the arrow
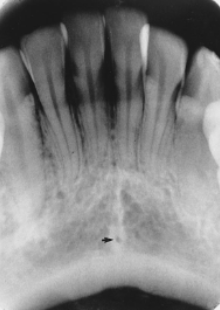
genial tubercle
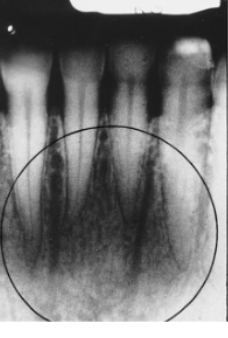
what is indicated by the circle
accessory foramen
what is indicated by the arrow
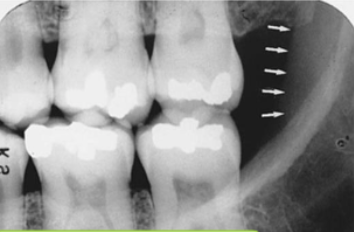
external oblique ridge
what is indicated by the arrows
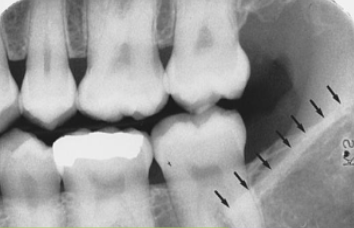
anterior border of ramus
what is indicated by the arrows
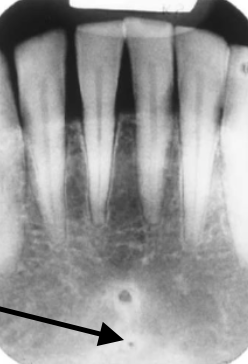
mental foramen
what is indicated by the arrow
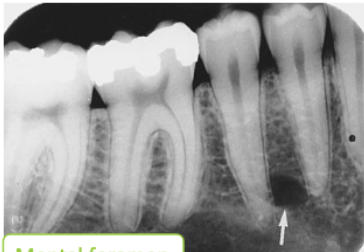
inferior alveolar canal
what is indicated by the arrows
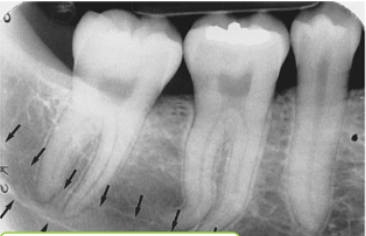
mylohyoid ridge
what is indicated by the arrows
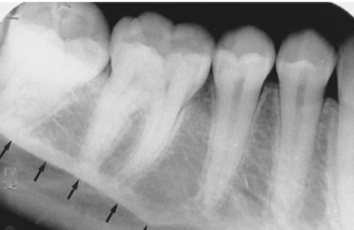
mandibular fossa
what is indicated by the arrows
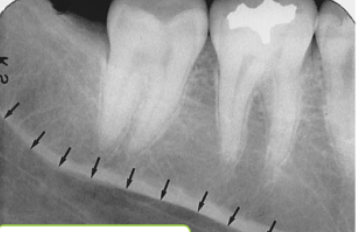
submandibular fossa
what is indicated by the star
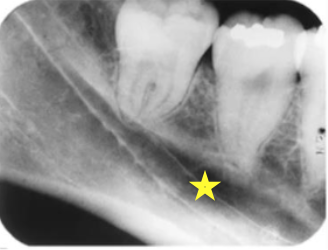
inferior alveolar canal
what is indicated by the arrows
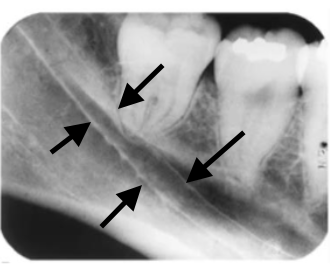
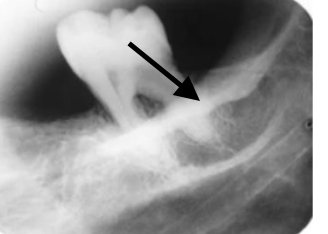
external oblique ridge
what is indicated by the arrow
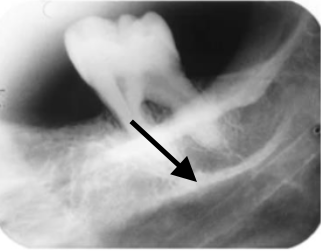
internal oblique/mylohyoid ridge
what is indicated by the arrows
distal
which direction would a LINGUAL object shift if the tubehead shifts DISTAL
mesial
which direction would a BUCCAL object shift if the tubehead shifts DISTAL
increased distance from reference object
when tube is shifted what would a increased shift AWAY from reference object indicate
separating root canals
what is the tube shifting technique useful for
buccal
where is the opaque foreign object relative to #3
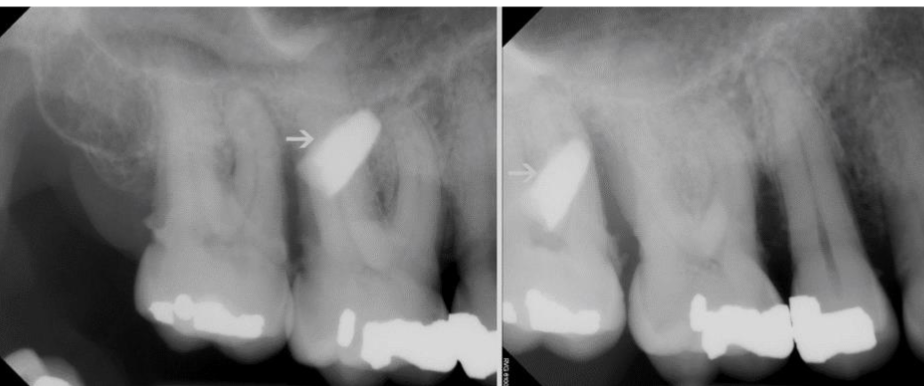
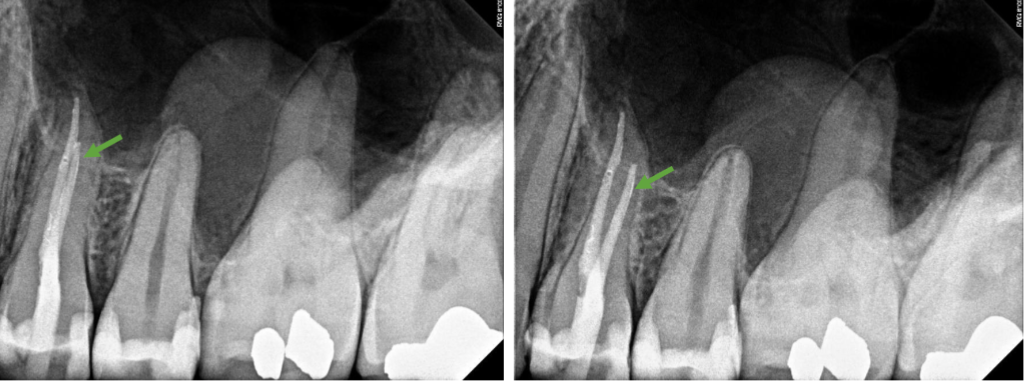
buccal
what is the position of the root canal indicated in green
down
what direction would a LINGUAL object shift if the tube head shifts DOWN
UP
what direction would a BUCCAL object shift if the tube head shifts DOWN
skull projections
radiographs of the whole head
cephalometric radiographs
types of skull projection with standardized projection geometry and known magnification