Biology chapters 7-11 final
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/111
Last updated 2:37 PM on 5/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
Very few cells are able to reproduce
Which of the following is NOT a principle of cell theory?
2
New cards
The cell lacks a nucleus
Looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokaryote. How do you know?
3
New cards
The cell is eukaryotic because it has a nucleus
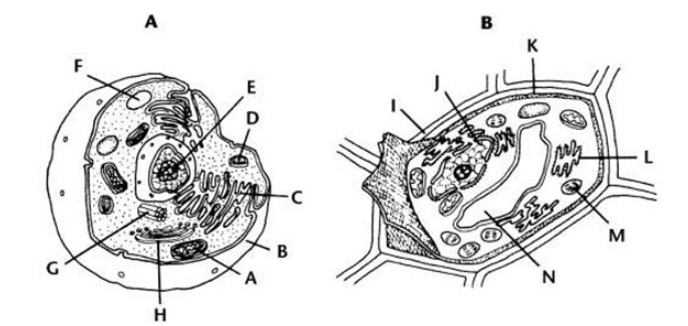
Which of the following conclusions could you draw about the cell shown in figure 7-1?
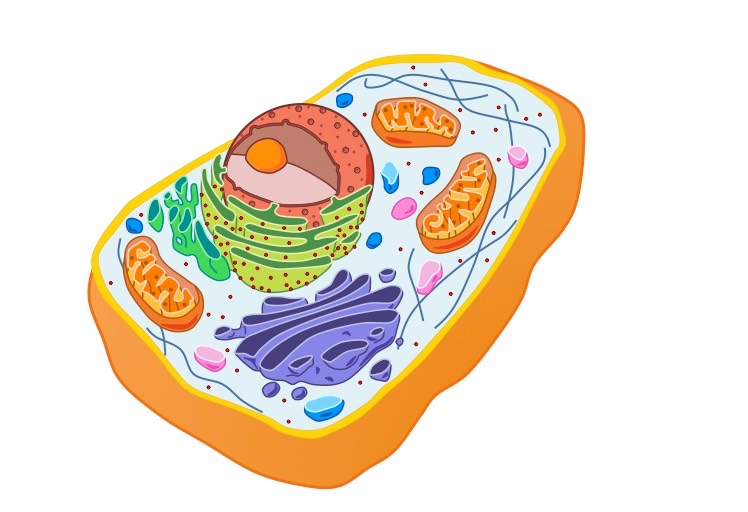
4
New cards
Stores DNA
Which of the following is a function of the nucleus?
5
New cards
The nucleus is the site of protein assembly
Which of the following statements about the nucleus is NOT true?
6
New cards
Structure C (vacuoles)
Which structure in the cell shown in figure 7-2 above stores materials, such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates?
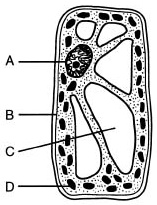
7
New cards
ribosome
Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus?
8
New cards
Structure A (golgi apparatus)
Which structure shown in figure 7-3 above modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release from the cell?
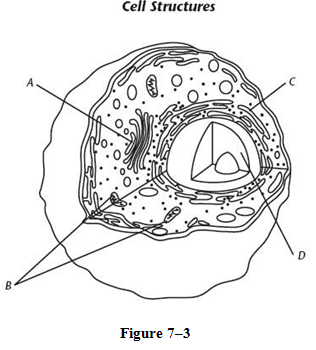
9
New cards
Mitochondrion
Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use?
10
New cards
chloroplast
Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells?
11
New cards
support and protect the cell
The primary function of the cell wall is to
12
New cards
cell membrane
which of the following structures serves as the cells boundary from its environment?
13
New cards
regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell
which of the following is a function of the cell membrane?
14
New cards
osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called
15
New cards
active transport
Which means of particle transport is shown in figure 7-4 above?
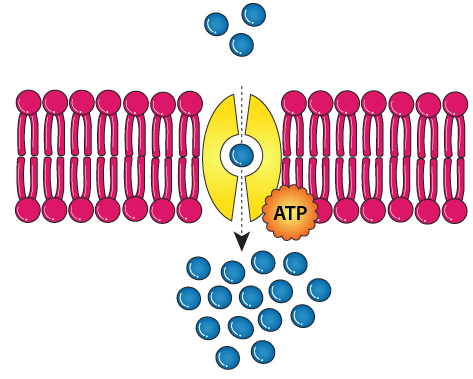
16
New cards
endocytosis
Which means of particle transport is shown in figure 7-5 above
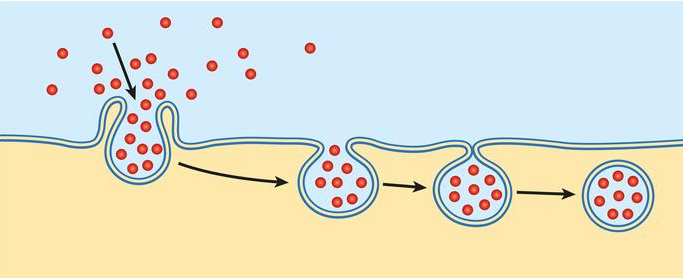
17
New cards
homeostasis
Which term describes the relatively constant internal conditions of an organism?
18
New cards
able to carry out all of the functions necessary for life
The cells of unicellular organisms are
19
New cards
adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups
What are the three parts of an ATP molecule?
20
New cards
A phosphate group is removed
Energy is released from ATP when
21
New cards
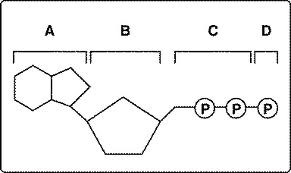
Structure D
Look at figure 8-1. All of the following are parts of an ADP molecule EXCEPT
22
New cards
autotrophs
Organisms, such as plants, that make their own food are called
23
New cards
heterotrophs
Organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain energy from external sources are called
24
New cards
Autotrophs produce carbohydrates
What happens during photosynthesis?
25
New cards
sunlight
Plants get the energy they need for photosynthesis by absorbing
26
New cards
does not absorb green light
Most plants appear green because chlorophyll
27
New cards
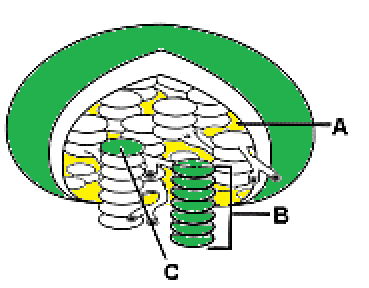
structure C
Which structure in figure 8-2 represents a single thylakoid?
28
New cards
thylakoids
The stroma is the region outside the
29
New cards
in the thylakoid membrane
Where in the chloroplast is chlorophyll found?
30
New cards
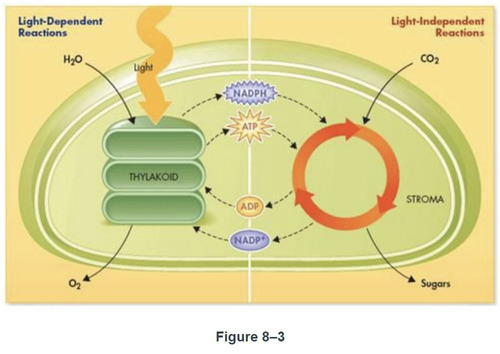
NADP+
Which chemical shown in figure 8-3 is an electron carrier molecule?
31
New cards
they can accept electrons and transfer most of their energy into another molecule
What makes certain molecules good electron carriers?
32
New cards
oxygen and high-energy sugars
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into
33
New cards
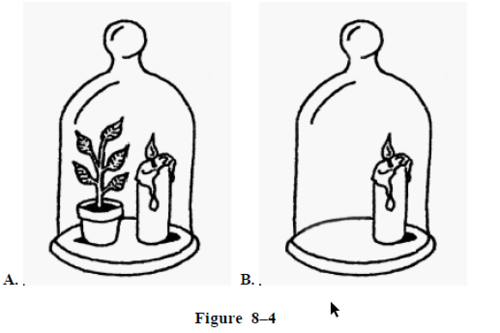
oxygen produced by the plant allows for the candle to burn longer
In figure 8-4, why might the candle in jar A burn longer than the candle in jar B?
34
New cards
Within the thylakoid membranes
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place?
35
New cards
ATP, NADPH, and oxygen gas
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
36
New cards
ATP and NADPH are used to produce high-energy sugars
Which of the following is NOT a step in the light-dependent reactions?
37
New cards
H+ ions are released as water splits
What action contributes to the inside of the thylakoid membrane becoming positively charged during the light-dependent reactions?
38
New cards
the calvin cycle produces sugars
Which of the following activities happens within the stroma?
39
New cards
light-independent reactions
The calvin cycle is another name for the
40
New cards
no sugars will be produced
If carbon dioxide is completely removed from a plant’s environment, what would you expect to happen to the plant;s production of high-energy sugars?
41
New cards
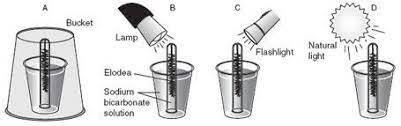
A
In which experimental setup shown above would you expect the elodea plant inside the test tube to produce the LEAST amount of oxygen?
42
New cards
By breaking down food molecules gradually and capturing their chemical energy
How do organisms get the energy they need?
43
New cards
glycolysis → krebs cycle → electron transport chain
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in cellular respiration?
44
New cards
6CO₂ + C₆H₁₂O₆ = 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy
What is the correct equation for cellular respiration?
45
New cards
food molecules
Cellular respiration releases energy by breaking down
46
New cards
oxygen
Cellular respiration is called an aerobic process because it requires
47
New cards
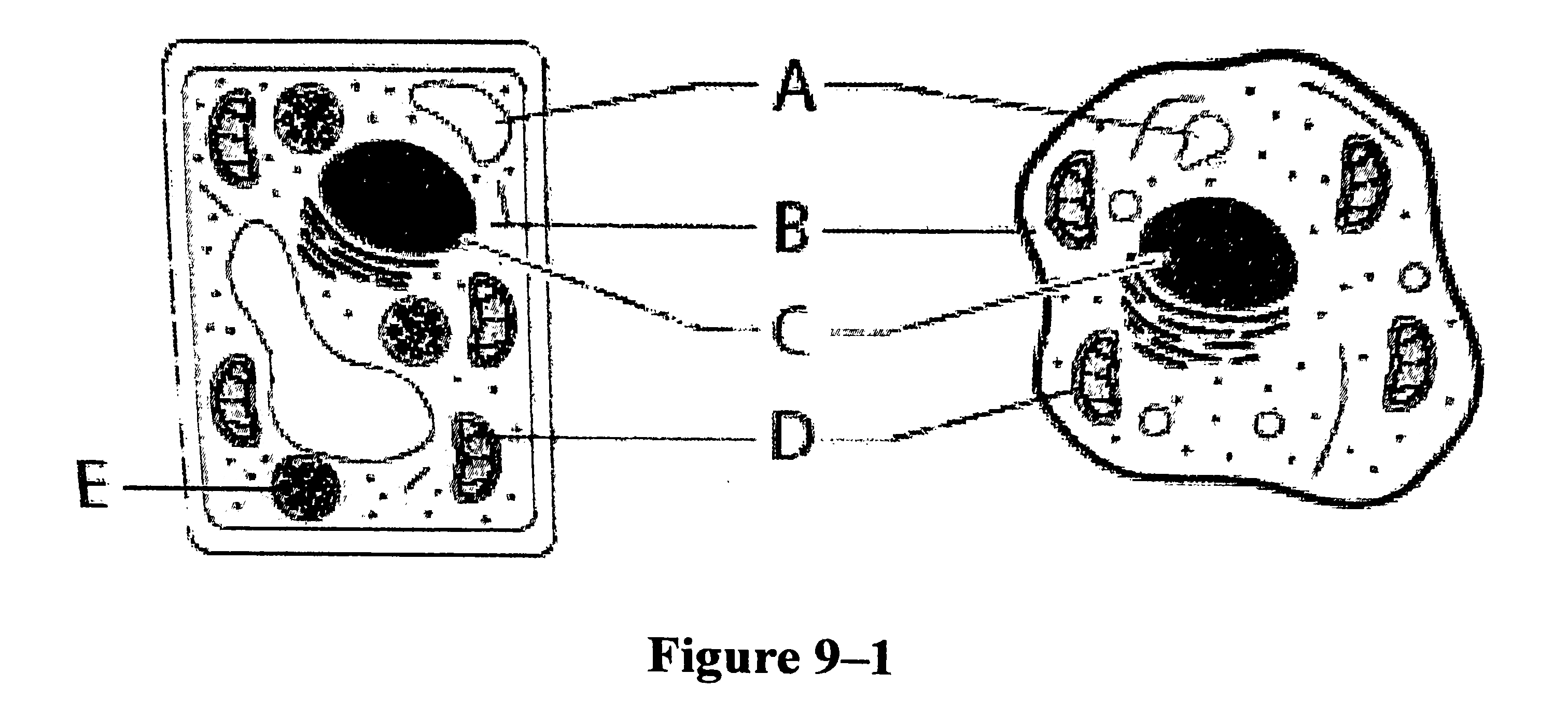
E: photosynthesis; D: cellular respiration
Using figure 9-1, which pairing matches the structures shown in the cell diagrams with the processes that take place within those structures?
48
New cards
Photosynthesis
Which process does NOT release energy from glucose?
49
New cards
photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back
Which of the following is one of the ways that cellular respiration and photosynthesis are opposite processes?
50
New cards
all eukaryotic cells
Unlike photosynthesis, cellular respiration occurs in
51
New cards
reactants of cellular respiration
The products of photosynthesis are the
52
New cards
2 ATP molecules
Glycolysis provides a cell with a net gain of
53
New cards
glucose
The starting molecule for glycolysis is
54
New cards
glucose
Which of the following is NOT a product of glycolysis?
55
New cards
NAD+
Which of the following is an electron carrier that plays a role in cellular respiration?
56
New cards
the krebs cycle
In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is followed by
57
New cards
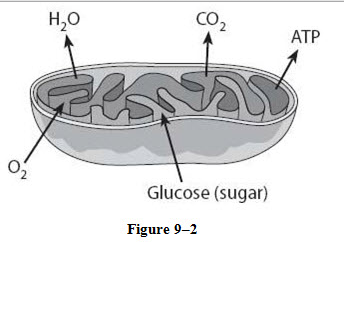
electron transport
What process do the arrows for oxygen going in and water coming out represent in the figure 9-2 diagram of the mitochondria?
58
New cards
inner mitochondrial membrane
In eukaryotes, electron transport occurs in the
59
New cards
convert ADP molecules into ATP molecules
High-energy electrons that move down the electron transport chain ultimately provide the energy needed to
60
New cards
36 ATP molecules
Cellular respiration uses 1 molecule of glucose to provide approximately
61
New cards
muscle cells
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in
62
New cards
repaying an oxygen debt
Breathing heavily after running a race is your body’s way of
63
New cards
cellular respiration
When the body needs to exercise for longer than 90 seconds, it generates ATP by carrying out
64
New cards
volume increases faster than its surface area
As a cell becomes larger, its
65
New cards
volume
The rate at which wastes are produced by a cell partially depends on the cell’s
66
New cards
moving needed materials in and waste products out
Compared to small cells, large cells have more trouble
67
New cards
each daughter cell recieves its own copy of the parent cell’s DNA
Which of the following happens when a cell divides?
68
New cards
cell division
The process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells is called
69
New cards
provides genetic diversity
An advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that sexual reproduction
70
New cards
during cell division, each daughter cell will get the same number of genes
Which advantage of having the cell’s DNA bundled into separate chromosomes is illustrated in figure 10-1 above?
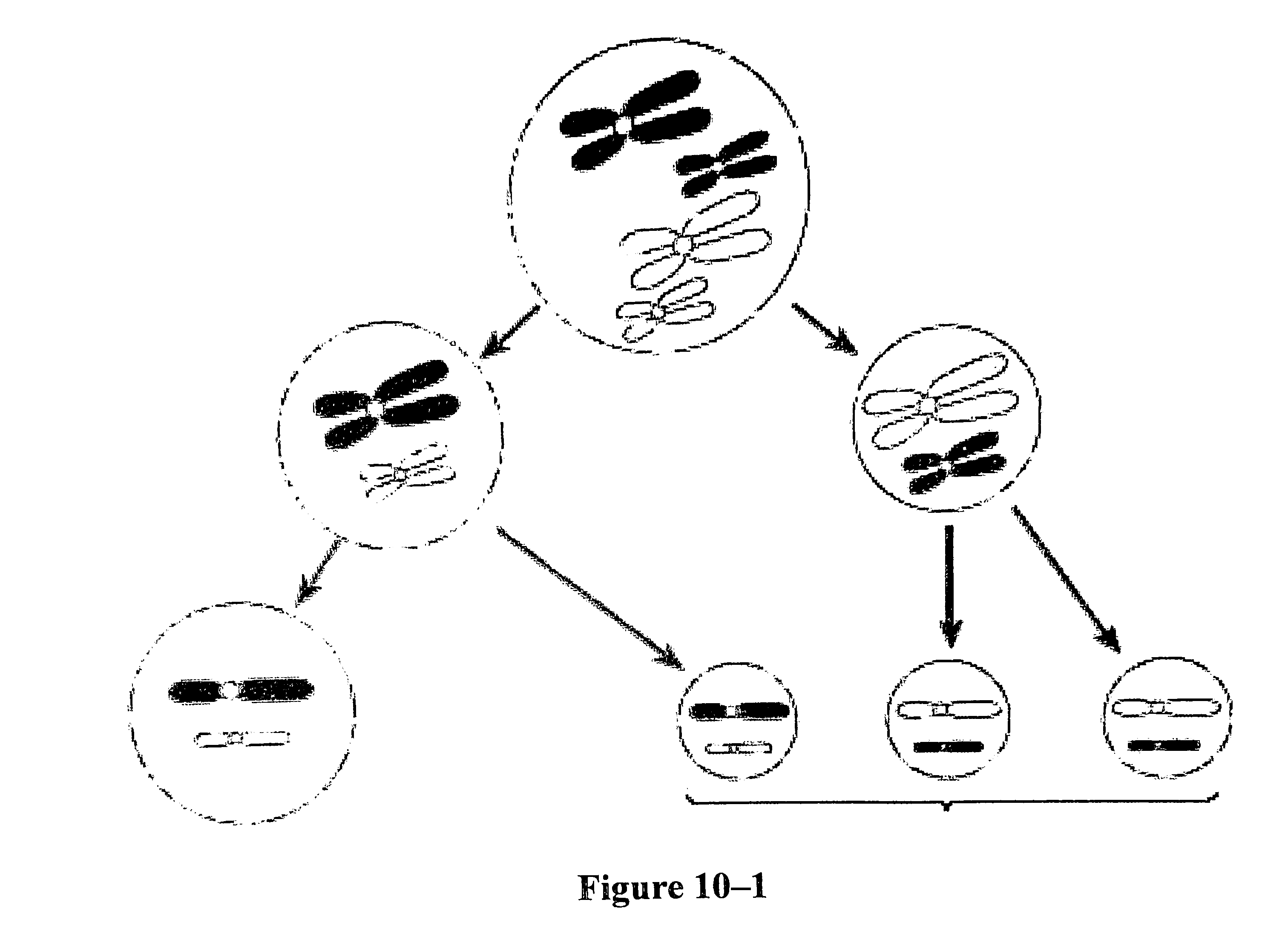
71
New cards
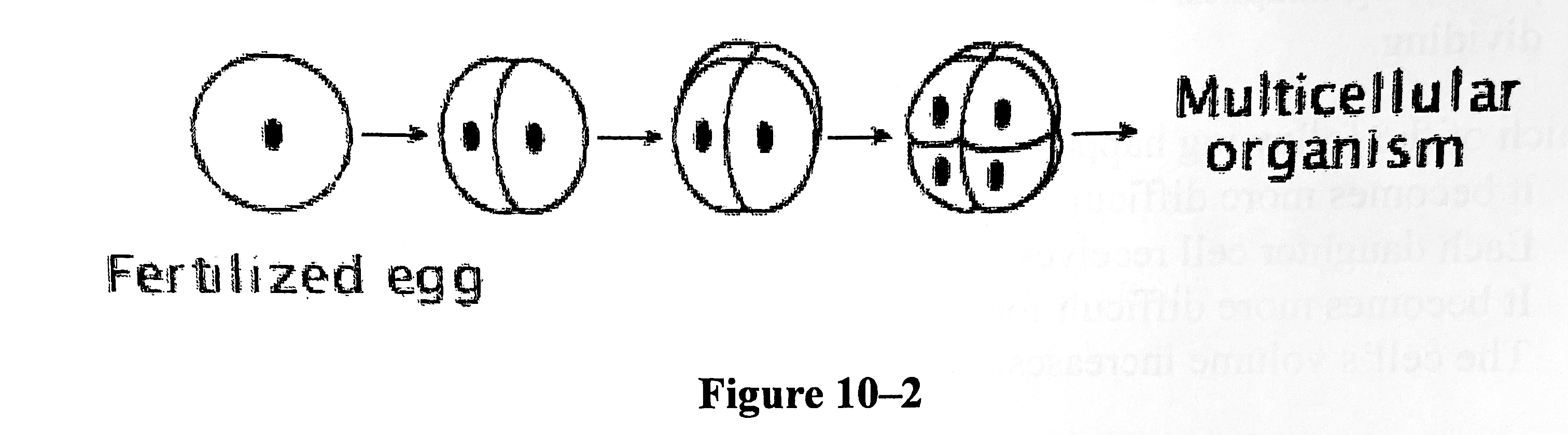
chromosomes are duplicated before cell division so that each new daughter cell has a complete set
A multicellular organism begins life as a single cell-- a fertilized egg with a complete set of chromosomes. The picture in 10-2 above shows how a cell divides to become two cells, then four cells, eight cells, and so on. Which of the following statements best describes what happens during the process?
72
New cards
only during cell division
When during the cell cycle are chromosomes visible?
73
New cards
S phase
When during the cell cycle is a cell’s DNA replicated?
74
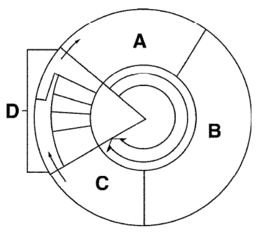
New cards
D
Cell division is represented in figure 10-3 by the letter
75
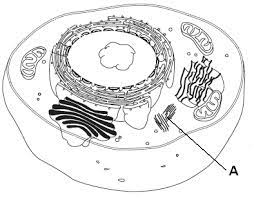
New cards
connect to spindle fibers
In figure 10-4, what role does structure A play in mitosis?
76
New cards
centromere
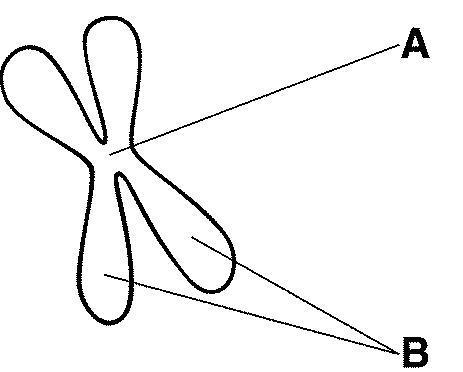
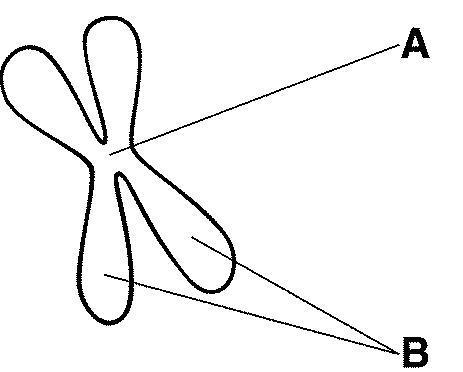
The structure labeled A in figure 10-5 is called the
77
New cards
sister chromatids
The structures labeled B in figure 10-5 are called the
78
New cards
prophase
Which of the following is a phase of mitosis?
79
New cards
metaphase
During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the dividing cell?
80
New cards
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Which of the following represents the phases of mitosis in their proper sequence?
81
New cards
they help separate the chromosomes
What is the role of the spindle fibers during mitosis?
82
New cards
mitosis and cytokinesis
The two main stages of cell division are called
83
New cards
four chromosomes
during normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell that has four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells each containing
84
New cards
only cell B forms a cell plate during cytokinesis
Some cells form a cell plate during cytokinesis. Which of the following is true of the cells in figure 10-6 above?
85
New cards
contact with other cells
When cells are grown in a laboratory, which of the following is a factor that can stop cells from dividing?
86
New cards
the controls on cell growth and division can be turned on and off
Cells grown in a petri dish tend to divide until they form a thin layer covering the bottom of the dish. if cells are removed from the middle of the dish, the cells bordering the open space will begin dividing until they have filled the empty space. What does this experiment show?
87
New cards
contact with other cells stops cell growth
Which of the following explains why normal cells grown in a petri dish tend to stop growing once they have covered to bottom of the dish?
88
New cards
cyclins
In eukaryotic cells, the timing of the cell cycle is regulated by
89
New cards
growth factors
Which of the following are external regulators of the cell cycle?
90
New cards
growth rate
Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost their ability to control their
91
New cards
tumors
Cancer cells form masses of cells called
92
New cards
differentiation
During early development, all cells in the embryo of a multicellular organism are identical. Later on in development, the cells will become specialized through a process called
93
New cards
they have the potential to develop into other cell types
Why are stem cells important?
94
New cards
reversing damage from a heart attack
Which of the following is a possible future benefit of stem cell research?
95
New cards
2
Each pea-plant has how many alleles for each gene?
96
New cards
alleles
The different forms of a gene are called
97
New cards
control crosses between plants
Gregor Mendel removed the male parts from the flowers of some plants in order to
98
New cards
green peas in it does not also have a dominant allele for yellow peas
If a pea plant has a recessive allele for green peas, it will produce
99
New cards
one allele from each parent
When Gregor Mendel crossed a tall plant with a short plant, the F₁ plants inherited
100
New cards
Both parents contributed a recessive allele
If a pea plant’s alleles for height are *tt,* what is true of its parents?