IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
IPv4 Address
a 32-bit hierarchical address that is made up of a network portion and a host
subnet mask
used to determine the network and host portions
Actual process to identify the host and network portions is called the (blank)
ANDing
Prefix Length
used to identify the subnet mask
Prefix length is the number of bits set to (blank) in the subnet mask
one
255.0.0.0
11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000/8
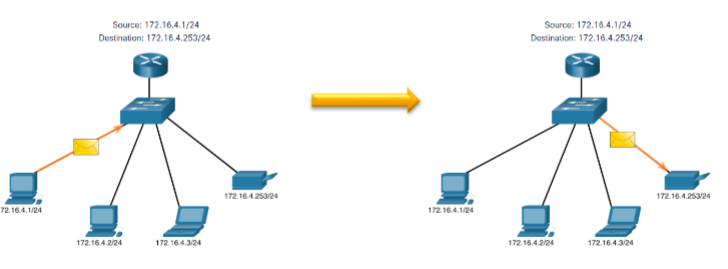
unicast
sending a packet to one destination IP address
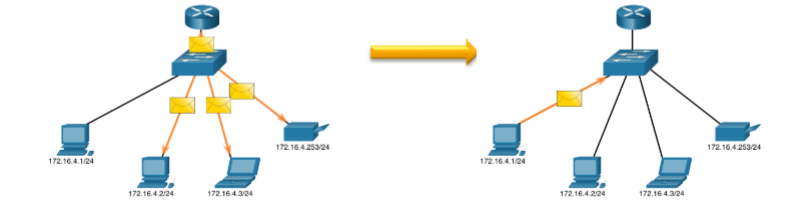
broadcast
sending a packet to all other destination IP addresses
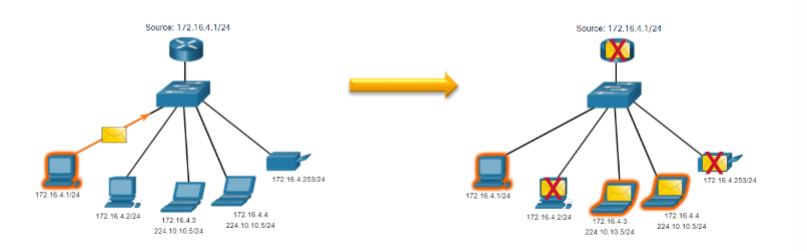
multicast
sending a packet to a multicast address group
These addresses are not unique and can be used internally within any network and are not globally routable
Private IPv4
Network Address Translation
translates private IPv4 to public IPv4
Loopback Address
commonly identified as only 127.0.0.1 and used on a host to test if TCP/IP is operational
Link Local Address
commonly known as automatic private IP addressing and is used by windows DHCP clients to self-configure when no DHCP servers are available
A problem with large broadcast domains is that these hosts can generate excessive broadcasts and negatively affect the network
True
Reasons for Subnetting
reduces overall network traffic and improves network performance
can be used to implement security policies between subnets
reduces number of devices affected by abnormal broadcast traffic
Broadcast
Unicast
multicast
Identify the network portion and host in the IP address
192.168.10.10
192.168.10- network
10- host
Which one is the IPv4 address and which one is the subnet mask
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.10.10 - IPv4 Address
255.255.255.0- subnet mask
IPv6 has
-a larger 128-bit address space
-340 undecillion addresses
-solves limitations w/ IPv4
-adds enhancements
IPv6 and IPv4 can coexist
true
Dual Stack
devices run both IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks simultaneously
Tunneling
a method of transporting an IPv6 packet over an IPv4 network. The IPv6 packet is encapsulated inside an IPv4 packet
Translation
NAT64 allows IPv6 enabled devices to communicate w/ IPv4 enabled devices using a translation technique similar to NAT for IPv4
For rule 1 in address representation is to omit any leading 0’s
2001:0db8:1111:0000:0000:0000:0200
omit the leading zeros
2001: db8: 1111: 0: 0: 0: 200
IPV6 has 2 unicast addresses, what are they?
Global Unicast Address and Link-Local Address
What is a global unique address that is used on the internet?
2000
IPV6 unique local addresses are used for local addressing within a site, can be used for devices that will never need to access another network, are not globally routed
true
For address representation in IPv6 rule 2 is Double Colon in which you replace any single, contiguous string of one or more 16-bit hextets consisting of all zeros and can only be used once
2001: 0db8: 0000: 1111: 0000: 0000: 0000: 0200
2001: db8:0: 11111 :: 200
anycast
any IPv6 unicast address that can be assigned to multiple devices, a packet sent to an anycast address is routed to the nearest device having that address
IPv6 global unicast addresses are globally unique and routable on the IPv6 internet
true