Session 1: Nutrients, Energy and Energy Balance
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Metabolism
All chemical reactions involved in maintaining living state of cells in our body
Catabolic reactions
Breaking down of larger molecules into smaller ones with the release of energy (exergonic)
Anabolic reactions
Using energy (ATP) to synthesise larger molecules from smaller ones
Macronutrients
carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
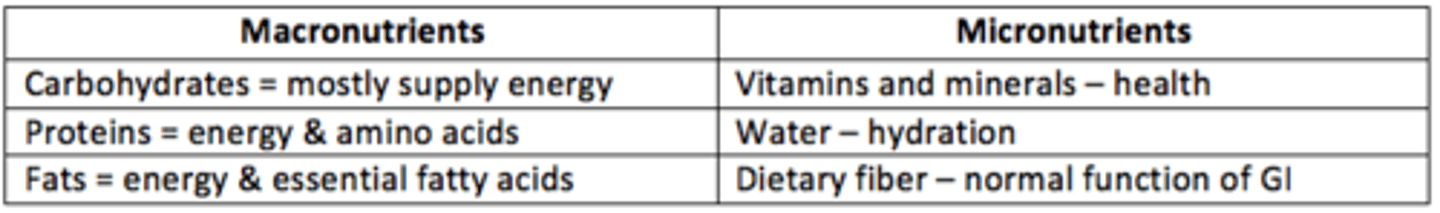
Micronutrients
- Vitamins & minerals = health
- Water = hydration
- Dietary fibre = GI function
Major dietary carbohydrates
Starch (polysaccharide - polymer of glucose)
Sucrose (disaccharide - glucose+fructose)
Lactose (disaccharide - glucose+galactose)
Fructose (monosaccharide)
Glucose (monosaccharide)
Predominant sugar in human blood
glucose
Proteins are broken down into
amino acids
How many different amino acids are there?
20
How many amino acids are 'essential' (cannot be synthesised by our body)?
9
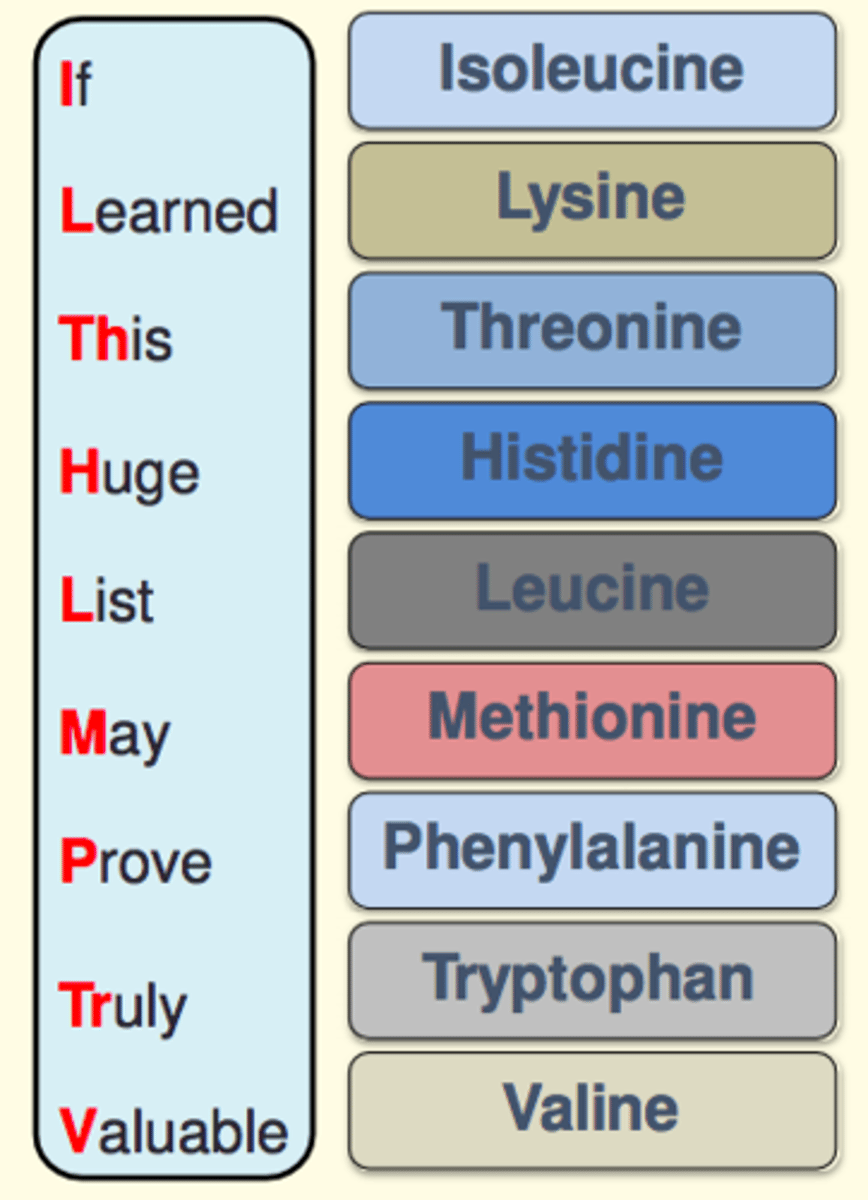
How many conditionally essential amino acids are there? What are they?
3 conditionally essential amino acids
Cysteine
Arginine
Tyrosine
When are these conditionally essential amino acids needed?
Children and pregnant women = high rate of protein synthesis
Most important class of dietary fats
Triacylglycerols (TGs)
Saturated fatty acids can be found in what foods
Dairy, meat, coconut oil, palm oil
Unsaturated fatty acids can be found in what foods
Plant-based and fish oils, nuts
Trans fatty acids can be found in what foods
Vegetable oils, ready-made cookies, deep-fried foods
Saturated (structure)
Only single bonds
Unsaturated (structure)
Double bonds present
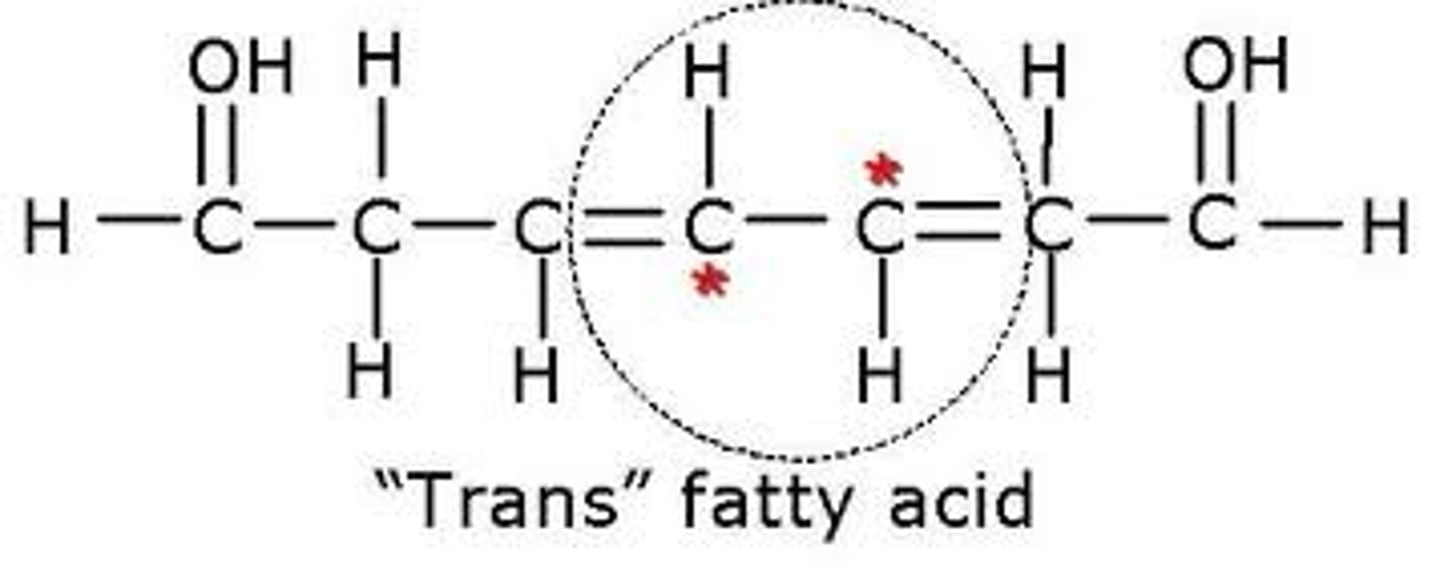
Trans fatty acid (structure)
Is an unsaturated fatty acid in which hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of the carbon-carbon double bond
Why are TGs important in our diet?
- Provide essential fatty acids (e.g., linoleic or omega-6 and α-linolenic or omega-3) = structural components of cell membranes & precursors of regulatory molecules (eicasanoids)
- Required for absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK) from gut
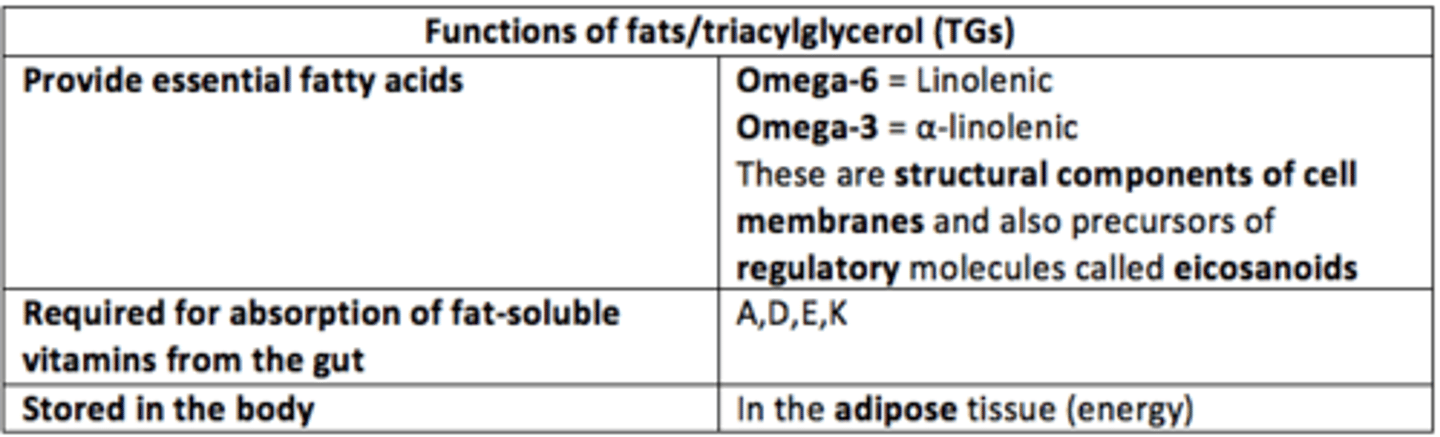
Where are TGs stored?
Adipose tissue
Give example of essential fatty acids
Linolenic (omega-6)
α-linolenic (omega-3)
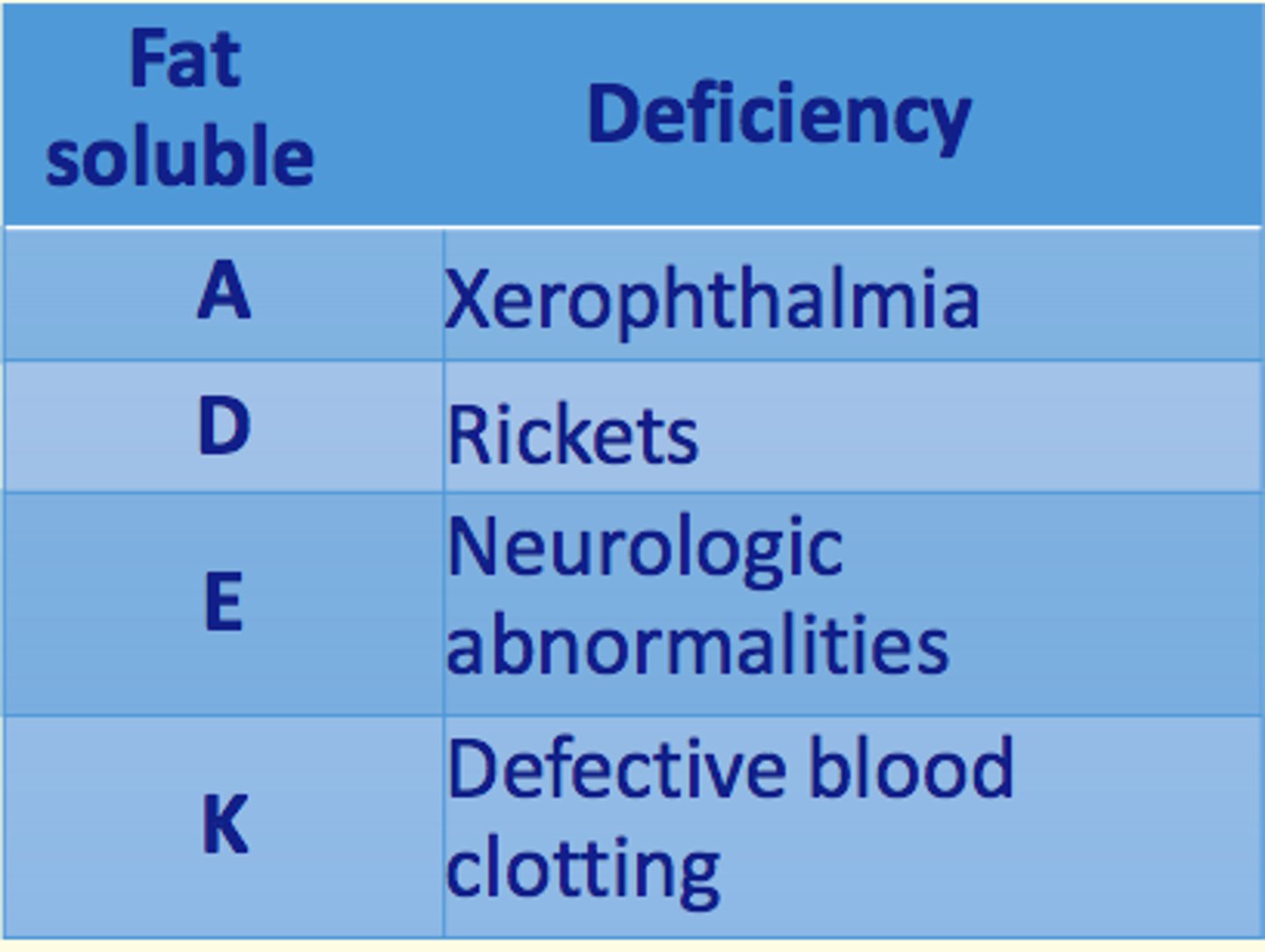
Fat-soluble vitamins
A, D, E and K
Water-soluble vitamins
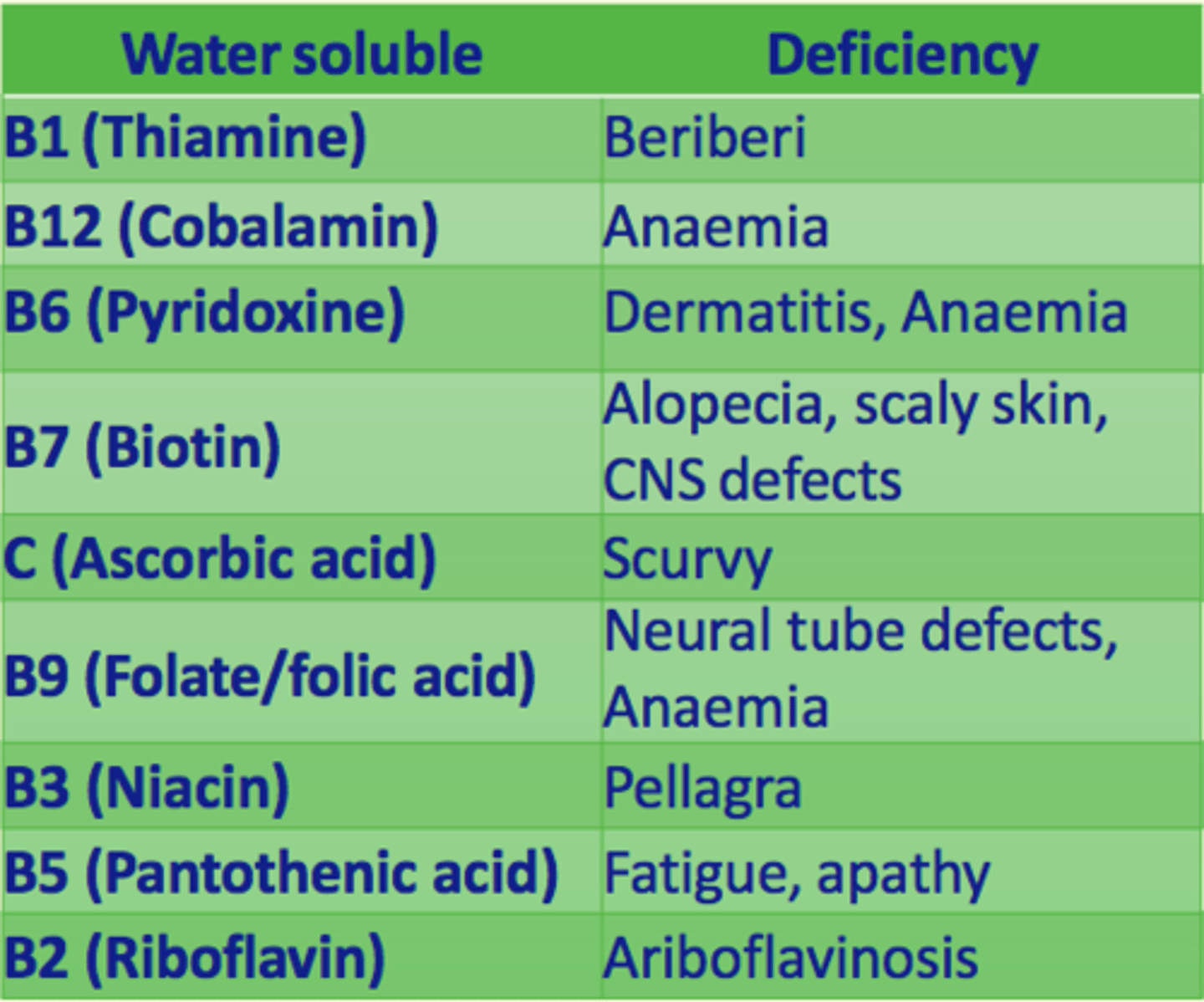
Vitamin deficiency leads to ___ if intake is inadequate
disease
Vitamins are required in ___ quantities to perform specific functions
small
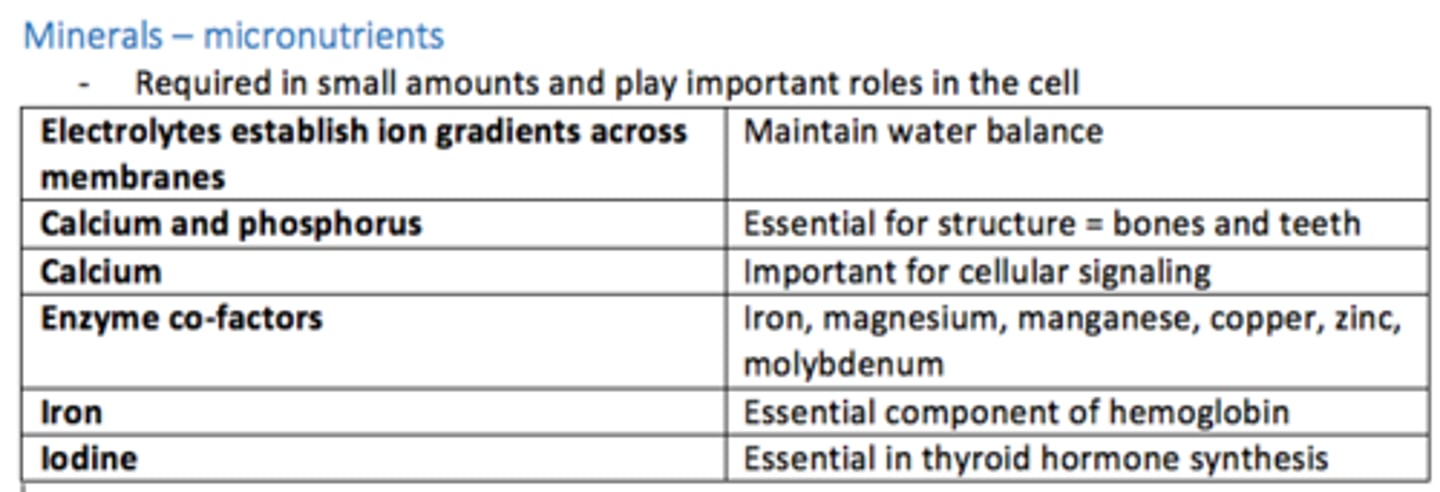
The functions of minerals (micronutrients) in the human body
1) Electrolytes establish ion gradients across membranes = maintain water balance
2) Calcium and phosphorus = essential for structure (bones & teeth)
3) Calcium = important in signalling
4) Enzyme co-factors (iron, magnesium, manganese, copper)
5) Iron = essential component of haemoglobin
6) Iodine = essential in thyroid hormone sythnesis
Dietary fibre found in what foods
Cereal foods (bread, beans, fruit and vegetables)
What polysaccharide cannot be broken down by the gut?
cellulose
Why can't cellulose be broken down by human gut?
Humans do not produce the required enzymes to break the β-1,4 linkages in cellulose
Give examples of some dietary fibre molecules
Cellulose
Lignin
Pectins
Gums
Why is dietary fibre important
For healthy functioning of GI tract
Recommended intake of dietary fibre per day (adults)
30g/day
Low fibre diet is associated with what conditions?
Constipation
Bowel cancer
High fibre diet is associated with a reduced risk of what conditions?
Reduced cholesterol
Reduced risk of diabetes
Dietary Reference Values (DRVs) depend on what factors?
- Age
- Gender
- Growth
- Level of physical activity
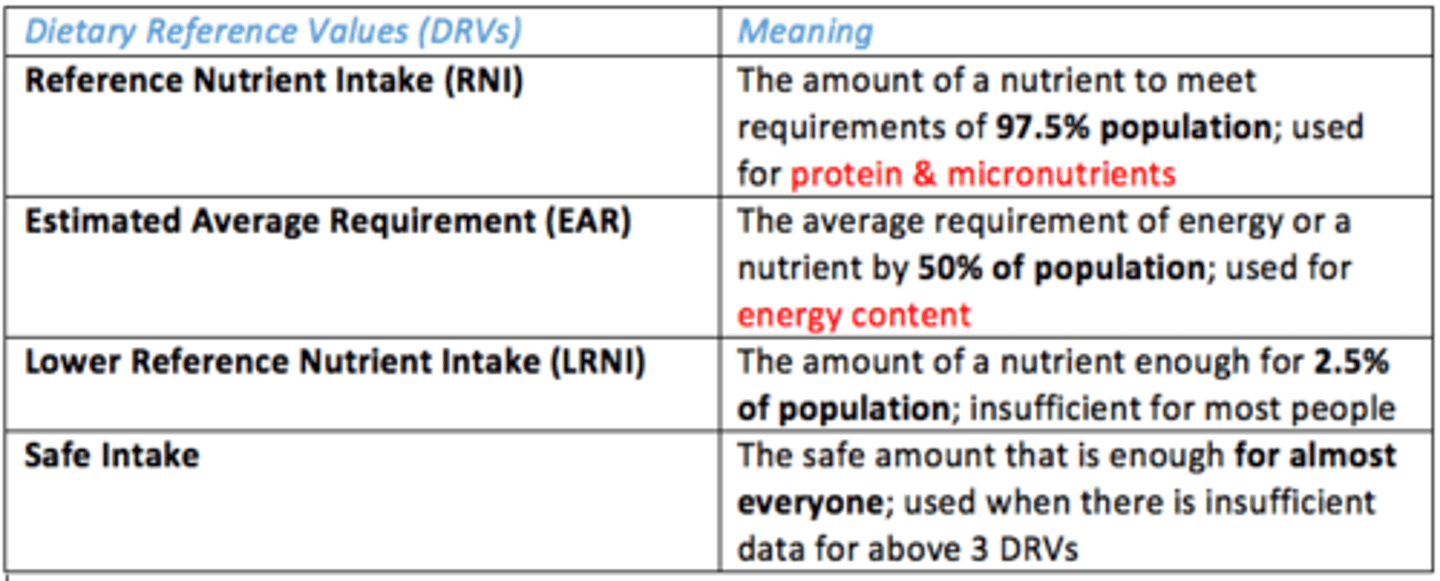
What are the Dietary Reference Values (DRVs)?
Values published by the SACN - series of estimates of the amount of energy and nutrients needed by different groups of healthy UK population
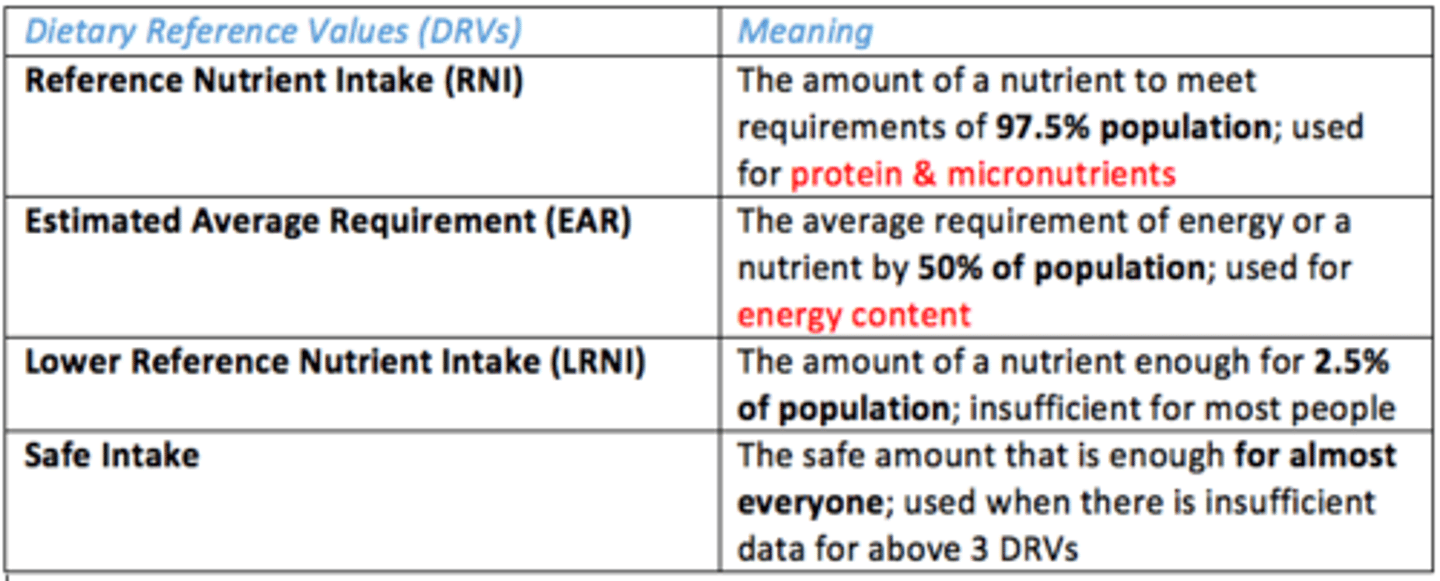
What are the different types of Dietary Reference Values (DRVs)?
List them
- Reference Nutrient Intake (RNI)
- Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
- Lower Reference Nutrient Intake (LRNI)
- Safe Intake
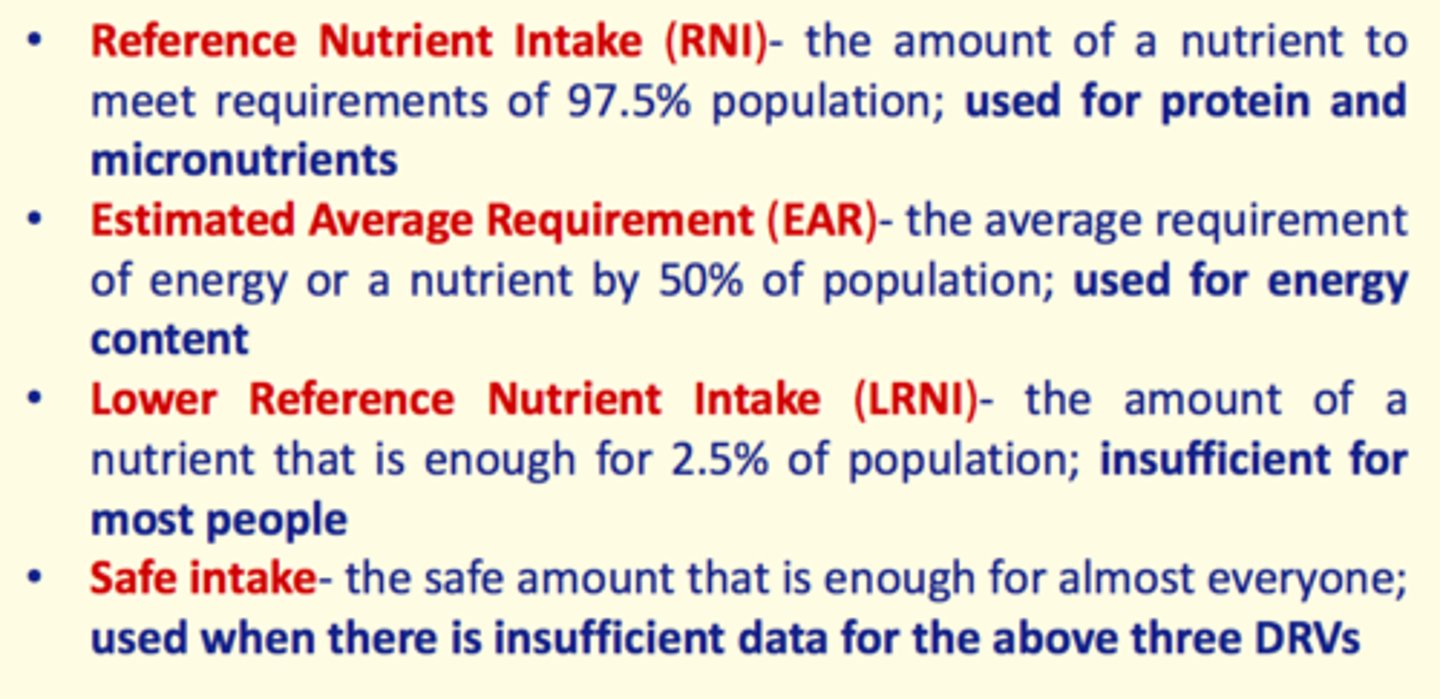
Reference Nutrient Intake (RNI)
Amount of nutrient to meet requirements of 97.5% population (used for protein & micronutrients)
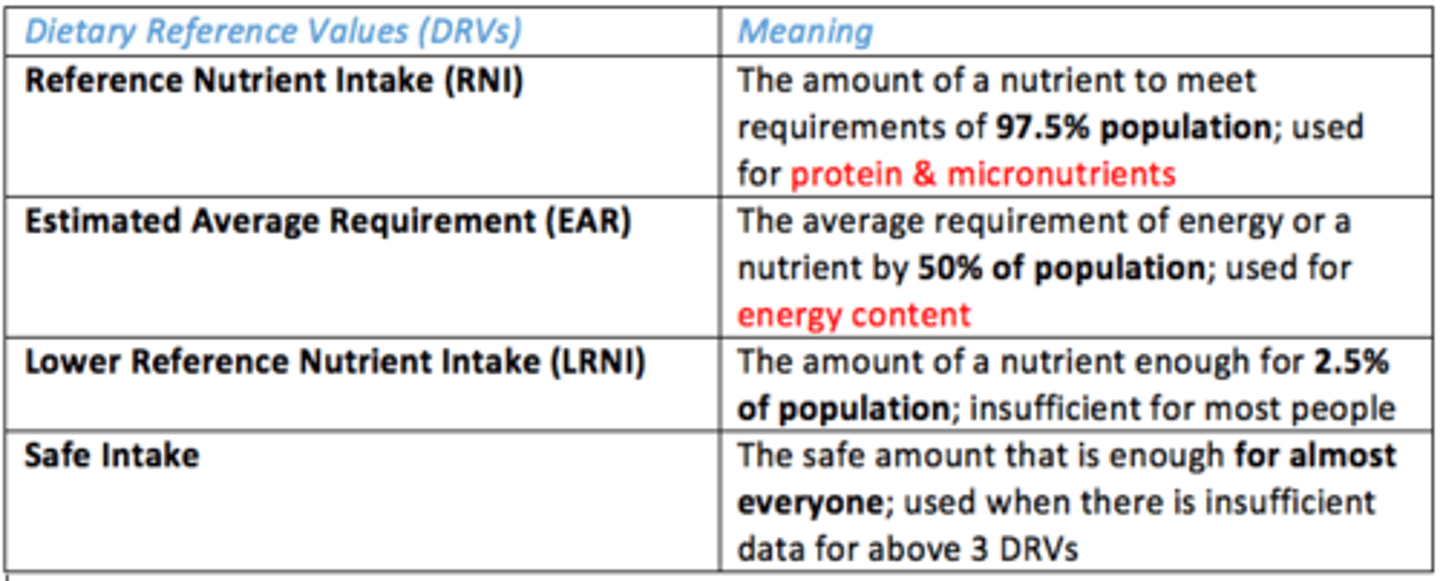
Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
Average requirement of energy or nutrient by 50% population (used for energy content)
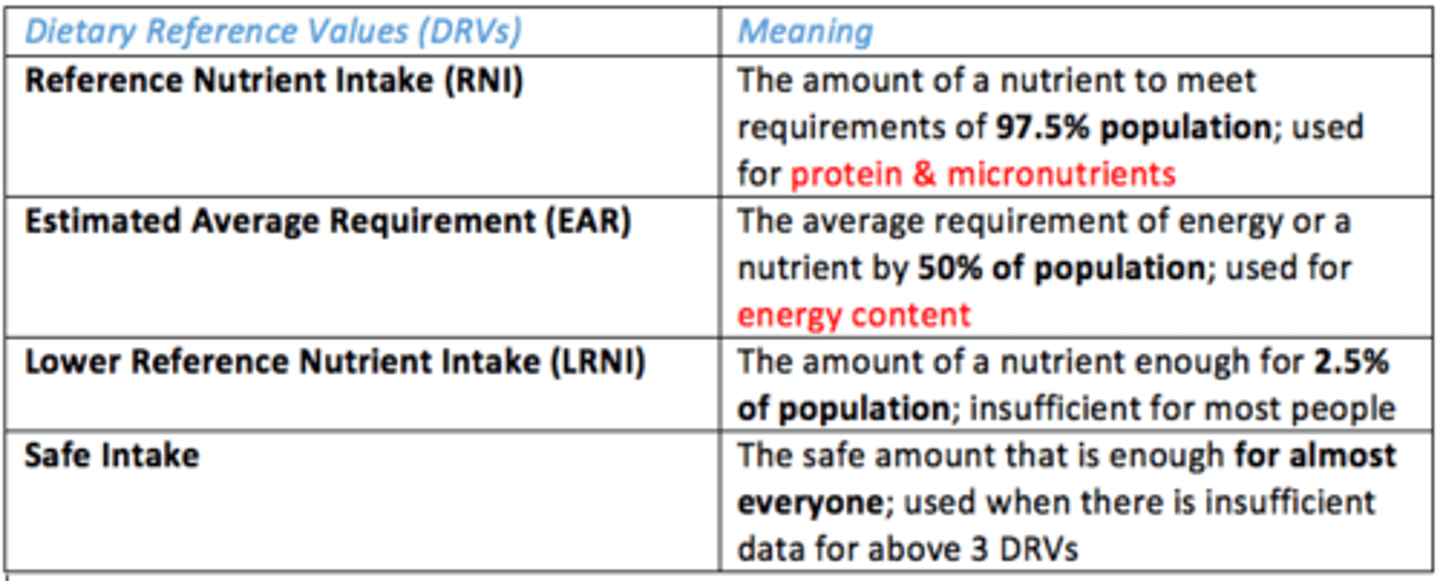
Lower Reference Nutrient Intake (LRNI)
The amount of nutrient that is enough for 2.5% of population; insufficient for most people
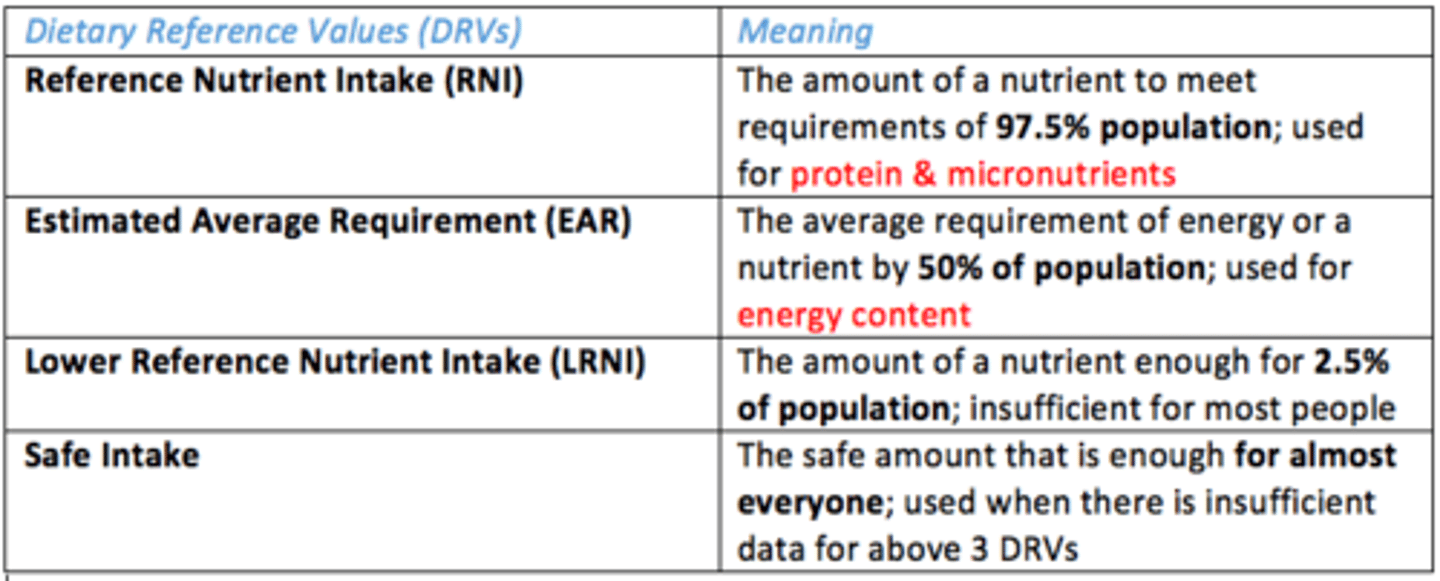
Safe Intake DRV
Safe amount that is enough for almost everyone (used when there is insufficient data for other DRVs)
The Eatwell Guide recommends women to consume how many calories per day?
2000kcal
The Eatwell Guide recommends men to consume how many calories per day?
2500kcal
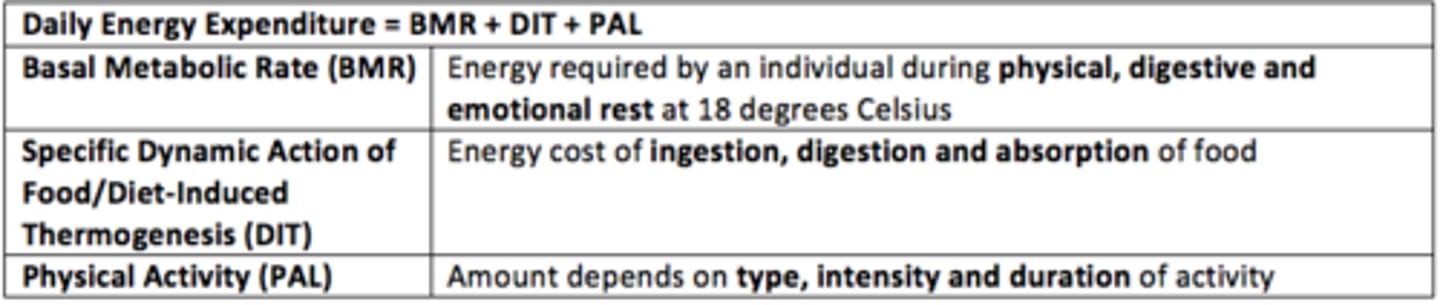
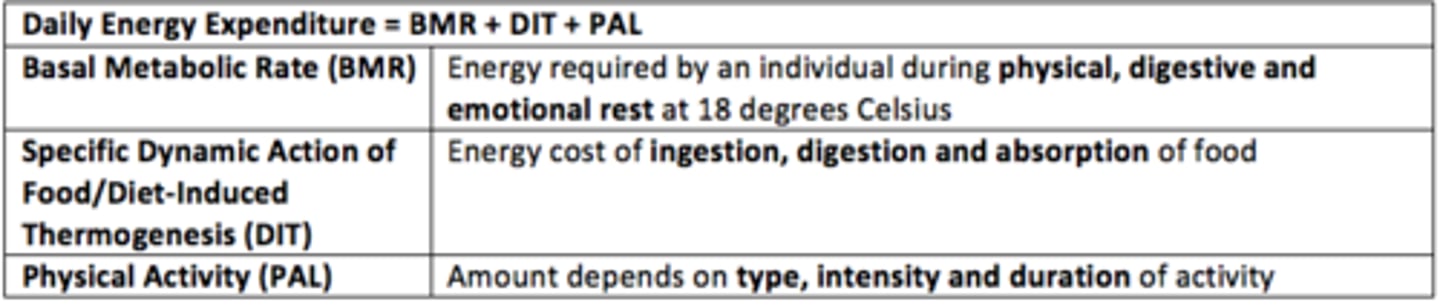
Daily energy expenditure is the sum of what three factors?
1) Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
2) Diet-Induced thermogenesis (DIT)
3) Physical activity level (PAL)
Energy requirements vary amongst individuals based on four factors...
1) Age
2) Gender
3) Body composition
4) Physical activity
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) definition
Energy required by an individual during physical, digestive and emotional rest at 18°C
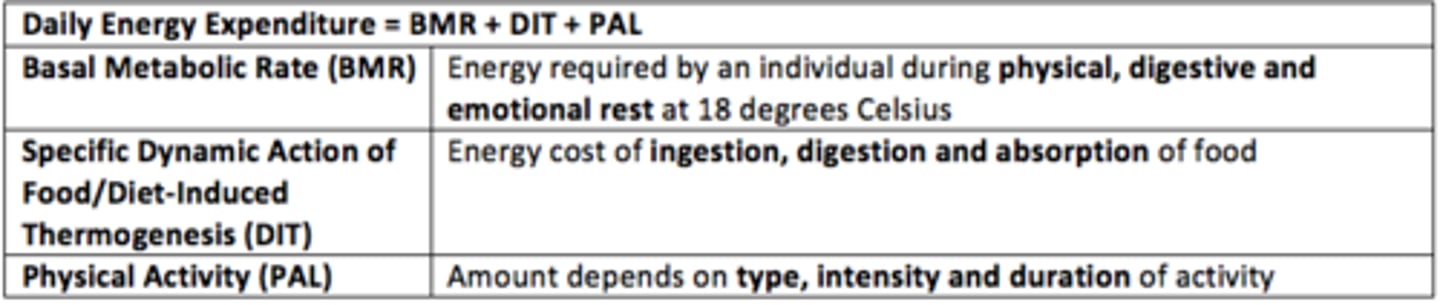
What is the specific dynamic action of food?
Energy cost of ingestion, digestion and absorption of food (~150 kcal)
What does the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) maintain?
1) Maintains resting activities of the body
2) Maintenace of cells = ion transport across membranes, biochemical reactions
3) Function of organs
4) Maintaining body temperature
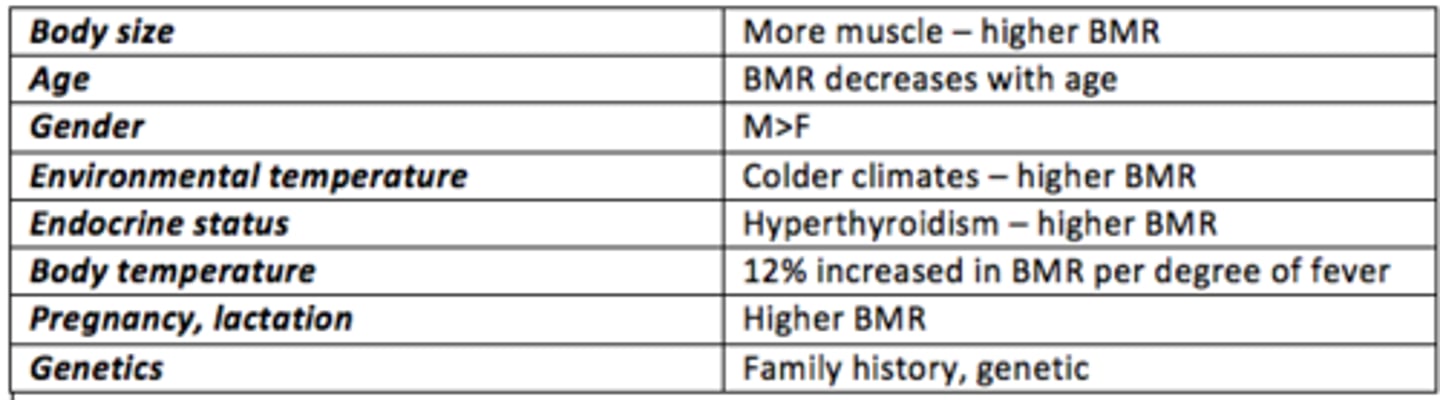
Key factors affecting the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
1) Body size (more muscle - higher BMR)
2) Age
3) Gender (higher in males)
4) Environmental temperature (BMR increases with cold)
5) Endocrine status (increased in hyperthyroidism)
6) Body temperature (~12% increased per degree of fever)
7) Pregnancy, lactation
8) Genetics
Which organ uses most BMR?
Skeletal muscle ~30% BMR

If intake = expenditure, body weight will be
stable
If intake > expenditure
energy stores increase
If intake < expenditure
energy stores deplete
other body components (protein) utilised for energy
BMI
Body Mass Index
- Used clinically to evaluate a healthy weight
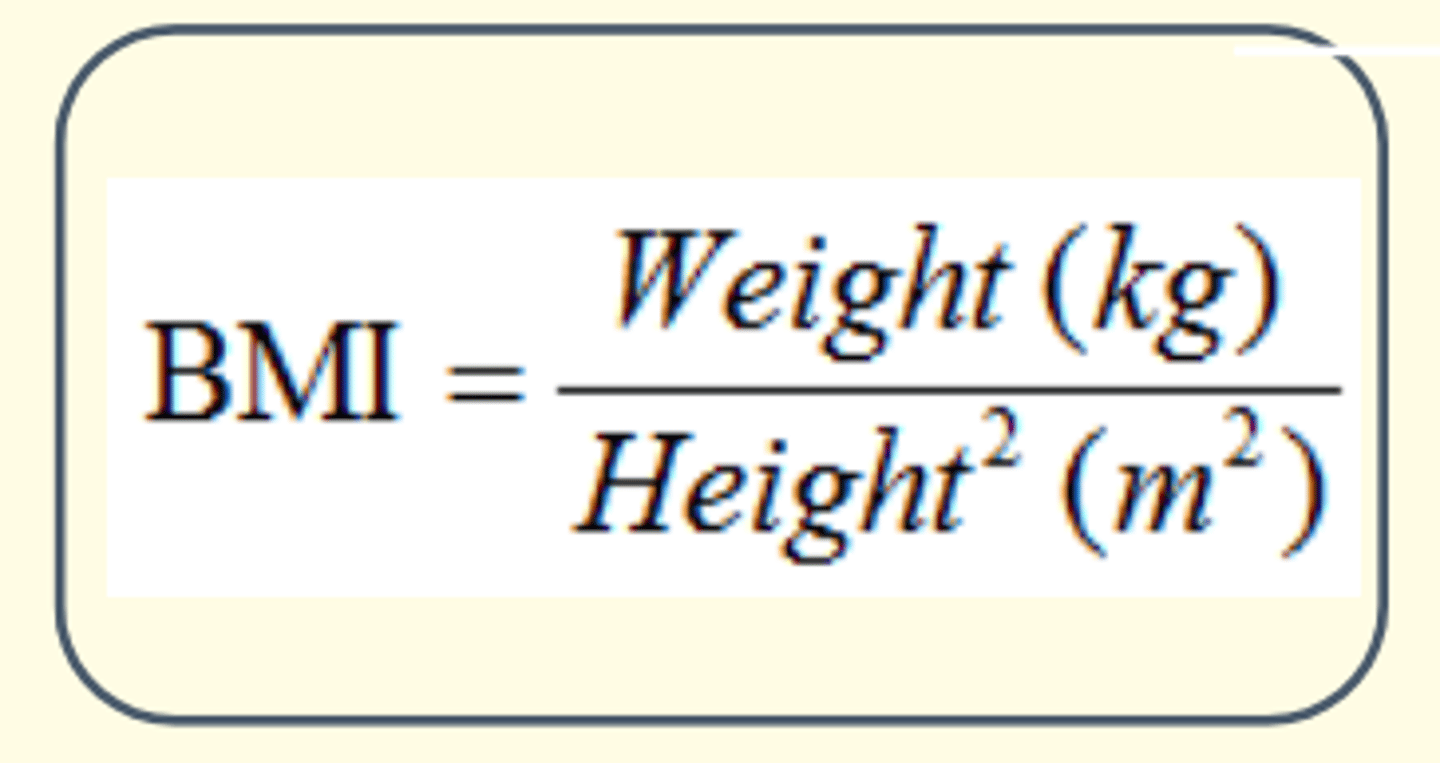
Benefit of BMI
Shows good correlation with body fat measurements
Weakness of BMI
Very muscular individuals - wrongly classified as obese
Alternative measurement to BMI
Waist/hip ratio (WHR)
A greater proportion of fat in the upper body (especially abdomen) compared to the hips is associated with an increased risk of what conditions?
1) Insulin resistance
2) Hyperinsulinemia
3) Type 2 diabetes
4) Hypertension
5) Hyperlipidaemia
6) Stroke
7) Premature death
Malnutrition results from...
eating a diet not providing the right amount of nutrients or energy (undernutrition, overnutrition or imbalance of nutrient/energy intake)
Causes of malnutrition?
- Famine
- Poverty
- Long-term or progressive conditions
- Drug/alcohol abuse
- Ageing
Kwashiorkor
Protein deprivation
Symptoms of Kwashiorkor
oedema, abdominal distension, stunted growth, decreased fat/muscle mass, hepatomegaly, anaemia
Marasmus
Calorie deprivation (when calorie deprivation is even greater than reduction in protein intake)
Marasmus symptoms
arrested growth, extreme muscle wasting, loss of fat, anaemia, does NOT present with oedema
MUST tool
Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool
The only evidence-based tool used to screen for malnutrition
What is MUST and why is it useful?
MUST is a five-step screening tool which identifies malnourished adults.
It includes management guidelines which can be used to develop a care plan.
The Eatwell Guide includes recommendations for hydration, what are these? How much fluid is needed each day for good hydration?
- The guide recommends 6-8 glasses of water every day - varies depending on body weight.
- Recommended: 30-35 ml/kg body weight
What fluids are considered good sources of hydration?
- Water, low-fat milk, fruit juices, soup, fruits, non-alcoholic drinks
If a patient has a BMI of 38 - what food/food groups on the Eatwell Guide would you suggest they eat?
More:
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Lower fat varieties of dairy foods
- Wholegrain foods
- Lean meats, chicken and fish
Less of:
- High fat food
- High sugar food
- Full fat dairy foods
- Remove fat on meat
- Processed foods e.g. meat pies, sausages as hidden fats
Which dietary macronutrient provides 9kcal per gram?
Fat
Which of the following is not a water-soluble vitamin?
a. folic acid
b. B12
c. pantothenic acid
d. C
e. B9
f. K
Vitamin K
What does the Physical Activity Level depend on? (PAL)
Amount/type/intensity and duration of exercise/activity
Why is oedema and swollen abdomens a symptom/sign of Kwashiorkor?
- The oedema is related to: decreased synthesis of albumin by the liver
- Swollen abdomens may have been due to hepatomegaly (swollen liver) and/or ascites (accumulation of fluid in peritoneal cavity)
Classify a BMI of <18.5
Underweight
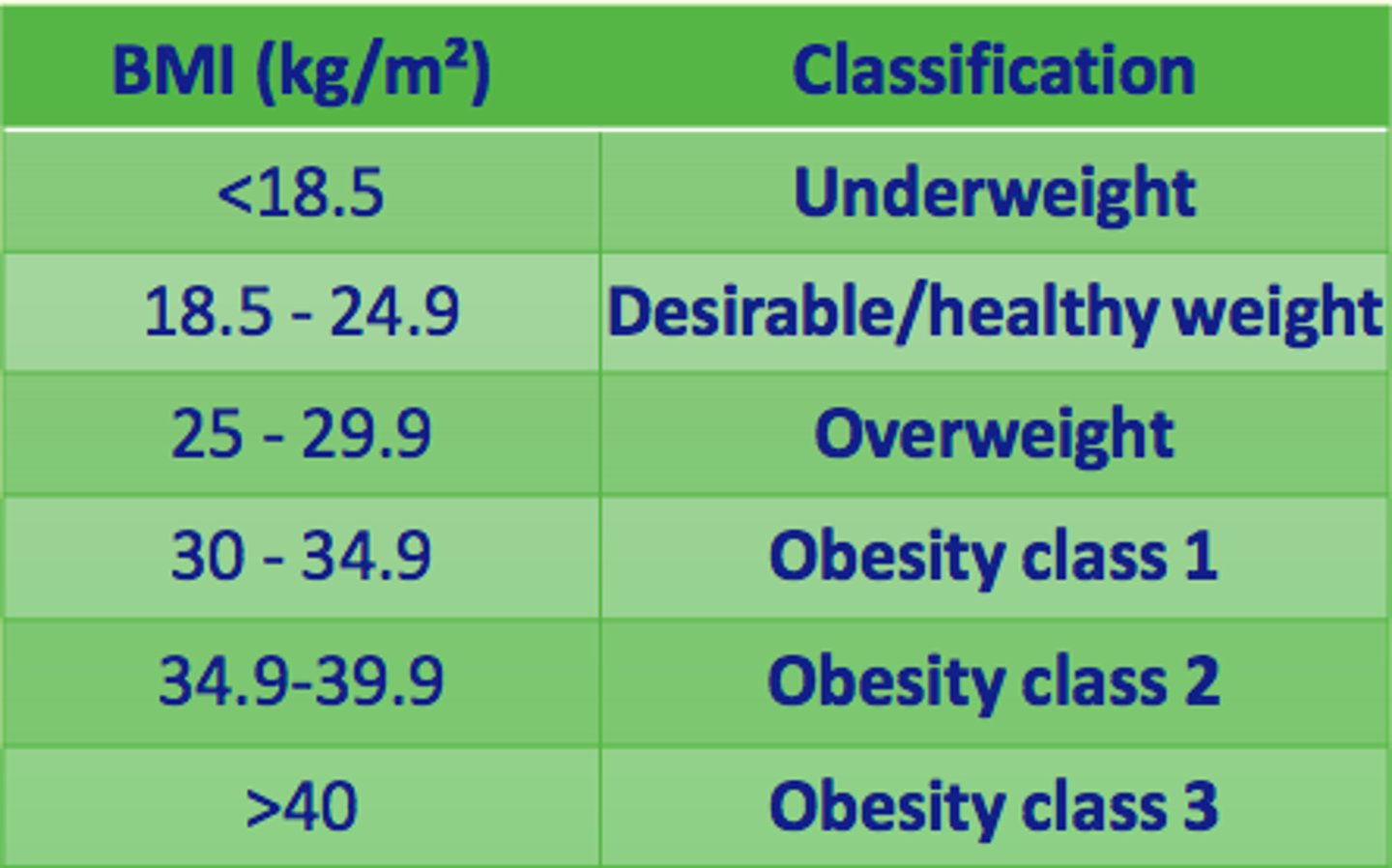
Classify a BMI of 27
Overweight
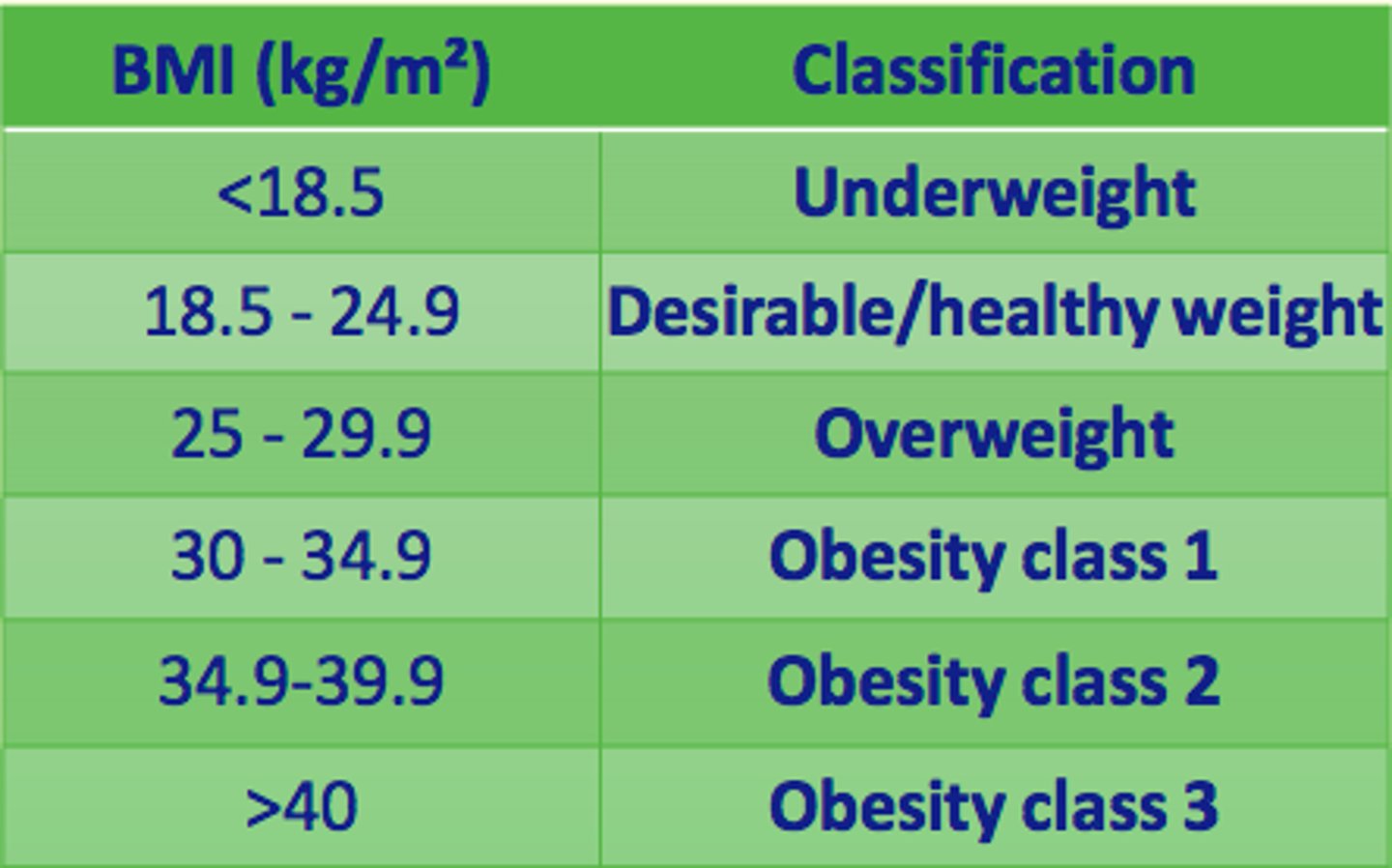
Classify a BMI of 32
Obesity class 1
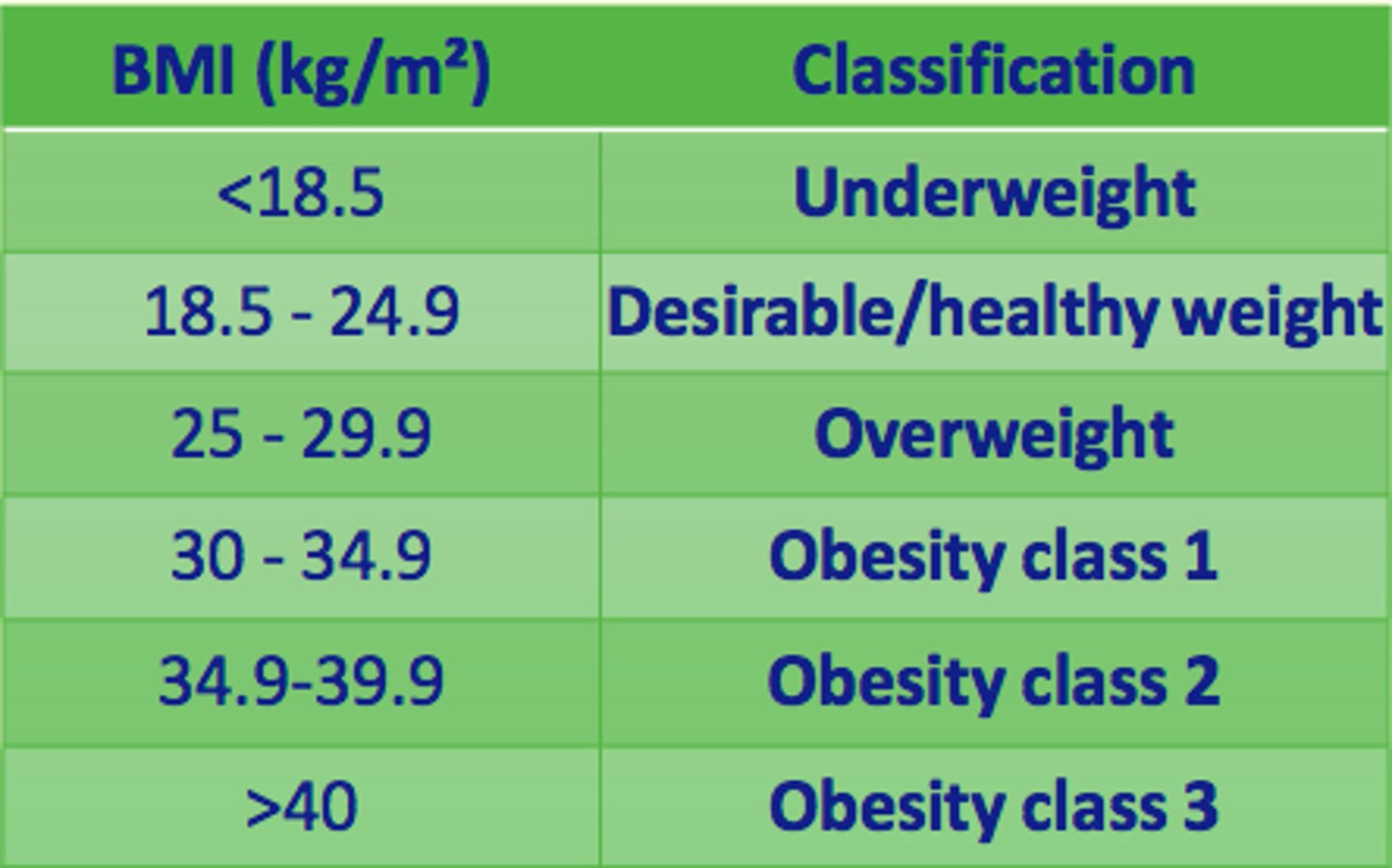
Classify a BMI of 38
Obesity class 2
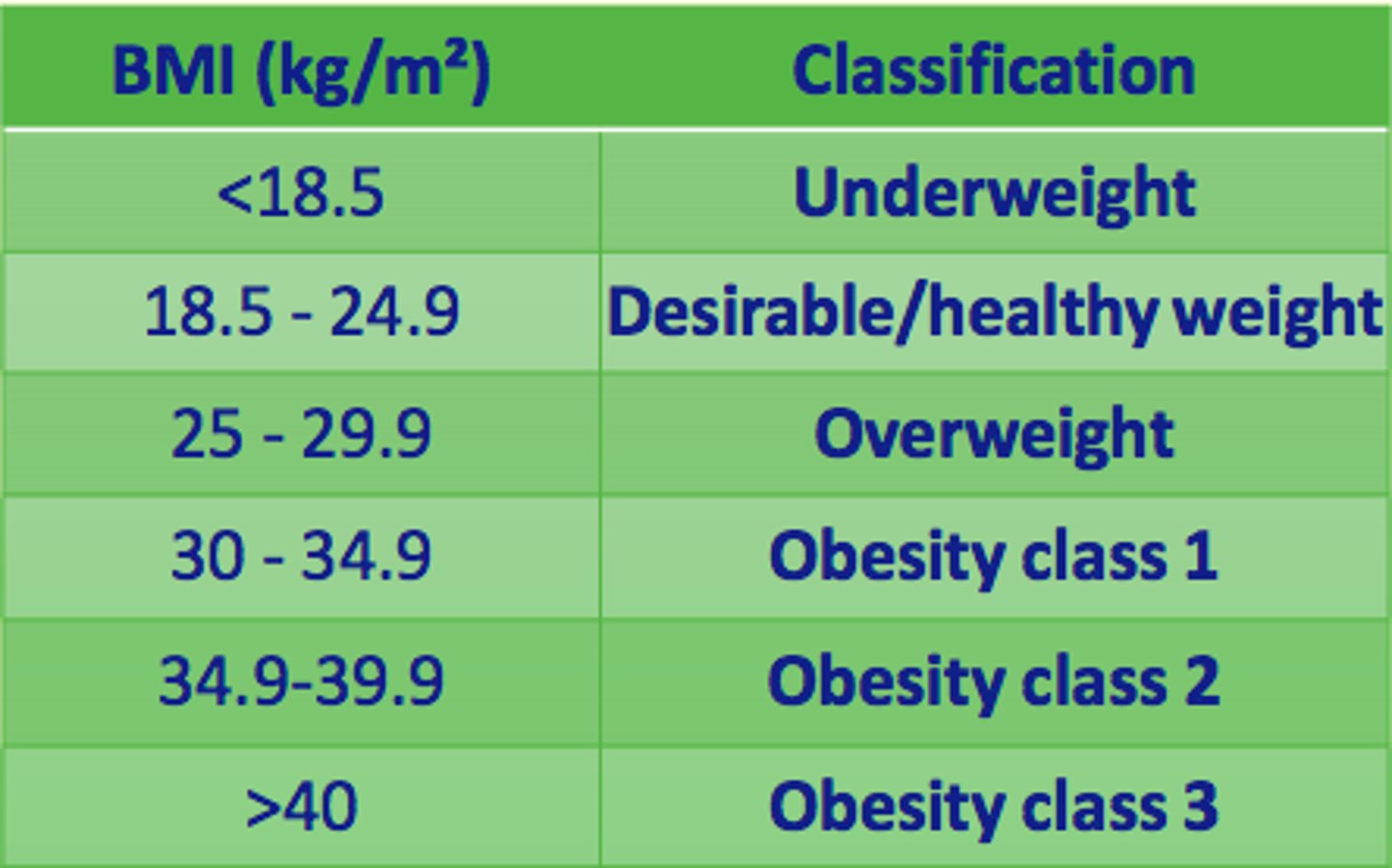
Classify a BMI of 41
Obesity class 3
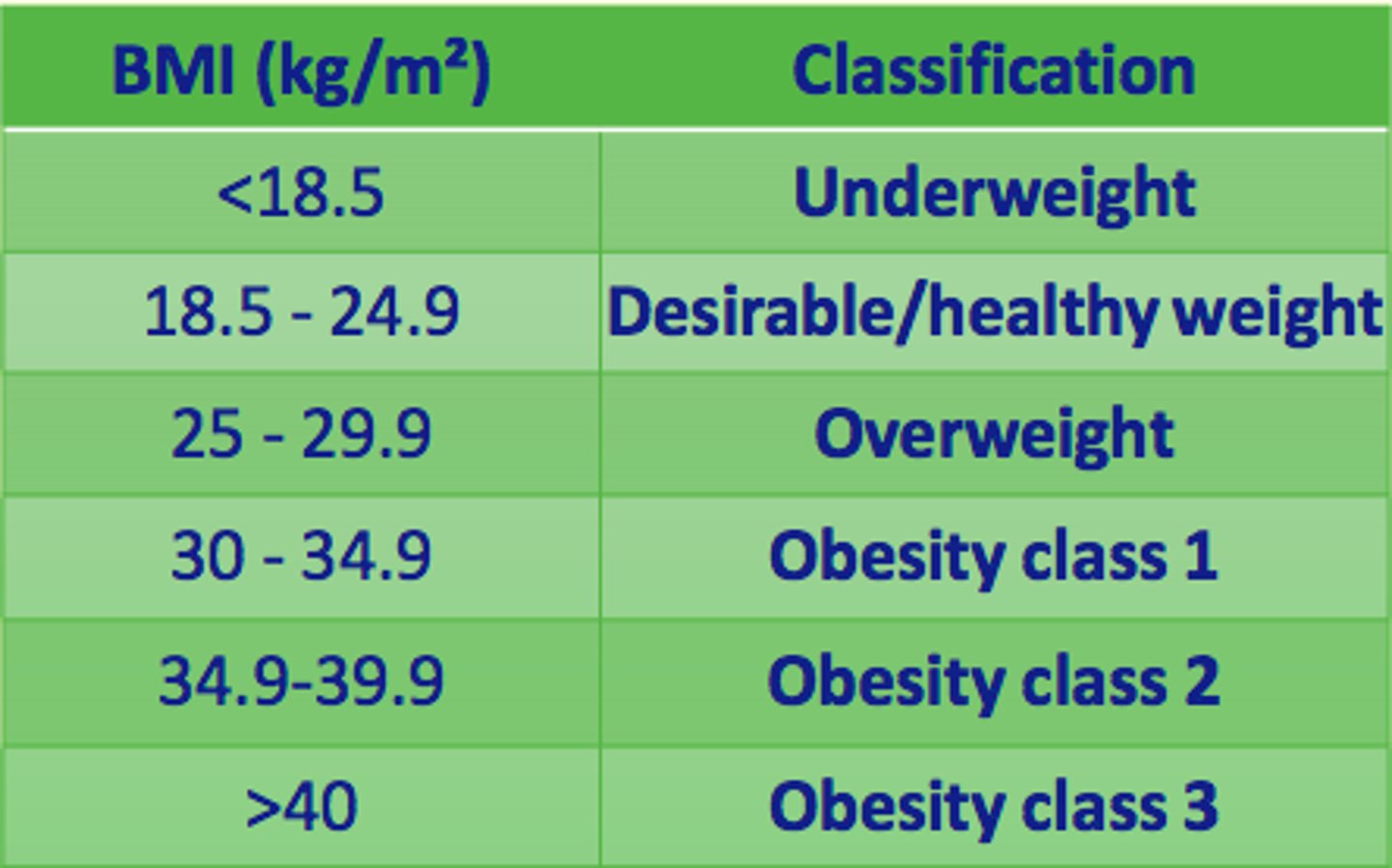
Compare Kwashiorkor and Marasmus
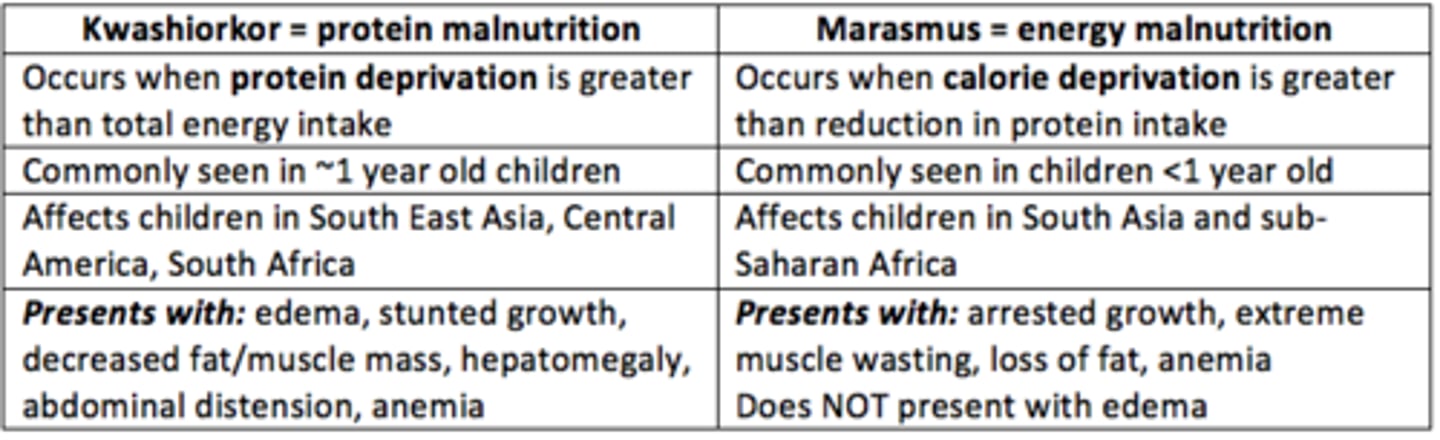
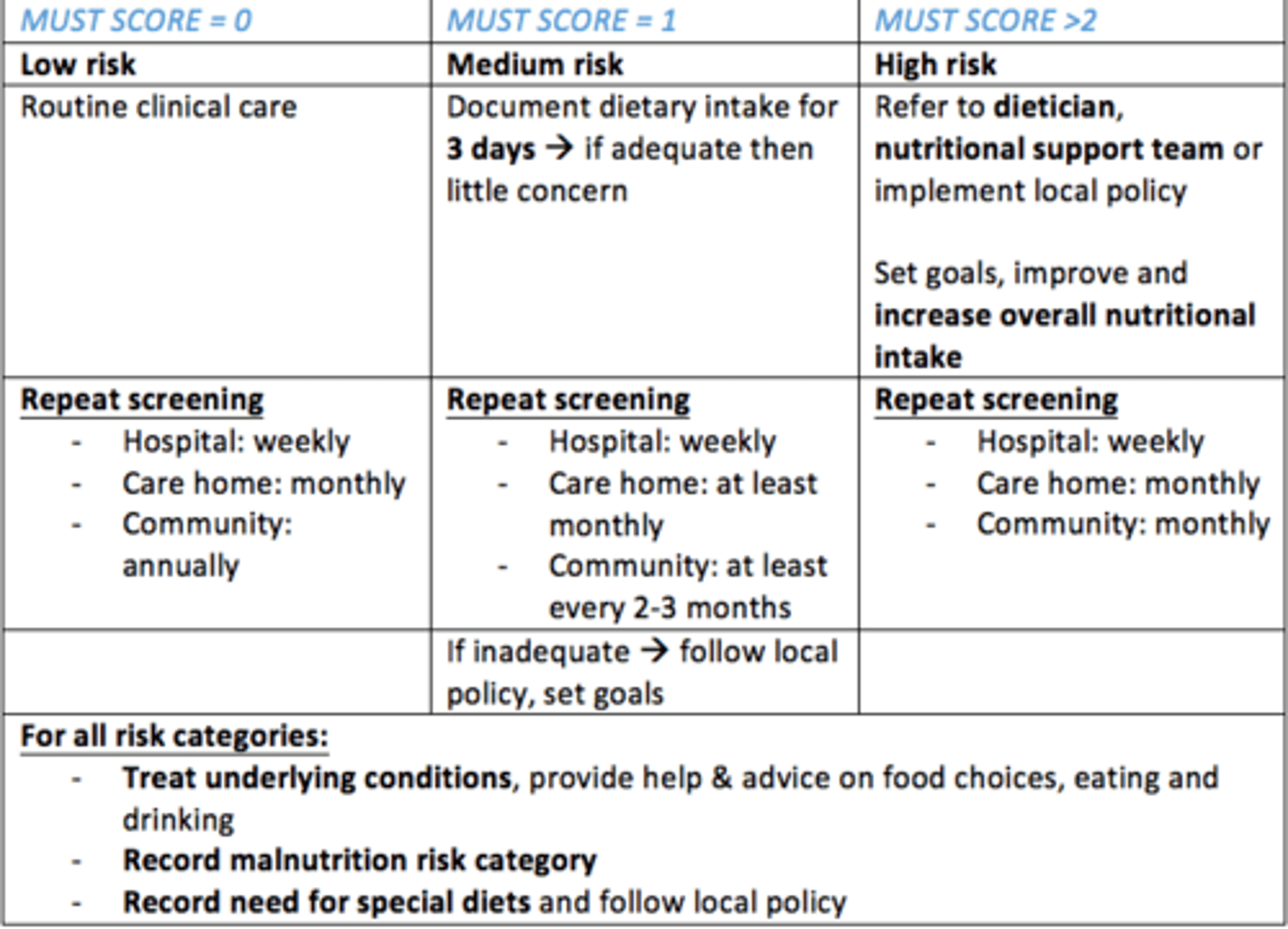
You calculate a MUST score of 0 - what does this mean for the patient?
Low risk
- Routine clinical care should be continued
- Repeat screening for...
Hospital = weekly
Care home = monthly
Community = annually
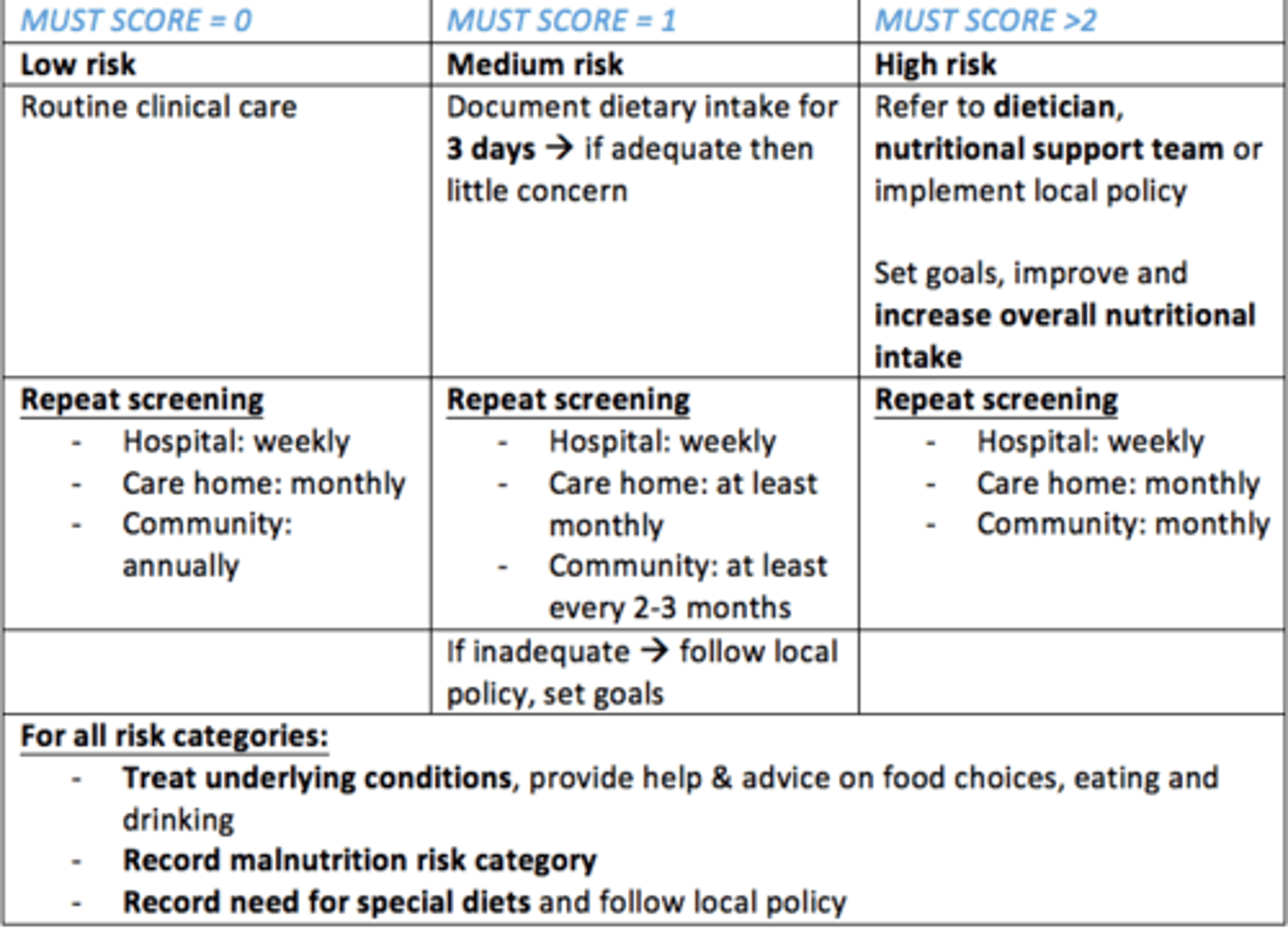
You calculate a MUST score of 1 - what does this mean for the patient?
Medium risk
- Document dietary intake for 3 days. If adequate, then little concern.
- Repeat screening for...
Hospital = weekly
Care home = at least monthly
Community = at least every 2-3 months
If inadequate - follow local policy, set goals, improve dietary intake
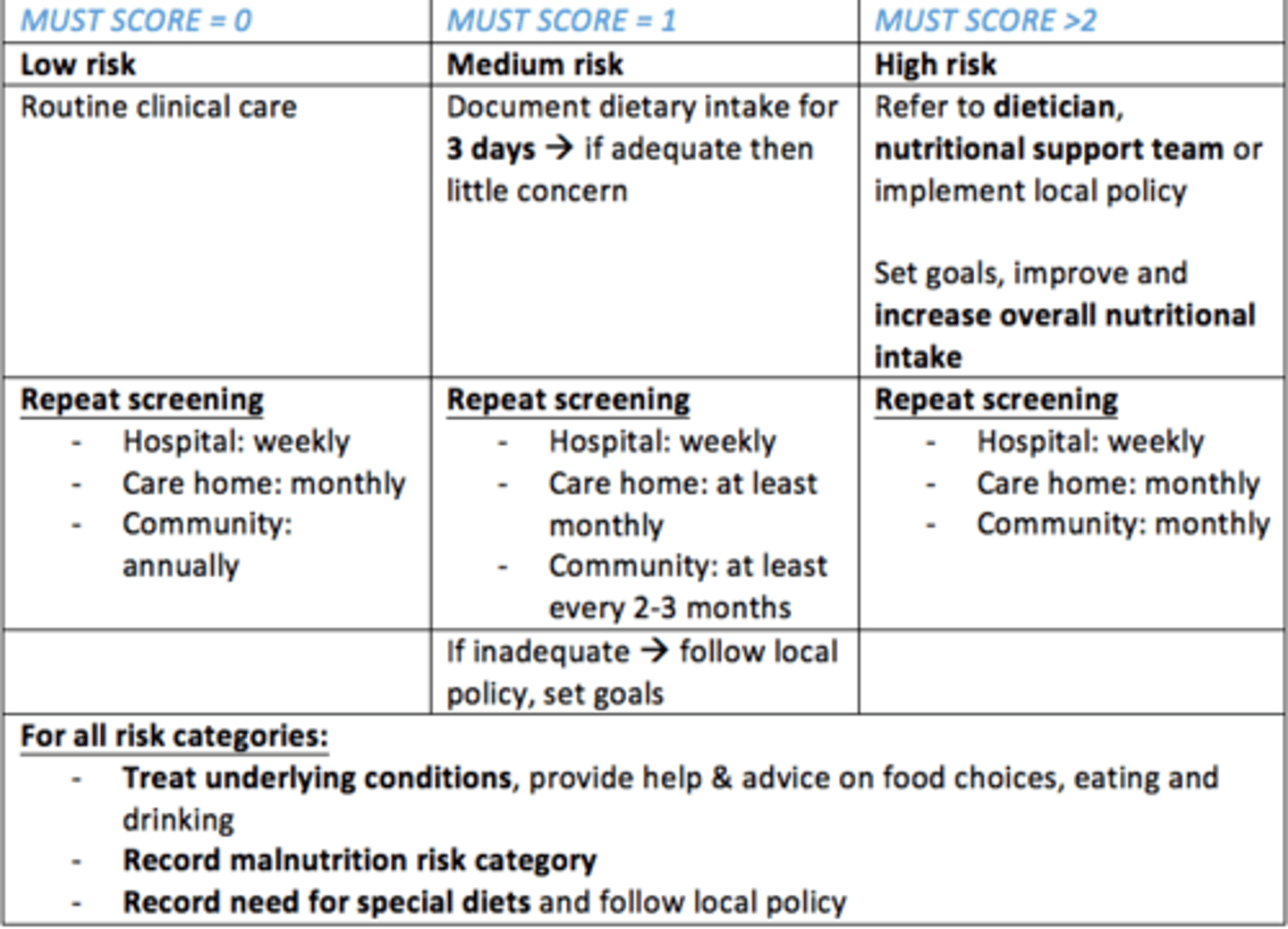
You calculate a MUST score of 2 - what does this mean for the patient?
High risk
- Refer to dietician, nutritional support team or implement local policy
- Set goals, improve and increase overall nutritional intake
- Monitor and evaluate/review care plan
- Repeat screening for...
Hospital = weekly
Care home = monthly
Community = monthly