Lecture 22: Masitits and udder health
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What is the most frequent disease in the dairy industry?
Mastitis
Costs of mastitis
Increased amount of non-salable milk
Decreased milk production
Decreased milk quality
Increased treatments/culling
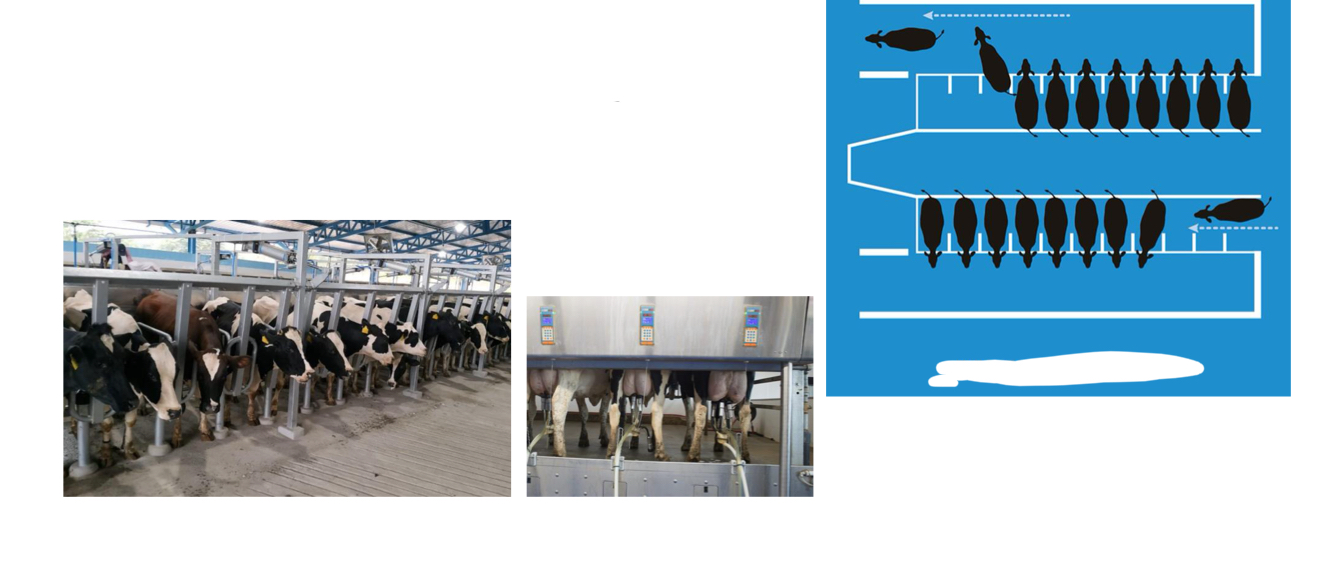

Parallel
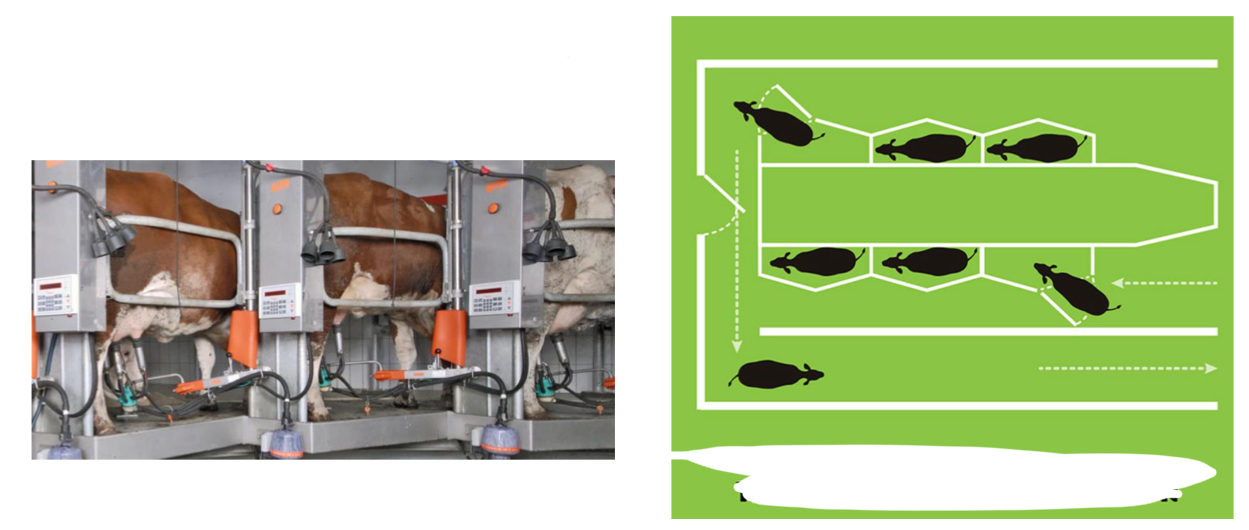
Tandem side opening

Herringbone
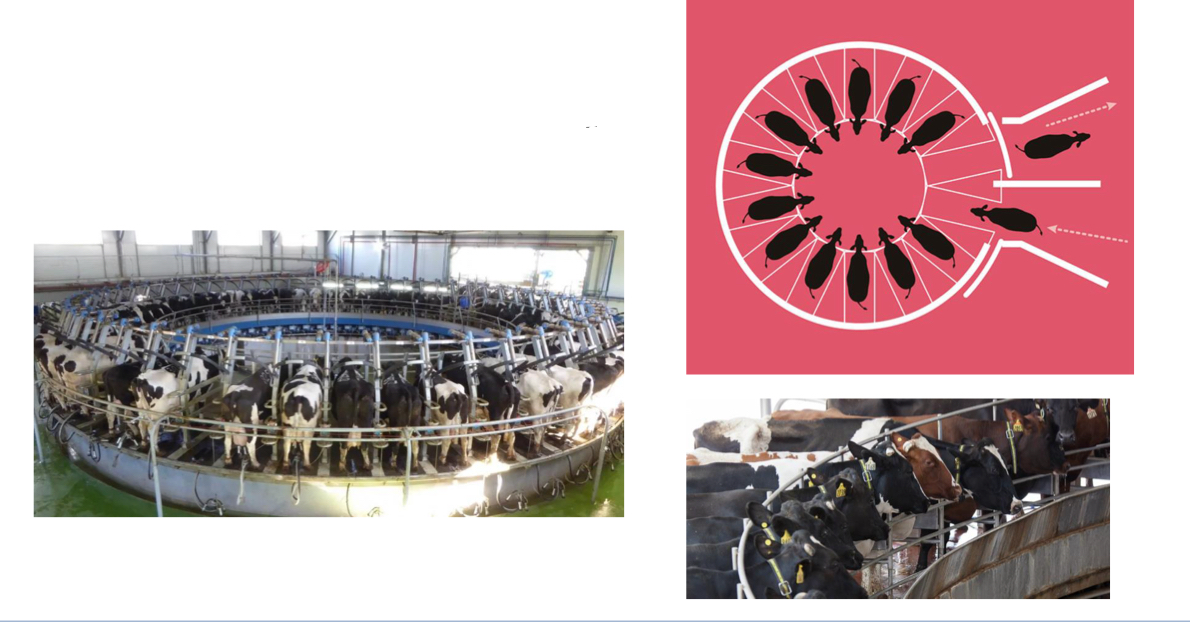

Rotary
Where the milk is collected to be transported to the milk company
Where the samples for milk cultures are collected
Only milk from cows more than 3 days fresh and/or not an antibiotic, NSAIDs, etc. are collected
Bulk tank
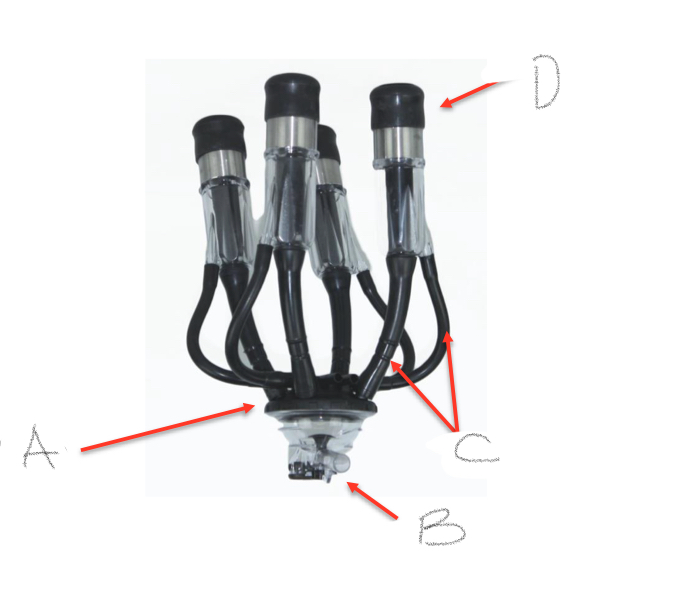

A- The Claw
B- Milk line/hose
C- Vacuum tubes
D- Teat cup
Benefit of herringbone over parallel?
Herringbone allows more cows to be milked in the same amount of space
What happens with the liner is opened?
Machine milk in creates a pressure difference that causes milk to flow, ad the teat canal is open

Automatic detacher or “take-offs”
Goal mean claw vacuum
10.5 to 12.5 Hg
Max claw vacuum flucation?
< 3 hg
__% of milking use manual mode when automatic takeoffs are used?
<5%
What is the time for D phase of the pulsations cycle
>150-200 ms
How do you have optimal milk letdown?
Optimize production and prevention mastitis
Process where the muscle surrounding in to the ducts and cistern for efficient milk harvest
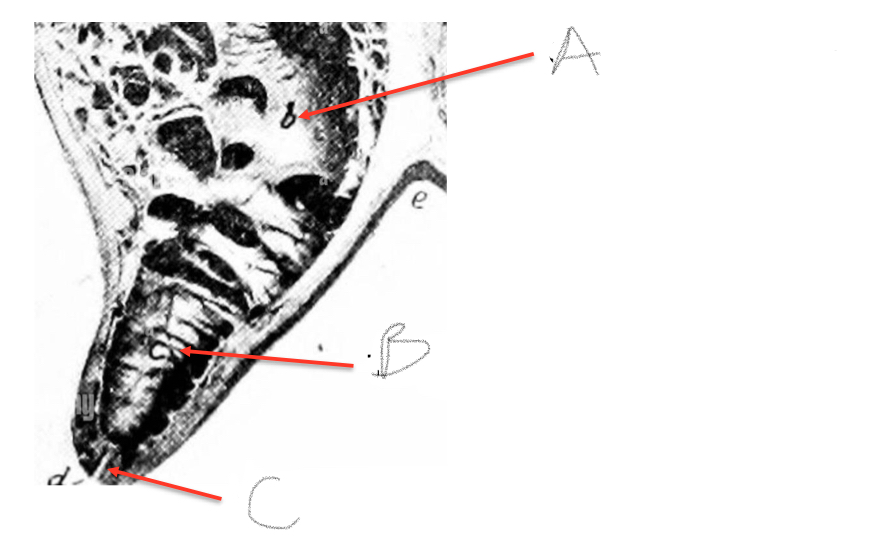
A- Gland cistern/sinus
B- Test cistern/sinus
C- Streak canal/papillary duct
How much milk is stored in the ducts and cisterns?
20%
Pathophysiology of milk letdown
Teat stimulation by milker and sound and smell of the milking area
Presence of milk in unit elicits constant oxytocin release during milking
Nerve impulse to hypothalamus then to posterior pitutary
Post pitutary releasing oxytocin
Oxytocin reaches myoepithelial cells in the mammary gland
Myoepithelial cells constrict causing milk to be screwed into the ducts
Milking units removes milk from ducts and cisterns
What is skill time?
The pre-dip time to reduce the bacteria load
What is stripping?
The first 2-3 streams of milk contains the highest number of somatic cell counts therefore milk quality is enhanced and allows the milkier to look for clinician mastitis
What is the benefit of wiping the teat?
Removes pre-dip and removed a large number of bacteria
__-__ seconds optimizes milking unit attachment to match max oxytocin effect
90-120 seconds
How can managers monitor if the milkers are following procedures
Cameras and electronic monitoring systems
What is the only what you can definitively diagnose a mastitis causing agent?
Culture
What can cause false negatives?
Pathogen load is below limit of detection
Pathogen has been cleared, abnormal milk has not resloved
Special media required
Inhibitors in milk
Sample was mishandled
What is bulk tank milk cultures used for?
Determine the presence or absence of a pathogen in the herd
ID the predominant bacterial groups in the herd
What affects the BTM frequency?
Size of the herd
Likelihood of down-grade
Presence/abscence of contagious pathogens
Owner’s tolerance for risk
Who are the only two who can take milk samples?
The owner or milk truck driver
SCC for grade A milk
<750,000 cells/mL
What can cause samples to be contaminated?
Dirty teat ends
Wet udders
Milker’s hands
Non-sterile containers
How do you properly collect a BTM sample?
Agitate the take for 10-15 minutes prior to sampling
Use a sterilized dipper or syringe to collect milk from the top of the talk
Where should you not collect BTM sample from?
Tank outlet valve
How do you collect individual cow milk sample?
Wear latex/nitrile gloves
Prep the cow as usual and dry udder
Clean teat ends with alcohol wipe
Sample the teats closes to you first then far teas
Discard 1-2 squirts of milk
What overrides oxytocin?
Epinephrine
What are the draw backs for freezing a sample?
Strep and staph no greatest affected
Nocardia can have reduced likelihood of isolating these organisms
Can reduce likelihood of E. coli isolation less
How often do you need to replace the liners of claw?
1-2 times a month
Expect __% of individual samples to be contaminated
10% (>20% need to discuss collection techinique)
Physical barriers to teat?
Teat end (sphincter
Keratin lining of the teat canal
Bacteriostat FA
Immune factors of the mammary gland?
NS immunity (neutrophils, macrophages)
Specific immunity
Lymphocytes
What is the only organism that causes mastitis after hematogenous spread?
Mycoplasma
Cow risk factors for teat end lesions
Teat shape
Teat position on udder
Production level
Stage of lactation
Parity
Main reservoir in the udder of infected cows
Infections resulted from cow-to-cow transmission
Via contaminated fomites
Examples: Staph aureus, Strep agalactiae, Mycoplasma
Contagious mastitis
Main reservoir is the environment
Infection is result of environmental exposure
Example: E. coli, Non-aureus Staph, Strep dysgalactiae/uberis
Environmental mastitis
According to the lecture, what is the primary reason why udder health is important in the dairy industry? a) It ensures cows are comfortable. b) It prevents environmental contamination. c) Mastitis is the most frequent and costly disease of the dairy industry. d) It improves the taste of milk.
c) Mastitis is the most frequent and costly disease of the dairy industry.
Which of the following is a direct economic cost associated with mastitis in dairy cows? a) Increased feed consumption b) Higher veterinary bills for routine check-ups c) Increased amount of non-saleable milk. d) Lower cost of labor
c) Increased amount of non-saleable milk.
Which of the following is NOT listed as a type of dairy milking parlor in the lecture? a) Parallel b) Tandem c) Herringbone d) Circular
d) Circular
The bulk tank in a dairy operation serves which of the following primary functions related to milk? a) Cooling milk before processing b) Separating cream from milk c) Collecting milk to be transported and providing a source for milk culture samples. d) Pasteurizing milk on the farm
c) Collecting milk to be transported and providing a source for milk culture samples.
What is the purpose of pulsation in a machine milking unit at the cow level? a) To increase the vacuum pressure for faster milking b) To filter impurities from the milk c) To provide a massaging action to keep the teat healthy. d) To measure the milk flow rate
c) To provide a massaging action to keep the teat healthy.
According to the lecture, what is the goal range for Mean Claw Vacuum during milking? a) 8.0 to 10.0” Hg b) 10.5 to 12.5” Hg c) 13.0 to 15.0” Hg d) Less than 3” Hg
b) 10.5 to 12.5” Hg
For optimal milk letdown and prevention of mastitis, what process involves the contraction of muscles surrounding the alveoli? a) Teat stimulation b) Milking unit attachment c) Milk ejection reflex d) Pulsation
c) Milk ejection reflex
What is the primary purpose of stripping 2-3 streams of milk from each teat during the milking procedure? a) To remove residual milk after machine milking b) To clean the teat before attaching the milking unit c) To enhance milk quality by removing milk with high somatic cell counts and to check for clinical mastitis, as well as stimulate oxytocin release. d) To pre-cool the milk before it enters the milking system
c) To enhance milk quality by removing milk with high somatic cell counts and to check for clinical mastitis, as well as stimulate oxytocin release.
According to the lecture, what is the optimal time interval between teat preparation (including pre-dip, stripping, and wiping) and milking unit attachment to match maximum oxytocin effect? a) 30-60 seconds b) 90-120 seconds c) Immediately after wiping d) More than 180 seconds
b) 90-120 seconds
A dairy farm has recently experienced an increase in clinical mastitis cases. The veterinarian recommends culturing individual cows to identify the specific pathogens involved. What type of milk culture is MOST appropriate in this situation? a) Individual Animal Culture b) Bulk Tank Milk Culture c) Composite sample d) Environmental culture
a) Individual Animal Culture
A bulk tank milk culture from a large dairy herd reveals a predominant growth of Streptococcus agalactiae. Based on this finding, which of the following management steps would be MOST relevant according to the lecture's implication (even though specific steps aren't detailed for each pathogen in the excerpt)? a) Improving barn ventilation to reduce environmental bacteria b) Reviewing milking procedures to prevent cow-to-cow transmission c) Focusing on teat end disinfection during the dry period d) Increasing the frequency of bulk tank
b) Reviewing milking procedures to prevent cow-to-cow transmission
What does "NG" indicate as a result of an individual animal milk culture? a) Growth of multiple colony types b) Growth of a pure culture c) No growth, suggesting the animal is free of mastitis (though false negatives can occur). d) The sample was contaminated
c) No growth, suggesting the animal is free of mastitis (though false negatives can occur).
According to the lecture, what is a key factor to ensure quality results when collecting milk samples for culture? a) Collecting a large volume of milk b) Sampling all cows in the herd at the same time c) Aseptic collection d) Freezing the samples immediately
c) Aseptic collection
Who is typically permitted to handle and collect Bulk Tank Milk (BTM) samples, according to the provided material? a) Any farm employee trained in sample collection b) The herd veterinarian c) The milk processor and the milk hauler d) Only the dairy owner
c) The milk processor and the milk hauler
When collecting an individual cow milk sample, which teats should generally be sampled first? a) Teats that appear most inflamed b) Teats farthest from you c) Teats closest to the milking machine d) It does not matter which teats are sampled first
b) Teats farthest from you
What is the general recommendation for storing milk samples for culture if there is a delay in delivery to the laboratory? a) Leave them at room temperature b) Store them in direct sunlight c) Freeze the samples d) Add a preservative
c) Freeze the samples
Which of the following is considered a physical barrier that helps protect the mammary gland from infection? a) Neutrophils b) Lactoferrin c) Teat end sphincter d) Immunoglobulins
c) Teat end sphincter
A dairy cow has recurrent mastitis infections that do not respond well to treatment. The farmer is considering removing her from the herd. According to the lecture's note on mastitis culling, which of the following factors should be considered in this decision? a) The current market price for cull cows b) The availability of replacement heifers c) The animal's age, chronicity of mastitis, and production level. d) The veterinarian's personal preference
c) The animal's age, chronicity of mastitis, and production level.
Which of the following is classified as a contagious mastitis pathogen in the lecture? a) E. coli b) Klebsiella pneumoniae c) Staph aureus d) Strep uberis
c) Staph aureus
According to the lecture, what is the main reservoir for environmental mastitis pathogens? a) The environment b) The udder of infected cows c) Contaminated milking equipment d) Milker's hands
a) The environment
How often should you perform BTM?
As often as possible
How much dose the dairy industry cause?
>2.8 million
Why does the US dairy industry cost so much?
Increased amount of non-saleable milk
Decreases milk production
Decreases the amount of saleable milk
Decreased milk quality
Increased treatments and culling
Why must we have optimal milk letdown time?
To prevent mastitis and optimize production
The length of time of the pre-dip has been in contact w/ the tear before drying off. 30 seconds is the minimum recommended time.
Contact time
The interval between manual stimulations and cluster attachment
Prep-lag time
How long should the prep lag time be?
90-120 seconds
What is the most powerful stimulation for Oxytocin release?
Stripping