S1.1.1 - Elements, compounds and mixtures
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
kill me!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
atom
The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of said element.
matter
A substance that has both mass and volume; typically classified as solid, liquid or gas.
pure substance
Consist of only one type of substance: either an element or a compound. Fixed composition
mixtures
Composed of more than one element or compound not in a fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded.
allotropes
Alternative forms of an elemental substance in the same physical state
Compounds
Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed ratios.
homogeneous
A type of mixture that a uniform composition and no visible phases or boundaries.
heterogeneous
A type of mixture with a non-uniform composition with visible phases or boundaries.
Separates a mixture of solutes in a solvent.
Mixture is dissolved in a solvent (mobile phase) and placed on chromatography paper (stationary phase).
Components move at different rates due to differences in solvation
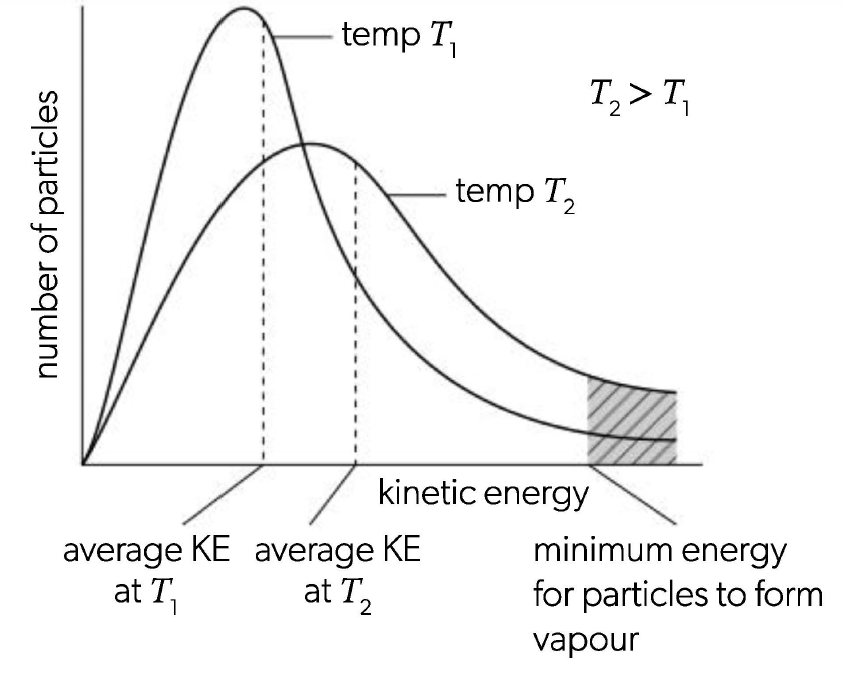
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
moving particles in a gas or liquid do not all travel with the same velocity — The distribution of kinetic energies is shown by a Maxwell-Boltzmann curve
since number of particles will stay the same the area under the graph does not change