Entomology & Anthropology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms
Phylum
Group of closely related classes
Class (taxonomy)
in classification, a group of closely related orders
Arthropoda
insects
entomology
study of insects
PMI
Post Mortem Interval
necrophagous
feeding on carrion
carrion
the decaying flesh of dead animals
Autolysis
the spontaneous breakdown of cells as they self-digest (0-4days)
putrefaction
Decomposition of body tissues. (4-10 days)
black putrefaction
Very strong odor. Parts of the flesh appear black. Gases escape and the corpse collapses. (20-50 days)
Butyric fermentation
Cadaver drying out. Some flesh remains at first; cheesy odor from butyric acid (20-50 days).
Dry decay (diagenesis)
Cadaver almost dry; slow rate of decay. May mummify (50-365 days).
insect life cycle
egg, larva, pupa, adult
Instar
stage between molts
What did Joe Keiper use to determine the age of the bodies
By looking at the bugs eating away at the bodies. Blowflies are reliable for the first 25 days, but the beetles eating away indicated up to three years.
Variables affecting metamorphosis
Temperature and habitat
degree day
a unit of measure of the energy absorbed by a biological system, causing growth
Diptera
They lay eggs that hatch to maggots and are the first to arrive. Other bugs eat the maggots/
Coleoptera
In rough order of appearance, from within hours to dry decay
How did Dr. Greenburg use entomology ?
He surmised that the larvae in the picture were fresh and common to urban Chicago. He then gathered information on that day's environment and the bug's life cycle. Determining that the death occurred within 21 1/2 days of the shooting.
Algor Mortis
The cooling of the body after death
Forensic Anthropology
the study of human remains applied to a legal context
Osteology
Study of bones
How many bones are in the body?
206
Bone functions
structure, produce blook cells, hold minerals, and dexoify the body
genus
A group of similar species
species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
family
Group of genera that share many characteristics
order
Group of similar families
kingdom
First and largest category used to classify organisms
livor mortis
The pooling of the blood in tissues after death resulting in a reddish color to the skin
rigor mortis
stiffness of the body that sets in several hours after death
osteons
Cylindrical structures that comprise compact bone
Os pubis/ Pubis
area on the anterior side of the pelvis where the hip bones come together.
Ventral Arc
a bony ridge that is formed on the ventral (lower) side of the female os pubis.
epiphysis
End of a long bone
Odontology
study of teeth
Caucasoid
European, Middle Eastern, and Indian descent
Negroid
African, Aborigine, and Melanesian descent
Mongoloid
Asian, Native American, and Polynesian descent
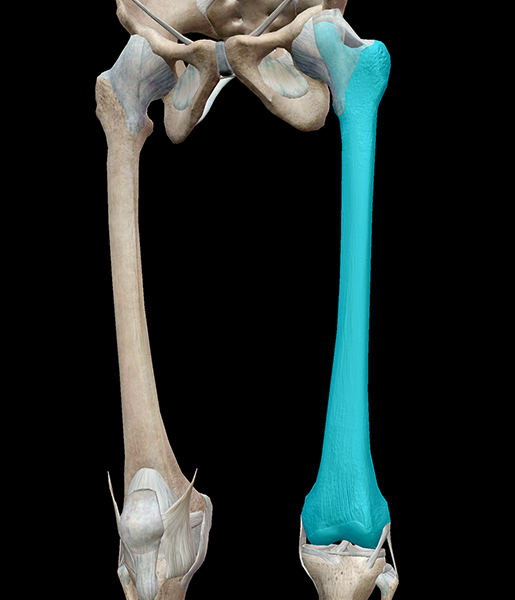
Femur
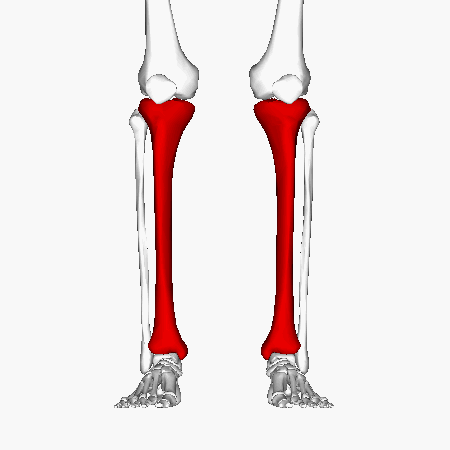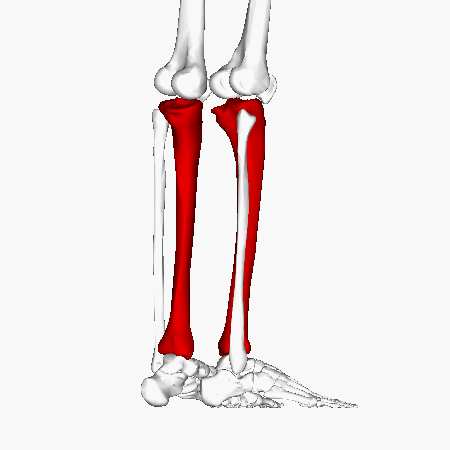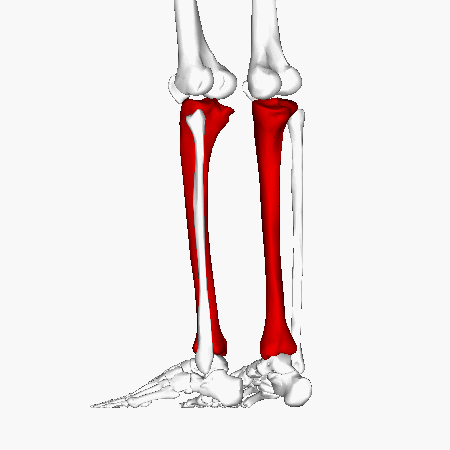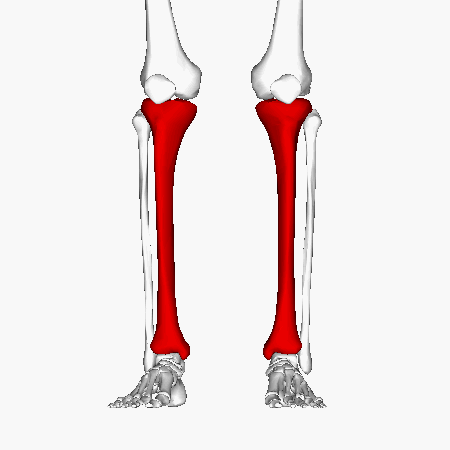
Tibia
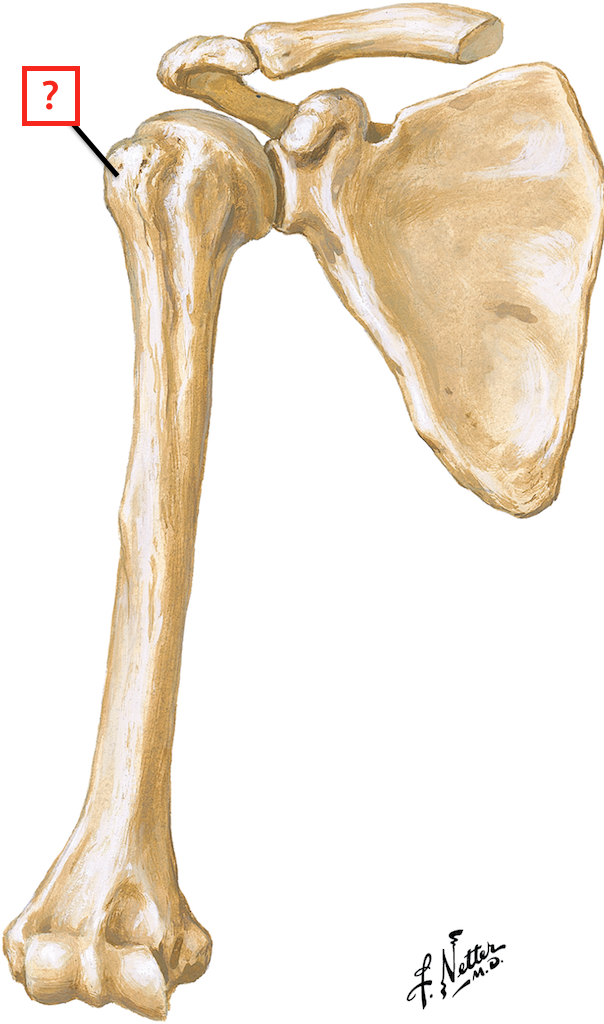
humerus
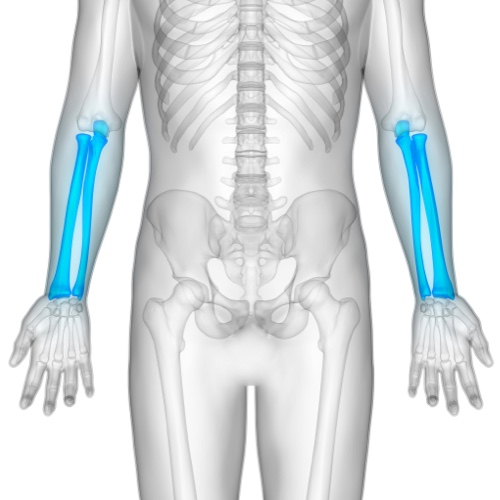
Radius
The bone in the forearm that extends from the elbow to the wrist, usually located on the thumb side.
Sagittal suture completely closed
M: 26 or older, F: 29 or older
Sagittal suture completely open
M: less than 32, F: less than 35
Complete closure of all three major structures
M: over 35, F: over 50
Stage 1
no epiphysis
Stage 2
non-union
Stage 3
partial union
Stage 4
complete union
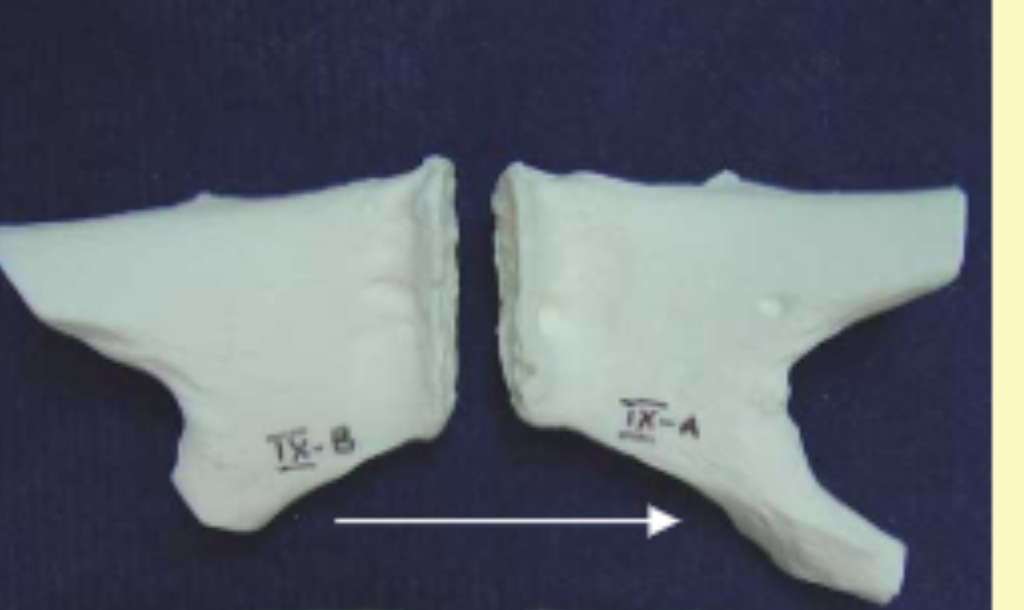
Male or female?
Male
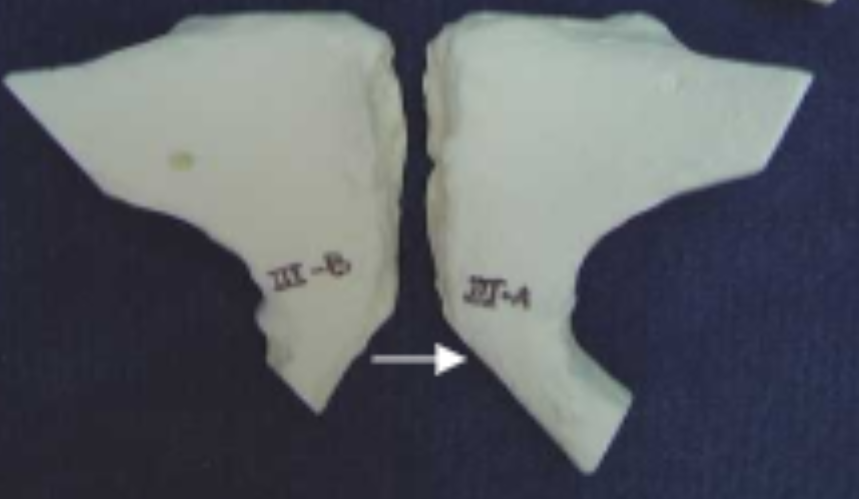
Male or Female Bones
Female