1. transcription factors
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
HOW TARGET GENES ARE EXPRESSED
GENES- sections of DNA that contain coded info in form of bases
code for specific AAs
gene is expressed when mRNA is actively produced using genes base sequence during transcription
mRNA carries code to produce a sequence of AAs i.e. a polypeptide
polypeptides then used to produce proteins, some of which control cell activities e.g. enzymes
CELL DIFFERENTIATION
in multicellular organisms every cell contains same DNA but perform diff functions
bc differentiate to form tissues and organs
as this happens diff types of cell produce more proteins specific to their function
shape of cell and arrangement of organelles will be diff as cell is now specialised
can measure degree of differentiation between cells by comparing proteins they produce using gel electrophoresis
GENE PROBES AND GENE EXPRESSION
gene probes allow particular sections of DNA and RNA to be identified
gene probes find unique sequences of nucleotides on DNA using RNA that is complimentary to it (DNA-RNA hybridisation)
DNA from cells is isolated and heated to denature it
fluorescently labelled RNA for the required gene (probe) is added
any hybridisation shows required gene is present
CONTROLLING GENE EXPRESSION
transcription of DNA to mRNA
translation of mRNA into proteins
having controls in place at any of these stages gives control over gene expression
can also change a protein once it has been synthesised
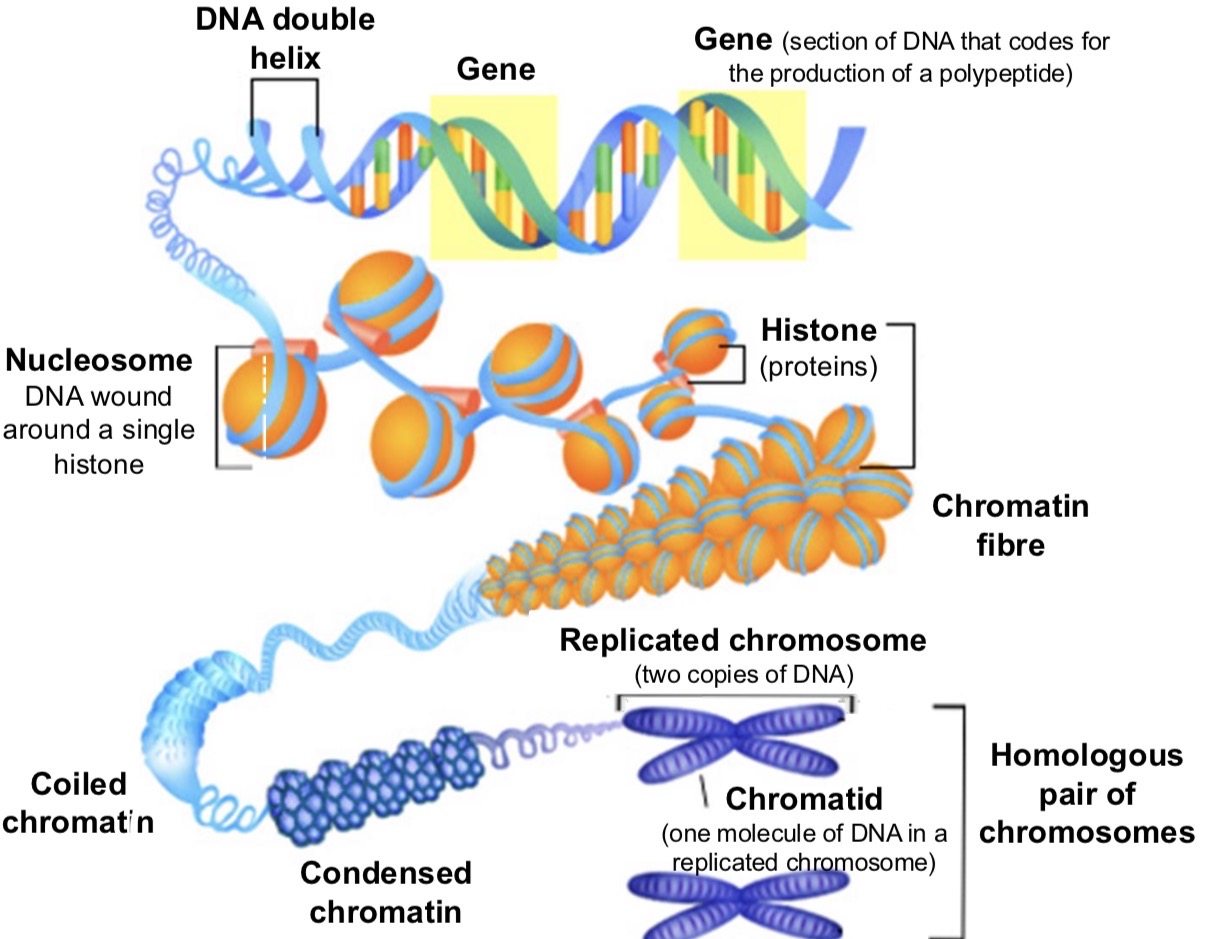
DNA STRUCTURE (RECAP)
when DNA condenses it has to be packaged efficiently
achieved using histones which are pos charged proteins
DNA winds round histone to form nucleosomes
interact to produce more coiling and then supercoiling
in supercoiled areas genes are not available to be copied to make proteins
one way cells are differentiated
TRANSCRIPTIONAL FACTORS (TF)
protein that controls transcription of genes by binding to a specific region of DNA
all have a DNA binding site which binds to either a promoter region in DNA or an enhancer region
TF- BINDING TO PROMOTER REGIONS
sequences of nucleotides next to a gene
if a TF binds here it can either enable or prevent binding of RNA polymerase at gene
if it enables binding- mRNA will be built and can be used in translation to make protein
if it prevents binding- prevents transcription so no mRNA is made
some TFs can perform both roles for diff genes
TF- BINDING TO ENHANCER REGIONS
binding sites in DNA that might be far away from gene itself
regulate transcription by changing structure of chromatin causing DNA to be more or less open to RNA polymerase
open chromatin structure makes a gene accessible so its available for transcription while a closed one makes it inaccessible so not available
TF- 2
often several diff TFs will be involved in expression of a gene, giving many levels of control
equally, a single TF might control expression of many diff genes
might stimulate expression of one and suppress expression of another
allows some genes to be expressed (switched on) and others to be repressed (switched off) at diff stages of development of an organism