intro to aphug- barrons book vocab
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
absolute distance
The distance that can be measured with a standard unit length, such as a mile or kilometer.
absolute location
The exact position of an object or place, measured within the spatial coordinates of a grid system.
accessibility
the relative ease with which a destination may be reached from some other place
aggregation
To come together into a mass, sum, or whole
azimuthal projection
A map projection in which the plane is the most developable surface.
breaking point
The outer edge of a city's sphere of influence, used in the law of retail gravitation to describe the area of a city's hinterlands that depend on that city for its retail supplies.
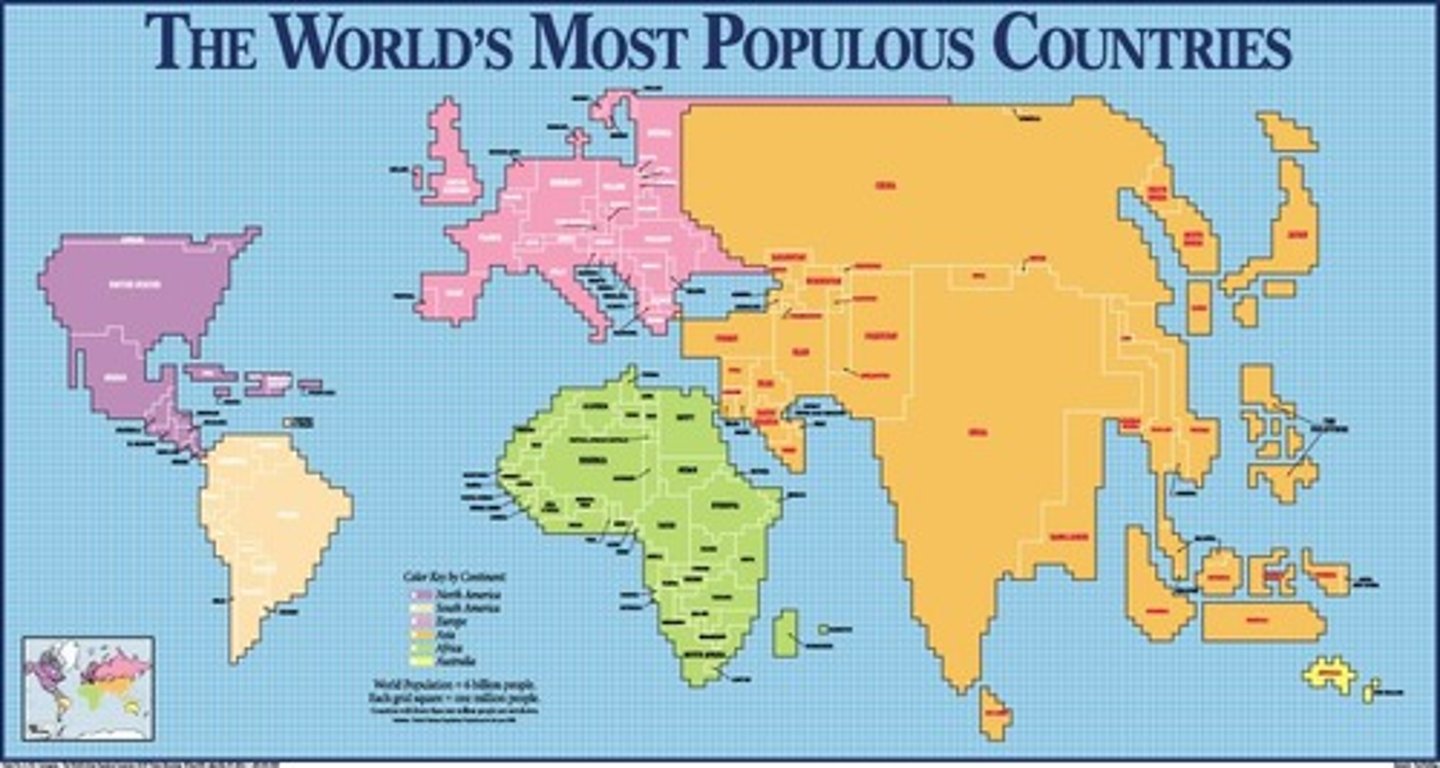
Cartogram (thematic)
A map in which the shape or size is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as travel, population or economic production
Cartography
The science of making maps
Chloropleth Map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment
Complementarity
The actual or potential relationship between two places, usually referring to economic interactions.
connectivity
The degree of economic, social, cultural, or political connection between two places
contagious diffusion
The distance-controlled spreading of an idea, innovation, or some other item through a local population by contact from person to person.
coordinate system
A standard grid, composed of lines of latitude and longitude, used to determine the absolute location of any object, place, or feature on Earth's surface.
Cultural Ecology
The multiple interactions and relationships between a culture and the natural environment
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape
distance decay effect
The decrease in interaction between two phenomena, places, or people as the distance between them increases.
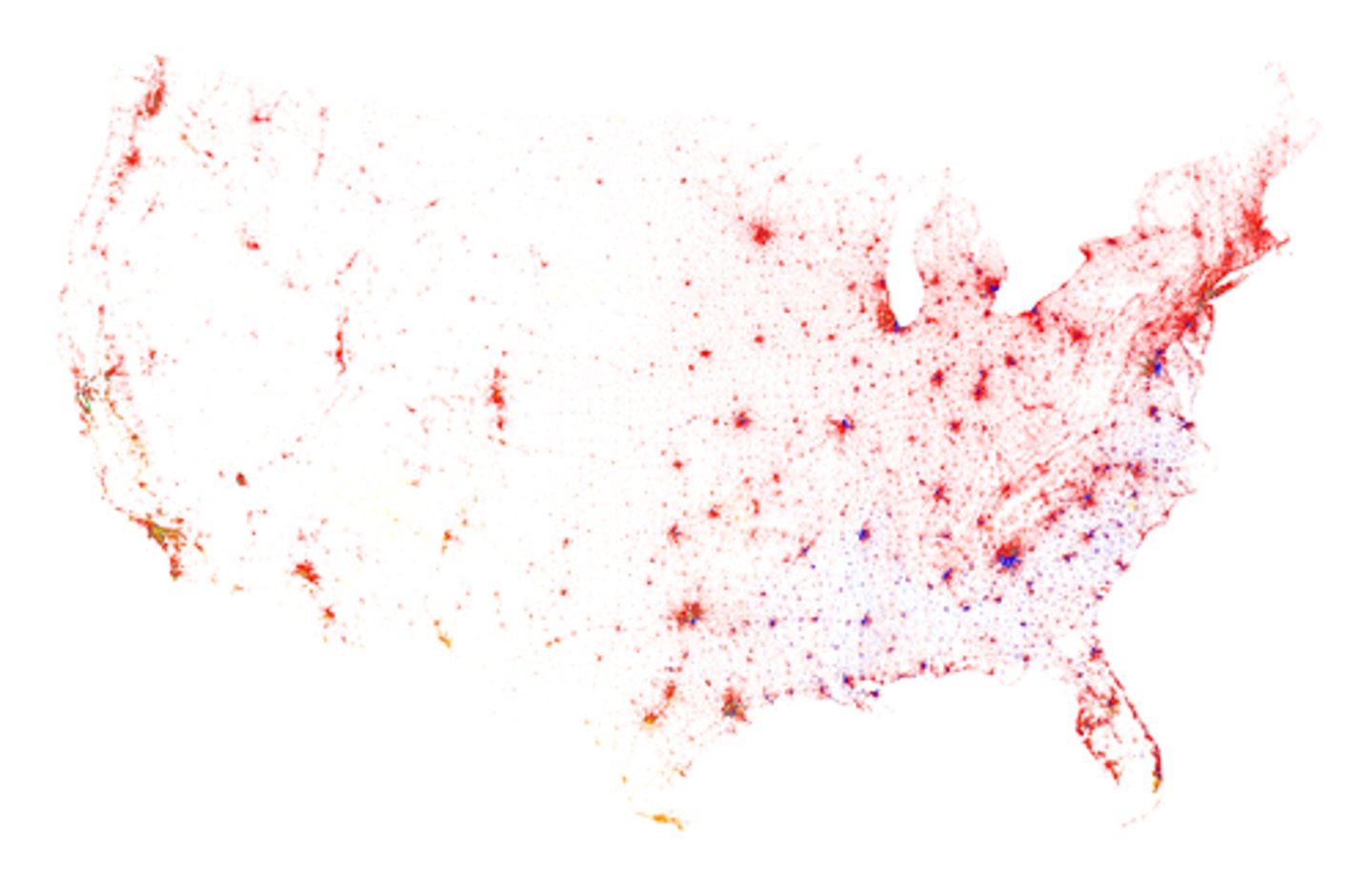
dot maps
Thematic maps that use points to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences, such as crimes, car accidents, or births.
environmental geography
The intersection between human and physical geography, which explores the spatial impacts humans have on the physical environment and vice versa.
expansion diffusion
the spread of ideas, innovations, fashion, or other phenomena to surrounding areas through contact and exchange
formal region
An area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics.
friction of distance
A measure of how much absolute distance affects the interaction between two places.
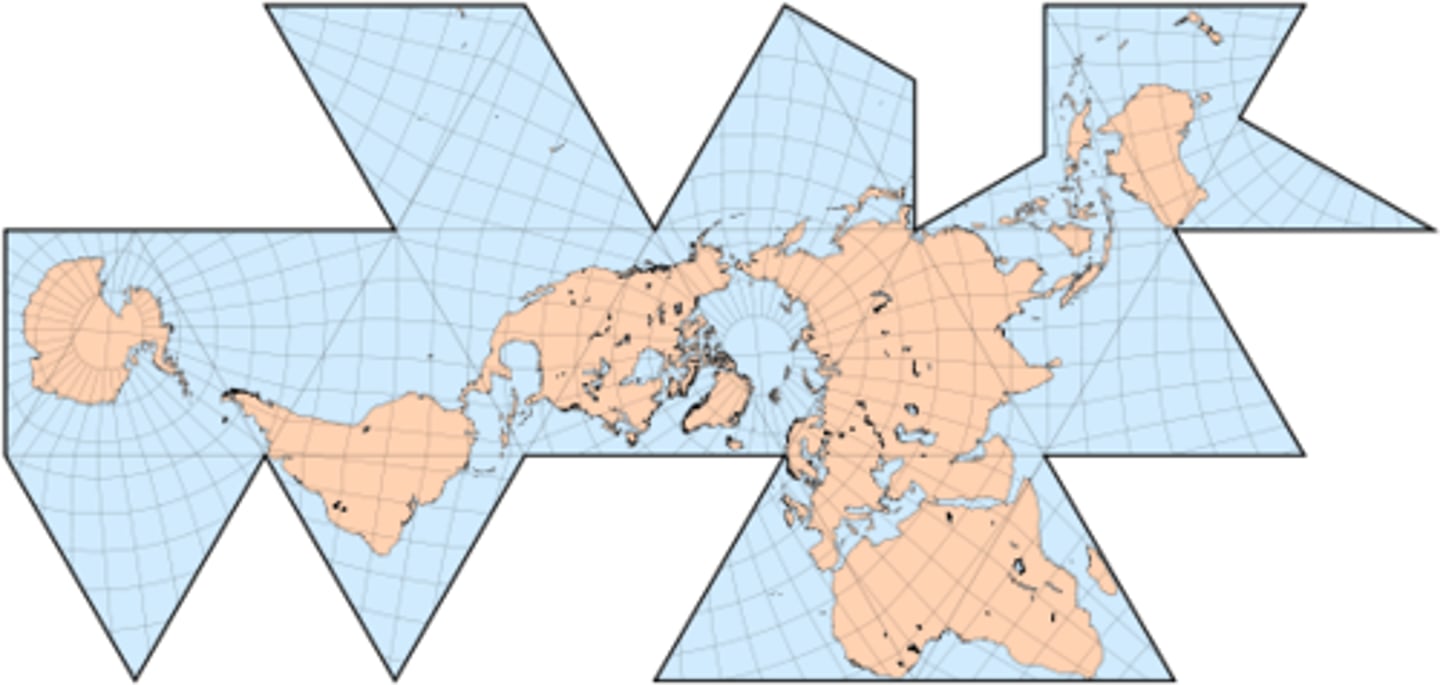
fuller projection
A type of map that maintains the accurate size and shape of landmasses, but completely rearranges direction such that the four cardinal directions - North, South, East, West - no longer have any meaning.
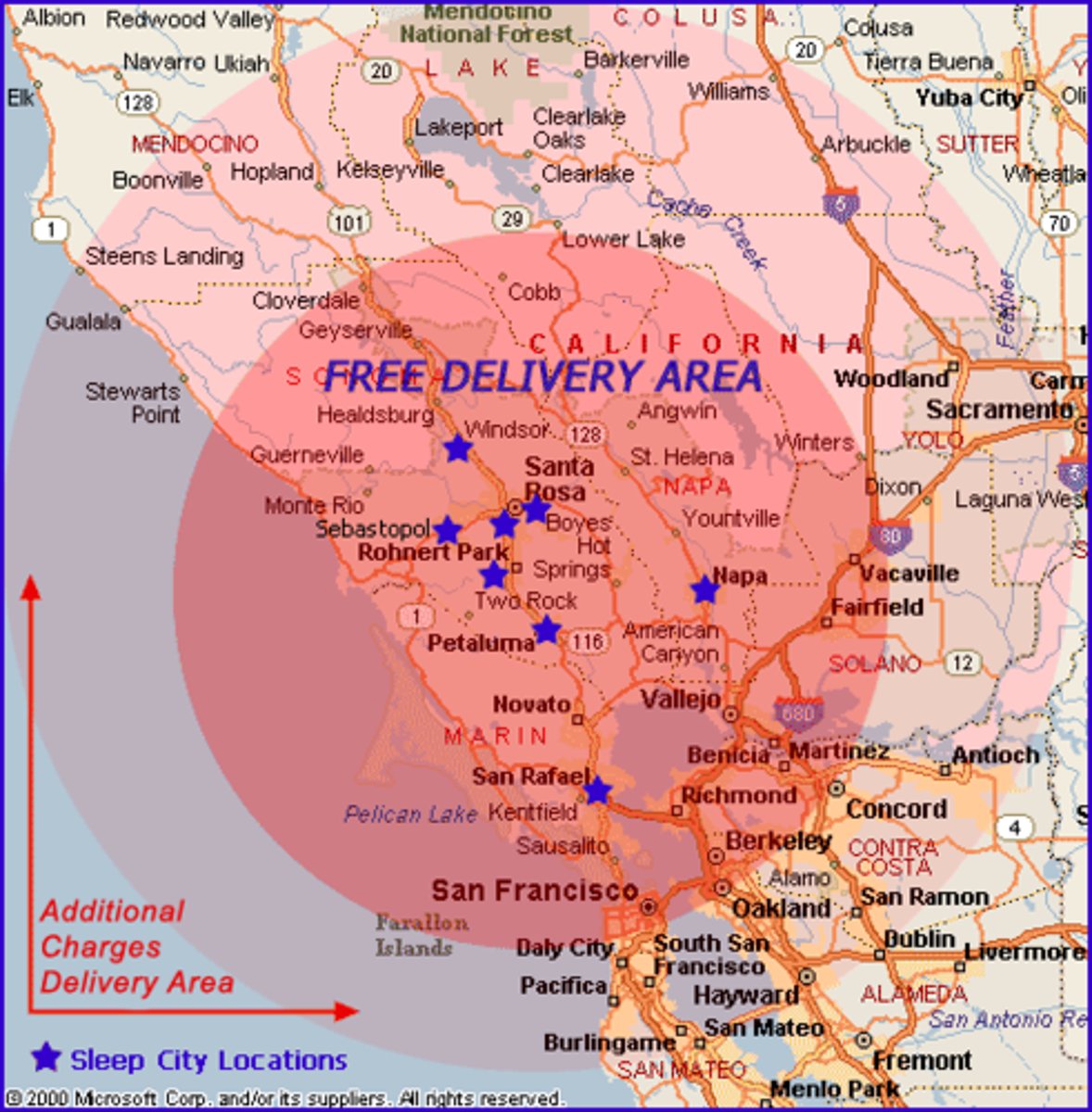
functional region
A region defined by the particular set of activities or interactions that occur within it
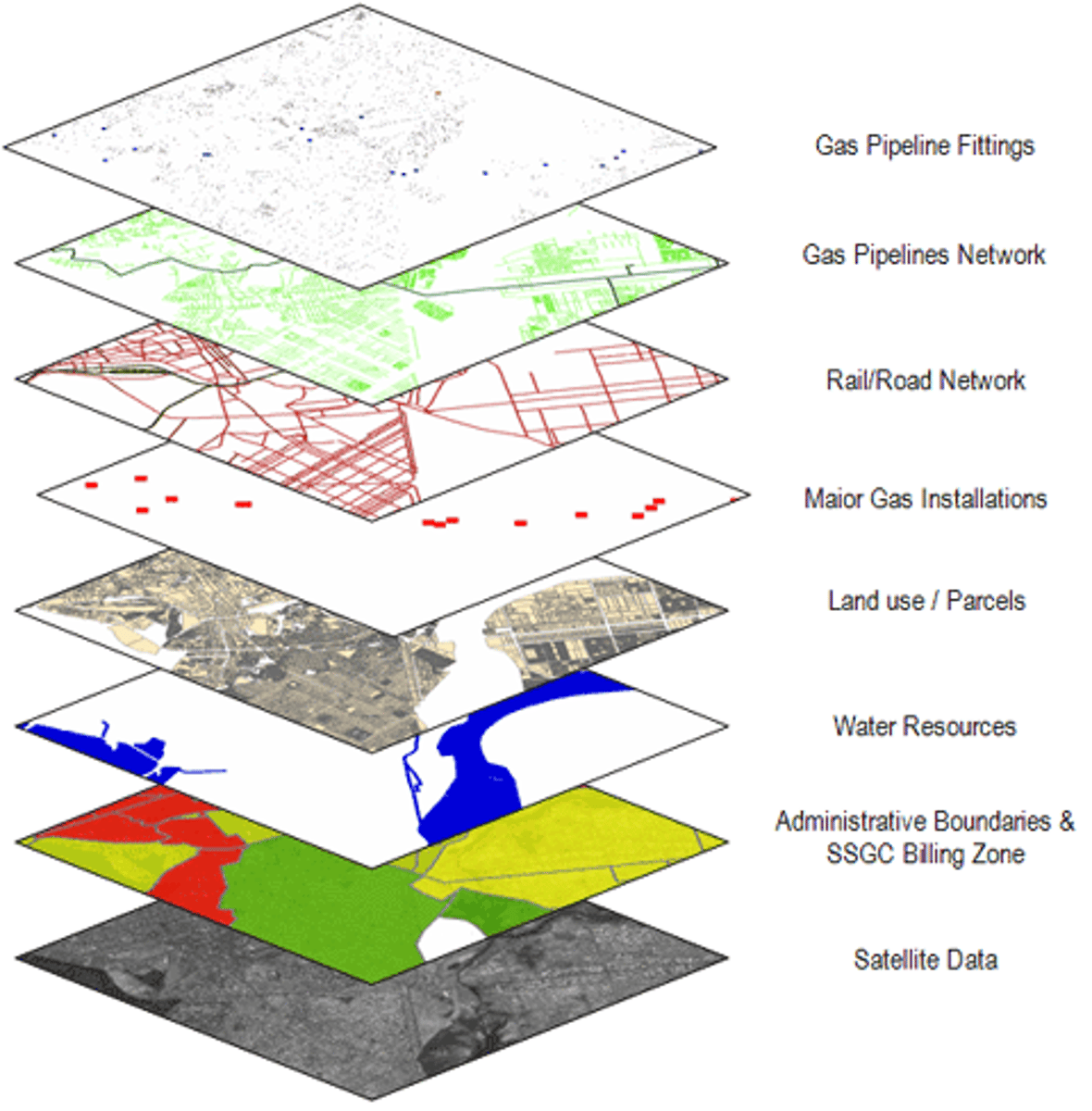
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
geographic scale
The scale at which a geographer analyzes a particular phenomenon, for example: global, national, census tract, neighborhood, etc. Generally, the finer the scale of analysis, the richer the level of detail in the findings.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A set of satellites used to help determine location anywhere on Earth's surface with a portable electronic device.
gravity model
A mathematical formula that describes the level of interaction between two places, based on the size of their populations and their distance from each other.
Hierarchical Diffusion
A form of diffusion in which an idea or innovation spreads by passing first among the most connected places or peoples.
human geography
The study of the spatial variation in the patterns and processes related to human activity.
international date line
the line of longitude that marks where each new day begins, centered on the 180th meridian
intervening oppurtunity
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.
isoline
A map line that connects points of equal or very similar values.
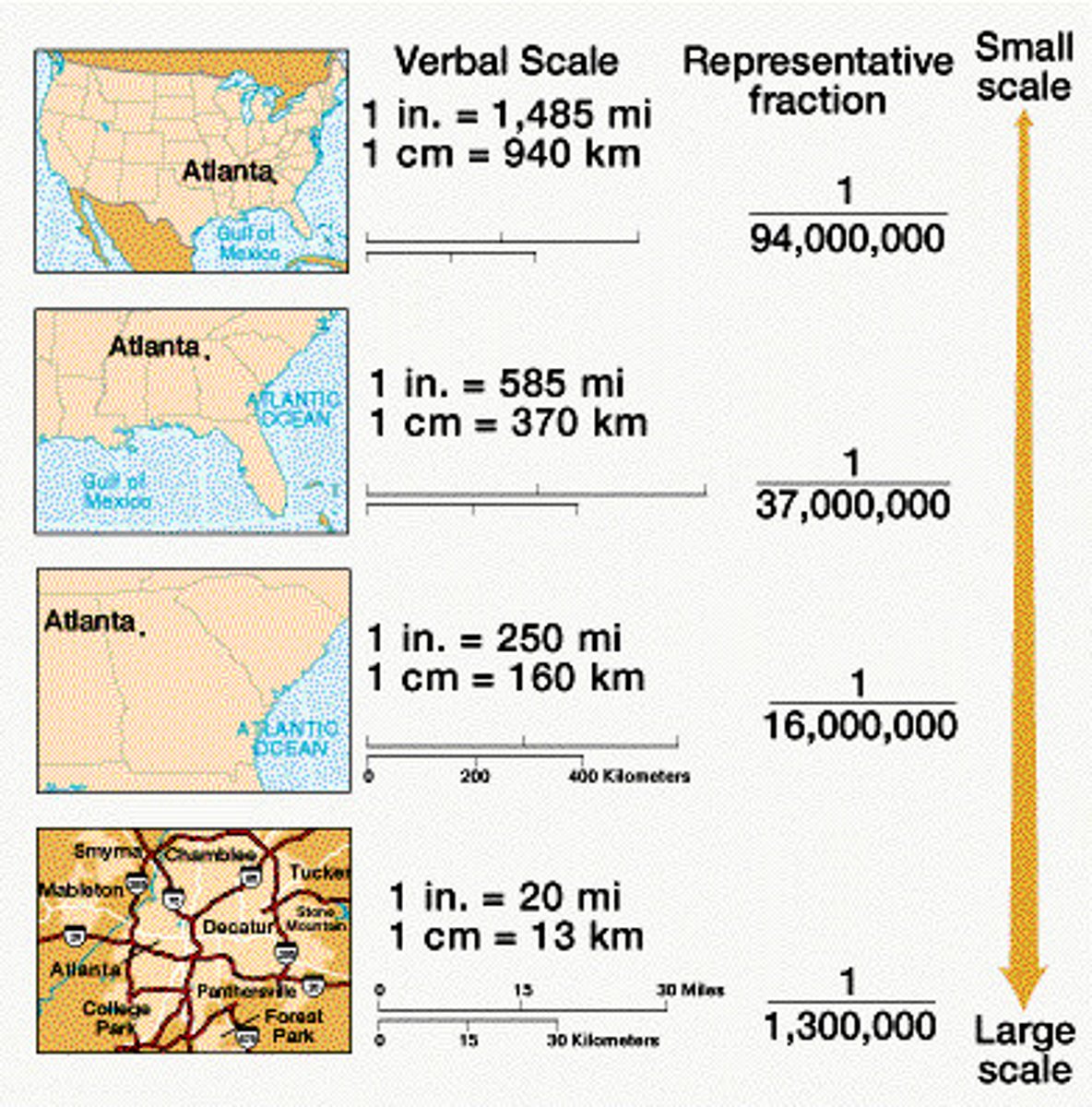
large scale
A relatively small ratio between map units and ground units. Large-scale maps usually have higher resolution and cover much smaller regions than small-scale maps.
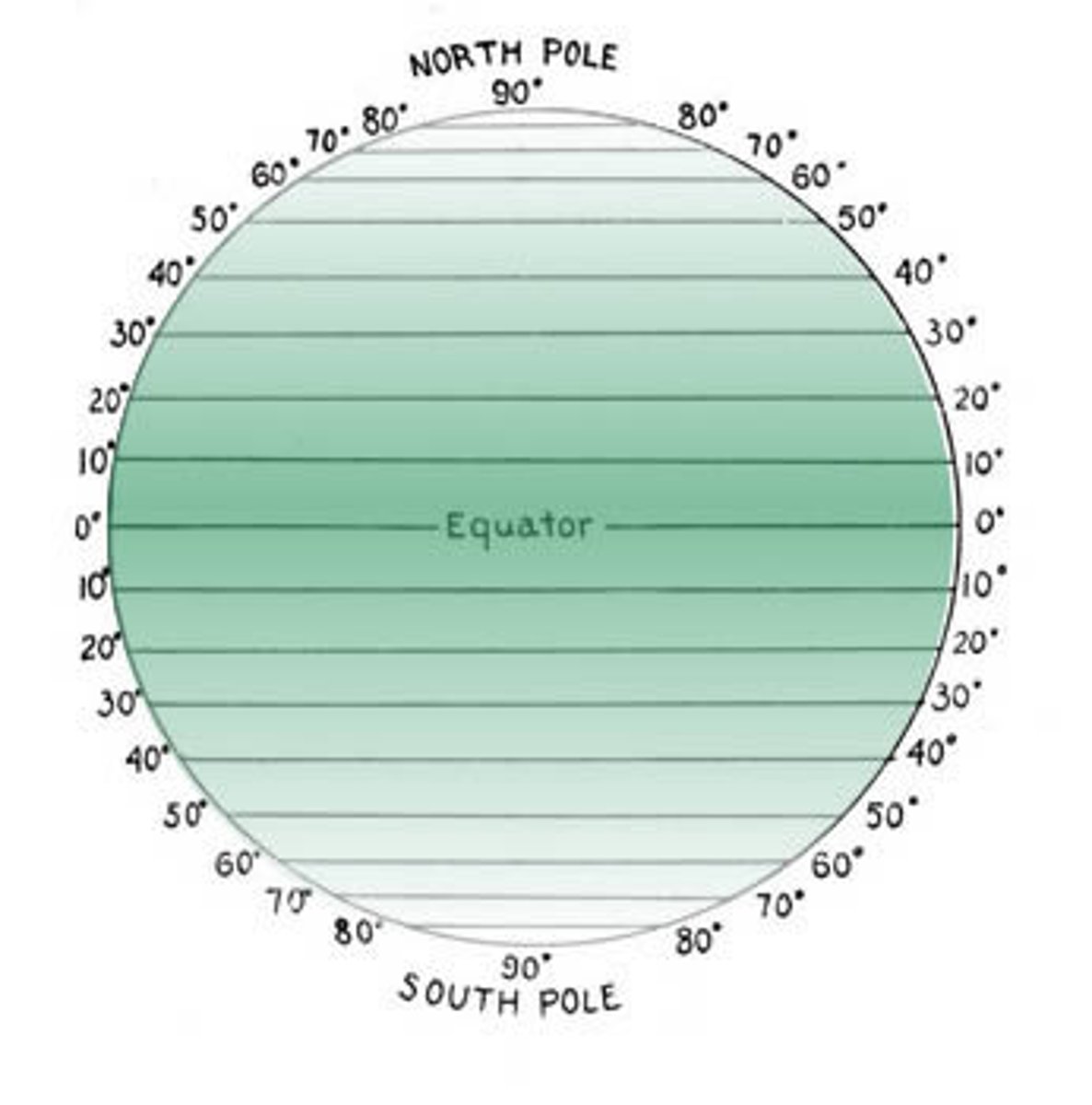
Latitude
distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees
law of retail gravitation
A law stating that people will be drawn to larger cities to conduct their business since larger cities have a wider influence on the surrounding hinterlands.
location chart
on a map, a chart or graph that gives specific statistical info about a particular political unit or jurisdiction
Longitude
Distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees
map projection
a mathematical formula used to represent the curved surface of the Earth on the flat surface of a map
map scale
The relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature on Earth's surface.
mercator projection
A true conformal cylindrical map projection, the Mercator projection is particularly useful for navigation because it maintains accurate direction. Mercator projections are famous for their distortion in area that makes landmasses at the poles appear oversized.
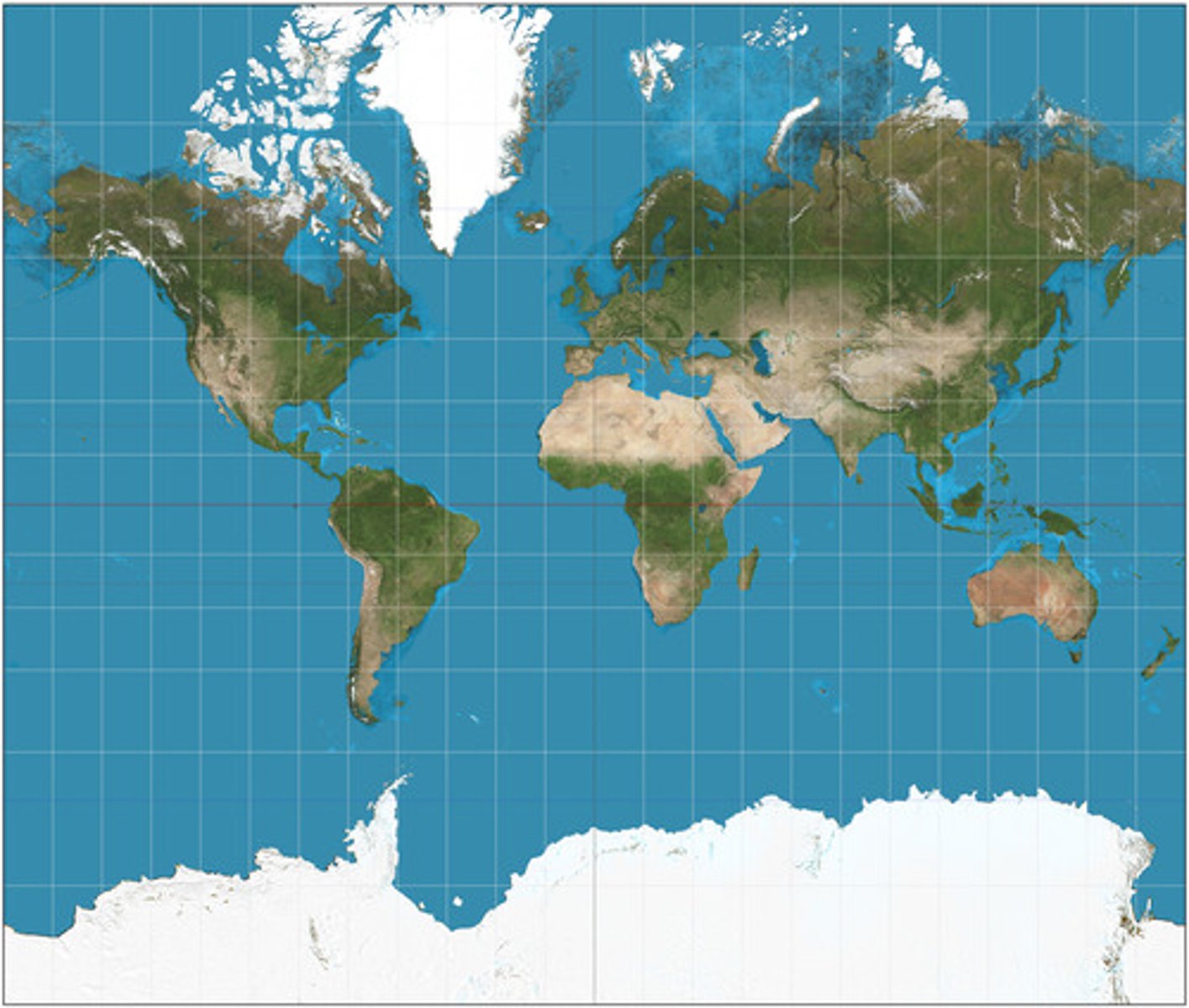
natural landscape
The physical landscape or environment that has not been affected by human activities.
nature-society
Also called nature-society geography, the study of the interactions between societies and the natural environments in which they live
parallel
an east-west line of latitude that runs parallel to the equator and that marks distance north or south of the equator
w. d. pattison
Claimed that geography drew from four distinct traditions; Earth-Science, Culture-Environment, Locational and Area-Analysis traditions
perceptual region
Highly individualized definition of regions based on perceived commonalities in culture and landscape.
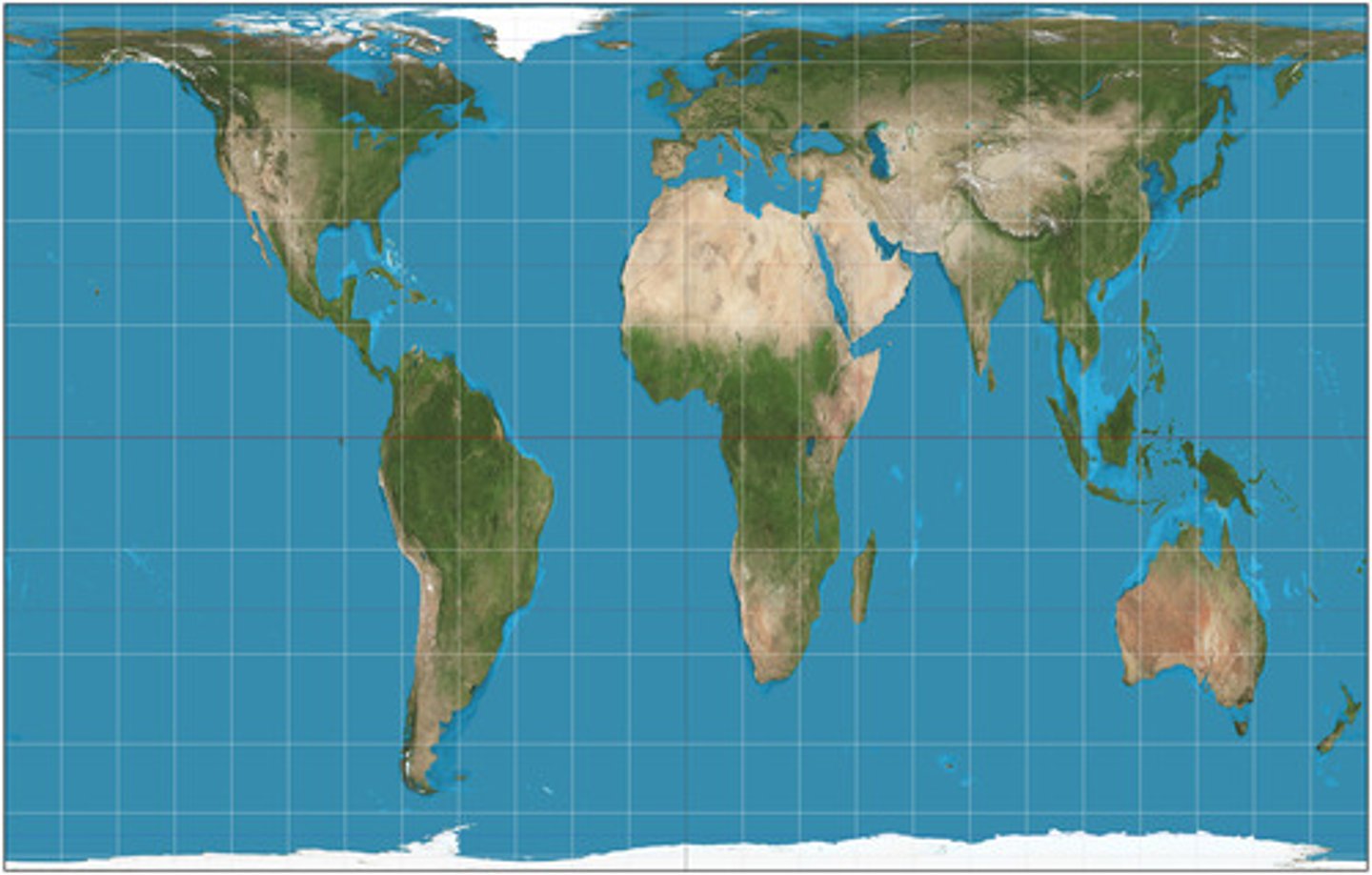
peters projection
An equal-area projection purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of Earth equally.
physical geography
One of the two major divisions of systematic geography; the spatial analysis of the structure, processes, and location of Earth's natural phenomena such as climate, soil, plants, animals, and topography.
preference map
A map that displays individual preferences for certain places.
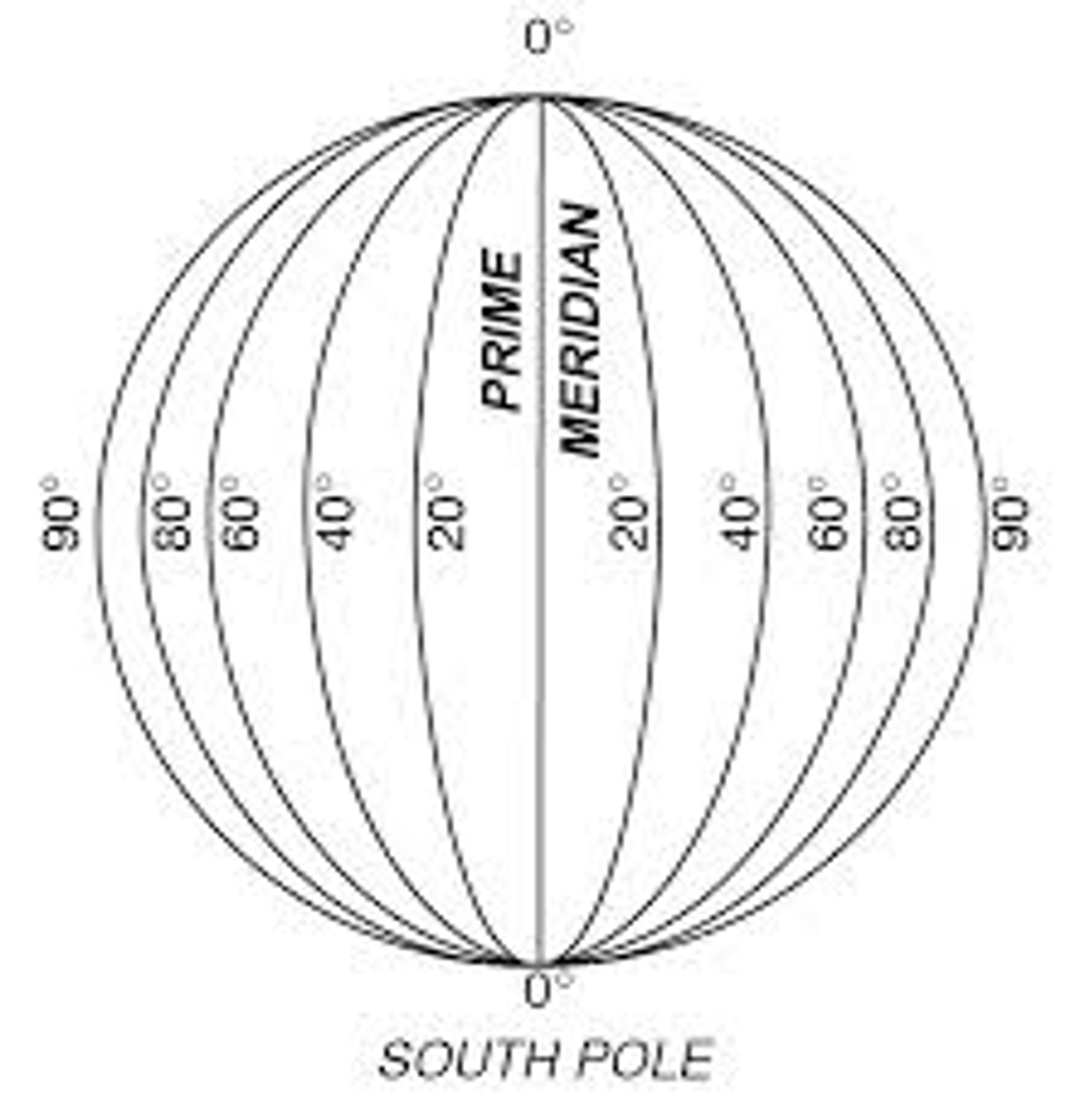
Prime Meridian
The meridian, designated at 0° longitude, which passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England.
projection
The system used to transfer locations from Earth's surface to a flat map.
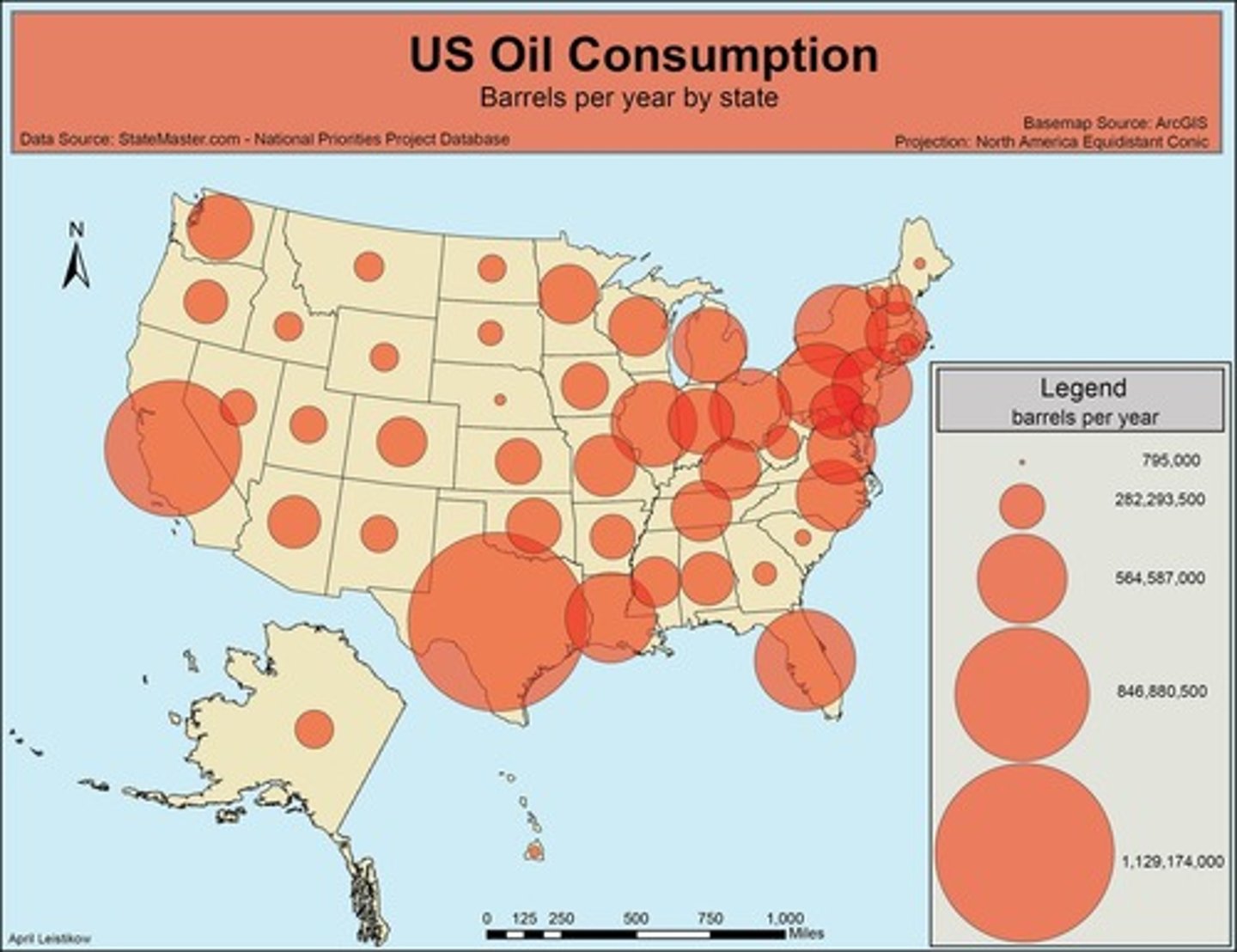
proportional symbols map
A thematic map in which the size of a chosen symbol-such as a circle or triangle-indicates the relative magnitude of some statistical value for a given geographic region.
ptolemy
Roman geographer-astronomer and author of Guide to Geography which included maps containing a grid system of latitude and longitude.
qualitative data
Data associated with a more humanistic approach to geography, often collected through interviews, empirical observations, or the interpretation of texts, artwork, old maps, and other archives.
quantitative data
Data associated with mathematical models and statistical techniques used to analyze spatial location and association.
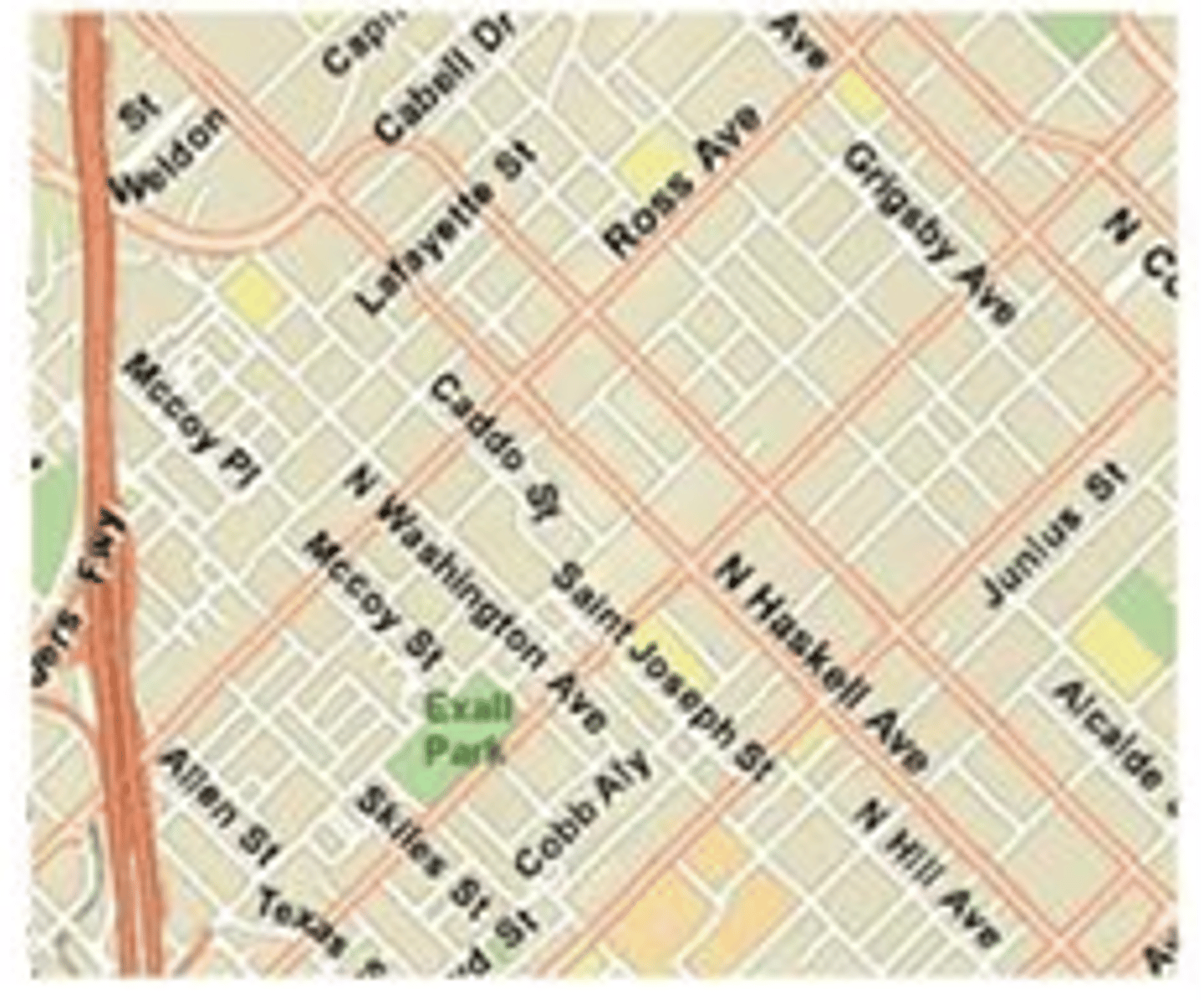
reference map
A map type that shows reference information for a particular place, making it useful for finding landmarks and for navigation.
region
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features.
regional geography
The study of geographic regions.
relative distance
A measure of distance that includes the costs of overcoming the friction of absolute distance separating two places. Often relative distance describes the amount of social, cultural, or economic, connectivity between two places.
relative location
The position of a place in relation to another place
relocation diffusion
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
resolution
a map's smallest discernable unit. if, for example, an object has to be one kilometer long in order to show up on a map, that map's resolution is one kilometer
robinson projection
Projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain completely accurate area, shape, distance, or direction, but it minimizes errors in each.
carl sauer
Geographer from the University of California at Bed defined the concept of cultural landscape as the fundamental unit of graphical analysis. This landscape results from interaction between humans and the physical environment. Sauer argued that virtually no land escaped alteration by human activities.
scale of analysis
a scale that determines what is being studied based on the size of the area being examined
sense of place
Feelings evoked by people as a result of certain experiences and memories associated with a particular place.
site
The physical character of a place
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
small scale
A map scale ratio in which the ratio of units on the map to units on Earth is quite small. Usually depicts large areas.
spatial diffusion
The ways in which phenomena, such as technological innovations, cultural trends, or even outbreaks of disease, travel over space.
spatial perspective
a way of looking at the human and physical patterns on Earth and their relationships to one another
sustainability
The use of Earth's renewable and nonrenewable natural resources in ways that do not constrain resource use in the future.
thematic layers
Individual maps of specific features that are overlaid on one another in a Geographical Information System to understand and analyze a spatial relationship.
thematic map
A type of map that displays one or more variables-such as population, or income level-within a specific area.
time-space convergence
The idea that distance between some places is actually shrinking as technology enables more rapid communication and increased interaction among those places
topographic maps
Maps that use isolines to represent constant elevations. If you took a topographic map out into the field and walked exactly along the path of an isoline on your map, you would always stay at the same elevation.

transferability
The costs involved in moving goods from one place to another
visualization
Use of sophisticated software to create dynamic computer maps, some of which are three dimensional or interactive.
anthropogenic
Human-induced changes on the natural environment
earth system science
A systematic approach to physical geography that looks at the interaction between Earth's physical systems and processes on a global scale.
eratosthenes
Greek mathematician and astronomer who estimated the circumference of the earth and the distances to the moon and sun (276-194 BC)
fertile crescent
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates
geoid
The actual shape of Earth, which is rough and oblate, or slightly squashed. Earth's diameter is longer around the equator than along the north-south meridians.
idiographic
Pertaining to the unique facts or characteristics of a particular place
george perkins marsh
A 19th century American geographer best known for his classic work, Man and Nature. He focused on the impact of human actions on the natural environment, so his thinking is basic to the field of human geography. He emphasized human destruction of the environment.
nomothetic
Concepts or rules that can be applied universally.
quantitative revolution
A period in human geography associated with the widespread adoption of mathematical models and statistical techniques.
topological space
The amount of connectivity between places regardless of the absolute distance separating them.