RTE 006: Chapter 13 Screen-Film Radiographic Technique
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
P2 Coverage •Exposure Factors ‒Kilovolt Peak ‒Milliamperes ‒Exposure Time ‒Distance •Imaging System Characteristics ‒Focal-Spot Size ‒Filtration ‒High-Voltage Generation •Patient Factors ‒Thickness ‒Composition ‒Pathology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
currently, 300 cm
currently, 120
Exposure factors
The factors that influence and determine the quantity and quality of x-radiation to which the patient is exposed are called
kVp and mAs
The factors principally responsible for x-ray quality and quantity.
mA/s (milliamperes / per second)
It determines the number of x-rays produced (radiation quantity) 1 A = 1 C/s = 6.3 x 1018 per second
-Higher beam quality
-Greater beam penetrability
-More scatter radiation
• Rationale: more Compton effect interaction
- Less differential absorption
-Result: reduced image contrast
-More electrons produced
-Higher x-ray quantity
-Higher patient dose
-No change in x-ray quality
(don't forget to convert to seconds)
------------------------=
mA (first exposure) time (first exposure)
Distance
It determines the intensity of the x-ray beam at the image receptor.
Inverse Square Law
Distance affects exposure of the image receptor according to
600 mA
Inexpensive radiographic imaging systems designed for private physician's offices normally have a maximum capacity of
1500 mA
Interventional radiology imaging systems may have the capacity of
mAs
What is the key factor on the control of OD (optical density) on the radiograph?
mAs value
It is a measure of the total number of electrons conducted through the x-ray tube for a particular exposure
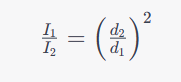
(Note that both the original mAs value and the original SID are in the denominator rather than reversed, as in the inverse square law.)
Inverse Square Law Formula
Distance (SID)
What affects OD?
Distance
____________ has no effect on radiation quality
- Ensures that sufficient mAs can be used to image thick or dense body
parts.
- Provides for a shorter exposure time, which minimizes motion blur.
- Produce more x-rays compared with small focal spot
relatively low.
-Always used for magnification radiography
- These are normally used during extremity radiography and in
examination of other thin body parts in which higher x-ray
quantity is not necessary.
The x-ray quantity or quality
Changing the focal spot for a given kVp/mAs setting does not change
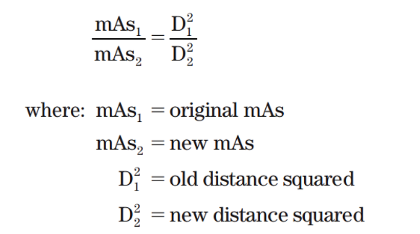
(Note that both the original mAs value and the original SID are in the denominator rather than reversed, as in the inverse square law.)
Direct Square Law Formula
relatively short SIDs?
Inherent filtration
It is made of glass or metal envelope.
approximately 0.5 mm Al equivalent
For general-purpose tubes, the value of inherent filtration is
Added filtration
1-mm Al filter is inserted between the x-ray tube housing and the collimator
that slides in grooves beneath the collimator.
These filters also balance the intensity of the x-ray beam so as to
deliver a more uniform exposure to the image receptor.
wave rectification, but the radiation quantity is halved.
- Used in mobile and dental x-ray imaging systems
- X-rays are emitted continually as pulses.
- The required exposure time for full-wave rectification is only
half that for half-wave rectification.
Three-phase power 6p (pulse) /12p (pulse)
Results in higher x-ray quantity and quality.
more efficient than singlephase power.
More x-rays are produced for a given mAs setting
The average energy of those x-rays is higher.
The x-radiation emitted is nearly constant rather than pulsed.
High-frequency generators
The voltage waveform is nearly constant, with less than 1% ripple.
High-frequency generation results in even greater x-ray quantity and quality.
Used increasingly with dedicated mammography systems, computed tomography (CT) systems, and mobile x-ray imaging systems.
Body habitus
The general size and shape of a patient is called
Sthenic
Meaning “strong, active”—patients are average patients.
Hyposthenic
Thin but healthy appearing; these patients require less radiographic technique.
Hypersthenic
Big in frame and usually overweight.
Asthenic
Small, frail, sometimes emaciated, and often elderly
the more x-radiation is required to penetrate the patient to expose the image receptor
The thicker the patient?
Sthenic, Hyposthenic, Hypersthenic, Asthenic
What are the four general states of body habitus?
Sthenic patients
Radiographic technique charts are based on
Calipers
Are available to the radiologic technologist for use to measure the thickness of the anatomy being imaged
This is due to the fact that the primary X-ray beam has not yet been attenuated by the tissue at this point, and also, that area is exposed by some of the scattered radiation from the body.
Why should we not guess the patient thickness?
They are image quality factors that consist of OD (optical density), contrast, detail, distortion
Second group of patient factors?
They are exposure technique factors that includes kVp, milliamperage, exposure time, SID, Grids, screens, focal-spot size, and filtration
Final group of patient factors?
The patient’s size, shape, and physical condition
What influences greatly the radiographic technique?
High subject contrast
The chest has
Low subject contrast
The abdomen has
Increased radiolucency or radiopacity
Pathology can appear with what?
Radiolucency or Radiopacity
Body tissues are often described by their degree of what?
Mass density
The radiologic technologist must estimate the __________ of the anatomical part and the range of ___________ involved. (Only one answer)
Low kVp and High mAs
Soft tissue requires ____ kVp and _____ mAs
Low kVp, thin
Extremity consists of soft tissue and bone, ___ kVp is used because the body part is ____
Low, high, intermediate
Lung tissue has very ___ mass density, the bony structures have ____ mass density, and the mediastinal structures have ____________ mass density.
It provides in an image with satisfactory contrast and low patient radiation dose
High kVp and low mAs can be used to good advantage as a result?
Type of pathology, size, and composition
The ______________, its ____, and its ___________ influence radiographic technique.
Destructive pathology
Causing the tissue to be more radiolucent.
Constructive pathology
Increasing mass density or composition, causing the tissue to be more radiopaque.
Patient examination request form and previous images.
(The radiologic technologist should also not hesitate to more information from the referring physician, the radiologist, or the patient regarding the suspected pathology.
In pathology, what do we need to help evaluate our patient before examination?
Increase
An increase in kVp will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Increase
An increase in mA will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Increase
An increase in exposure time will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Increase
An increase in mA/s will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Decrease
An increase in distance will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Decrease
An increase in voltage ripple will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Decrease
An increase in filtration will result in ________ x-ray quantity
Increase
An increase in kVp will result in ________ x-ray quality
No change
An increase in mA will result in ________ x-ray quality
No change
An increase in exposure time will result in ________ x-ray quality
No change
An increase in mA/s will result in ________ x-ray quality
No change
An increase in distance will result in ________ x-ray quality
Decrease
An increase in voltage ripple will result in ________ x-ray quality
Increase
An increase in filtration will result in ________ x-ray quality
manipulation
Secondary exposure factors require ____________ for particular examinations