Substance dualism
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms

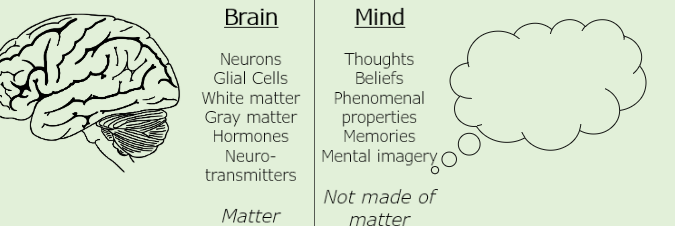
Dualism
Mental states are not physical.
Consciousness is beyond the physical realm and inexplainable in terms of the laws of nature and science .
Knowledge about physical facts would not tell us everything there is to know about the mind
Everything is either mental or physical
Define Substance Dualism
The belief that minds are not identical to our bodies they are ontologically distinct and independent
metaphysical theory
Reality is made of two kinds of stuff :
Matter/ physical substance/ res extensa
Mind /mental substances/ res cogitans
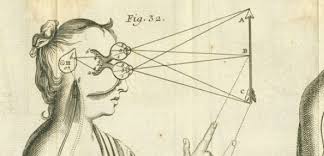
Outline Descarte’s argument from indivisibility
P1. My mind is invisible
P2. My physical body is divisible
P3. Leibn’z law states that two substances that have different properties cannot be the same substance
P4. The mind and body have different properties and substances
C. Mind is not my body , and is not a physical thing
For example : the body is public the mental is private
locatable / unlocatable
Outline the argument from the problem of other minds argument
P1. If substance dualism is true , then we cannot know the mental states of others
P2. We do , on at least some occasions know the mental states of others
C. Therefore substance dualism is false
Sceptical problem affceting dualists

What is response by Mill to the problem of other minds
Argument from analogy , kind of inductive argument
Similarity in antecedent/subsequent marks of sensation
P1. Understand our own actions in terms of stimulus , mental state and response
P2. Stubbing your toe , feeling that pain causes a verbal reaction of ‘ OW ‘
P3. See the stimulus and response in other people
P4. Empathise can understand the pain and know from own experience
C. Conclude that other people have mental states
Supervenience
One set of facts supervenes on another set of more basic facts
example - materialists believe all mental facts supervene on the physical facts about you
Define qualia
subjective qualities which cannot be objectively described
Intrinsic and non intentional phenomenal properties that are introspectively accessible

Name a substance dualist
Descartes

Outline a criticism of the indivisibility argument mental is divisible
Mind has parts thinking imagining , willing
Plato and Freud on dividing
mind mental illness multiple personality and split brain

Outline a criticism of the indivisibility argument Not everything thought of as physical is divisible
Quantum physics quarks subatomic particles have not been found to be divisible and are the smallest parts of all physical matter
Energy is neither destroyed or created it is converted Cannot divide energy
Processes like flowing or running cannot be divided but are still physical
Define substance
An entity or thing that does not depend on another entity for its continued existence it has ontological independence
Define properties
Attributes or qualities or characters of something
Outline the argument from conceivability , Descartes
Deductive argument
P1. It is conceivable for my mind to exist without my body
P2: If it is conceivable for one thing to exist without another, then it is metaphysically possible for one to exist without another
C1: Therefore, it is metaphysically possible for my mind to exist without my body
P3: If it is metaphysically possible for one thing to exist without another, then they are not identical.
C2: Therefore, my mind is not identical with my body.
Outline the criticism that the mind without the body is not conceivable
Imagine mental states without behaviour is impossible , behaviourism
Supposing that you can imagine removing consciousness or leaving all cognitive system intact is like supposing you can imagine removing health or leaving all body functions and power intact
Outline the criticism that what is conceivable may not be metaphysically possible
Masked man fallacy
Outline the criticism that what is metaphysically possible tells us nothing about the actual world