Unit 6: External Business Influences
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What does the economy consist of?
Households/consumers: buy things and produce labour
Business: create products and provide jobs
Government: Controls the public sector, sets tax levels, provides infrastructure
Banks: provide loans and stores money
Government objectives
Low inflation
Low unemployment
Healthy balance of payments
Economic growth in terms of GDP
Low inflation
The lowering in value of money, if inflation is high, people’s savings become worth less
Makes people poorer and damages their confidence to buy goods and services
Inflation
Increase in price of products over time
Low unemployment
Governments want everyone to have a job
People will have money to spend on goods and services
Employed people pay taxes which helps develop infrastructure
Creates better environment for business
Healthy balance of payments
Increased exports enriches businesses e.g more jobs, higher tax
Importing gives consumers more choice and satisfies them
Imports
Buying from another country
Exports
Selling to other countries
Economic growth in terms of GDP
Good GDP means healthy economy
GDP
Value of all combined goods and services consumed and sold/produced in a country
The business cycle
The economy’s development through recession and recovery over time
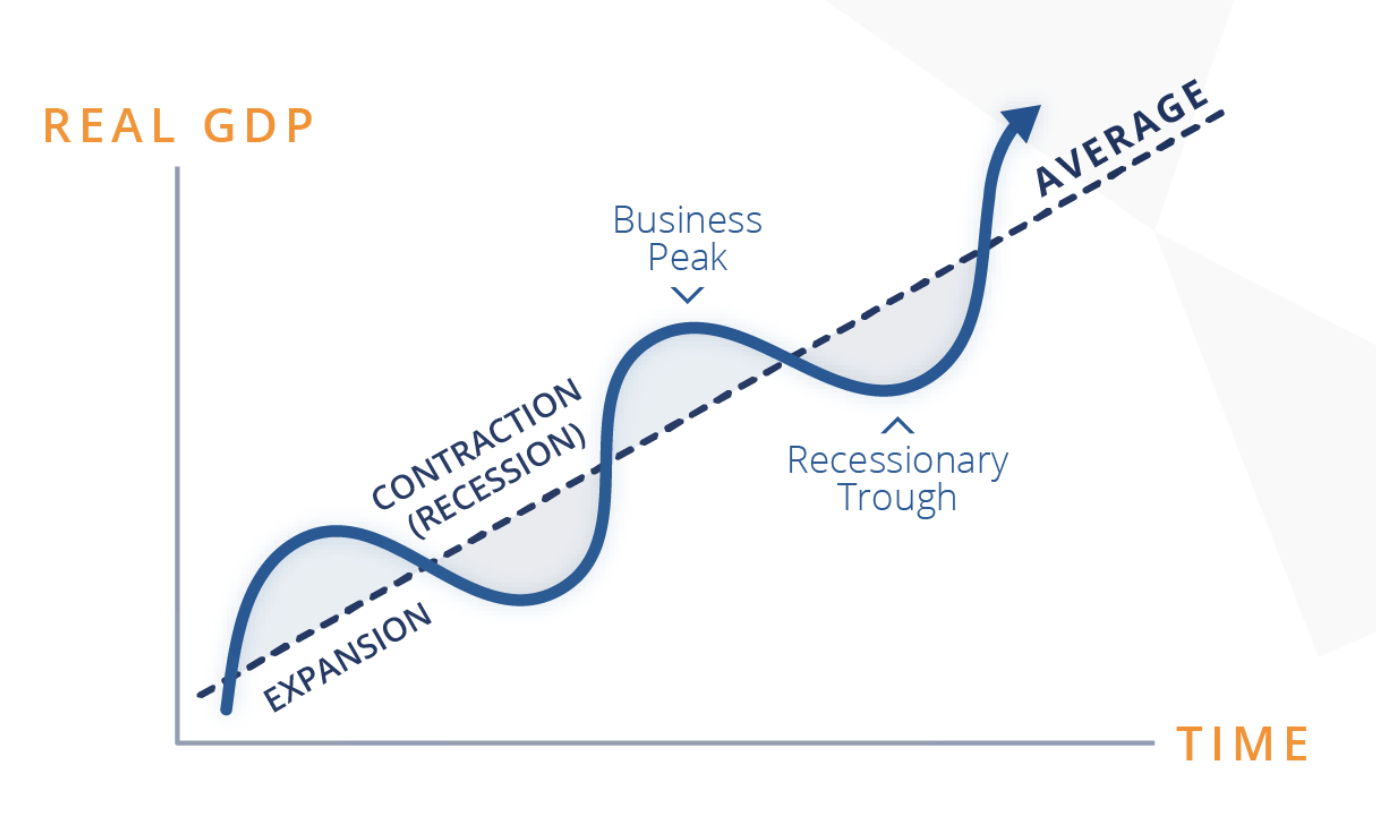
Growing economy
Unemployment goes down
People spend more as they have more jobs that provide money
Business revenue goes up → more profits
Causes inflation
Tax revenue collection goes up
Government can spend more on services for citizens
Consumer confidence is high
Recession/shrinking economies
Some businesses earn less/fail/close down
Unemployment
Consumer confidence decreases
Government tax revenues decreases
Services get worse and less infrastructure
Less jobs are provided by the government
How can government help an economy grow?
Offer cash grants to citizens
Government spending on infrastructure
provides jobs and gets them spending again
Lower tax
people have more disposable income → boosts demand
Encourage foreign direct investment
look for global businesses to set up in their country
Foreign direct investment
Money invested in one country by a company or government in another country
Fiscal policy
A government policy where they tax businesses and people, and spend money on projects within the country
Advantages of fiscal policy
Consumer confidence increases
Decreasing taxes give people more disposable income to spend in the economy
Building infrastructure leads to short-term employment
but in the long-run, it becomes better for business to utilise the infrastructure
encourages FDI
Disadvantages of fiscal policy
They receive less money from tax and have less to spend on other things
Need to find other sources of finance to fund other projects
Infrastructure is very expensive
tax may need to go up or borrowing money is needed
Income tax
Being taxed on the amount you earn
If we increase income tax, people will have less to spend
When reduced, people will be richer
Corporation tax
Taxing businesses based on how much profit they make
Value added tax
Adding tax onto every product/service sold
Lowering sales tax gives more disposable income
Import tariffs and quotas
Taxes placed on importing goods and services from other countries
Advantages of tariffs
Encourages people to buy local
local businesses will be more successful
higher tax revenue as local businesses makes more profit
more job employment
Generate revenue from sales of foreign goods
Disadvantages of tariffs
Reduces choice for local people as foreign goods become too expensive
Drives inflation, makes country poorer
Quotas
Limits the number of something that can be imported into a country, has similar effects as tariffs
Advantages of quotas
Limits sales opportunities of foreign companies
Local businesses don’t need to compete
keeps market shares and limits competition
Disadvantage of quotas
Consumers have less choice over products
Direct tax
Business and individuals pay from their income and profits
corporation/profits tax and income tax
Indirect tax
Placed on goods, products and services
sales tax/VAT, import tariffs
Monetary policy
A government policy that adjusts bank interest rates
Interest rates
Rewards you for saving or the cost of borrowing
What happens during low interest rates?
People are encouraged to save less and spend more
creates demand
Encourages to borrow money
borrowing is cheap, encourages people/businesses to borrow and spend
What happens during high interest rates?
Encourages saving and discourages borrowing as it is expensive
reduces demand to control inflation
Also encourages businesses not to take loans/invest
less investments → less demand → makes inflation fall
Supply side policies
Policies that increase competitiveness of the economy
improve infrastructure, spend more on education, cut business taxes, remove regulations that restrict businesses
Advantages of supply side policy
Makes country more competitive, this encourages FDI
Good for growing GDP and reduces unemployment
Disadvantages of supply side policy
May reduce tax revenue
High costs to implement
only rich countries can afford large scale infrastructure improvements
Usually takes years for benefits to show
but benefits will be long term
Environmental impacts from business activity
Pollution, landfills, deforestation, extinction, global warming, water usage, shipping
Externalities
When businesses locate in areas that create both costs and benefits to the local community and environment (the external costs and benefits of business activity)
Private benefits
Benefits enjoyed by the business
Increase sales and potentially profit
Improves brand reputation
Creates loyal customers
Private costs
Costs a business has to pay for (not always monetary)
Set-up costs
Cost of labour/salaries
Advertising costs
External benefits
Gains to the rest of society
More choice of options
Job opportunities
Service is provided
Attracts people closer to the business location
Builds foot traffic and benefits local community/other businesses
External costs
Costs to the wider society
Noise pollution
More traffic
Public disruptions
Environment impact
Sustainable development
Development which does not put at risk the living standards of future generations
Unsustainable practices
Nuclear power, single-use plastics, pollution, use of fossil fuels, overfishing
Sustainable development
Circular economy, renewable energy sources, bio-created products, reducing carbon emissions
Pressure groups
Made up of people who what to change unsustainable business decisions and take action to force them through boycotts or protests
Ways pressure groups change business behaviour
Educate the public so they can make better decisions
Protests, petitions to publicise something
Boycotts of products/services
Publicity
Positive business reaction to pressure groups
Changes behaviour or the better
Low sales from boycott
Amount of criticism
Staff may have minds changed
Business will change to improve public image
Negative business reaction to pressure groups
Behaviour will not change
Cost of change is too high
Most of the public don’t care
If demand does not change, they won’t change
Greenwashing
Pretending to be sustainable and to lead better practices, while not actually changing their methods
What can governments do to protect the environment?
Create laws and restrictions
Fines for breach of rules
Bans on specific materials/ingredients
Extra taxes for polluting
Giving subsidies for green alternatives
International cooperation
Carbon trading
Carbon trading
Buying and selling of credits that allow a business to emit a certain amount of CO2
Government subsidies
Where the government pays for a portion of the fee consumers pay to reduce their costs
Ethics
The difference between right and wrong
Ethics in pricing
Price gouging: charging too high for products
Pricing very low for unhealthy products
Ethics in products
Making unhealthy products or dangerous ones
Ethics in production
Child labour or low cost labour
Animal testing
Ethics in promotion
Misleading information
Promotion to children
Ethics in human resources
Discrimination
Bribery
Low wages
Costs of acting ethically for businesses
Business have to spend more
paying for ethically sourced supplies
treat workers better
invest in green technology
more safety equipment
Competition is always high but towards less ethical business
they will be cheaper
Less profitability
Benefits of being ethical for businesses
Better reputation
can charge more for quality
loyal customers
May attract ethical investors
Help attract better employment who will be more motivated
less staff turnover
Unique selling point
competitive advantage
Globalisation
Interconnectedness/Interdependence of national economies
Why has the world become more globalised?
Technology and media
Transportation overseas
Migration
Colonisation
Government policies
Advantage of globalisation for businesses
Wider market
higher potential sales
Better access to raw materials/global resources
Employ people from around the world
more likely to find specialists
Access low-wage labour in developing countries → less costs → higher profits
Advantage of globalisation to people
Access to goods and services has expanded
more choice
prices go down and quality goes up as competition is higher
Travel opportunities
Work/migration opportunities
More FDI → more jobs in home country
Disadvantages of globalisation to businesses
More competition from abroad
for all markets mass and niche
Quotas and tariffs may disrupt businesses
Recession in other countries can disrupt businesses
Disadvantages of globalisation to people
Loss of culture
Possible exploitation of low wage labour
Loss of specific types of jobs in some countries (deindustrialisation)
Loss of jobs to business that are able to move nations
Protectionism
When governments favour local businesses and protect them from foreign firms with quotas and tariffs
Protectionism advantages
Protects local jobs
Potentially boosts economy: local business will make more sales and will provide more jobs
Higher tax revenue for government
Lowers competition
Protectionism disadvantages
Reduces choice for consumers
Drives inflation, foreign goods are more expensive
Multinational businesses
Business that sells goods/services in more than one country and generate revenue from more than one country
Why are multinational businesses so strong?
Globalisation
Well-known/good reputation due to large market budgets
Can afford to be high quality
Benefit from economies of scale
Benefits of multinational businesses to host nation
Increased tax revenues
Lots of chance for consumers in the country
FDI - inflow of money and reinvest in local economy
Lower price due to increased competition
Drawbacks of multinational businesses to host nation
Expatriation of profits
Loss of culture
Competition
Exploitation of natural resources
Expatriation of profits
Sending profits back to their original country rather than to the host country
Exchange rates
The price of one currency in the terms of another
Depreciation
When currency falls in value vs other countries
Appreciation
When currency gains value over other countries
Effects of depreciation on people
Decreases confidence as inflation occurs
People will try to buy local
Drives inflation
Makes holidays to other countries more expensive
Effects of depreciation to businesses
Pay more for imports → higher costs
Inflation
Will consider local supplies
Some businesses benefit such as businesses that target foreigners or exports
Effects of appreciation for people
Lowers inflation
More consumer confidence
Gives people more choice
Effects of appreciation for businesses
Imports are cheaper
More difficult to export
as it is more expensive for foreign customers