37) Oral cavity to stomach
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Discuss the proximal GI tract
1) Oral cavity
- parotid/submandibular/salivary gland
→ saliva contains salivary amylase, linguil lipase
- palatine, linguial, pharyngeal tonsil
→ lymphatic tissue
2) Pharynx
- oropharynx,laryngopharynx = share resp/digestive system
Within the oral cavity, whats mechanical digestion?
chewing (mastication)
- teeth
- tongue
→ manipulate food
→ mix w/ saliva
→ create bolus
Within the oral cavity, what’s CHEMICAL digestion?
-salivary amylase = breakdown CHO
-lingual lipase = breakdown fats (activated by low pH; acid)
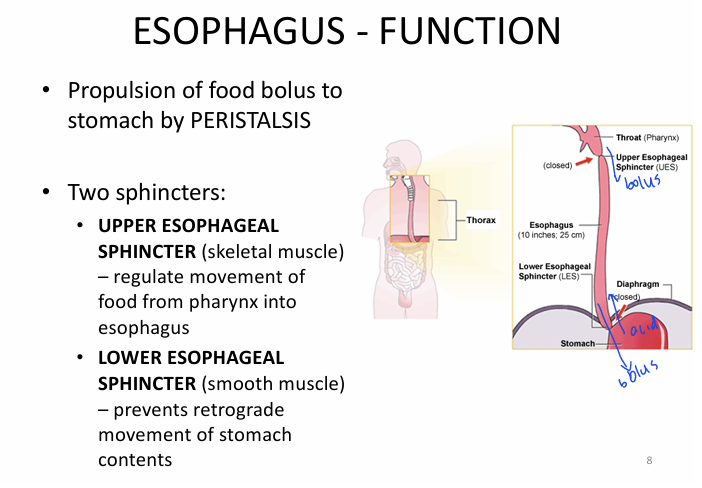
What is the FUNCTION of the esophagus?
move bolus of food into stomach via peristalsis
The esophagus has 2 sphincters. What are they?
1) upper esophageal sphincter = skeletal
- Mm of food from pharynx → eso
2) lower esophageal sphincter = smooth
- Mm of food from eso → stomach
- prevent reflux from stomach
How does SWALLOWING (deglutition) occur?
Deglutition
1) Voluntary (oral) phase = tongue pushes food posteriorly into oropharynx
2) Pharyngeal phase = activate deglutition centre in medulla oblongata
- uvula soft palate close nasopharynx
- contract larygneal muscle
- contract pharyngeal
- temporary apnea
3) esophageal phase = peristalsis in esophagus

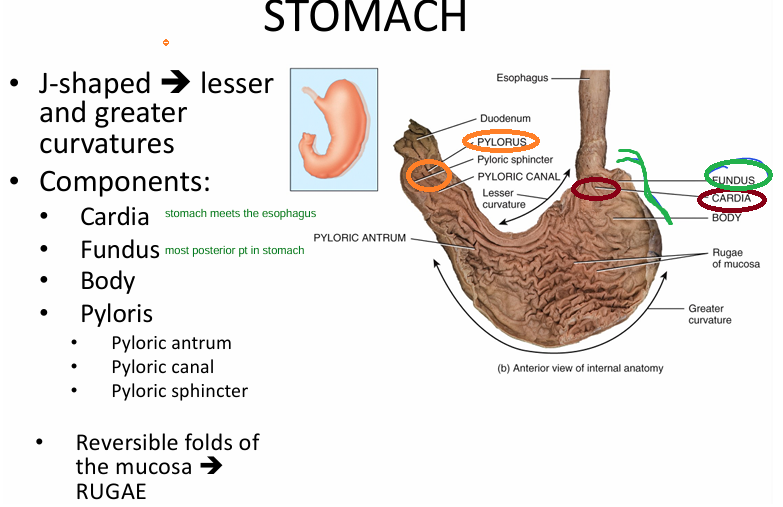
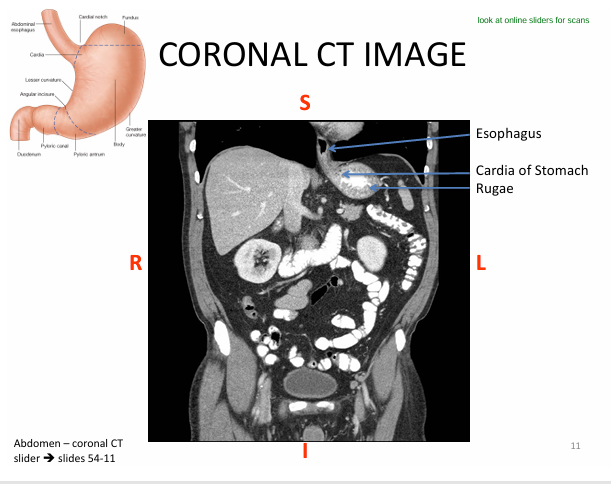
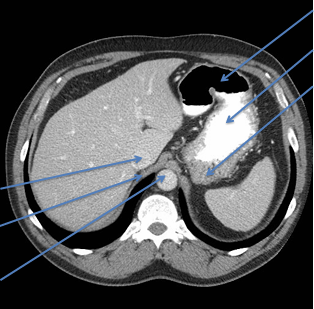
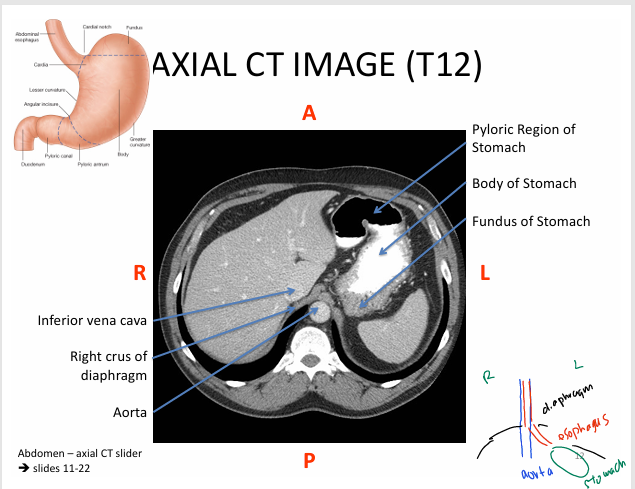
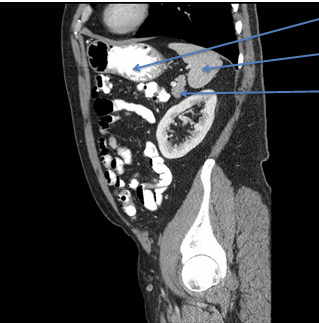
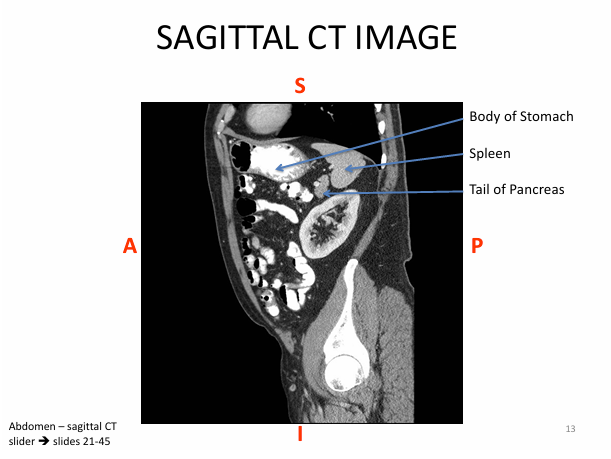
Anatomy to know for CT imaging:
-stomach is J SHAPED
Components to know:
- cardia = esophagus meets stomach
- fundus = posterior stomach
- body
- pyloris = stomach to SI
- rugae = folds of mucosa
Label
What is the function of the stomach?
1) Storage of food (via rugae folds)
→ rugae expands for more space
2) Digestion
- mechanical = churning
- chemical = gastric enzyme + stomach acid
3) Absorb ethanol
What are the cells of the stomach?
1) Surface mucus = secrete mucus
2) Mucus neck = secrete mucus
3) Parietal cell = hydrochloric acid
4) Chief cell = pepsinogen + gastric lipase
5) G cell = gastrin
What’s special about the stomach’s muscularis?
3 layers instead of 2.
- has inner oblique = churning bolus w/ gastric juice = CHYME
How is gastric secretions regulated?
What are the phases gastric secretion?
1) CNS
2) enteric nervous system - short reflex
3) hormones of GI tract
—
1) Cephalic
2) Gastric
3) Intestinal
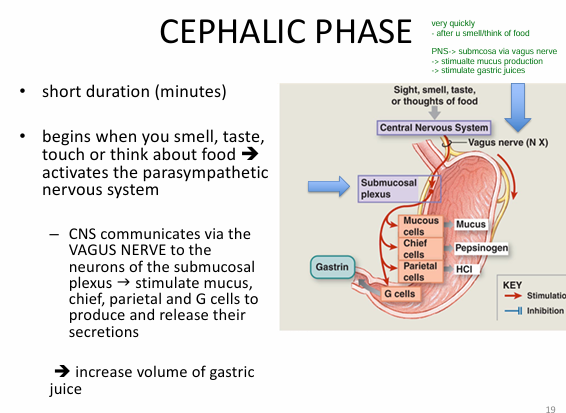
What is the 1) Cephalic phase?
(beginning)
Duration: short (minutes)
Activation:
- moment you think, touch food
→ activate parasymph NS
Process:
- CNS sends info to submucosal plexus via vagus nerve
→ stimulate mucus, chief, parietal, G cells
Outcome:
- increased GASTRIC JUICES
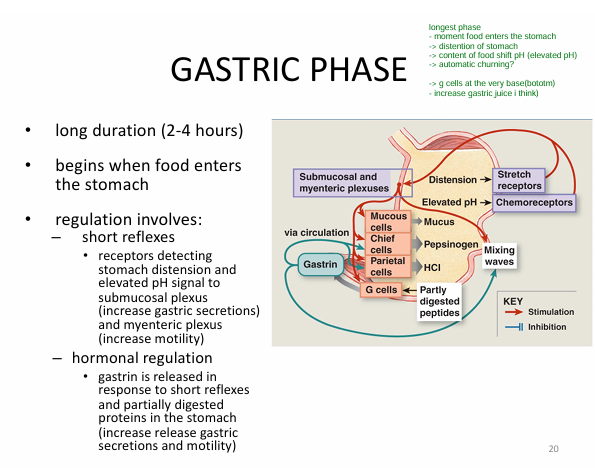
What is the 2) Gastric phage?
(digesting food)
Duration: Longest (2-4hr)
Activation:
- foot enters stomach
Process:
1) short reflex
- detect stomach distention (from food)
- detect increase pH
→ send info to submucosal plexus (increase gastric secretion)
→ send info to myenteric plexus
(increase motility)
2) hormonal regulation
- increase gastrin release
(increase gastric secretion + motility)
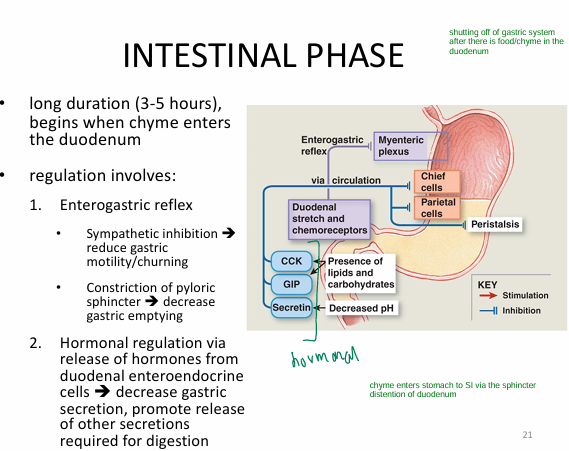
What is the 3) intestinal phase?
(foods digested, now in SI → stop stomach actions)
Duration: Long (3-5hrs)
Activation:
- chyme enters duodenum (SI)
Process:
1) Enterogastric reflex
- sympathetic inhibition
(no more churning/motility)
- constrict pyloric sphincter
(no more chyme from stomach → SI)
2) hormonal regulation
- enteroendocrine cells release hormones
→ decrease gastric secretion
→ promote other secretions for digestion
What hormones act during the intestinal phase?
CCK + secretin
→ act on stomach to REDUCE GASTRIC SECRETION
(aka stop digesting b/c we’ve gone to the point where everythings been digested)
Discuss mechanical digestion in the stomach.
1) Churning/mixing (using all 3 layers)
- mix food w/ gastric juice to produce CHYME
- peristalsis
2) Gastric emptying
- if chyme too big, pushed back into stomach for more digesting
- peristaltic waves squirt chyme into duodenum
Discuss chemical digestion in the stomach
1) Stomach acid
- low pH deactivates salivary amylase
- activate pepsinogen (to pepsin) + lingual lipase
2) Pepsin
- breakdown proteins (peptide bonds)'
3) Lipase
- lingual lipase + gastric lipase
- digest triglycerides
Why is absorption limited in the stomach?
1) layer of mucus
2) lack of transport mechs in epithelial cells
3) nutrients not broken down enough into appropriate size for absoprtion
*exception to alcohol (passes through mucus layer)
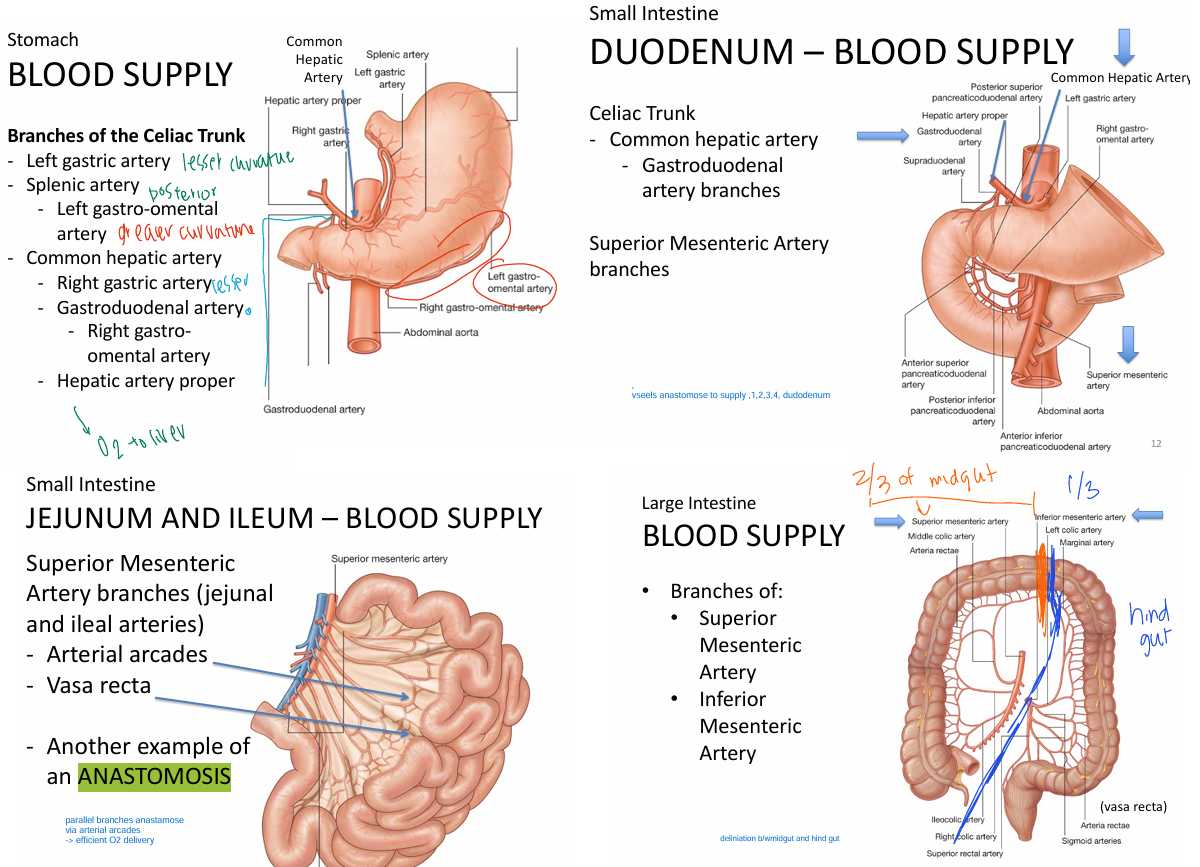
Blood supply of the stomach
Stomach
Branch of celiac trunk
left gastric artery
splenic artery
left gastro-omental artery
common hepatic artery
right gastric arteryer
gastroduodenal artery
right gastro-omental
hepatic artery proper
Duodenum (SI)
Celiac trunk
Common hepatic artery
gastroduodenal artery BRANCHES
superior mesenteric artery
Jejunum + ileium (SI)
Superior mesenteric artery
arterial arcades
vasa recta
= form ANATAMOSIS
Large intestine
Superior mesenteric artery branches (2/3 of mid gut)
Inferior mesenteric artery branches (1/3 hind gut)